Chapter 10: Adaptive Immune System
1/91
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
92 Terms
Dengue Fever
Tropical viral disease spread by mosquitoes.
RNA virus
easily mutable
viral disease
only female mosquitoes sting for their eggs
we react to mosquito spit
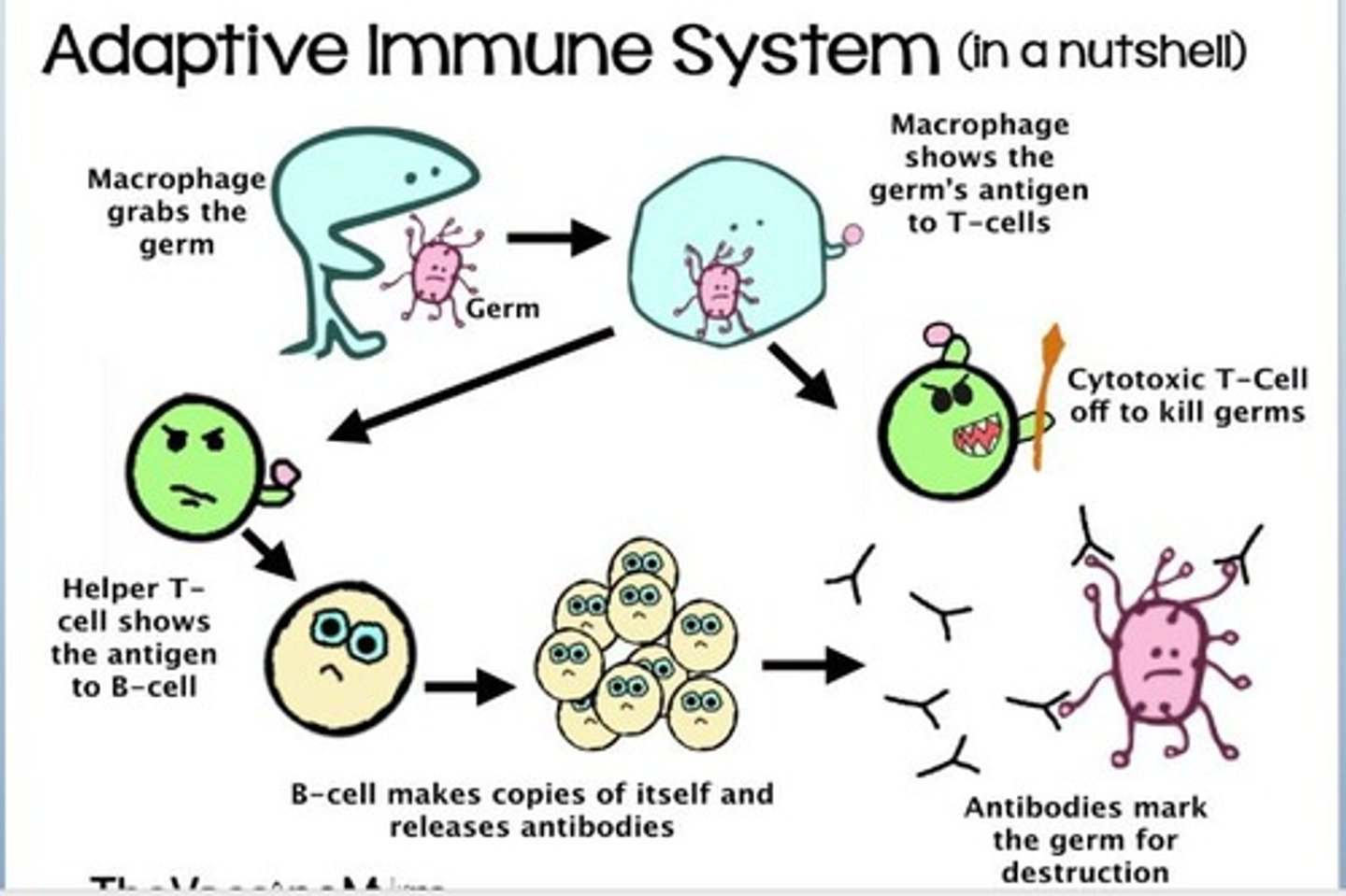
adaptive immune system pathway
Macrophage engulfs the germ (doesn’t kill)
Presents antigen to T cell
Helper T can show the antigen to the B-cell
Cytotoxic T-cell can kill other germs
B-cell makes copies of itself and releases antibodies
Antibodies mark the germ for kill
pathogen specific; takes longer to develop
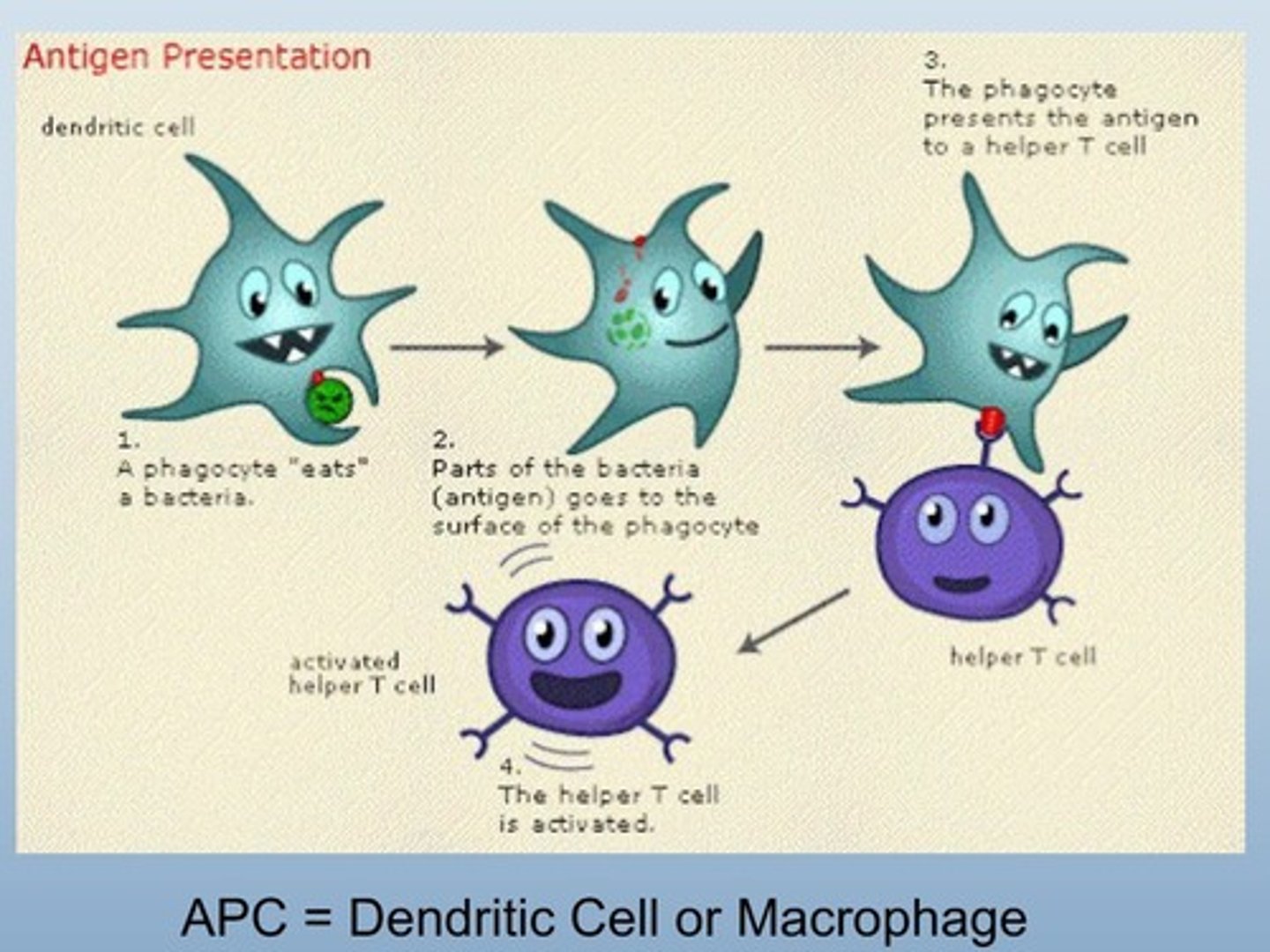
Macrophage
Engulfs pathogens and presents antigens
antigen presenting cell
Antigen
Substance that triggers an immune response.
foreign
T-Cell
Lymphocyte that attacks infected cells.
