Drug Receptors
1/88
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
89 Terms
What are drug receptors?
Macromolecule that binds a drug and mediates its pharmacological action
What can be a drug receptor?
Enzymes
Nuclei acids
Specialized membrane bound proteins
The magnitude of the response is proportional to the number of drug receptor complexes. True or false?
True
Where can drug receptors be located?
Cell surfaces
Within cell cytoplasm
Within cell nucleus
How can a drug receptor be linked when on a cell surface?
Linked directly to ion channels
Linked directly to enzymes
Linked directly to regulatory proteins/secondary messenger
When membrane receptors are on a cell surface and linked directly to ion channels, what do they act as? What does that allow them to do?
They act as an ion pore which allows them to change membrane permeability. They are the lock.
What are some examples of drug receptors that are on cell surfaces and that are linked directly to ion channels?
Acetycholine receptors at NMJ
GABA-benzodiazepine-chloride ion channel complex CNS
Transmembrane channels
What kind of drug receptors are on cell surfaces and linked directly to enzymes?
Proteins that span the entire width of the cell membrane
What are the different domains for drug receptors that are on cell surfaces and that are linked directly to enzymes?
Binding domain that’s on extracellular receptor sites
Catalytic domain that’s the intracellular enzymatic component
How do drug receptors that are on cell surfaces and linked directly to enzymes effect cells?
They change the enzyme activity inside the cell which leads to an altered biochemcial function inside of the cell
How do drug receptors that are on cell surfaces and linked to regulatory (G) proteins effect cell function?
By linking to an intermediate regulatory/G protein located on the inner surface of the cell
What are the different types of G proteins?
Stimulatory G proteins (Gs)
Inhibitory G proteins (Gi)
What do stimulatory G proteins (Gs) do?
Increase cellular response
Allows for a drug to couple with a Gs type GPCR which opens ion channels or turns on an enzyme
What do inhibitory G proteins (Gi) do?
Decrease cell activity
Allows for drugs to couple with Gi type GPCR which inhibits ion channels from opening and inhibits ion activity
Once a drug has left a binding site, cell function is no longer affected by a G protein. True or false?
False! Cell function is affected for a while after the drug leaves the binding site by G protein
What diseases can alter the synthesis, function, and/or regulation of G proteins?
Alcoholism
Diabetes Mellitus
Heart failure
Some tumors or cancers
What kind of substances often use intracellular receptors?
Endogenous hormones
Hormone like drugs
What is an agonist?
A compound that binds to a receptor and produces the biological response
What is a partial agonist?
A compound that produces a biological response but cannot produce 100% of the biological response even at high doses
What does efficacy mean?
The maximal response a drug can produce
What does potency mean?
The measure of a dose that is required to produce a response
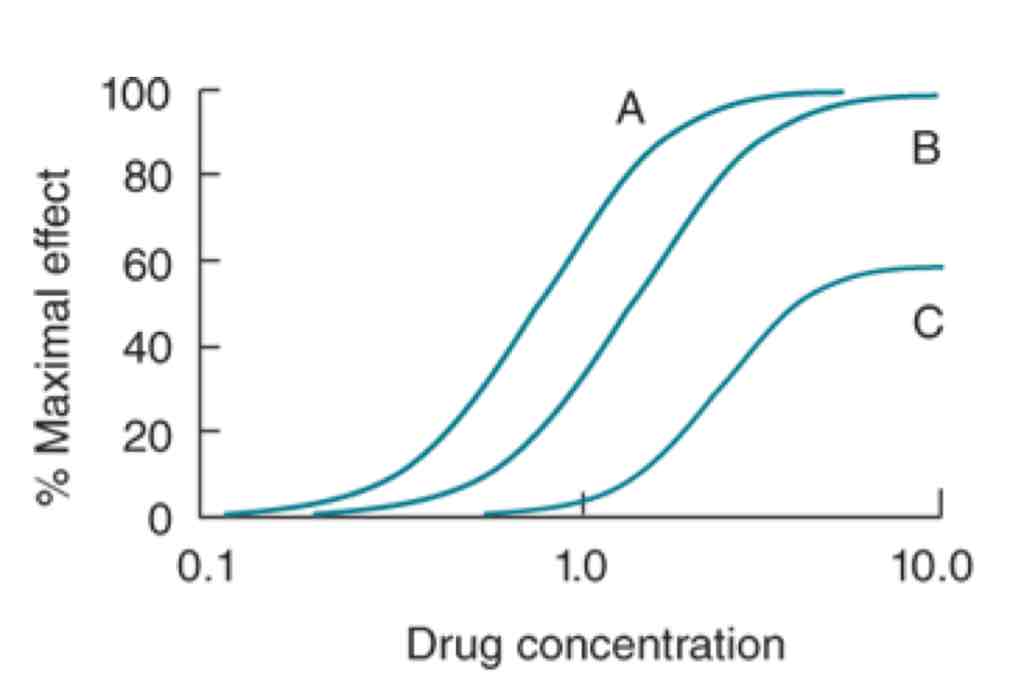
Which drugs here have the same efficacy? Why is that?
