AP Psych unit 1
1/61
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
62 Terms
structuralism
used introspection to reveal the structure of the mind
functionalism
explored how mental and behavioral processes function + enable organisms to adapt, survive and thrive
introspection
examining one’s own mental and emotional processes
behaviorism
view that psychology (1) should be an objective science that (2) studies behavior without reference to mental processes.
psychologists today disagree with part 2
Freudian psych/psychoanalytic perspective
emphasizes the way our unconscious mind and childhood experiences shape our behavior. big on personalities and sexual conflicts
humanism
emphasizes peoples’ potential growth. rejected Freud & behaviorists, focusing on how we need to be loved/accepted and how our environments aid or limit our growth
cognitive psychology
the study of mental processes— how do we perceive/learn/remember/solve?
behavior
anything an organism does, observable & recordable
mental processes
internal, subjective experiences inferred from behavior
nature-nurture issue
question of the relative contributions of genes vs experiences in the development of psychological traits/behaviors
differences can be attributed to each side
biopsychosocial approach
integrated approach that incorporates biological, social-cultural, and psychological factors into analysis
neuroscientific/biological perspective
focused on how the body + brain enable emotions, memories, and sensory experiences. ex. how does brain chemistry effect mood?
evolutionary perspective
focused on how natural selection has promoted the survival of certain genes. ex. how does evolution influence behavioral tendencies?
psychodynamic perspective
investigates how behavior springs from the unconscious (less strange version of Freud’s stuff)
how can a person’s personality be explained by childhood traumas?
behavioral perspective
examines how we learn observable responses
how do we alter bad habits such as smoking?
cognitive perspective
investigates how we encode, process, store, and retrieve information
how do people use information while solving problems?
social-cultural perspective
examines how behavior and thinking different across (social) situations and cultures.
how is our behavior effected by those around us?
basic research
studies conducted with the aim of increasing the scientific knowledge base
applied research
studies conducted with the aim of solving practical issues
positive psychology
the study of human flourishing! goal is to discover and promote strengths that help people and communities thrive
industrial-organizational psychology
studies human behavior in organizations and the workplace, and uses that to solve problems at work
personality
one’s characteristic pattern of thinking, feeling, and acting.
various perspectives have different takes on how it develops
free association
in psychoanalysis, a method of exploring the unconscious where a person relaxes and says whatever comes to mind
what Freud used
psychoanalysis
Freud’s theory of personality that attributes thoughts and actions to unconscious motives and conflicts. also a technique used in therapy!
unconscious
(Freud def.) a reservoir of ‘unacceptable’ thoughts, wishes, feelings, and memories, the denial of which leads to psychological issues.
contemporary def.: info processing of which we’re unaware
id
unconscious energy that wants to satisfy basic sexual + aggressive drives. operates by the ‘pleasure principle’. devil on one’s shoulder
ego
conscious, executive part of the brain that mediates other parts’ wants
superego
represents internalized ideals and provides standards for judgement and aspirations. angel on your shoulder
preconscious
things you aren’t actively thinking of but not suppressing. they’re there, you just haven’t thought of them yet!
defense mechanisms
ego’s protective methods of reducing anxiety by distorting reality. always indirect + unconscious
repression
defense mechanism that underlies every other defense mechanism. banishes anxiety-causing thoughts/feelings/memories/wishes from the conscience
reaction formation
when one switches “bad” impulses into their opposites. ex. acting overly happy while really angry
defense mechanism
projection
disguises one’s own ‘bad’ impulses by attributing them to others
defense mechanism, now called false consensus effect
rationalization
offers justifying explanation in place of the real, threatening reasons for one’s actions
defense mechanism
displacement
shifts sexual/aggressive impulses to a more acceptable/less threatening object/person (ex. toddler kicking a dog when angry at parent)
defense mechanism
denial
when one refuses to believe painful realities
defense mechanism
regression
when one retreats to an earlier psychosexual stage that they are still fixated on (ex. nervous kid sucks thumb)
defense mechanism
sublimation
a “mature” defense mech. where unacceptable impulses are transformed into acceptable, even productive, actions
Freud liked this one
psychodynamic theory
views personality with a focus on the unconscious + childhood experiences
behavior = conscious mind + unconscious motives & conflicts
projective test
personality test that provides ambiguous images designed to trigger projection of one’s inner dynamics, ex. Rorschach
some work quite well! others not so much
false consensus effect
the tendency to overestimate the extent to which others share our beliefs and behaviors
modern version of projection!
humanistic theories
theories that view personality with a focus on the potential for healthy personal growth
self-actualization
(Maslow def.) one of the “ultimate psychological needs”, at the top of Maslow’s pyramid. the motivation to fulfill one’s potential
unconditional positive regard
a caring, accepting, nonjudgemental attitude, which Carl Rogers believed would help people develop self-awareness and self-acceptance
self-concept
all our thoughts and feelings about ourselves
trait
a characteristic pattern of behavior or a disposition to feel and act in certain ways
factor analysis
a statistical procedure that identifies clusters of test items that reflect a particular trait
ex. many introverted people like quiet, at-home activities like reading
personality inventories
a questionnaire where people respond to items designed to gauge a wide range of feelings and behaviors + used to assess personality traits
more objective than projective tests
big five theory
a set of 5 ‘dimensions’ of personality (CANOE). tests that specify where one lies on each of the dimensions say a lot about your personality
conscientiousness
how organized, careful, and disciplined one is
agreeableness
how sympathetic, trusting, and helpful one is
neuroticism
how anxious, insecure, and self-conscious one is
openness
how imaginative, willing to try new things, and independent one is
extraversion
how sociable, fun-loving, and affectionate one is
social cognitive perspective/theory
proposed by Bandura, views behavior as influenced by the interaction between people’s traits (including their thinking) and their social context
reciprocal determinism
(by Bandura) the interacting influences of behavior, internal cognition, and environment
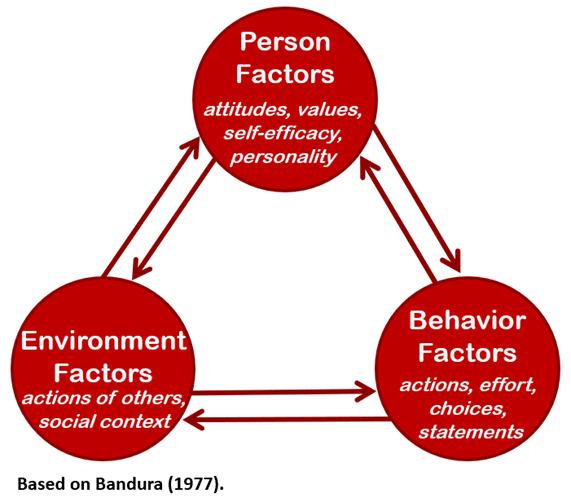
internal locus of control
the belief that you are in control of and responsible for your actions
too much = extreme guilt over things that are out of your control
external locus of control
blaming outside forces for what happens to you
too much = extreme anxiety from feeling a lack of control
self
(in contemporary psych) assumed to be the center of personality, the organizer of our thoughts, feelings, and actions.
self-esteem
one’s feelings of high or low self-worth
self-efficacy
one’s sense of competence and effectiveness
self-serving bias
a readiness to perceive oneself favorably