helper T
cytotoxic T
responsible for memory cells
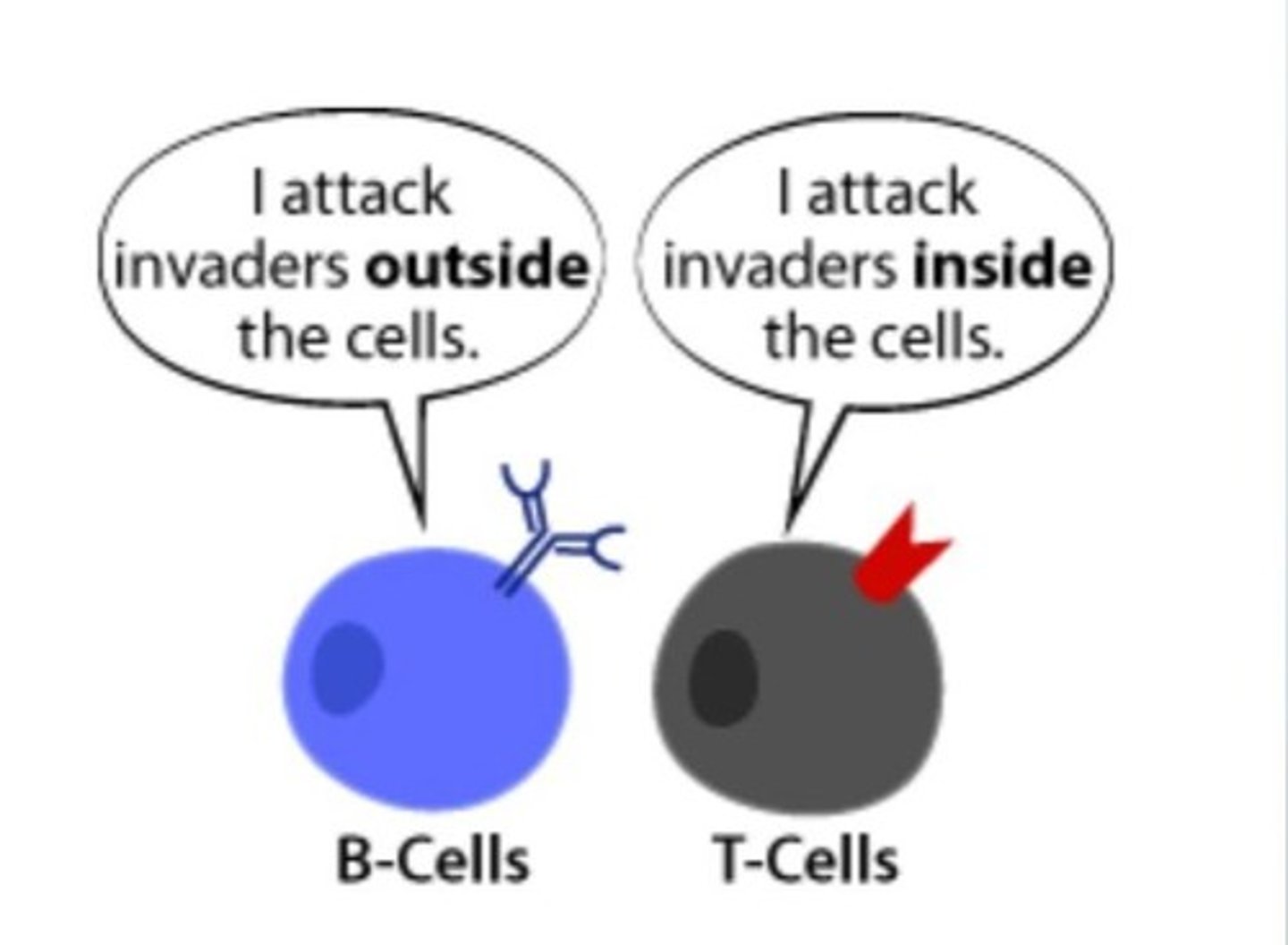
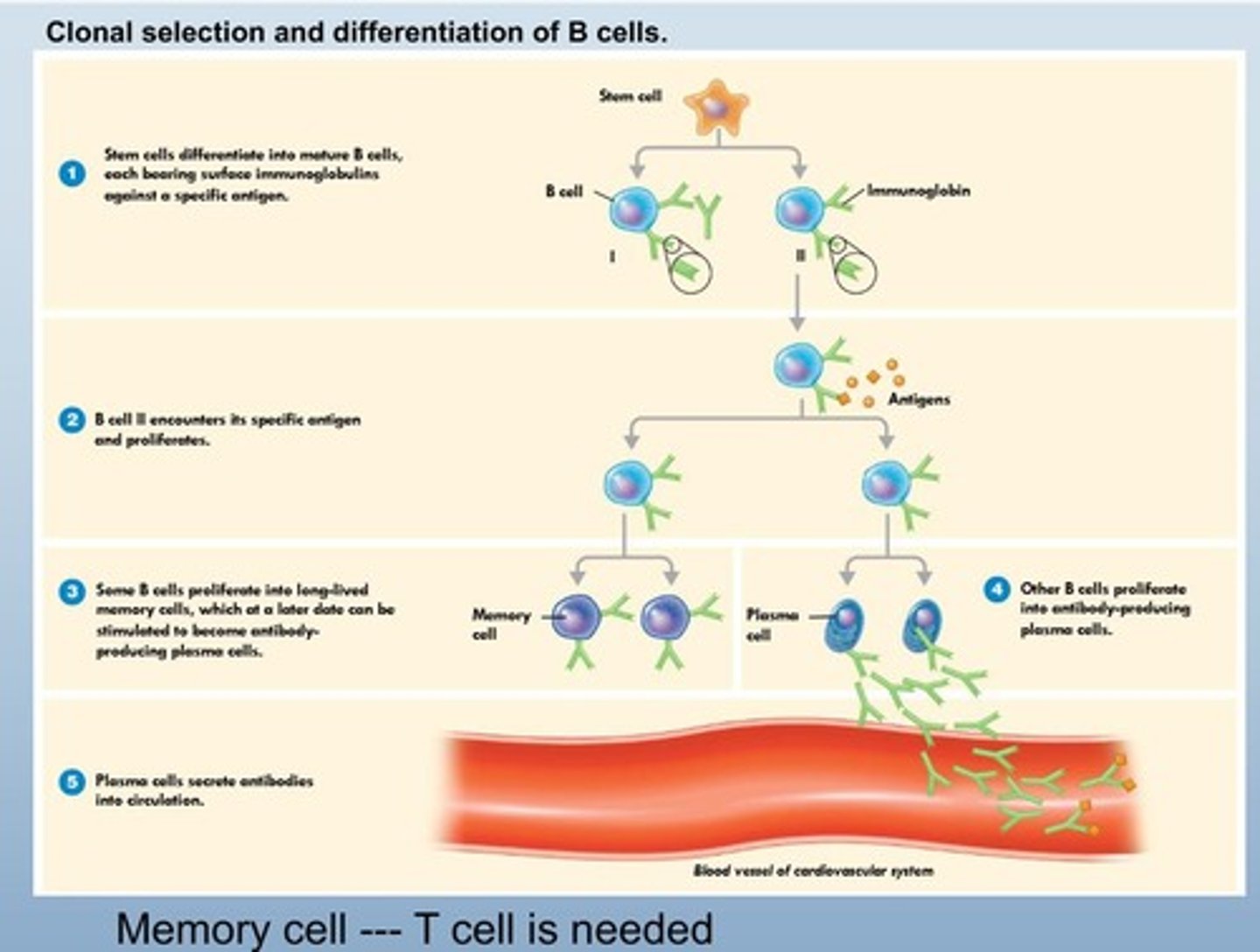
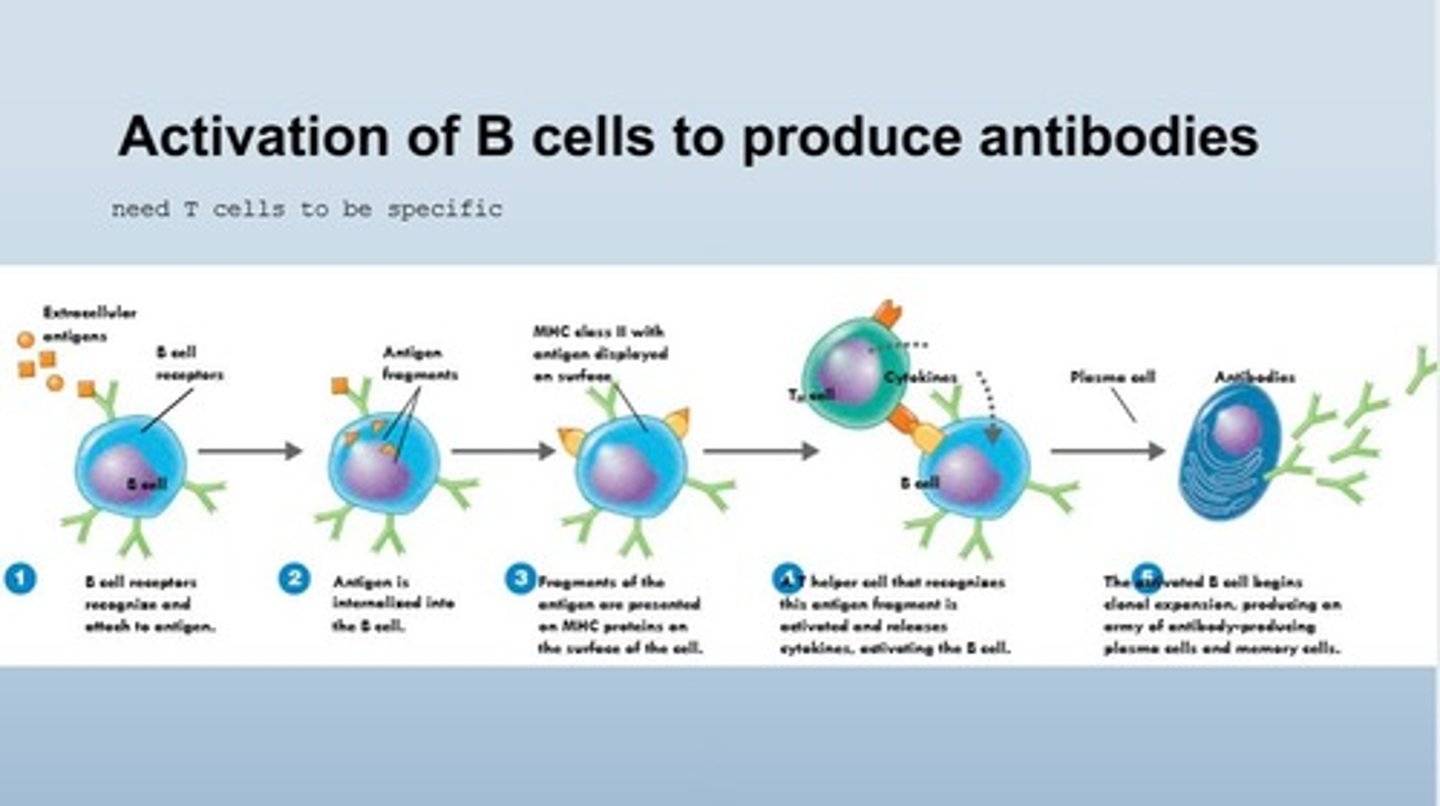
B Cell
Lymphocyte that produces antibodies.