Drugs A & B because they have the same plateau
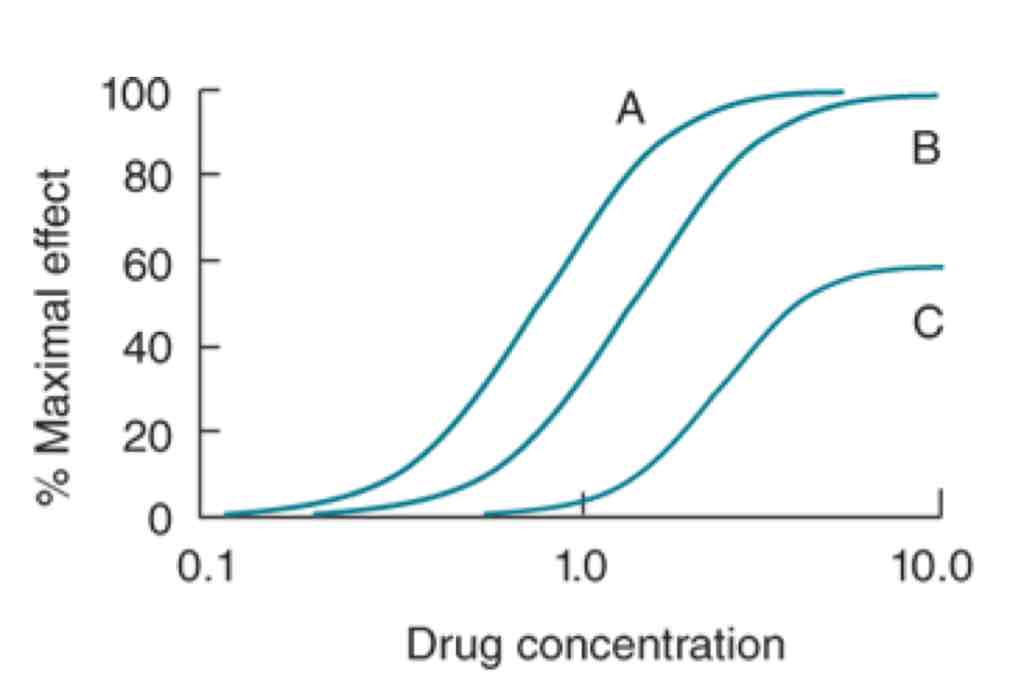
Which drug here is the most potent? Why is that?
