BME 4252: Midterm Review
1/27
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Covers Lectures 2-11 (all relevant material up through band-pass filters)
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
28 Terms
Define measurand.
The physical quantity, property, or condition that the system measures.
Amplifying and filtering are both forms of…
Signal conditioning.
What is the frequency of noise produced by powerlines (in the United States)?
60 Hz.
What does the Fourier Transform do?
Breaks a waveform (function or signal) into an alternate representation consisting of sinusoidal functions (i.e. sin and cos).
What’s the characteristic difference between analog and digital signals?
Analog is continuous, digital is discrete.
What is the Nyquist’s theorem?
fs = 2 * fmax
If you know what the minimum sampling frequency should be, how do you determine what the minimum sampling period should be?
Ts = 1 / fs
The resolution of the A/D converter determines the ___ that are available for ___.
number of bits; storage
Define aliasing.
Distortion created when a signal reconstructed from samples is different from the original continuous signal.
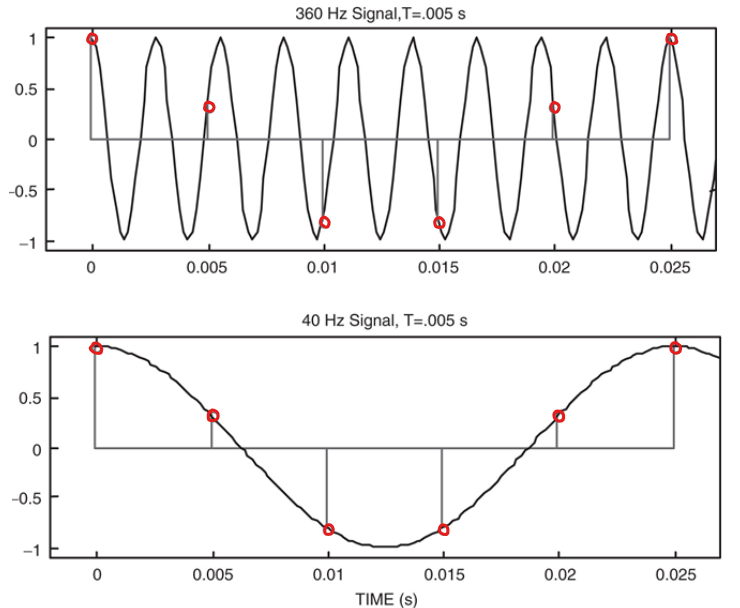
How many possible amplitude values is a quantizer with N bits capable of representing?
2N possible amplitudes.
What is the formula for resolution (in terms of volts and bits)?
Res = (voltage range) / (2N)
What does “frequency response” refer to?
The distribution of the amplitude and phase shift of the output to sinusoidal inputs.
What formula is used to convert gain from a unitless ratio to decibels?
20 * log(gain)
Is linearity (in regards to output vs. input) desirable or undesirable for simplifying signal processing?
Highly desirable.
What’s the difference between accuracy and precision?
Accuracy: how close experimental values are to the true value (i.e. correctness)
|true - experimental| / true
Precision: how close experimental values are to each other (i.e. consistency)
# of sig figs to which a value has been reliably measured
Define resolution (in terms of measurement characteristics).
The smallest incremental quantity that can be measured with certainty.
How do you determine “sensitivity” based on an output vs input graph?
Determine the slope.
What’s the difference between zero drift (aka baseline drift) and sensitivity drift?
Zero/Baseline: change in intercept (but no change in slope)
Sensitivity: change in slope (but no change in intercept)
What is always true in regards to any DC signal and its frequency?
The frequency of a DC signal is always zero.
What is the (primary) role of a diode?
To prevent current backflow (i.e. serve as “one-way electrical valves”).
What is the key characteristic of photoresistors?
Photoresistors change their resistance by the amount of light detected.
What are the characteristic equations for capacitors?
I = C * (dV/dT)
V(t) = (1/C) * ∫t0(I(𝜏) * d𝜏)
What is the formula for a capacitor charging?
V = Vi + A * e(-t) / (R C)
(t = 0): A = -Vi
What is the formula for a capacitor discharging?
V = A * e(-t) / (R C)
(t = 0): A = Vi
What is the formula for electric power (in joules)?
P = I * V
Where P is the power consumed by a resistor
What is an inductor?
A passive energy storage element that stores energy in the form of magnetic field.
What are the characteristic equations for inductors?
V = L * (dI/dT)
I(t) = (1/L) * ∫t0(V(𝜏) * d𝜏)
Lecture 7
Still haven’t gone through HW1 and 2 completely either