Geometry skills final exam review
1/34
Earn XP
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
35 Terms
Midpoint
cuts a segment into 2 congruent segments
Segment bisector
passes thru the midpoint
Angle bisectors
lines or segments that divide an angle into two equal parts.
Vertical angles
Vertical angles are the angles opposite each other when two lines intersect, and they are congruent.
Supplementary angles
are two angles whose measures add up to 180 degrees.
Complementary angles
are two angles whose measures add up to 90 degrees.
Triangle side theorem
Largest angle is the opposite of the largest side
Smallest angle is opposite smallest side
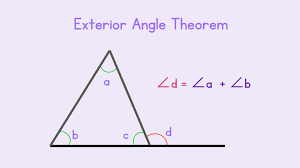
Exterior angle sum theorem
Sum of 2 remote interior angles is equal to the exterior angle
Alternate interior angles
Makes a Z, congruent
Corresponding angles
Makes a F, congruent
Same Side interior Angles
Makes a C, supplementary
Slope of parallel lines
Congruent slopes
Slope of perpendicular lines
slopes are negative reciprocals
Slope-intercept form
y=mx+b
point-slope formula
y-y1=m(x-x1)
Horizontal lines
zero slope
Vertical lines
No/undefined slope
Interior angle sum
(sides-2)180
Exterior angle sum
360
1 interior angle sum
(sides-2)180/sides
when you get the “find 1 interior 1 exterior” DO EXTERIOR FIRST
1 exterior angle
360/sides
parallelogram properties
opposite sides parallel
opposite sides congruent
opposite angles congruent
diagonals bisect each other
consecutive angles are supplementary
Rectangle
diagonals congruent
4 congruent (right) angles
Rhombus
4 congruent sides
perpendicular diagonals
diagonals bisect angles
Square
all properties
Trapezoids median
base1+base2/2
AA similarity theorem
Compare little triangle to big triangle
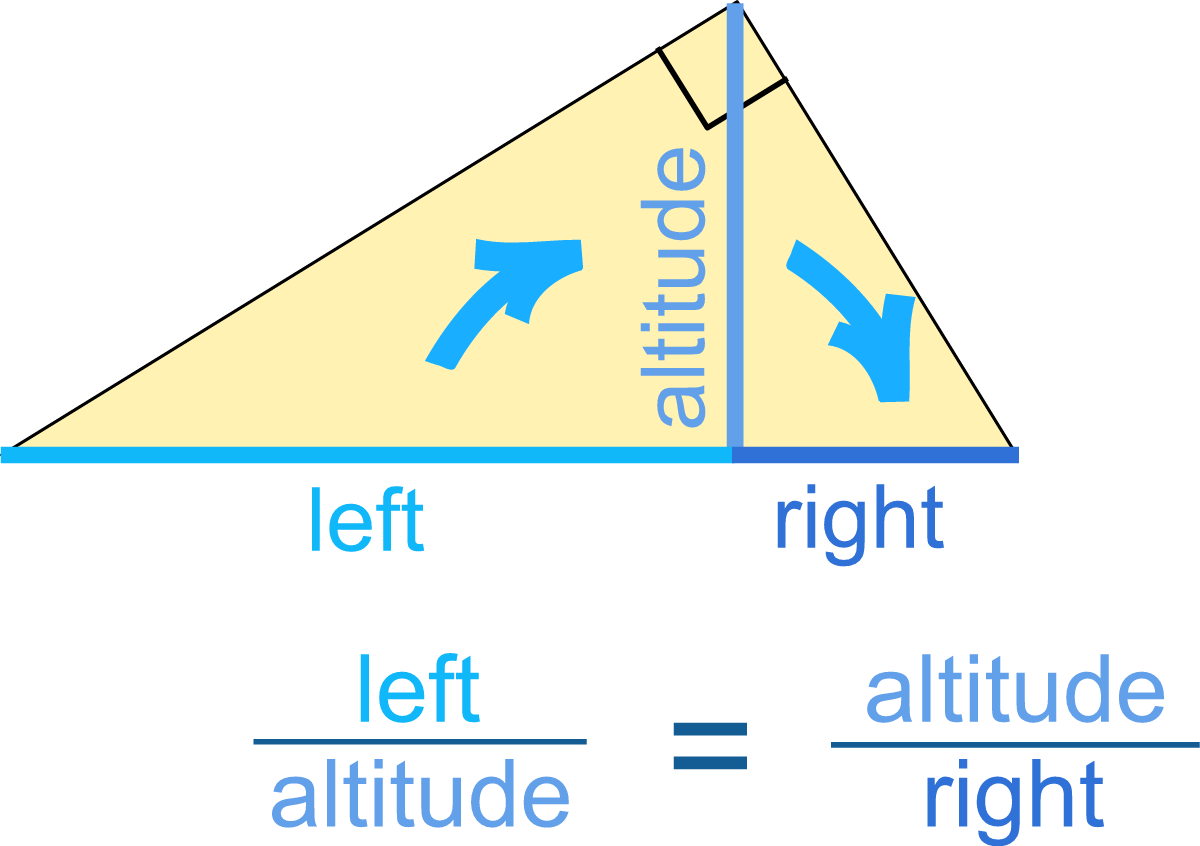
Altitude rule
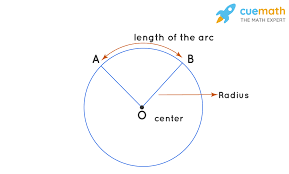
Central angle…
Equals arc
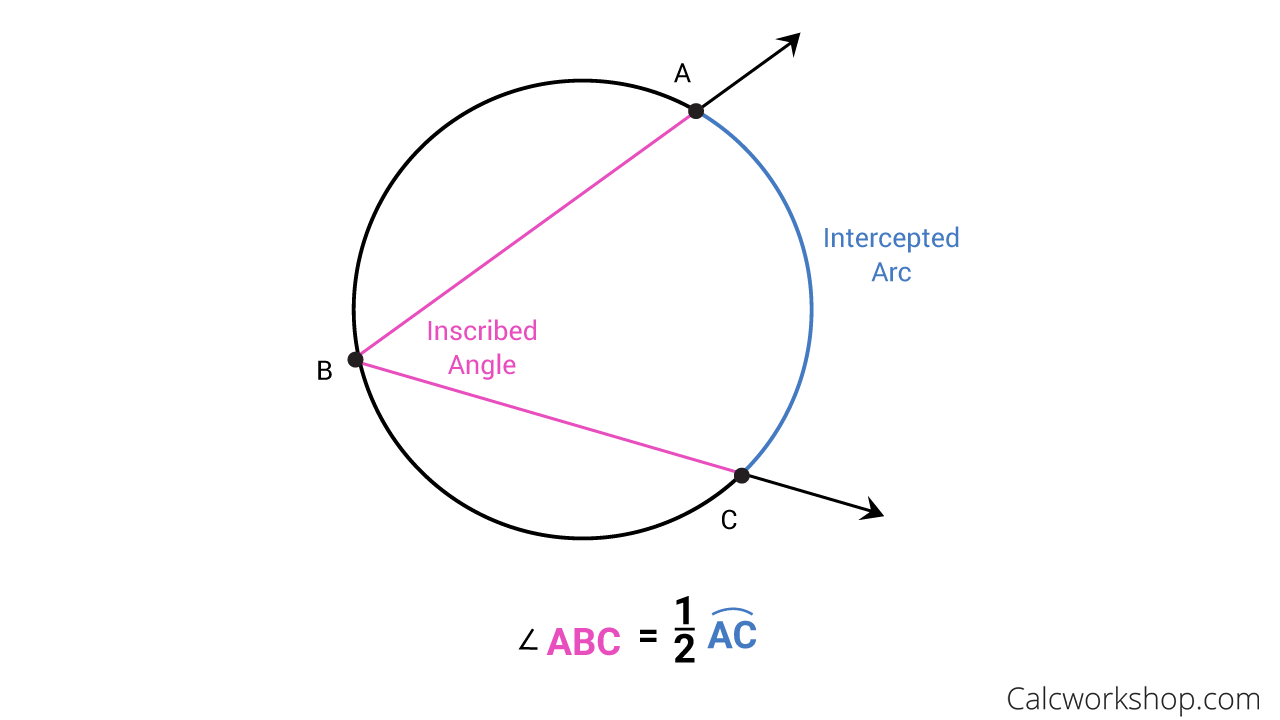
Inscribed angle
½ of the arc
Slope formula
m= y2-y1/x2-x1
Midpoint formula
m=(x1 + x2)/2, (y1 + y2)/2
Distance formula
d = ( x 2 − x 1 )2 + ( y 2 − y 1 )2
Arc length
Central angle/360 × 2π(radius)
Sector (slice of circle) Area
Central angle/360 × 2π(radius)2