formulation of liquid medicines
1/33
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
34 Terms
what is the kinetic theory of matter: gases
assumptions of kinetic molecular theory:
consist of a large number of tiny particles
are in constant, rapid, linear motion → collisions are soon to be completely elastic, with no net loss or gain of kinetic energy
molecules are independent of one another, unless during collisions → no forces of attraction/repulsion
there is a wide range of molecular speeds that contribute to kinetic energies
how well does the kinetic theory of matter correlate with observed gas properties
majority of gas volume is empty space → gas is very compressible
gases will expand to fill the container → Brownian motion supports the random nature of gas molecules
they move in a random, rapid motion
the ability to fill a container at any pressure supports the lack of forces between molecules
there is distribution of kinetic energies
what are the key properties of liquids
flow readily
not locked in fixed position
more resistant to deformation than gases
diffuse slower than gases
greater IMFs
less space between molecules
less compressible
little free space
repulsion occurs between electron clouds
can maintain a characteristic volume
shape depends on container
volume doesn’t change
conversion of a gas to a liquid is depend on..
temperature and pressure
what is critical temperature, Tc
the maximum temperature at which a gas becomes a liquid at critical temperature
what is critical pressure, Pc
the pressure that is required for gas to become a liquid at critical temperature
what are the three different forms of of solids
crystalline
polymorphism
amorphous (non-crystalline)
what are the feature of crystalline solids
sharp transition from solids to liquids
defined melting point
incompressible due to fixed structure
fixed geometric pattern/lattices
have different conformations of arrangement: cubic/hexagonal
each small unit is called a unit cell, each each unit cell has the same number of molecules or ions in it, all arranged in the same way
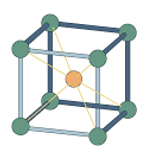
what are the features of polymorphism solids
molecules arranged differently in the crystal
exist in different states
internal structure detected by X-ray diffraction
different chemical/physical properties to original (causes challenges when formulating products, as well as different therapeutic/adverse effects)
examples: paracetamol and spironolactone
what are the features of amorphous (non-crystalline) solids
without form → molecules are arranged randomly
similar arrangement to supercooled liquids (liquids that are heated, then cooled very quickly)
change gradually and continuously → eventually crystallise to become more stable
in morphic state, flow when sufficient pressure applied over time
no discrete melting point
recrystallise over time
example: novobiocin, is absorbed and active when in amorphous state
what are the two types of pharmaceutical liquids
non electrolytes
electrolytes
electrolytes → ions are able to migrate and therefore conduct electricity
what is a solution
a type of dispersion that is a homogenous, physical mixture of two or more substances, in a single phase system
in terms of dispersion, what are the three types of solutions
solution
a chemically and physically homogenous mixture of 2 or more substances
solute (solid) → minor component, is completely dissolved
solvent → major component
colloidal solution
solution of particulate material that is more than 1μm
not completely dissolved
suspension
a mixture of insoluble material in a fluid
concentration expressions
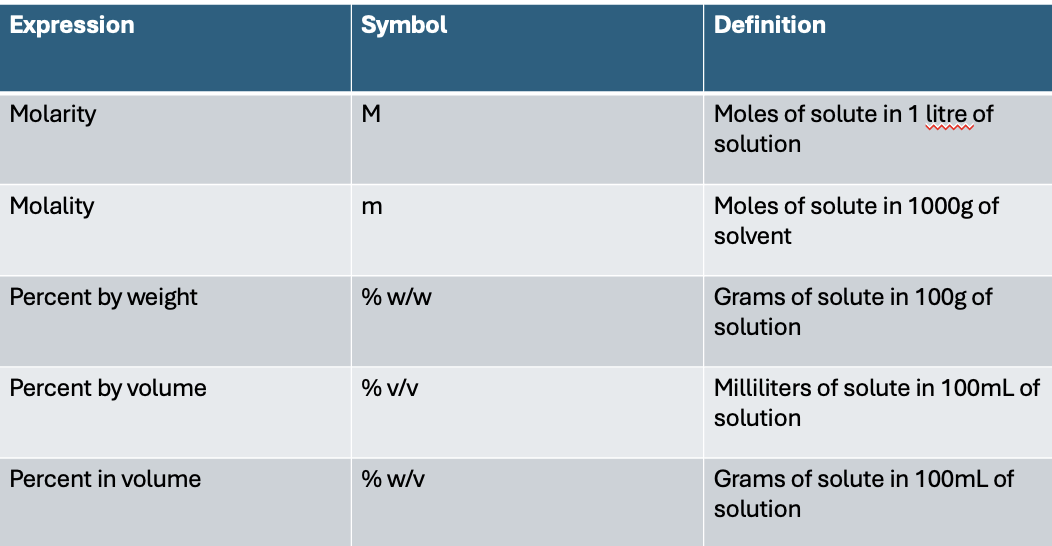
what are the types of pharmaceutical solutions
internal
oral for GI (local) or systemic disorders
parenteral (often injected for systemic effects)
external
local or tropical effects
otic (ear)
ophthalmic
vaginal
rectal
oral rinses/gargles
dermal
what are the advantages of pharmaceutical solutions
complete and rapid release of API due to higher bioavailability compared to other formulations
ease of use/swallowing
uniform dose
only dosage form that can be given by IV route
what are the disadvantages of pharmaceutical solutions
bulky for storage/transport
specialist containers required
may have poor chemical stability
taste-masking is difficult
preservatives required to prevent microbial growth
what do colligative properties for ideal solutions depend on
depend on the number of solute molecules present, not physical or chemical characteristics
if one property is known, the can calculate another → number of moles of substance can be calculated
colligative properties → the properties of a solution that are dependent on the ratio between the total number of solute particles (in the solution), to the total number of solvent particles
what is vapour pressure of a liquid
when a liquid is in an enclosed container, some molecules have enough kinetic energy → gaseous molecules are released and turn into liquid vapour
as more molecules enter the vapour phase, some of them collide with the liquid surface and condense back into the liquid.
eventually, the rate of molecules vaporising equals the rate of molecules condensing back to liquid → dynamic equilibrium
no molecules turn to vapour
what happens when you add a solute to a solvent
reduces vapour pressure → increases boiling point → decreases freezing point
this is controlled by Raoult’s law

what determines the phase of a solution
a solvent
what is dissolution
transfer of molecules from a solid into a solution
what is solubility
the extent to which dissolution proceeds under a set of experimental conditions
what is saturation
amount of dissolved solute = amount of undissolved solute
what can you change if a drug has poor aqueous solubility
increase dose to achieve desired effect
change or add in other solvents
but all this increases the risk of adverse effects in the end product