Ch 8: Human system and resource use
8.1 - Human Population Dynamics
Human population can be calculated using many formulas, some of the ways to measure population changes are:
- Crude birth rate: is the number of live births per 1000 people in a population. CBR does not calculate the age and gender structure of the population
- Total number of births / total population * 1000 = CBR
Fertility: Total Fertility rate (TFR) is the average number of births per women of childbearing age. The average number of children each woman will have in her lifetime.
GFR: General fertility rate is the number of births per thousand women aged between 15-49 years old
ASBR: Age specific birth rate is the number of births per 1000 women of any specific year group
Death rate: CDR, crude death rate: is the number of deaths per thousand people in population. CDR not a completely accurate indicator as many old people (MEDC’s) have higher CDR’s than countries with more younger populations.
- CDR = number of deaths/total population *1000
- ASMR: Age specific mortality rates is the number of deaths per 1000 women of any age group
- IMR: infant mortality rates is the number of deaths in children under 1 years old per 1000 live births
Doubling time: is the time it takes for a population to double in size/value
- DT = 70/percentage growth rate
Natural increase:
- NIR: natural increase rate in the CDR from the CBR
- CBR - CDR = NIR. This formula excludes migration
- Crude birth rate - CDR / 10
- A NIR of 1% will make a double of a population in 70 years. This doubling time is 70 divided by the NIR
Human development Index (HDI): is a statistic composite index of health (life expectancy), wealth (gross domestic product, GDP), and education, all in one value
- Factors influencing birth rates:
- Level of education, low education will lead to people having kids with little to no plans to sustain their lifestyle (lack of knowledge about birth control for example)
- Political Policies, such as taxes and poor job security
- Economic prosperity, urbanisation which reduces the physical space needed to raise a large family
- Need for children, for example, businessmen need children in order to pass on the family business
- Factors affecting mortality:
- Age structure, areas which house older adults are more likely to be subject to death and health problems than younger populations
- Social class, low social class cannot afford medical care to sustain a healthy lifestyle
- Occupation, some occupations put the employees health at risk due to their socioeconomic position
- Child Mortality, higher child mortality leads to lower fertility and reproduction
Global human population has followed a rapid growth curve, but there is uncertainty as to how this may be changing. It is also considered to be a rapid and unprecedented growth in recent years. Exponential growth or geometric growth is when the population is growing, but there are no limiting factors slowing the growth. The impacts of exponential growth are huge amount of extra resources needed to sustain the basic needs of the population.
- The world’s population is increasing very fast, due to many factors such as education, economic growth, health, poverty, and so on.
- For this reason, population growth in less economically developed countries is more common as they are less educated and do not have proper education to help them be able to lead a healthy sustainable life. Population growth mainly occurs in LEDC’s. In order to reduce birth rates in LEDC’s, the standard of living in those countries must be improved.
- MEDC’s, More economically developed countries, believe that they cannot raise children with low income, which is why they only have children if they do not affect their current way of life or lifestyle
An Increase in human populations leads to an increase in stress on Earth’s systems. As population number increase, resources will deplete.
- Fossil fuels: is the burning of fuels which leads to an increase in sulfur dioxide in the atmosphere, which causes acid rain. The effects of acid rain are devastating for the environment, such as the dissolvement of nutrients which treets need for healthy growth. Therefore, the aluminium released into the soil due to acid rain makes it difficult for trees to take in water.
- Sewage: untreated sewage left to be released as food for bacteria, which use up a lot of oxygen supply of the water. As a result, there will be a decrease in species diversity since only low oxygen concentrations species will survive.
