Brain terms
1/38
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
39 Terms
Cerebral cortex
outer region of the cerebrum, containing sheets of nerve cells; gray matter of the brain
Temporal lobe
lobe that houses memories, emotions, and language comprehension
Wernicke's area
part of the left temporal lobe that allows language comprehension, both written and spoken
Cingulate cortex
inner part of the cerebrum involved in processing the emotional distress of pain; considered to be part of the limbic system
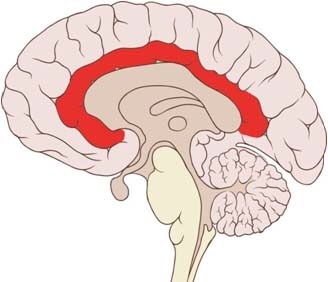
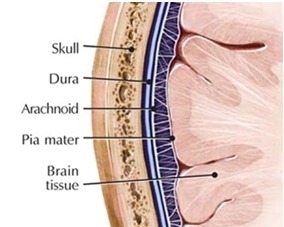
Meningeal layers
3 membranes that lie underneath the skull: the dura mater (tough mother), arachnoid (spider web-like), and pia mater (tender mother); arteries and veins bring blood to and from brain and heart in this area
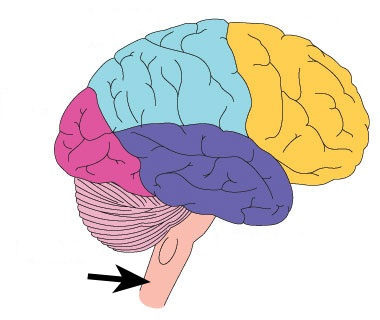
Brain stem
directs heart rate and breathing; involved in sleep-wake cycle, attention, temperature regulation, vision, hearing, and motor control of muscles in the face and neck; divided into 3 structures: midbrain, pons, medulla oblongata, and the reticular formation
Midbrain
cluster of dopamine-producing cells in the brain stem that help regulate movement
Pons
part of the brain stem that contains the locus ceruleus, an area important for attention
The Human Brain
organ that serves as the center of the nervous system in all vertebrate and most invertebrate animals; weights 3 lbs; consumes 20% of the body's oxygen supply; it consists of 86 billion neurons and 85 billion glial cells
Neuron
specialized cell transmitting nerve impulses; a nerve cell
Right & Left cerebral hemispheres
the two sides of the cerebrum joined by the corpus callosum; comprised of 4 lobes; some functions shared by redundant areas, while others (e.g. speech--Broca's area) are focused on one side
Frontal lobe
lobe that includes behavioral traits (personality, decision making), motor control, and makes sense of information about the environment, memories, and emotions
Motor cortex
part of frontal lobe that ensures movements are intentional, precise and coordinated with sensory perception
Broca's area
part of the left hemisphere of the frontal lobe responsible for production and coordination of speech
Occipital lobe
lobe that decodes visual signals from the retina via the thalamus
Parietal lobe
lobe that integrates information from our senses
Somatosensory cortex
part of the parietal lobe that receives information from touch receptors
Medulla oblongata
part of the brain stem that controls breathing
Reticular formation
part of brain stem that has a central role in states of consciousness like alertness and sleep
Spinal cord
bundle of nerves that run through the backbone from the medulla oblongata to the lower back
Limbic system
consists of group of structures responsible for motivation, emotion, learning and memory; includes: the olfactory bulb, hippocampus, amygdala, hypothalamus, basal ganglia, and cingulate gyrus/cortex
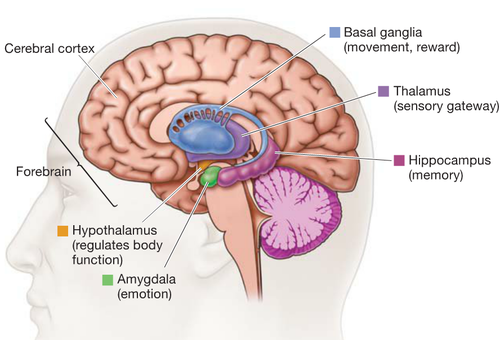
Amygdala
small, almond-shaped part of the limbic system that links fear, aggression, and anxiety to knowledge of people or places; ensures that threats can be recognized and avoided in the future
Hippocampus
part of the limbic system responsible for short and long-term memory; produces new neurons even when the rest of the brain stops growing early in childhood; creates mental maps of places (spatial memory)
Hypothalamus
part of the limbic system that links the brain and spinal cord (the CNS or central nervous system) with the endocrine system (glands that release hormones); controls the pituitary gland; regulates body temperature, thirst, hunger, circadian rhythms; promotes bonding between family members; bridges subconscious signals from brain stem with signals from the cerebral cortex
Thalamus
"grand central station" located in middle of brain; relays information about most of our senses (vision, hearing, touch, proprioception--awareness of body position, and taste) with the rest of the brain
Ventricles
4 cavities; contain cerebrospinal fluid which protects, nourishes, and cleans up after brain; supports weight of brain
Pituitary gland
produces & releases hormones controlling bodily functions and behaviors; relays signals from hypothalamus to glands throughout body
Basal ganglia
group of structures in the limbic system (including the caudate nucleus which is associated with pursuing rewards) that control voluntary movements, habitual behaviors, and emotions
Cerebellum
the "little brain" which coordinates muscular activity, maintains equilibrium; important in honing practices talents; contains 70 billion neurons (5x cerebral cortex);
Corpus callosum
thick wide bundle of neural connections linking the left and right hemispheres
Olfactory bulb
specialized area of the cortex that processes sense of smell; closely tied to emotion and memory due to direct connections with amygdala and hippocampus
Cranial nerves
group of 12 fiber bundles that transmit impulses of sensation; control muscles in the neck and head; 10 originate in the brain stem, 2 originate in the cerebral cortex
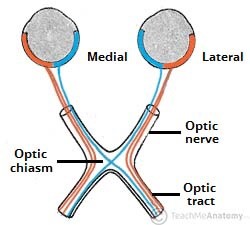
Optic nerve
cranial nerve that carries neural impulses from the eye to the brain
Optic chiasm
point at which optic nerve fibers cross in the brain
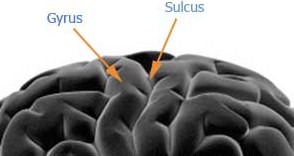
Sulci
shallow grooves that separate gyri
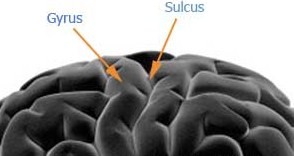
Gyri
ridges of the brain
Glial cells
cells in the nervous system that support, nourish, and protect neurons
Cerebrum
largest part of the brain; responsible for voluntary muscular activity, vision, speech, taste, hearing, thought, memory
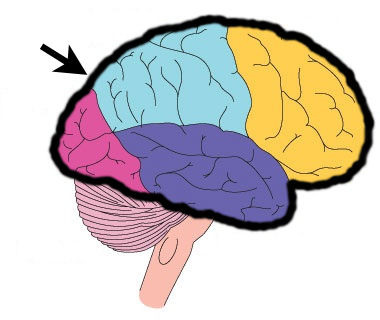
Prefrontal cortex
part of the the frontal lobe that exercises executive function--the ability to make complex & socially mindful decisions based on memories and predictions