Drug A is most potent because it has the smallest amount of drug needed to reach max efficacy
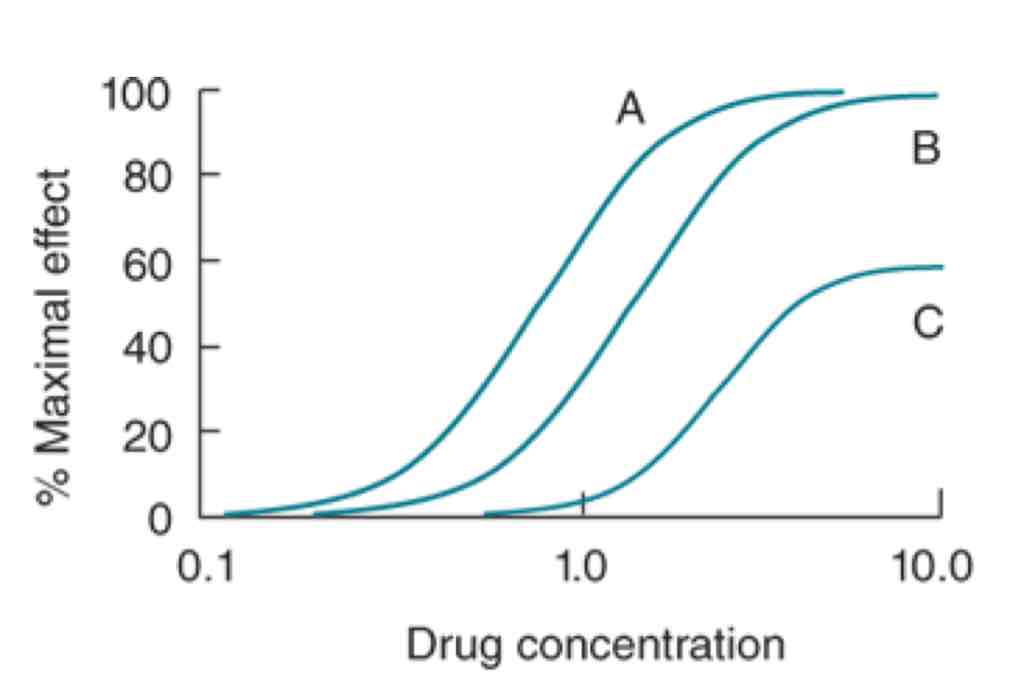
Which drug here might be a partial agonist?
Drug C
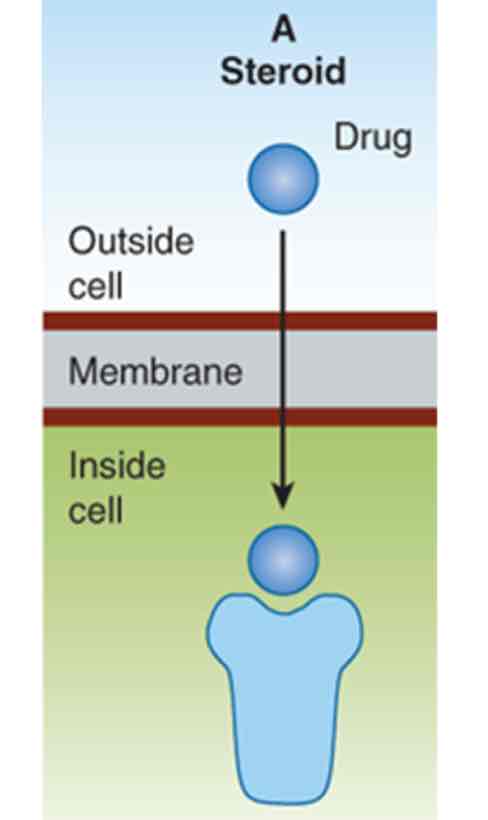
This is an example of what kind of receptor? What process is the drug using to get to the receptor?