also makes plasma cells which turn into memory cells
attacks outside the cell
Helper T Cell
Activates B cells and cytotoxic T cells.
messenger
Cytotoxic T Cell
Kills infected or cancerous cells.
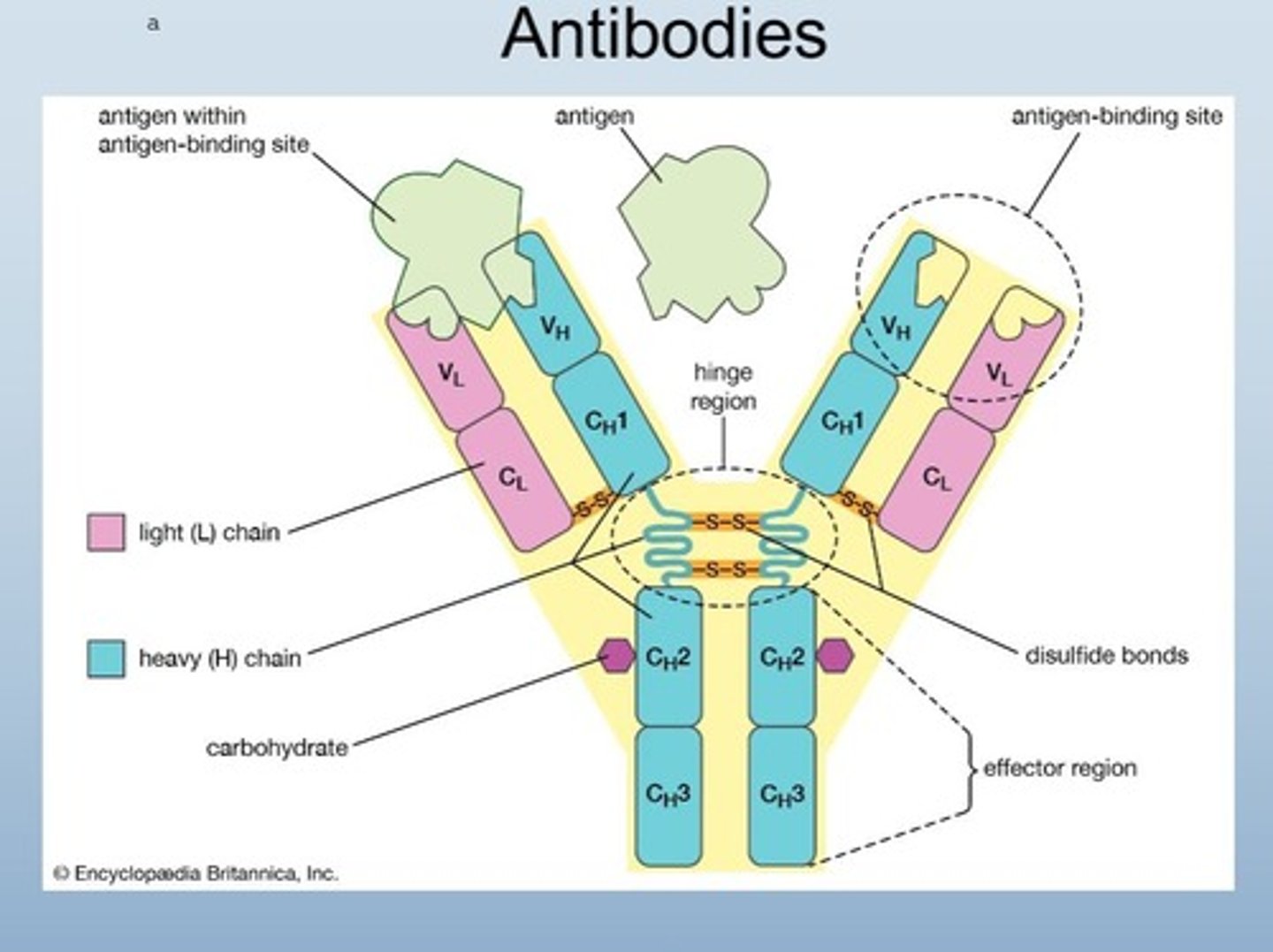
Antibodies
Proteins that bind to specific antigens to indicate to APC to attack
takes weeks to produce
Antibodies are in plasma coming from proteins
Tips have specific antigen-binding site
T cell is needed
Immunological Memory
Ability to remember past antigens for faster response.
Herd Immunity
Protection of a population through widespread immunity.
Innate Immunity
Natural, immediate immune response to pathogens.
non-specific
quick
epithelial barriers, antimicrobial proteins, phagocytes, dendritic, NK cells
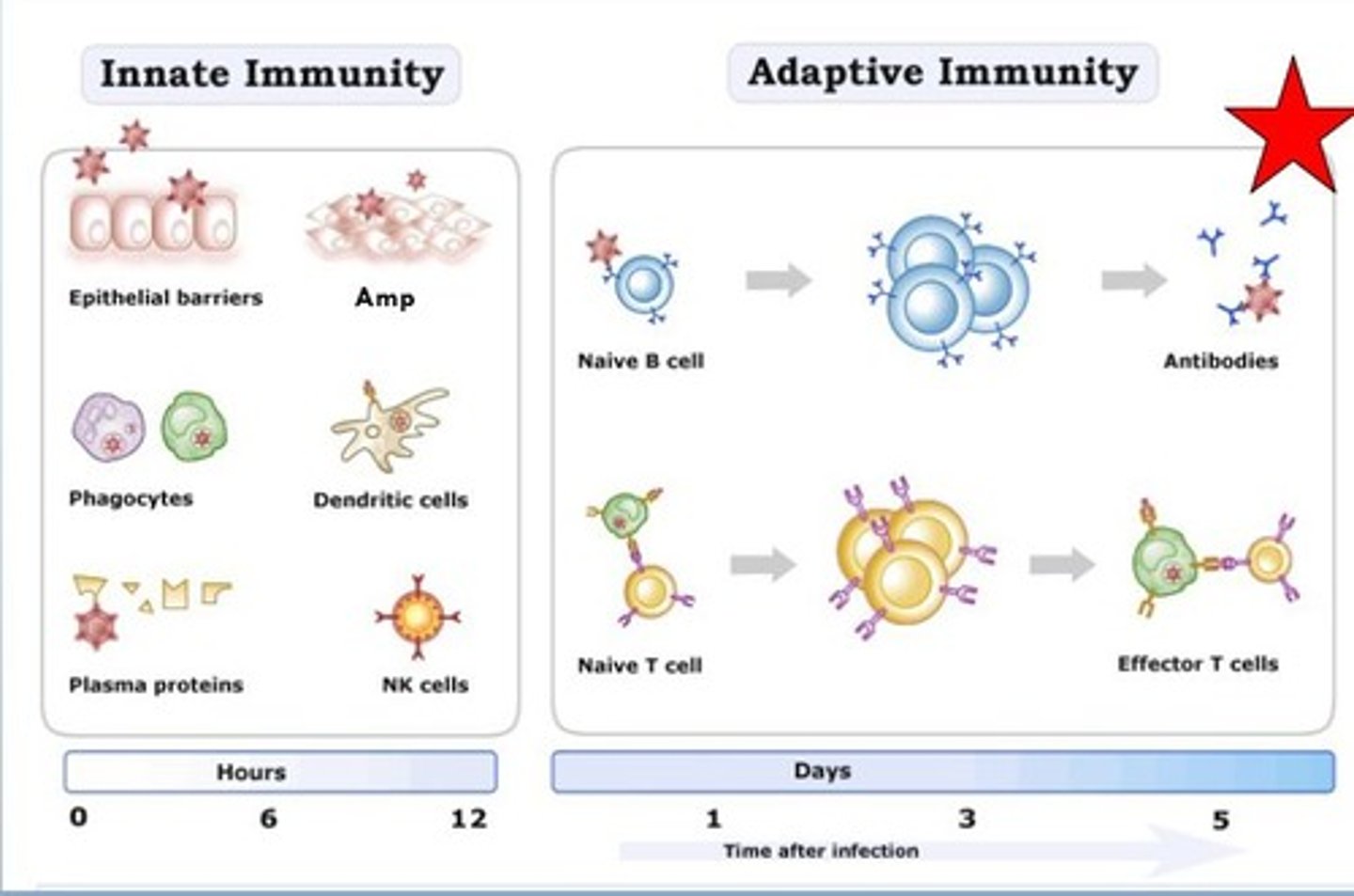
Adaptive Immunity
Specific immune response that develops over time.
leads to immunological memory
B and T cell
takes weeks to develop
specific lifelines for viruses vary
Phagocytes
Cells that engulf and digest pathogens.
