Bonding in Chemistry
1/42
Earn XP
Description and Tags
These flashcards cover key concepts such as bonding types, molecular geometry, hybridization, and the role of formal charge in Lewis structures, which are essential for understanding chemistry at a higher level.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
43 Terms
Covalent Bonding
Results from the overlap of atomic orbitals.
Sigma Bond (σ)
Formed by the direct head-on overlap of atomic orbitals, with electron density between the nuclei of the bonding atoms.
Pi Bond (π)
Formed by the sideways overlap of atomic orbitals, with electron density above and below the plane of the nuclei of the bonding atoms.
Formal Charge (FC)
The charge an atom would have if all atoms in a molecule had the same electronegativity. Used to determine preferred Lewis structures.
Lewis Structure
A diagram that uses dots to represent the valence electrons of atoms within a molecule.
Octet Rule
Atoms tend to form bonds until they are surrounded by eight valence electrons.
Delocalization π electrons
Delocalization involves electrons that are shared by more than two nuclei in a molecule or ion as opposed to being localized between a pair of atoms.
Rather than the electrons being contained in specific bonds, delocalised π electrons exist in π bonded regions.
Resonance
Using multiple Lewis structures to represent a molecule or ion that cannot be described by one structure alone.
VSEPR Theory
Predicts the shape of molecules based on electron domain geometry.
Electron Domain Geometry
The arrangement of electron domains around a central atom.
Trigonal Bipyramidal
A molecular geometry with five bonding domains and bond angles of 90° and 120°.
T-shaped
A molecular geometry resulting from three bonding and two non-bonding electron domains.
Square Planar
A molecular geometry that arises from four bonding and two non-bonding domains.
Bond Order
The number of chemical bonds between a pair of atoms; indicates bond strength.
Hybridization
Mixing of atomic orbitals to form new hybrid orbitals used for bonding. hybridization also enhances the stability of a compound.
sp Hybridization
Involves the mixing of one s and one p orbital, forming two hybrid orbitals with a linear geometry.
sp2 Hybridization
Involves the mixing of one s and two p orbitals, forming three hybrid orbitals with a trigonal planar geometry.
sp3 Hybridization
Involves mixing one s and three p orbitals, forming four hybrid orbitals with a tetrahedral geometry.
Sulfur Dioxide (SO2) Lewis Structure
The Sulfur Dioxide (SO2) Lewis structure depicts a central sulfur atom bonded to two oxygen atoms, with one of the oxygen atoms forming a double bond to sulfur, while the other forms a single bond. Each atom also has lone pairs that contribute to the overall shape and polarity of the molecule.
Dichlorodifluoromethane (CCl2F2)
A chlorofluorocarbon involved in ozone layer depletion.
Ozone Depletion
Caused by pollutants like CFCs and NOx, leading to destruction of ozone molecules.
Ozone (O3)
A molecule consisting of three oxygen atoms, crucial for blocking UV radiation.
Carbonate Ion (CO32-)
An ion with delocalized π electrons distributed over four atoms.
Benzene (C6H6)
A hydrocarbon with resonance structures and delocalized π electrons.
Bond Length
The distance between the nuclei of two bonded atoms.
Bond Strength
The measure of the energy required to break a bond.
Catalysis
The process by which a catalyst increases the rate of a chemical reaction.
Electron Density
A measure of the probability of electron presence in a region of space.
Nitrogen Dioxide (NO) Production
Generated in combustion engines combining nitrogen and oxygen at high temperatures.
Chlorine Free Radical (Cl•)
An intermediate in ozone depletion that catalyzes the breakdown of ozone.
Intermediate Bond Strength
Bonds in molecules with delocalized π electrons are intermediate between single and double bonds.
Trigonal Planar Geometry
The geometry associated with sp2 hybridization, characterized by 120° bond angles.
Linear Geometry
The geometry of sp hybridized molecules with a bond angle of 180°.
Electronegativity
The tendency of an atom to attract electrons towards itself in a bond.
Valence Electrons
Electrons in the outermost shell of an atom that are involved in bonding.
Non-bonding Domains
Regions of electron density that do not participate in bonding.
FC formula
FC= V-N-1/2B where FC is formal charge, V is valence electrons, N is non-bonding electrons, and B is bonding electrons.
