dopamine
1/51
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
52 Terms
roles of dopamine
catecholamine neurotransmitter that:
controls movement
emotional response
controls pleasure and pain
how is dopamine synthesised
in presynaptic terminals of dopaminergic neurones
made from amino acid tyrosine
stored in large dense core vesicles
how is dopamine released
by vesicle exocytosis
where does released dopamine bind
binds to dopamine receptors and produces excitatory or inhibitory postsynaptic effects depending on type of postsynaptic receptor
how is dopamine removed from the synaptic cleft
by dopamine transporters and it is degraded by enzyme monamine oxidase
dopamine receptors are G protein coupled receptors. what are the 2 main classes
D1-like dopamine receptors (D1, D5)
D2-like dopamine receptors (D2, D3, D4)
what do D1-like dopamine receptors activate
activates Gs heterotromeric G-proteins
what happens when dopamine binds to D1-like receptor
α-subunit of the Gs protein dissociates from the βγ subunits
what enzyme does α-subunit of Gs protein stimulate
adenylyl cyclase
what is the effect of adenylyl cyclase activation
increases cAMP levels inside postsynaptic neurone
what does cAMP activate in D1 receptor signaling
protein kinase A (PKA)
how does activation of PKA affect neuronal excitability
PKA phosphorylates and stimulates voltage-gated ion channels, leading to increased excitability (EXCITATION) of the postsynaptic neuron
which G-protein class do D2-like dopamine receptors activate
Gi/o heterotrimeric G-proteins
what happens when dopamine binds to D2-like receptor
α-subunit of the Gi/o protein dissociates from the βγ subunits
what enzyme does α-subunit of Gi/o inhibit
adenylyl cyclase
what is the effect of adenylyl cyclase inhibition
reduces cAMP production leading to decreased activity of cAMP dependent pathways
how does inhibition affect neuronal excitability
causes inhibition of voltage-gated channels producing an overall inhibitory effect on postsynaptic neurone
how is dopamine action terminated at synapse
by reuptake of dopamine into presynaptic neurone via dopamine transporters (DAT)
true or false: process of dopamine reuptake is an energy-dependent process
true
which enzyme provides energy for dopamine reuptake
sodium/potassium ATPase which creates ion gradient that drives transporter function
how does dopamine transporter DAT move dopamine into the neurone
uses the Na⁺ and Cl⁻ ion gradient to co-transport dopamine from the synaptic cleft into the presynaptic terminal
what is the role of K⁺ ions in the dopamine transport cycle
K⁺ ions bind to the transporter, allowing it to reset to its outward-facing position after dopamine transport
why is K+ release back into synaptic cleft important
it restores ionic gradient across presynaptic membrane which enables another transport cycle
why is dopamine reuptake crucial for brain function
terminates synaptic signaling, prevents overstimulation and allows recycling of dopamine for future neurotransmission
what are the 3 main sources of dopamine in brain
1) ventral tegmental area
2) substantia nigra
3) arcuate nucleus of hypothalamus