Dendritic Cells
Antigen-presenting cells that activate T cells.
Natural Killer Cells
Cells that destroy infected or cancerous cells.
Histamine
Chemical released during allergic reactions.
Mast Cells
Cells involved in allergic responses and inflammation.
hypersensitivity
secondary bacterial infection
hypersensitivity
body overreaction to an invasion to a foreign particles such as pollen
secondary bacterial infection
immune system encounters an antigen it has previously been exposed to
symptoms last longer than 10-14
Vaccine
Substance that stimulates immunity against diseases.
Differentiation
Process of stem cells developing into specialized cells.
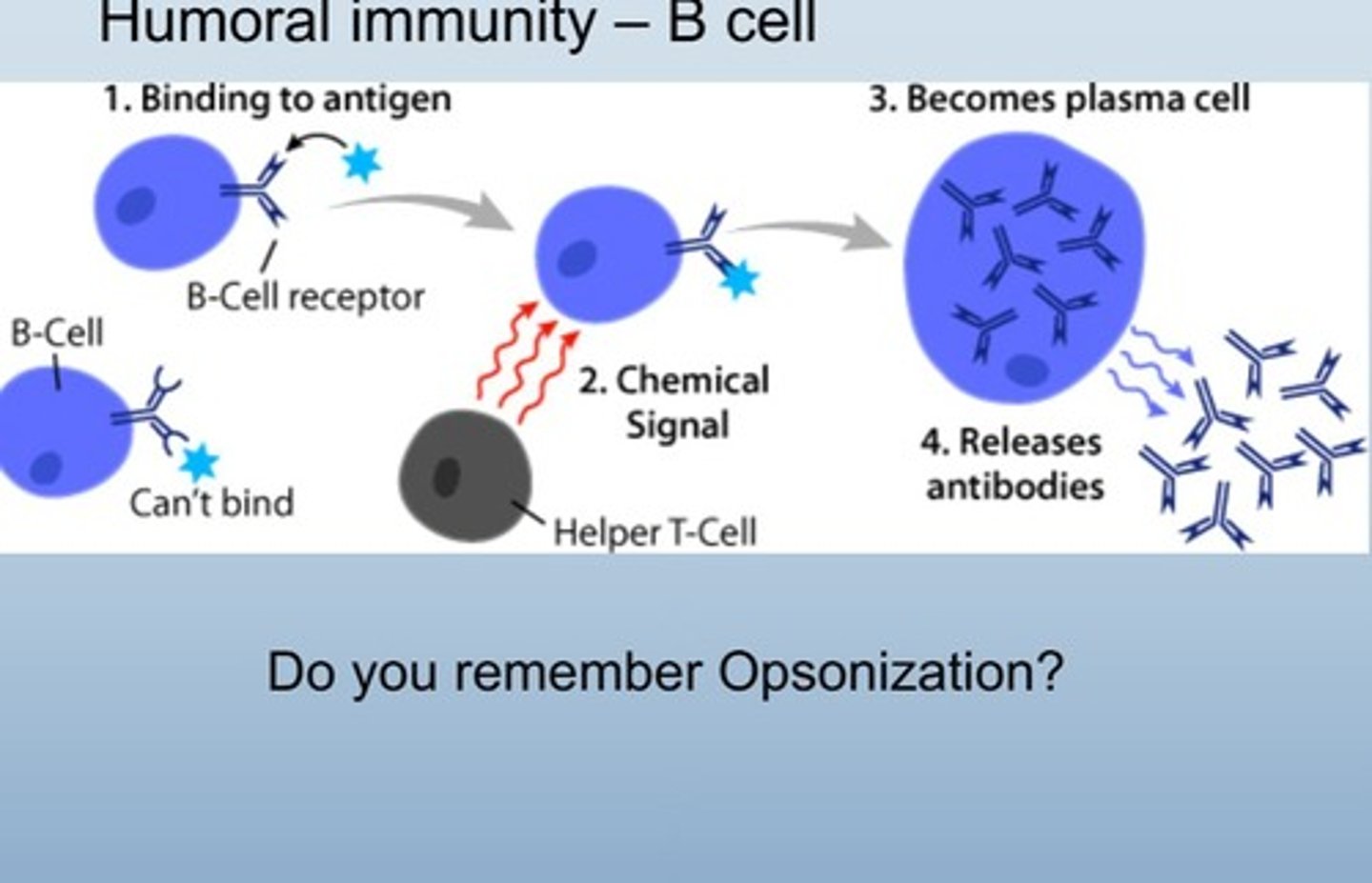
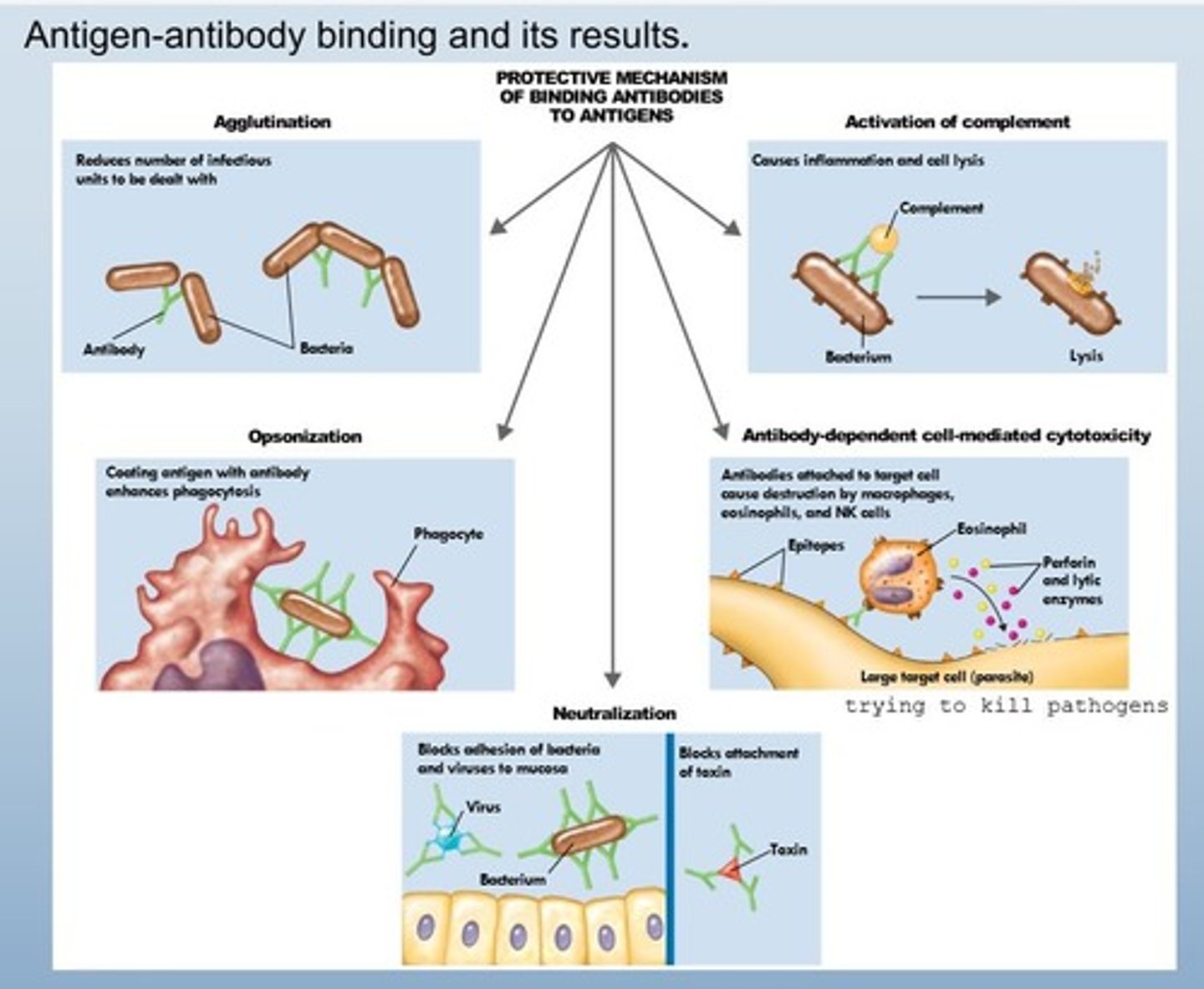
Opsonization
Making pathogens more susceptible to phagocytosis by coating them in antibodies
MMR Vaccine
Vaccine effective against measles, mumps, rubella.
