MCAT Psych/Soc
1/126
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
127 Terms
Hindbrain/Rhombencephalon
controls balance, motor coordination, breathing, digestion, and arousal. Divides to myelencephalon (medulla oblongata) and metencephalon (pons and cerebellum) in embryonic development
Medulla oblongata
controls regulation of vital functions like breathing, heart rate, and digestion
Pons
controls sensory and motor pathways between the cortex and medulla
cerebellum
controls posture and balance
midbrain (Mesencephalon)
recieves sensory and motor information from the rest of the body. Holds the colliculi
Superior colliculus
receives visual sensory input
Inferior colliculus
receives sensory information from the auditory system and plays a role in auditory reflexes.
Forebrain (prosencephalon)
involved in complex perceptual, cognitive and behavioral processes. Involved in emotion and memory. During development, divides into telencephalon (cerebral cortex, basal ganglia, limbic system) and diencephalon (thalamus, hypothalamus, posterior pituitary gland, pineal gland)
Acetylcholine location and functions
Seen in the CNS and PNS. In PNS functions in providing impulses to muscles. IN CNS, functions in attentiveness and arousal.
3 Catecholamines and their overall function
Epinephrine, norepinephrine, and dopamine. Function in emotions
Epinephrine (adrenaline)
involved in alertness and wakefulness. Involved in fight or flight response. Secreted from medulla oblongata and acts as a hormone.
Norepinephrine (noradrenaline)
involved in alertness and wakefulness. Involved in fight or flight response. Works as a local neurotransmitter. When low, depression can develop. When high, anxiety or mania can develop.
Dopamine
controls movement and posture. Also aligned with schizophrenia with higher levels being aligned with higher levels or sensitivity of dopamine
Serotonin
controls mood, eating, sleep, and dreaming. Similar to norepinephrine plays a role in depression and mania/anxiety
GABA
creates inhibitory postsynaptic potentials to stabilize neural activity
Glycine
similar to GABA, creates inhibitory postsynaptic potentials to stabilize neural activity (specifically increases Cl- influx)
Glutamate
acts as a excitatory neurotransmitter
Neuromodulators/neuropeptides
use a more complex series of events in the postsynaptic neuron to impose slow/long lasting effects
Endorphins
natural pain killers in the brain
Innate behavior
behavior that is genetically programmed as a result of evolution (independent of environment or experience)
Learned behavior
behaviors that are not based on heredity but on environment and experience
Adaptive value
the extent to which a trait/behavior positively assists a species survival
Family studies
studies that examine individuals that have similar genetics due to their familial relations
Twin studies
studies that examine individuals that have similar genetics as twins and similar environments as family
Adoption studies
studies that examine affects of genetics by comparing individuals that have environmental similarities (adopted) and genetic similarities (blood)
Bottom up processing
object recognition by parallel processing and feature detection. First time seeing a object and understanding it by its parts
Top down processing
object recognition by memories and expectations. You’ve seen the object before and recognize it as a whole
Perceptual organization
ability to use both bottom up and top down processing to understand a object or idea
Monocular cues
visual cues that can be seen with one eye
Relative size
objects appear larger the closer they are
Interposition
when two objects overlap, the one in the front is closer
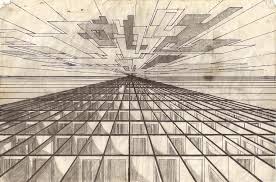
Linear perspective
as two parallel lines converge, the longer their convergence, the further the distance
Binocular cues
visual cues that involve the differences in images when projected on two retinas
Convergence
when the brain detects the angle between the two eyes required to bring a image to focus
Constancy
The ability to perceive constant characteristics in a object despite changes in environment
Gestalt Principles
rules that account for the fact that the brain tends to complete incomplete stimuli is a calculative manner
Law of proximity
elements near to one another are perceived as a unit
Law of similarity
elements that are similar are grouped together
Law of good continuation
elements that appear to follow a similar pattern are grouped together
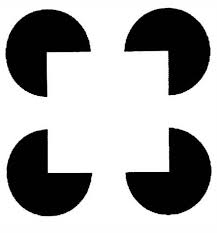
Subjective contours
ability to perceive contours and shapes that are not actually present in a stimulus
Law of closure
when a space is enclosed, it is perceived as a complete figure
Law of pragnanz
Law that governs the gestalt principles which states that perceptual organization will always be as regular, simple, and symmetric as possible
Dishabituation
