5.2 circular motion
1/11
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
12 Terms
what are radians a unit of?
Angle
how do you convert degrees to radians?
to convert an angle from degrees to radians, divide it by 360 and then multiply by 2 pi
what is meant by the period of an object in circular motion?
the time taken for one full rotation
what is meant by angular velocity?
the angle traveled through divided by the time taken. this is similar to linear speed, except we’re interested in rate of rotation rather than distance/time
what kind of force is required to keep an object moving in a circle at constant speed?
a constant centripetal force (a force applied always towards the corner of that circle)
true or false? the centripetal force and velocity of an object moving in a circle are always in the same direction
false. velocity is always at a tangent to the circle, force is always along a radius. they are perpendicular
how are liners and angular velocity related?
V=WR
where v = linear velocity
w = angular velocity
and R = radius
true or false? an object moving in a circle at a constant speed is not accelerating?
false. the direction is changing hence the velocity always changing which means it is accelerating
what equation gives acceleration in terms of angular velocity?
see image
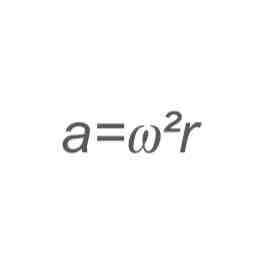
what is acceleration in terms of linear velocity?
a=v² / r
what are the equations for centripetal force?
F=mv² / r
or
F=Mw²/r
describe the steps how one can investigate circular motion through an experiment?
Circular motion can be investigated experimentally by tying a bung, with mass m, to a piece of string, and threading it through a glass tube.
The other end of the string has a weight, with mass M, suspended from it. This provides the centripetal force, F =Mg, as the tension throughout the string is constant.
The string is whirled in a circle, and the time taken for a complete rotation is recorded.
The mass of the weight is altered and the experiment repeated.We equate Mg and the centripetal force mv⅔r so Mg=mv⅔r
By measuring the radius of the circle and using the time for one complete oscillation, the velocity can be determined. When v^2 is plotted against M, a straight line graph which passes through the origin should be produced