Intracellular receptor
Drug is getting to the receptor via diffusion
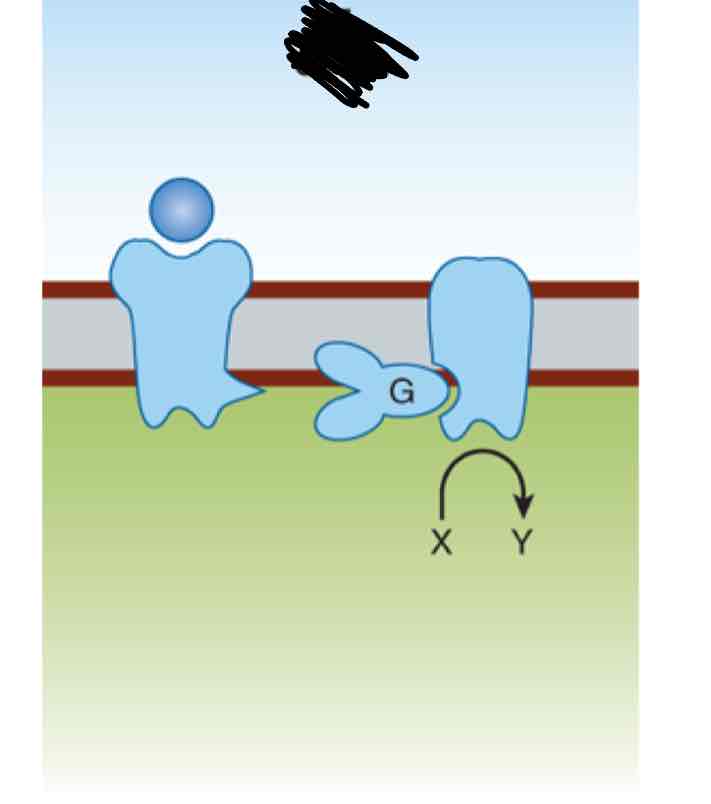
This image is an example of what kind of drug receptor?
G protein couple receptors
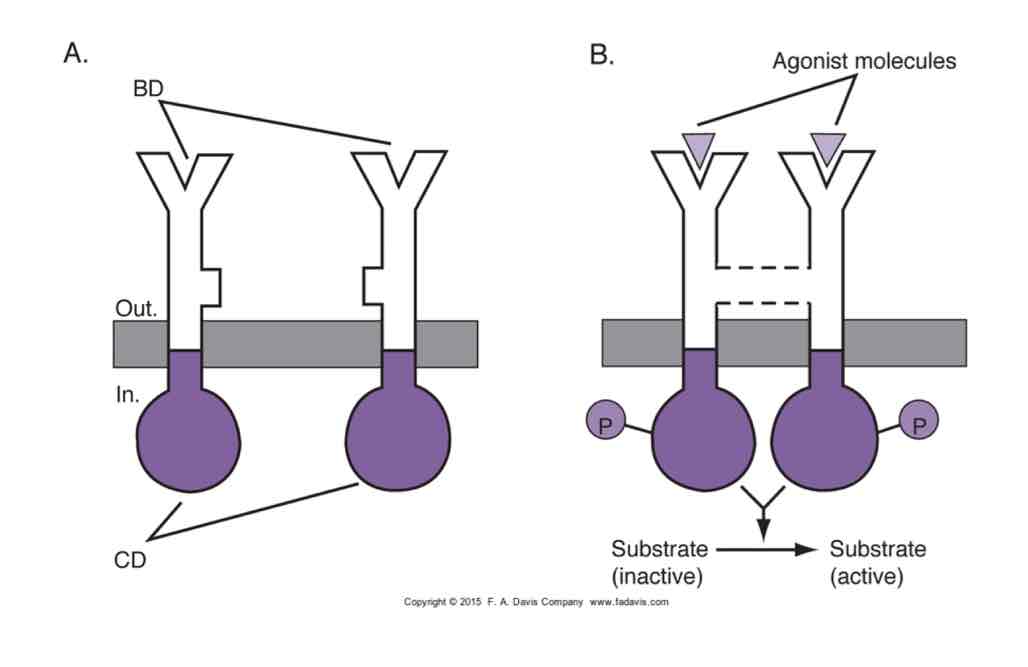
This image shows an example of what?
