TBBOL- Week 7
1/66
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
67 Terms
How are amino acids joined?
Peptide bonds.
What is the name of the reaction that forms proteins?
Condensation reaction.
How are polypeptides written?
From the N-terminus to the C-terminus.
What are the three types of bonds in a polypeptide?
Amide nitrogen to alpha-carbon, alpha-carbon to carbonyl carbon and carbonyl carbon to amide nitrogen.
What is the name of the angle of rotation around the bond between ‘NH’ and the alpha-carbon group?
Phi angle.
What is the name of the angle of rotation around the bond between the alpha-carbon and the carbonyl carbon?
Psi angle.
What is the name of the angle of rotation around the peptide bond which forms between amino acids?
Omega angle.
How do peptide bonds have partial double bond?
Because the electrons from the carbonyl oxygen are delocalised.
What shape is the peptide bond?
Planar.
What configuration of omega bond angle is most frequently found in polypeptides?
Trans.
What does the Ramachandran experiment show?
That some combinations of bond angles are never observed.
Why are some combinations of bond angles never observed?
Due to the steric clashing between phi and psi bond angles.
What are the three types of secondary structures found in proteins?
Beta sheets, alpha helices and random coils.
What are beta strands held together by?
Hydrogen bonds.
Where are hydrogen bonds formed in the backbone of polypeptides?
Between N-H and C=O bonds
What configuration are alpha helices typically found in?
Coiled or ‘squashed’.
What can quaternary structure proteins involve?
Cofactors (Non-protein units).
What do many proteins need in order to activate them?
Post-translational modifications.
What are some examples of tertiary structure?
Stertic restrictions, hydrogen bonds, proline-induced kinks, disulphide bonds, ionic bonds and hydrophobic interactions.
What are the four components of an amino acid?
An ‘amino’ group, a carboxylic acid, a carbon atom connecting those groups and a ‘R’ group.
What are the basic and acidic parts of amino acids respectively?
The ‘amino’ group and the carboxylic acid.
What differs in all amino acids?
The ‘R’ group.
What is the amino acid with symbol A?
Alanine.
What is the amino acid with symbol G?
Glycine.
What is the amino acid with symbol I?
Isoleucine.
What is the amino acid with symbol L?
Leucine.
What is the amino acid with symbol P?
Proline.
What is the amino acid with symbol V?
Valine.
What is the amino acid with symbol F?
Phenylalanine.
What is the amino acid with symbol W?
Tryptophan.
What is the amino acid with symbol Y?
Tyrosine.
What is the amino acid with symbol D?
Aspartic acid.
What is the amino acid with symbol E?
Glutamic acid.
What is the amino acid with symbol R?
Arginine.
What is the amino acid with symbol H?
Histidine.
What is the amino acid with symbol K?
Lysine.
What is the amino acid with symbol S?
Serine.
What is the amino acid with symbol T?
Threonine.
What is the amino acid with symbol C?
Cysteine.
What is the amino acid with symbol M?
Methonine.
What is the amino acid with symbol N?
Aspargine.
What is the amino acid with symbol Q?
Glutamine.
What is the smallest amino acid with a stereocentre?
Alanine.
What are some examples of hydrophobic amino acids?
Alanine and valine..
What are some examples of basic amino acids?
Arginine and histidine.
What is the charge of basic and acidic amino acids respectively?
+1 and -1.
What configuration of amino acids are used in protein synthesis?
L-amino acids.
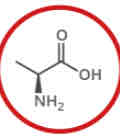
What amino acid is this?
Alanine.

What amino acid is this?
Glycine.
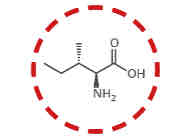
What amino acid is this?
Isoleucine.
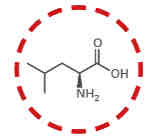
What amino acid is this?
Leucine.
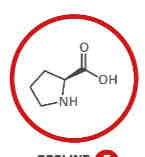
What amino acid is this?
Proline.
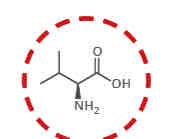
What amino acid is this?
Valine.
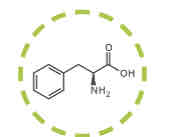
What amino acid is this?
Phenylalanine.
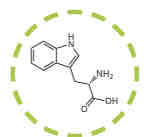
What amino acid is this?
Tryptophan.
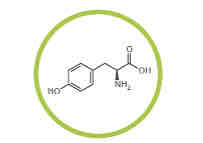
What amino acid is this?
Tyrosine.
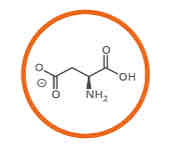
What amino acid is this?
Aspartic acid.
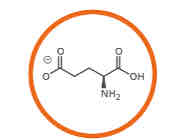
What amino acid is this?
Glutamic acid.
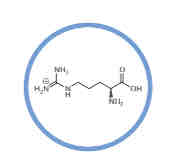
What amino acid is this?
Arginine.
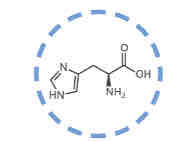
What amino acid is this?
Histidine.
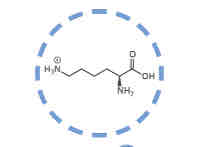
What amino acid is this?
Lysine.
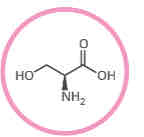
What amino acid is this?
Serine.
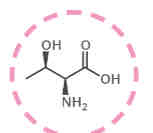
What amino acid is this?
Threonine.
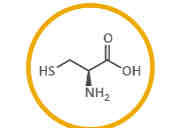
What amino acid is this?
Cysteine.
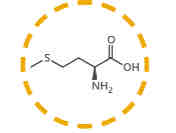
What amino acid is this?
Methionine
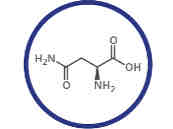
What amino acid is this?
Asparagine.
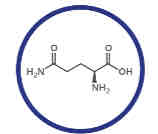
What amino acid is this?
Glutamine.