the recovery of a response to a stimulus often due to a second stimulus being introduced
Classical conditioning
associative learning that creates associations between two unrelated stimuli
Acquisition
process of turning a reflexive, unconditioned stimulus to a conditioned stimulus
Extinction
the loss of a conditioned response
operant conditioning
the consequences of behaviors changes the frequency of behaviors
Fixed ratio schedules
reinforce a behavior after a specific number of instances of the behavior
Variable ratio schedules
reinforce a behavior after a varying number of instances of the behavior
Fixed interval schedules
reinforce the behavior at the first instance and then after a specific time interval after
Variable interval schedules
reinforce a behavior the first instance and then after a varying amount of time after
Latent learning
Learning that is done without a reward but can be repeated for a reward
Automatic processing/controlled processing
unintentional collection of information vs active memorization of information
Conformity
The tendency for individuals to align their beliefs with a similar group of individuals even if the belief is incorrect
Context effects
memory aided when in the same environment as when the memory was created
State dependent memory
memory aided when in the same mental state as when the memory was created
Serial position effect
The phenomenon where individuals are more likely to remember the list and last items on a list over what was in the middle
3 meninges of the brain (DAP)
From outer to inner; Dura mater, Arachnoid mater, and Pia mater. These layers are located in the skull
Periosteum
A layer of connective tissue above the skull
Thalamus
Sensory relay station
Hypothalamus
controls metabolism, temperature, and water balance
Pituitary gland
controls endocrine glands
Confirmation bias
tendency to pay more attention to opinions that supports ones views
Belief perseverance
When one holds a specific belief despite evidence to the contrary
Simple denial
refusing to admit that something is true despite knowing deep down that it is true
Overconfidence
Believing that ones beliefs are infallible
Sustained/Executive attention
When one focuses on one thing and ignores all other things
Divided attention
The ability to focus on multiple tasks
Piaget States and their years
Sensorimotor= birth-2 years
Preoperational= 2-7years
Concrete operational= 7-11 years
Formal operational= 11 years and beyond
Some People Cant Fly
Authentic self
who we actually are (good and bad)
Backstage self
who we are when we are not being observed and can act freely
Front stage self
who are are when we are in a audience and want to perform to keep an image
Ideal self
who we would like to be
Tactical self
who we advertise ourselves to be when we adapt to others expectations
Overrepresentation
When there is a higher percentage of cases than percent total
Underrepresentation
When there is a lower percentage of cases than percent total
Generalizability
when the results of a study can be placed onto a general population
Accuracy
checks that the researchers measured the proper data
Precision
consistency of measurements
Confounding
variable that influences both independent and dependent variables
Context effects
a retrieval cue that aids memory when one is in the same sensory condition as when the information was encoded
Semantic memory
type of declarative memory that includes facts and concepts
State dependent memory
memory that is recalled when in a similar mental/emotional state as when the information was encoded
What are the three ways of encoding information?
Visual, acoustic, and semantic
What are the strengths of the forms of encoding information?
Semantic>acoustic>visual
Primacy effect
tendency to remember terms early in a list
Serial position effect
retrieval cue to remember terms at the beginning and end of a list
Recency effect
tendency to recall terms at the end of the list
What is the strongest recall effect in a list
Primacy effect
Elaborative rehearsals
attaches new information to old information to place it into long term memory
Maintenance rehearsals
usage of repetition to keep information in the short term
Spreading activation
when a new term is associated with other learned related terms unknowingly
Priming
a retrieval cue that aids recall by first presenting a term that is closed to the desired memory
Source amnesia
memory loss of how the term was acquired
Clustering
group of related terms together in a chunk
Projection
when one places their emotions onto another person
Reciprocal determinism
states that there are personal AND environmental motivation that influence behavior
Trait theory
a personality is a sum of characteristic behaviors
What does behaviorism/behaviorist believe?
all behaviors are conditioned
What is synesthesia
condition where sounds result in visual flashes of colors