A receptor-enzyme system
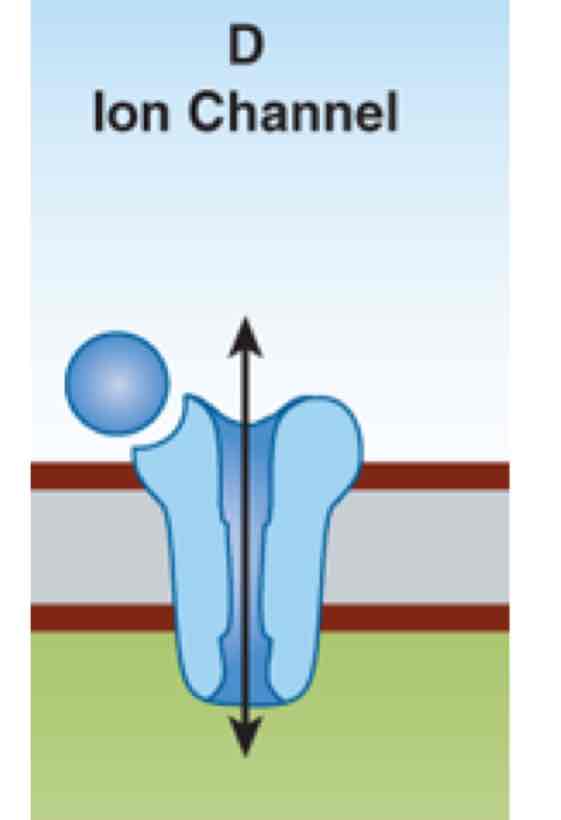
This image shows an example of what?
A surface receptor that is linked to an ion channel
The therapeutic index (TI) is a measure of what?
A measure of drug safety
A drug with a higher therapetuic index is not as a safe as a drug with a lower TI. True or false?
False! The higher the TI, the safer the drug
What is TD50 representative of?
A dose that is toxic in 50% of those that receive it
What is ED50 representative of?
A dose that is effective in 50% of those that receive it
What is meant by therapeutic window?
The range of plasma concentration of a drug that will elicit a desired response in a population of patients
What is an antagonist?
A compound that blocks or reverses the effect of an agonists or endogenous substance. It itself does not produce a biological effect
What is an example of an antagonist that blocks the effects of an agonist?
Naloxone (an antagonist) blocks the effects of opioids (an agonist)
What is an example of a antagonist that reverses or blocks the effect of an endogenously produced compound?
Beta blocker (antagonist) that blocks the effect of norepinephrine/epinephrine (endogenously produced compound)
How does a competitive antagonist make an agonist look less potent?
By shifting the dose-response curve to the right (aka it takes a higher agonist concentration to elicit the same effect)
When a competitive antagonist is introduced, can an agonist reach the same maximal effect?
You betcha
Why is it that competitive antagonists increases the dose requirement of an agonists to achieve desired effects?
Because competitive antagonists and agonsits are competing for the same site on a receptor
What is a noncompetitive antagonist?
An antagonist that reduces the maximal response of an agonist, irreversibly binds to a receptor, and binds to a different receptor site than an agonist yet still is able to prevent an agonist from binding or the effect of the agonist
What is the only way to get rid of a noncompetitive antagonist?
For the receptor complex it is attached to, to die
What kind of antagonist reduces the maximal response of an agonist?
Non competitive antagonist
What kind of antagonist reduces the potency of an agonist?
Competitive antagonist
What is an inverse/reverse agonists?
An agonists that has the opposite effect of a full agonists
What are the different drug classifications?
Agonist
Antagonist
Mixed agonist-antagonist
Inverse agonist
What is affinity?
The amount of attraction between a drug and a receptor
A drug with a low or high affinity will bind easily to open receptors?
Drug with a high affinity
What does drug selectivity mean?
The amount of different cells/tissues a drug can effect
What makes a drug selective?
WHen it only affects one type of cell or tissue and produces a specific response
The shape of a dose response curve is related to what?
The number of receptors occupied by a specific drug
What is receptor desensitization?
The brief and transient decrease in receptor responsiveness that last only a few minutes
What is receptor downregulation?
The decrease in the number of receptors that are available for binding that lost for a few days
When does normal sensitivity return after receptor downregulation occurs?
Once a cell replaces all the receptors that were eliminated
What is receptor super sensitivity?