Memory Cells
Cells that remember past infections for faster response.
Lymphoid Tissue (spleen)
Tissue where immune cells mature and activate.
lymph nodes
trillions of antibodies in memory cells that our body keeps track of
Molecular Weight Threshold
Minimum size for immune recognition of invaders.
Antihistamines
Medications to counteract allergic reactions in immune response.
High Affinity Antibodies
Strongly binding antibodies for effective immune response.
Helper T Cells
Cells that assist in activating B cells and immune response.
Antigen Presentation
Process of displaying antigens to activate T cells.
Professional Antigen Presenting Cells
Cells specialized in presenting antigens to T cells.
has specific ID
Humoral Immunity
B cell-mediated immunity involving antibody production.
binds to specific antigen
ex. antivenom
prevents further damage from toxin getting to nerve
B Cell Receptors
Surface proteins that bind specific antigens.
Cellular Immunity
T cell-mediated immune response targeting infected cells.
B Cell Activation
Process initiated by T cells to produce antibodies.
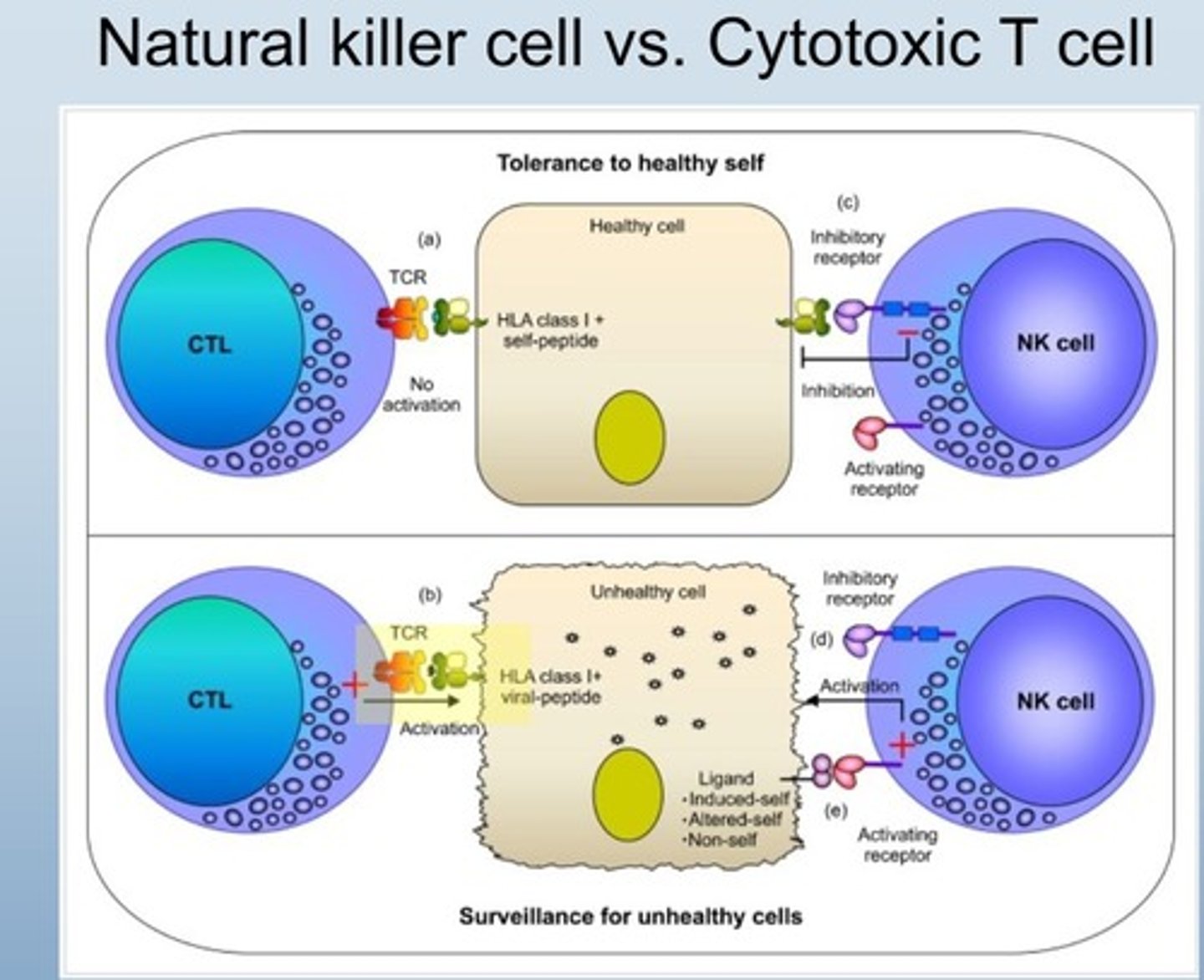
Cytotoxic T cell recognition
Identifies infected cells via HLA and black dots.
Natural Killer (NK) cell recognition
Destroys unhealthy cells lacking proper HLA.
HLA
Human leukocyte antigen, identifies healthy cells.
black dot = infection/compromise
Cytokines
Chemical messengers regulating immune responses.
blanket term
trigger inflammation
Interleukines
Cytokines facilitating communication between white blood cells.
Chemokines
Chemical signals guiding immune cell movement.
Interferons
Cytokines responding to viral infections.
when you feel sick but dont get sick
Tumor necrosis factor
Cytokine that induces cell death.
involved in inflammation of autoimmunity
Hematopoietic cytokines
Stimulate production of immune cells.
control stem cells
Cytokine storm
Excessive immune response causing inflammation.
body keeps thinking its under attack
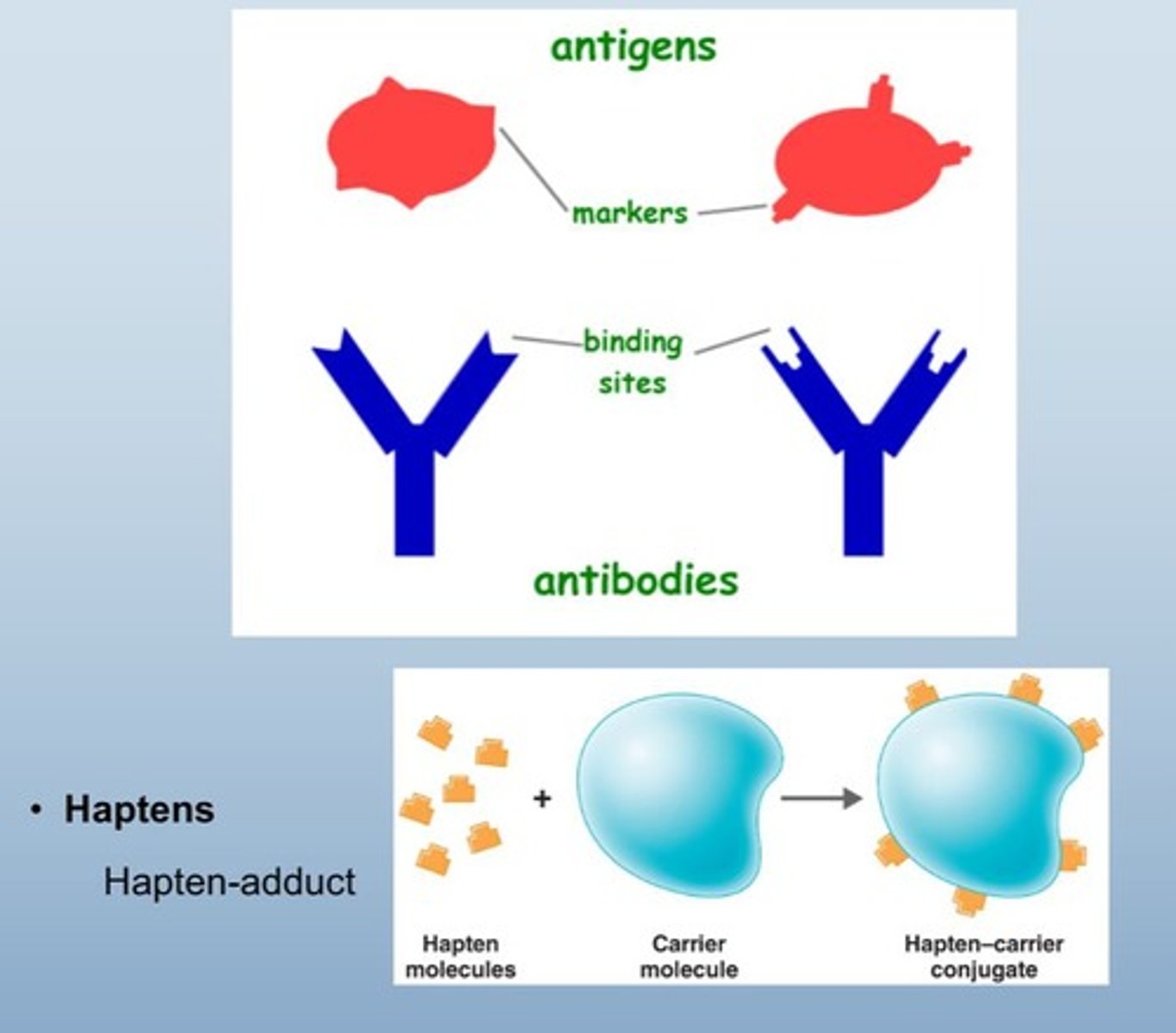
Haptens
Small molecules requiring carriers to trigger immunity.
attaches to skin carrier molecule to get big enough to invade
Hapten-adduct conjugate
Complex formed when haptens bind to carrier molecules.