where are neurones of mesolimbic dopamine pathway located
in ventral tegmental area of midbrain
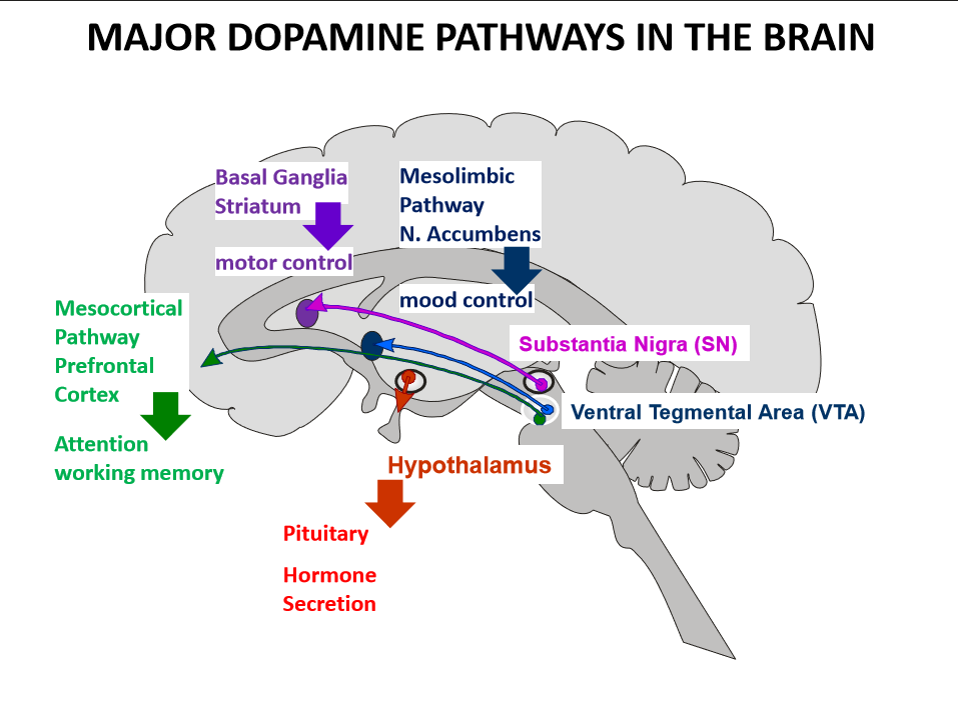
where do ventral tegmental area neurones of mesolimbic pathway project to
limbic areas especially in nucleus accumbens
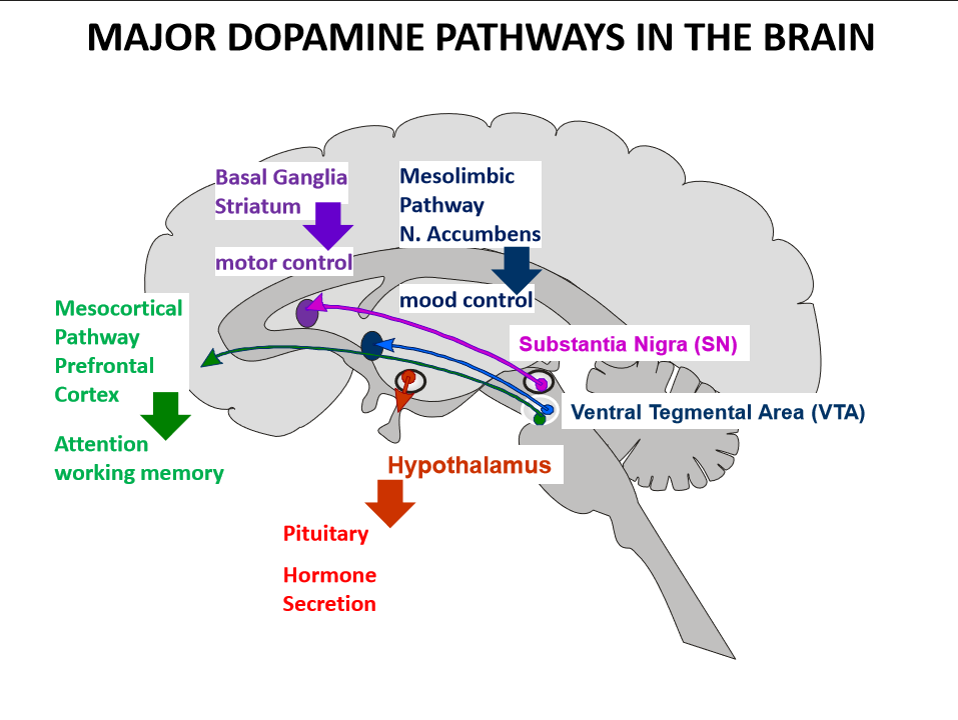
what is main function of mesolimbic dopamine pathway
regulates mood, motivation and reward processing
what happens when dopamine release is increased in the mesolimbic pathwa
can produce positive psychotic symptoms (e.g., hallucinations, delusions) and lead to aggressive or hostile behaviour
which mental health condition is associated with overactivity of the mesolimbic pathway
Schizophrenia (positive symptoms)
where do neurons from the VTA project in the mesocortical pathway
to prefrontal cortex
what does the mesocortical dopamine pathway regulate
attention
working memory
executive functions
what symptoms are linked to reduced dopamine activity in the mesocortical pathway
cognitive impairment
apathy
negative symptoms of schizophrenia
where are the neurons of the nigrostriatal dopamine pathway located
in the Substantia Nigra of the midbrain
where do nigrostriatal neurons project to
the Striatum of the Basal Ganglia
what is the main function of the nigrostriatal dopamine pathway
regulation of movement and motor control
what are the effects of dopamine deficiency in nigrostriatal pathway
rigidity
akinesia
bradykinesia
tremor
what disease is caused by degeneration of nigrostriatal dopamine neurons
Parkison’s disease
what symptoms result from hyperactivity of nigrostriatal pathway
chorea
dyskinesias
tics
where are the neurons of the tuberoinfundibular dopamine pathway located
in the Arcuate Nucleus of the Hypothalamus
where is dopamine released in the tuberoinfundibular pathway
into the portal blood system connecting the hypothalamus and the anterior pituitary
what is the main target of dopamine in the tuberoinfundibular pathway
Prolactin-secreting cells (lactotrophs) in the anterior pituitary
what is the effect of dopamine on prolactin secretion
it inhibits prolactin release
what happens when dopamine activity in tuberoinfundibular pathway is reduced
Prolactin levels rise, leading to hyperprolactinaemia (which can cause galactorrhea and menstrual disturbances)
what are dopamine receptor agonists or mimetics
drugs that increase dopamine activity by stimulating dopamine receptors directly or indirectly
examples of drugs that increase dopamine availability by inhibiting dopamine reuptake
amphetamine and cocaine
what is the mechanism of action of amphetamine
reverses dopamine transporter (DAT) function, increasing dopamine release into the synaptic cleft and blocking reuptake
what is mechanism of action of cocaine
blocks dopamine reuptake by inhibiting the dopamine transporter (DAT), causing dopamine accumulation in the synaptic cleft
what example of dopamine precursor is used therapeutically
L-DOPA (levodopa)
what is L-DOPA used to treat
Parkinson’s disease, to restore dopamine levels in the nigrostriatal pathway
what are dopamine receptor antagonists (D2 antagonsits)
anti-schizophrenic or anti-psychotic drugs