The bond length and strength in molecules with delocalised pi electrons are ___ between the a single and a double bond.
Intermediate
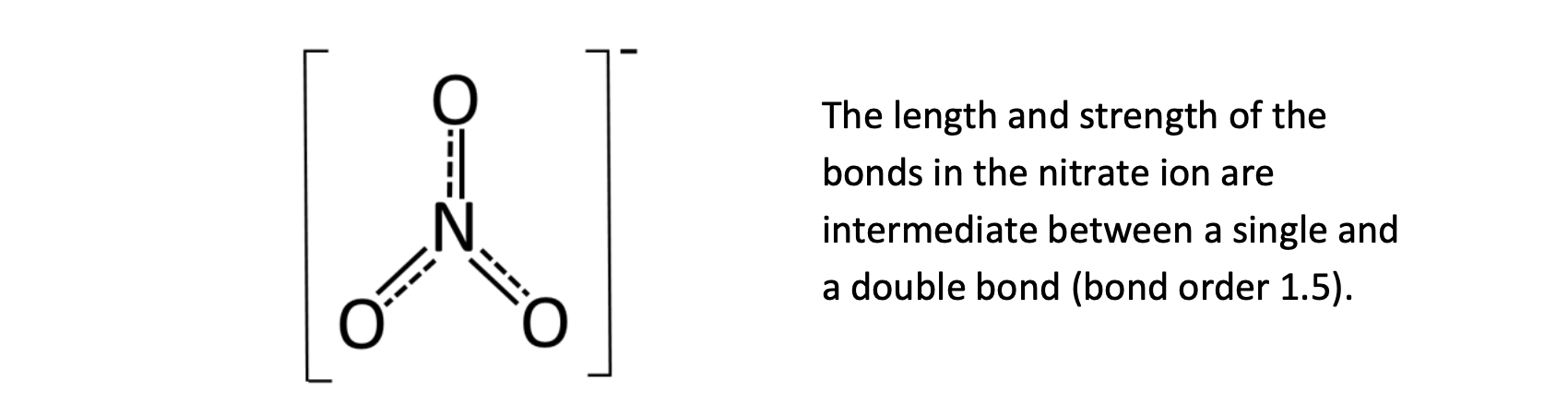
The length and strength of the bonds in the nitrate ion are intermediate between a single and a double bond, so what is the bond order?
Bond order is 1.5
How many nuclei’s are the delocalized pi electrons shared between?
Delocalized pi electrons are shared between more than two nuclei.
How are the bond lengths and bond strengths between a single and double bond?
Bond lengths and strengths are intermediate. Bond order 1.5
How do delocalized electrons affect a molecule?
Delocalized electrons bring extra stability to a molecule through resonance energy.
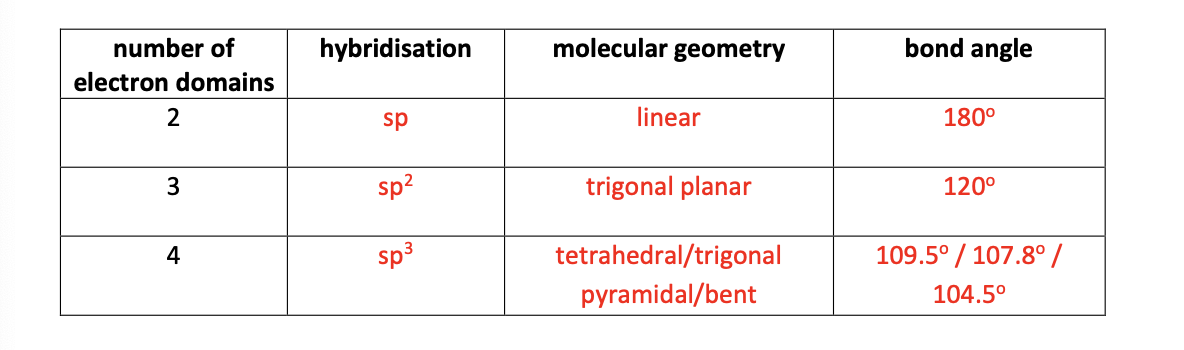
sp - linear - 180
sp2 - trigonal planar - 120
sp3 - tetrahedral - 109.5
trigonal pyrimidal - 107.8
bent - 104.5