Poison ivy reaction
Sensitization occurs on first exposure, reaction on second.
the first time was spent producing antibodies
Penicillin reaction
Can induce hemolytic anemia by altering RBC appearance.
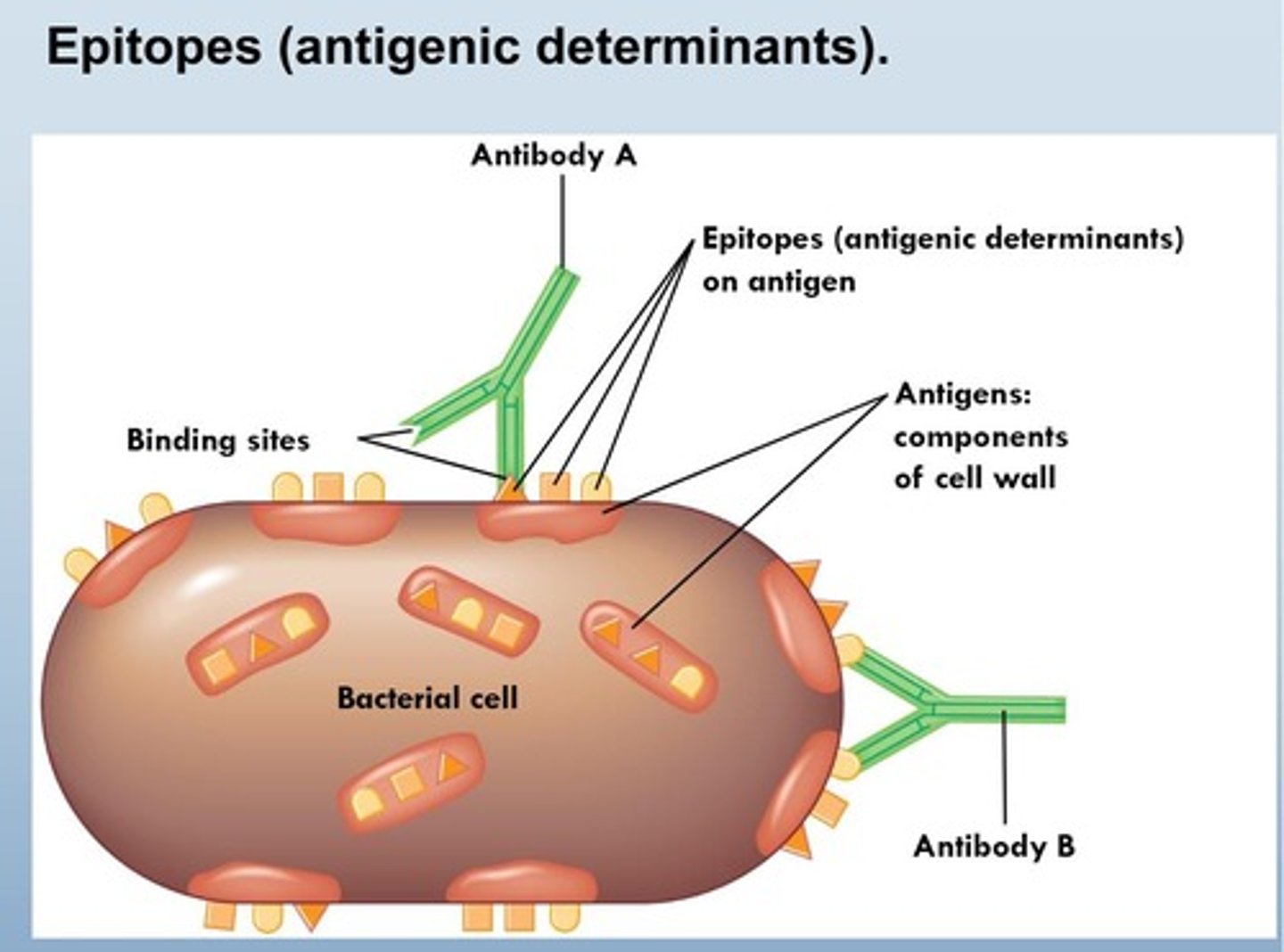
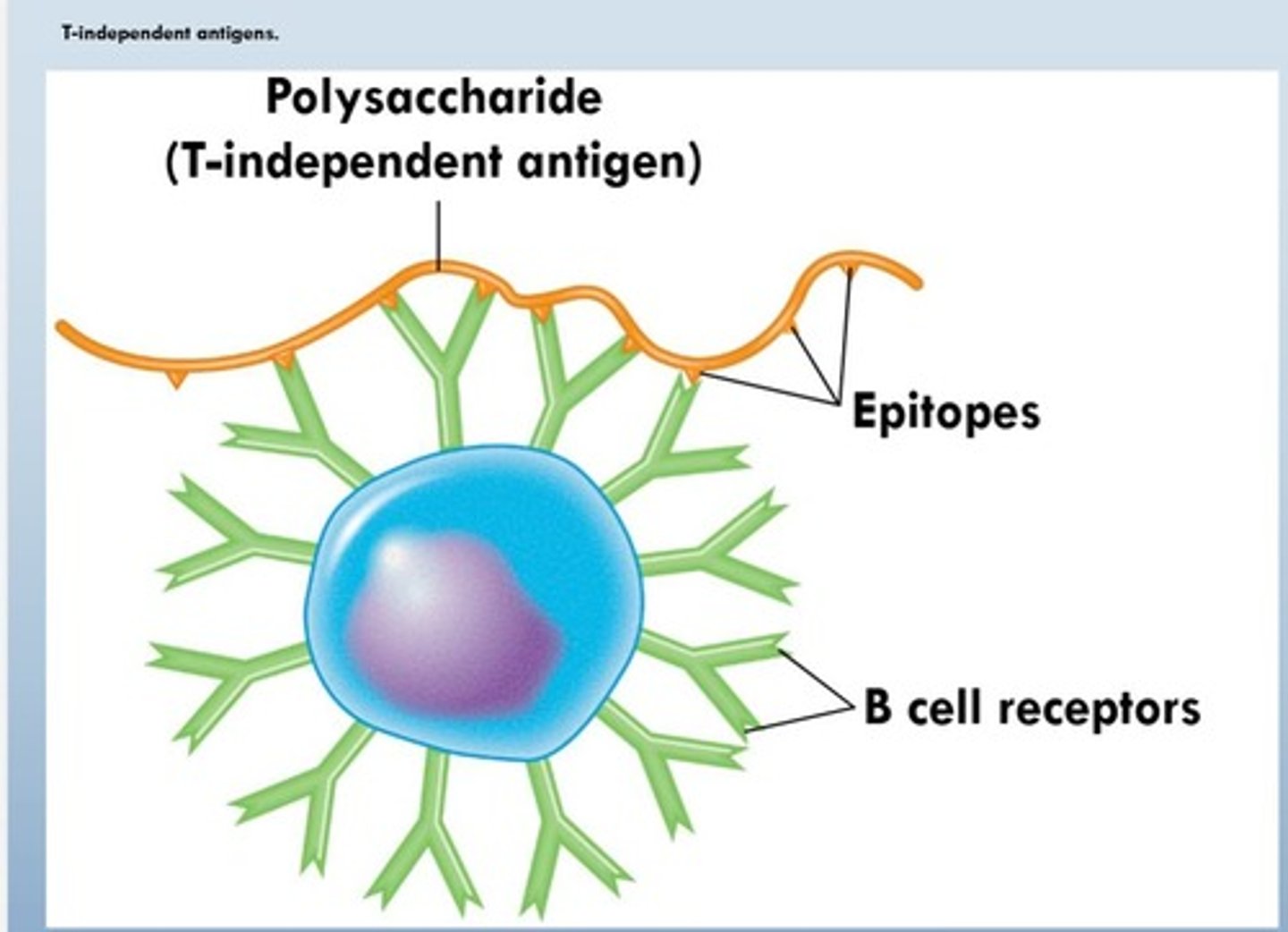
Epitopes
Specific regions on antigens recognized by immune system triggering an immune response
Immunosuppressants
Medications reducing immune response in transplant patients.
Infection susceptibility
Increased risk due to lowered immune function.
Massive inflammation
Result of cytokine storm, causing severe symptoms.
Steroids
Medications used to reduce inflammation in cytokine storms.
Immunoglobulin G (IgG)
Most abundant antibody, 80% of serum antibodies.