The prolonged decrease in stimulation of receptors that results in an increase in receptor sensitivity to substances. This last for a short time
What is receptor upregulation?
The increase in the number of receptors that results in an increase in function. Long process
What are some examples of non receptor drug mechanisms?
The process by which chemotherapy agents incorporate themselves into different cellular structures
Antacids which directly neutralize stomach acids via a chemical reaction
What macromolecule forms cellular receptors?
Proteins
What is the primary role of receptors?
Recognize a specific cehmical and initiate a change in cell function by interacting with a specific agent
What are some reasons that older adults often are more sensitive to adverse effects of drug therapy?
Their pattern of drug use (aka they often take a crap ton of drugs)
They sometimes have an altered response to drugs
They often have multiple diseases
They is not much drug testing done in older adults
Lack of proper drug regulation
Problems with pt education and nonadherence to drug therapy
Pt diet
Excessive use of OTC products
The geriatric population makes up ___% of the population but they purchase over ____% of all prescription drugs
15, 30
Define polypharmacy
The excessive or inappropriate use of medications
What are some characteristics of polypharmacy in older adults?
Use of meds for no apparent reason
Use of duplicate meds
Concurrent use of interacting meds
Use of contraindicated meds
Use of inappropriate dosage
Use of drug therapy to treat adverse drug reactions
Pt improves when meds are discountinued
What are some reasons that older adults have altered GI function?
Decrease in gastric acid
Decrease in stomach emptying
Decrease in motility
Decrease in absorbing area
What are some reasons that older adults have altered drug distribution?
Decrease in body water
Increase in body fat
Decrease in lean body mass
Decrease in plasma proteins
What are some reasons that older adults have an altered hepatic metabolism?
Decrease in liver mass
Decrease in liver blood flow
Decrease in enzyme activity
What are some reasons that renal excretion is altered in older adults?
Decrease in kidney mass
Decrease in kidney blood flow
Decreaes in tubular function in nephrons
What is the BEERS criteria?
An expert panel that developed a list of meds that pose an especially high risk of ADR for older adults
Who published the BEERS criteria?
American Geriatric Society
Most drugs taken by pregnant women can cross the placenta. True or false?
True
What are some factors that affect placental drug transfer?
Physicochemical properties of drugs
Rate at which the drug crosses the placenta
Amount of drug that reaches the placenta
Duration of exposure
Distribution characteristics in different fetal tissues
Stage of placental and fetal development at the time of exposure to the drug
Effects of drugs used in combo
How long should a mother wait before taking medication after nursing?
30-60 min
How many hours before nursing should a mother take meds if she needs to?
3-4 hours
What drug is known to be found in large amounts in breast milk and have significant effects on infants?
Amiodarone
If an infant is exposed to Amiodarone, the function of what structure should be checked?
Thyroid function
What level of effect does aspirin have on an infant? Minimal, moderate, significant, or variable?
Minimal
What level of effect does caffeine have on an infant? Minimal, moderate, significant, or variable?
Minimal
What effect level does ethanol have on an infant? Minimal, moderate, significant, or variable?
Moderate
What effect level does lithium have on infants? Minimal, moderate, significant, or variable?
Variable
What effect level does oral contraceptives have on an infant? Minimal, moderate, significant, or variable?
Minimal
What effect level does penicillin have on infants? Minimal, moderate, significant, or variable?
Minimal
What effeect level does tetracycline have on infants? Minimal, moderate, significant, or variable?
Moderate
What drug has the possibility of staining a babies teeth?
Tetracycline
Drug metabolizing activity of the liveris higher in neonates compared to adults. True or false?
False! It’s actually lower
Drug excretion is impaired in infants and children. True or false?
True
What is an elixir?
An alcoholic solution where a drug is dissolved and evenly distributed. Do not have to shake before using
What is a suspension?
A solution that contains undissolved particles of a drug. Must shake before using.
In children, what is drug dosing based on?
The child’s weight
Do drug dosage based on child weight often underestimate or overestimate the required dose?
Underestimate
What is the best way to calculate drug dosage for children?
Based on the childs surface area