Reactions of Aldehydes & Ketones
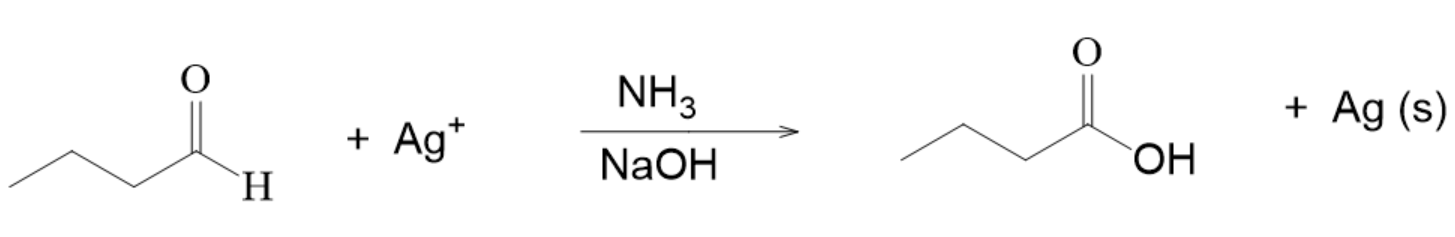
Oxidation of Aldehydes
- aldehydes can be oxidized to carboxylic acids by
- chromic acid
- Tollen’s Reagent is made of silver ion, ammonia, and hydroxide ion
- this reaction can also be called the silver mirror test or Tollen’s test
Example with Chromic Acid
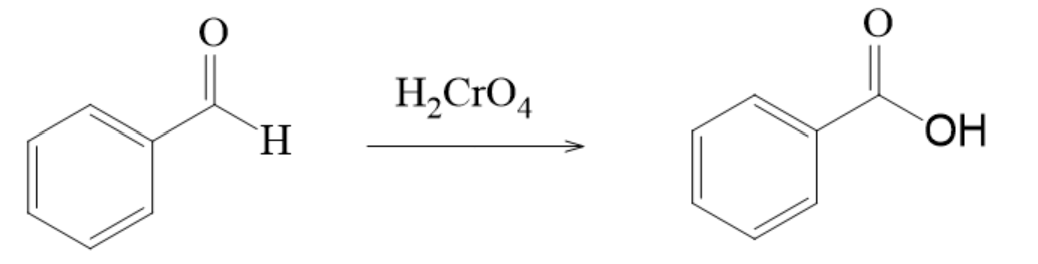
Example with Tollen’s Reagent
Formation of Hemiacetals & Acetals with Alcohols
Formation of Hemiacetals
aldehydes/ketones and hemiacetals exist in equilibrium when dissolved in an alcohol
the reaction to form a hemiacetal is an example of an addition reaction
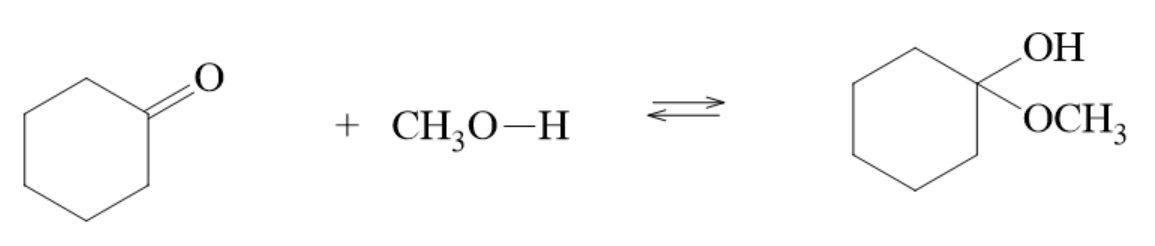
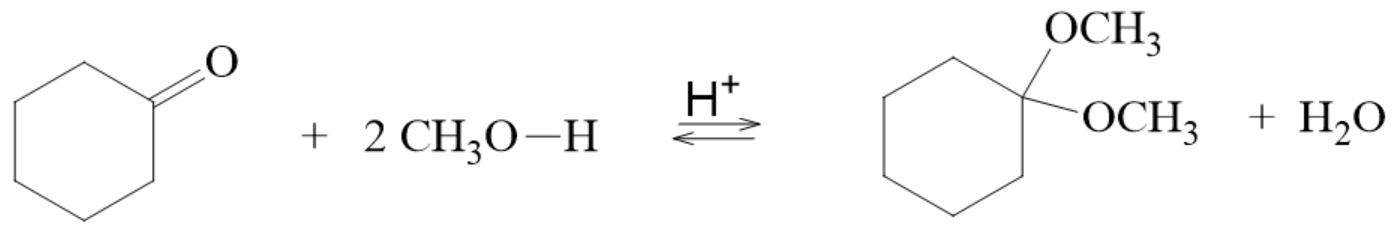
Formation of Acetals
aldehydes/ketones can be formed into acetals in the presence of
- an acid catalyst
- excess of alcohol
this reaction results in the loss of a water molecule
the aldehyde/ketone actually reacts with 2 molecules of the alcohol
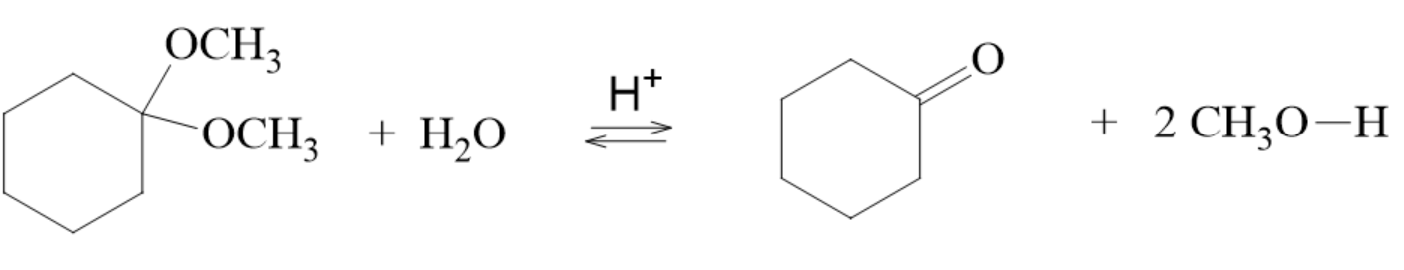
Hydrolysis of Acetals
Hydrolysis reaction: a reaction where water breaks the bonds in a compound
The hydrolysis of an acetal is the reverse reaction of acetal formation
This is a reversible reaction and is controlled by the amounts of reactants used
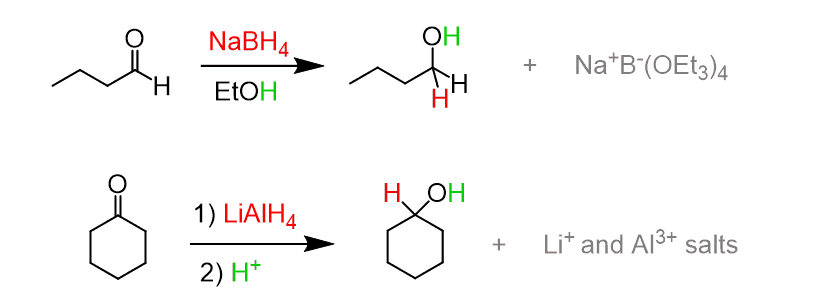
Reduction of Aldehydes to Alcohols
This reaction can be done using one of two agents
- Sodium borohydride
- Lithium aluminum hydride (LAH)
- also reduces carboxylic acids, esters, and amides