Autoimmune
Condition where body attacks its own cells.
Antigen-binding site
Region on antibody that attaches to antigens.
4 heavy chains
2 light chains
B cells
Adaptive immune cells that produce antibodies.
T cells
Cells required for specific antibody production.
Clumping
Aggregation indicating presence of antibodies.
Memory cells
Long-lasting cells that remember past infections.
IgM
First antibody produced, first to respond
pentamer structure with J chain
primitive
sticky; can attach up to 10 locations
IgA
Antibody found in mucous membranes and breastmilk
dimer
4 valence locations
blocks attachment of pathogens
IgD
Antibody found on
B-cell surface
blood
lymph
IgE
Antibody involved in allergic reactions
0.002% of serum
crosses placenta
monomer
on mast cells, basophils, and in blood
binds to toxin to prevent tissue from getting damaged
Vasodilation
Widening of blood vessels, often due to IgE.
Histamine release
Response causing allergy symptoms, triggered by IgE.
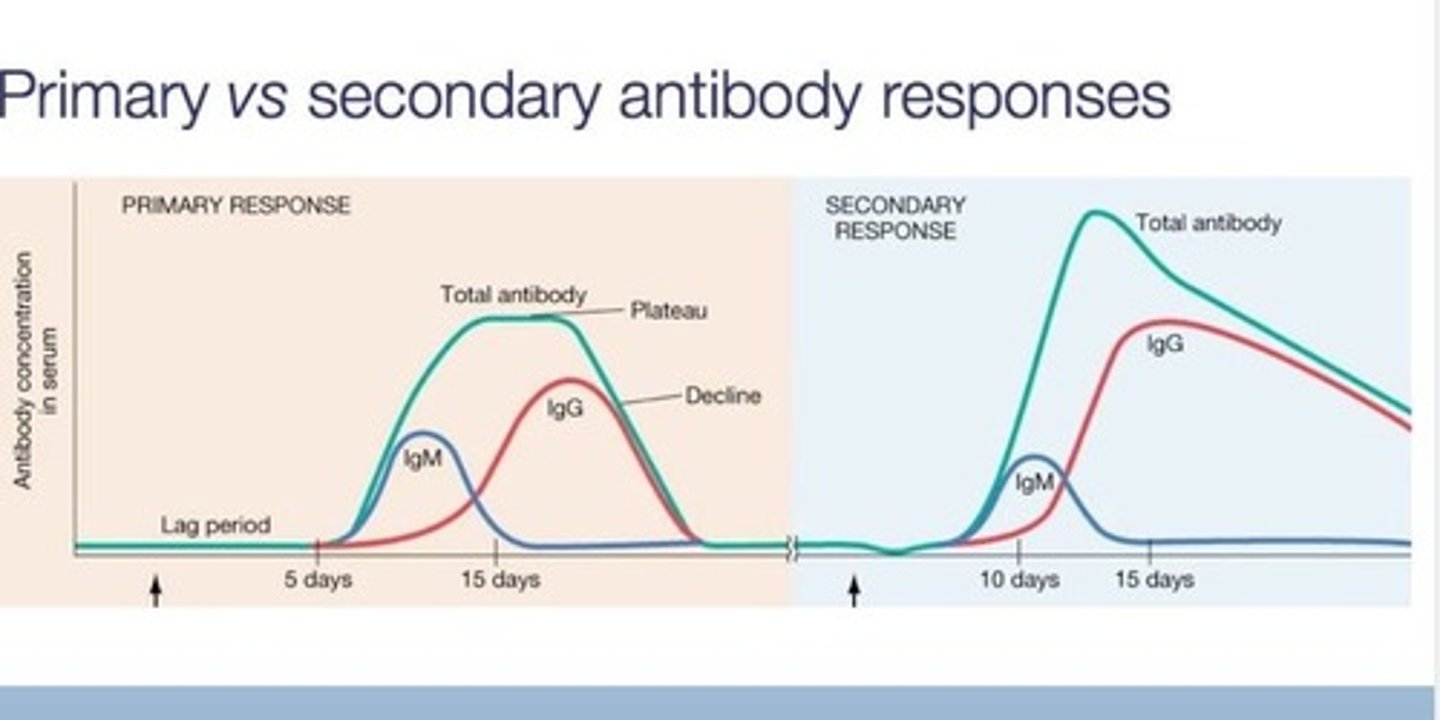
Primary response
Initial immune response to first exposure to antigen.
takes 15 days for antibodies to kick in
Secondary response
Faster immune response upon re-exposure to antigen.
memory cells kick in
Immunotherapy
Treatment to build immunity against allergens.
Competitiveness of igG vs. igE
Increasing igG outcompetes to intercept igE (histamine release; less chance)
IgE = 0.002%
IgG 80%
Competitiveness of IgG
IgG can outcompete IgE in immune response.
igG
most abundant amount of antibodies
monomer
igG booster
Some goes to placenta to baby, gets protection from mom
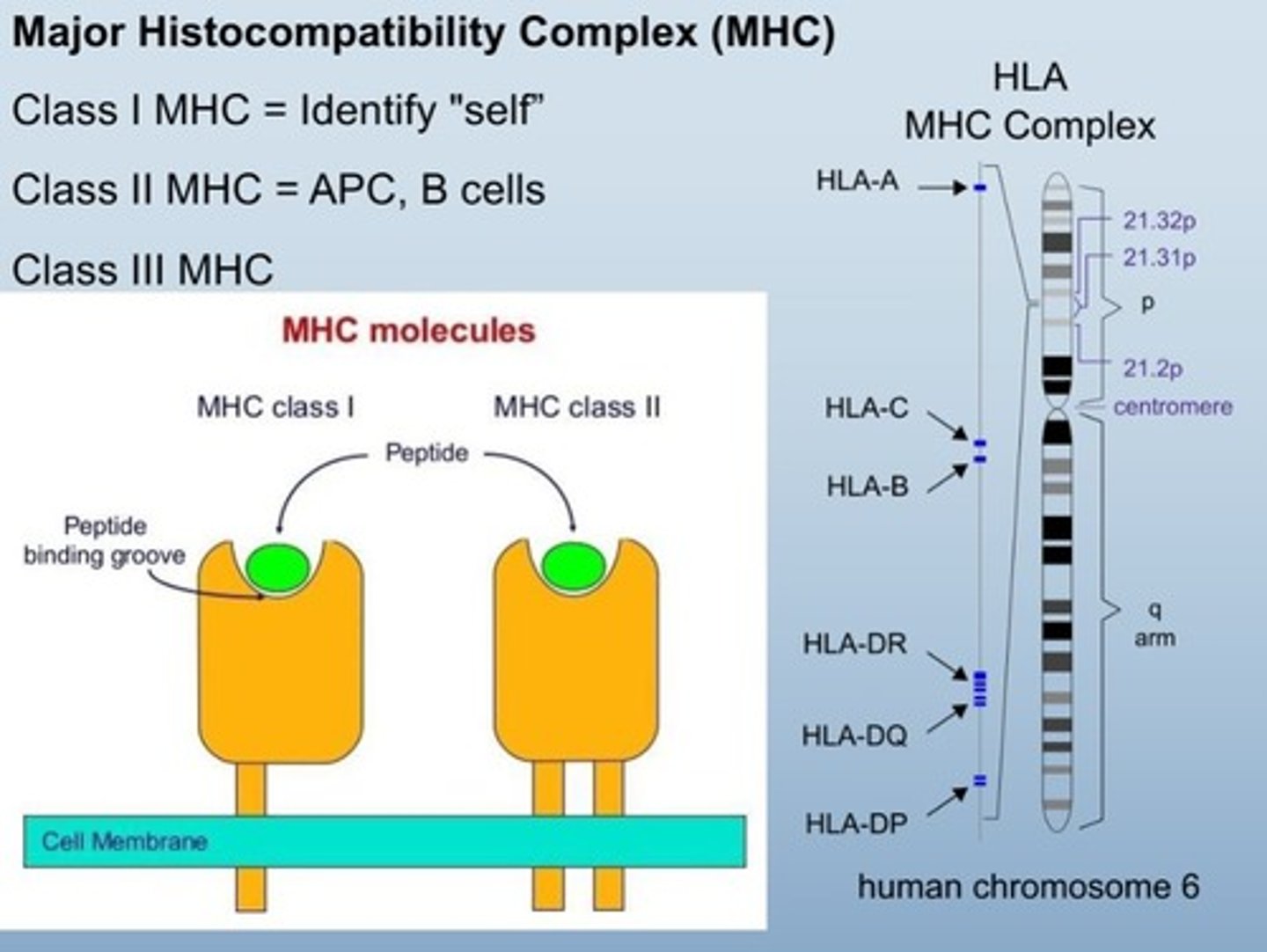
MHC
Major histocompatibility complex for organ matching.
HLA MHC complex
Human leukocyte antigen for organ transplant identification.
Class I MHC
Present on all nucleated cells.
Class II MHC
Found on antigen presenting cells (APCs) and B cells
dendrites, macrophages
Immunosuppressants
Medications that reduce immune response so that T-cell won’t tell macrophage and cytoplasmic t-cell to kill foreign organ
Crispr Cas9
Gene-editing tool used in transplants.