- Deforestation: is the clearing of forested land on purpose, which is intended for other uses. As a result, this also causes habitat destruction for certain species as there will be a reduction in soil fertility and soil structure which leads to a decrease in biodiversity
- Grazing: livestock grazing is the feeding of herbivores which feed on plants such as grass and other organisms. This method contributes negatively to the environment, such as deforestation, overgrazing, soil degradation, and ecosystem stability
DTM: Demographic transition model shows us that countries progress through recognized stages through the process in transition from LEDC to MEDC. This is a pattern of decline in mortality and fertility of a country as a result of social and economic development
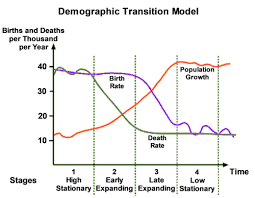
DTM has 5 stages:
- High stationary (pre-industrial societies): high birth rate due to lack of birth control, high child mortality. This is due to the population’s low education and low socioeconomic status
- Early Expanding (LEDC’s): death rate decreases as quality of life improves, and diseases decrease which ensures that their lifespan increases. However, birth rate is still high which is still high which means that population increases rapidly as well. Also, as a result of improved healthcare, child mortality decreases
- Late Expanding (Wealthier LEDC’s): as a country develops, contraception becomes more evolved which leads to decreased birth rates. Healthcare improves, education improves, and emancipation of women improves. Population levels off and the desire for material goods decreases, and people have smaller families due to low infant death rates.
- Low stationary (MEDC’s): population sizes stabilise, birth and death rates decrease in industrialised countries
- Declining (MEDC’s): Here occurs problems with the aging workforce, as population may not be replaced may not be replaced as fertility rate is low
8.2 - Resource Use in Society
Renewable Natural Capital: can be generated and/or replaced as fast as it is being used. It includes living species and ecosystems that use solar energy and photosynthesis. It also includes non-living items, such as groundwater and the ozone layer
- Natural Capital is a resource which has some value to humans, these are the goods and services that we use
- Natural income: is the rate of replacement of a particular resource or natural capital
- Capital includes: natural resources which have value to us, trees, soil, water
Natural resources that provide services, such as flood and erosion, photosynthesis, and the water cycle
Renewable natural capital can be utilized sustainable or unsustainable. If renewable natural is used beyond its natural income this use becomes unsustainable
Non-Renewable Natural capital: is either irreplaceable or only replaced over geological timescales, such as fossil fuels, minerals, soil, water in aquifers. These are resources that exist in infinite amounts on earth and are not renewed or replaced after they have been used or depleted. As resources are used, natural capital or stocks are depleted, new sources of resources need to be found
- Natural capital as a concept is dynamic, the marketable value of that capital varies regionally and over time. These changes are influenced by technological, political, environmental, economic, social, and cultural factors
Renewable natural capital:
- Use valuation: natural capital we can put a price on, such as the economic price of marketable goods, ecological functions, recreational functions
- Non-use Valuation: natural capital that is impossible to put a price tag on, such as if it has intrinsic value, future uses we do not know yet, if it has value by existing for future generations
Organisms or ecosystems have value:
- Intrinsic values: values that are not determined by their potential use to humans, their value is given vary by different factors such as culture, religion
- Ecological value: value that have no formed market price byt are essential to humans (photosynthesis for example)
- Economic value: value that is determined from the market price of the good and service a resources produce
- Aseptic Value: no market price, similar to ecological value
8.3 - Solid Domestic Waste
Solid Domestic Waste (SDW): or municipal solid waste is the trash, garbage, rubbish from residential and urban areas which we produce. This is a mixture of paper, packaging, dust, glass, metals, plastic, and others. This waste is different from other waste due to the fact that even though it is collected from homes and shops and makes up around 5% of total waste, we are able to control that waste
- There are different types of SDW of which is the volume and composition changes over time
Types of SDW:
- Biodegradable: such as food waste, paper, green waste
- Recyclable: glass, paper, metals, plastics, clothes, batteries
- Toxic: pesticides, herbicides
- Medical: needles, syringes, drugs
- Mixed: tetra packs, plastic toys
- Waste electronic and electronic equipment: TVs, computers, phones, fridges
- Waste electrical and electronic equipment (WEEE): is a term from the european community.
The abundance of non-biodegradable pollution in particular has become a major environmental issue
The Circular Economy: we find the raw materials or natural capital (take) as we use energy to produce goods (make). These goods either break down or get replaced. Our economy is built on sustainability, which indicates that our resources are finite, and will eventually run out, no matter how much we decrease the usage of fossil fuels. Waste disposal options include landfill, incarceration, recycling, and composting.
It is a sustainable model which aims to:
- Be restorative of the environment
- Use renewable energy sources
- Eliminate or reduce toxic waste
- Eradicate waste through careful design
There are many varieties of strategies that can be used to manage SDW influenced by cultural, economic, technological and political barriers. Economies depend on goods and these require raw materials. These include:
- Altering human activity: includes reduction of consumption and composting of food waste
- Controlling release of pollutant: separate waste into different types, legislate about waste separation, educate for waste separation, tax disposable items
- Clean-up and Restoration of Damages Systems: reclaim landfills, incinerate SDE for energy, collect plastics.