UAB pig kidney
Immunotherapy
Treatment aiming to enhance immune response.
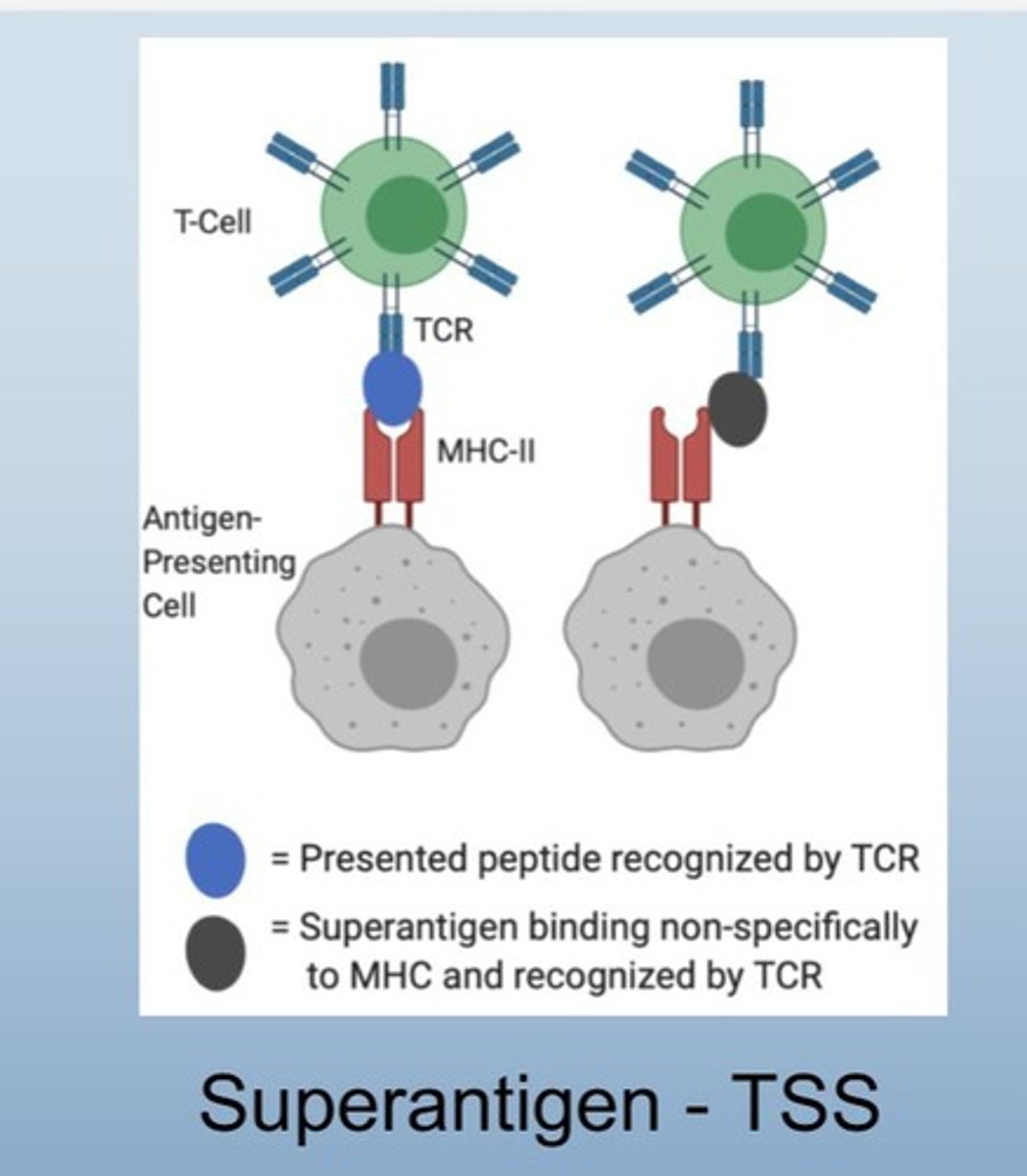
Superantigen
Stimulates T cells non-specifically, causing inflammation.
Helper T and APC do not know what is invading because there is an empty receptor
Over 20% T cell is stimulated meaning cytokines are going out = massive inflammation, large number
T-independent antigens
Antigens that can stimulate B cells to produce antibodies without T cell hel
produces IgD
no high affinity
no memory cells come out
Agglutination
Clumping of antigens and antibodies together.
Complement system
Enhances inflammation and lyses pathogens.
Antibody dependent cell mediated cytotoxicity (ADCC)
Mechanism where NK cells kill antibody-coated cells.
usually for larger pathogens like tapeworms
Neutralization
Antibodies surround toxins to prevent tissue damage.
snake and spider antivenom
botox
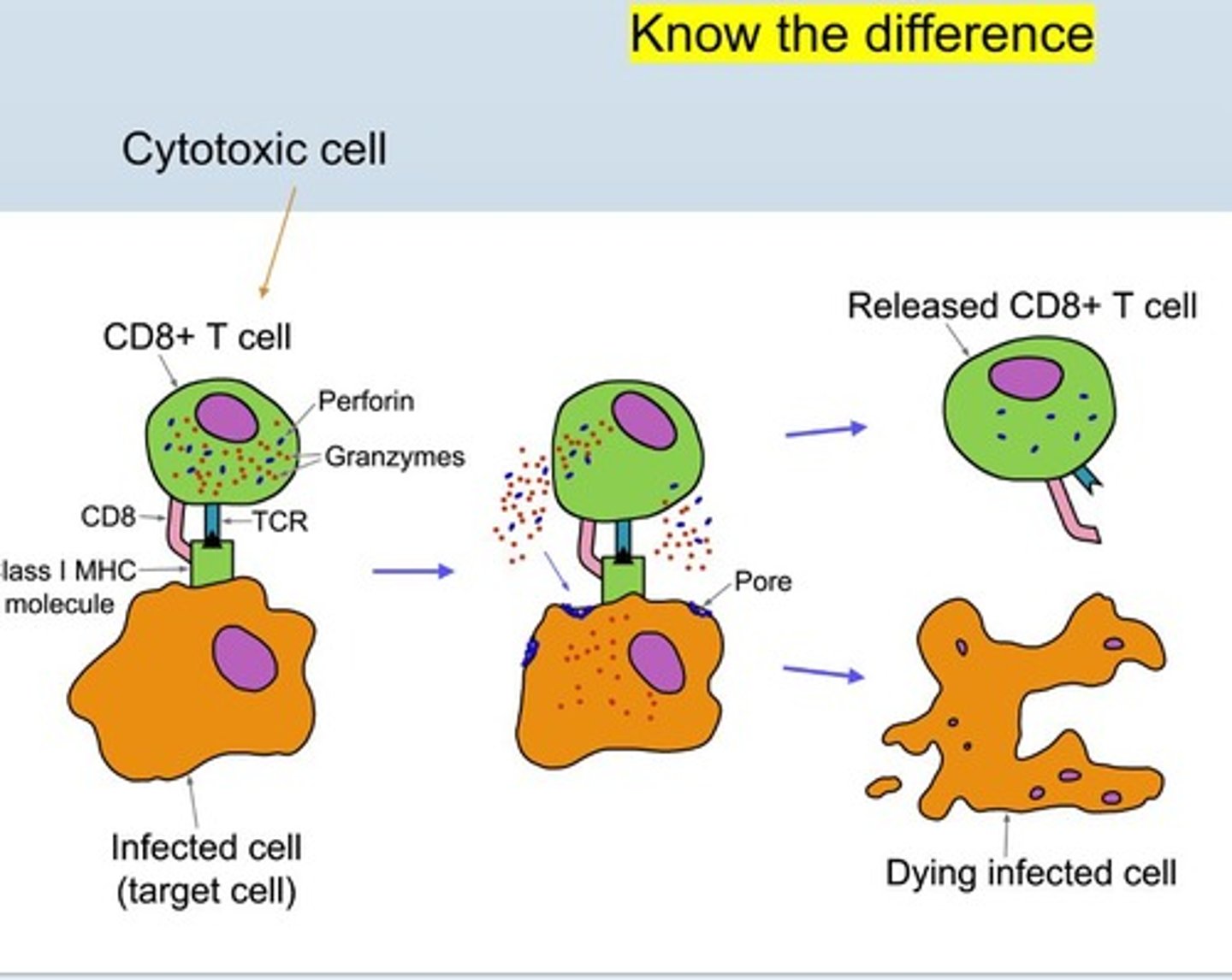
T cytotoxic cells (CD8+ T cells)
Cytotoxic cell infuses target cell with chemicals and induces apoptosis
Apoptosis
Programmed cell death induced by cytotoxic T cells.
Like a switch
Self-destruction
Acquired/adaptive immunity
Immunity gained through exposure or vaccination.
naturally acquired immunity
immunity acquired naturally through life
Active - getting sick
Passive - breastfeeding, transfer of antibodies
artificial immunity
actively seeking and receiving immunity
Active - getting vaccinated
Passive - antibody transfer
Helper T cells (CD4+-)
Cytokine signaling with B cells; interact directly with antigens
• Bind MHC class II molecules