Managing SDW:
- Strategies to minimise waste: These can be summarised into the three R’s, reduce, reuse, recycle.
- Reduce: Means to use fewer resources and to stress Earth’s resources less. Some examples of this include: purchasing items with less plastic packaging, buying products made from recycled material, avoiding imported products, being mindful of the resources being used in your home
- Reuse: This is where the products are used for something other than their original purpose, or they are returned to their manufacturer and used once more. Examples of this would be Reusable bottles, composting of food waste, reusing old clothes as cleaning rags, reading e-books instead of physical books
- Recycle: This waste is converted into reusable material. This includes recycling bins in homes, charging households more if they produce more than the standard amount of waste, producing little food waste (feeding leftovers to dogs for example). Recycling involves collecting and separating waste materials and processing them for reuse, if the materials are reused without processing in some way, this is called reuse
- Strategies for waste disposal:
- The other forms of waste disposal are landfills, composting, and incinerators, however, if waste is not disposed through these forms, waste is thrown in the sea or composted into organic waste. Landfills are the main method of disposal, where it is taken to a site and buried there, and hazardous waste can be buried with everything else and and the initial cost is cheap.
- Incinerators are able to burn the waste at high temperatures up to almost 2,000 degrees celsius. Waste is pre-stored to remove materials which could be recycled instead of burned, and to remove incombustible materials as well. The heat produced from incinerators is used to generate steam to provide electricity to areas such as turbines or to heat buildings. This process is called waste-to-energy incineration.
- Anaerobic digestion is when biodegradable matter is broken down by microorganisms in the absence of energy. Methane produced here can be used as fuel. While domestic organic waste can be composed or put into anaerobic bio-digesters. Composting is as easy that it can be done at home. Anaerobic digestion is able to break down waste and produce methane, which is used as fuel and digestate that is used as a fertilizer.
8.4 - Human Population Carrying Capacity
Carrying capacity: maximum number of species or ‘load’ that can be sustainably supported by a given area
Difficulties in Measuring Human Capacities:
- Humans use a greater range of resources than any other animal, therefore, measuring human carrying capacity requires more than just understanding what we eat and drink, and the space needed for housing.
- We are able to substitute some resources with others, such as using coal instead of wood. However, this depends on our lifestyle as depending on our cultural and economic situation, our usage of resources also varies.
- We are also able to import resources from their environment, and the way it’ll react depends on its geographic position, which is why we cannot just look at its local environment to see how many people it can support.
- Developments in technology are able to change the resources we use, this means that machines become more efficient or it means that we use more resources as we can exploit new ones.
Ecological Footprint (EF): Human beings have enormous impact on natural environment, and ultimately on each other. The way we function and treat Earth’s resources determines and effects the long term availability of those resources and also the well-functioning Earth systems such as climate change, hydrological cycle, and other nutrient cycles in the atmosphere.
Ecological Footprint can be increased by:
- More reliance on fossil fuels
- Higher usage of technology (it can also decrease footprint)
- Large per capita production of carbon waste (high energy and fossil fuel use), and large per capita consumption of food
Ecological Footprint can be reduced by:
- Reducing use of resources, Recycling resources, reusing resources
- improving efficiency of resource use, reducing amount of pollution produced
- Transporting waste to other countries to deal with
- Improving country to increase carrying capacity
- Importing resources from other countries, reducing the population to reduce resource use
- Using technology to intensify land and increase carrying capacity
Personal ecological footprint:
- A fair Earthshare is the amount of land each person would get is all the ecologically productive land on Earth were divided evenly among the present world population
- A person’s geographical location affects their measure of sustainability, as individuals in MEDC’s usually tend to have a technocentric view, in which people increase their consumption of resources in the expectation that technology will replenish these resources and decrease the harmful impact on the environment.
- Individuals in LEDC’s tend to be ecocentrists, who try to reduce their use of non-renewable resources to decrease their use of renewable ones. People in LEDCs do not extra resources to waste, which is why they opt to decrease their personal usage of resources.