Physical Education and Health
1/102
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
103 Terms
body composition
body’s relative amount of fat to fat-free mass
formula for Body Mass Index (BMI)
weight (kg) / height (m)²
underweight
normal
overweight
obese
classifications of bmi
below 18.5
underweight
18.5 - 24.9
normal
25.0 - 29.9
overweight
30.0 and above
obese
weight
heaviness or lightness of a person
weighing or bathroom scale
equipment for weight
light clothing
evenly distributed; center
For the Tester - weight
Wear _____ before weighing
on bare feet, stand erect and still with weight _____ on the _____ of the scale
zero point
score; kilograms
For the Partner - Weight
before the start of weighing, adjust the scale to ____
record the _____ in _____
nearest 0.5 kilograms
scoring for weight
height
distance between the feet on the floor to the top of the head in standing position
tape measure laid flat to a concrete wall where zero point starts on the floor
L-square
even and firm floor and flat wall
equipment for height
heels, buttocks, shoulder
For the Tester - Height
stand erect on bare feet with ___, ____, and _____ pressed against the wall where the tape measure is attached
L-square; straight and parallel
meters
For the Partner - Height
place the _____ against the wall with the base at the top of the head of the person being tested. Make sure that the L-square when placed on the head of the student, is _____ and _____to the floor
record the score in ____
record standing heigh to the nearest 0.1 centimeter
1 meter = 100 centimeter
scoring for height
flexibility
ability of the joints and muscles to move through its full range of motion
zipper test
to test the flexibility of the shoulder girdle
ruler
equipment for zipper test
erect
right arm; zipper; shoulder blades
over
For the Tester - zipper test
stand _____
raise your ____, bend your elbow, and reach down across your back as far as possible, to test the right shoulder; extend your left arm down and behind your back, bend your elbow up across your back, and try to reach/cross your fingers over those of your right hand as if to pull a ____ or scratch between the _____
to test the left shoulder, repeat procedures a and b with the left hand ____ the left shoulder
overlapped; middle fingers
distance; centimeters
For the Partner - zipper test
observe whether the fingers touched or _____ each other, if not, measure the gap between the _____ of both hands
record the ____ in _____
record to the nearest 0.1 centimeter
scoring for zipper test
6; excellent
fingers overlapped ___ cm and above
4; very good
fingers overlapped by ___ cm to 5.9 cm
3.9; good
fingers overlapped by 2 to ____ cm
0.1; fair
fingers overlapped by ___ cm to 1.9 cm
needs improvement
just touched the fingers
poor
gap of 0.1 or wider
sit and reach
to test the flexibility of the lower extremities (particularly the trunk)
tape measure or meter stick
equipment for sit and reach
12 inches apart
thumbs; elbows
middle fingers; sliding
jerking
twice
For the Tester - sit and reach
sit on the floor with back, head, and shoulders flat on the wall. feet are ______.
interlock _____ and position the tip of the fingers on the floor without bending the _____
after the partner has positioned the zero point of the tape measure/meter stick (at the top of the _____), the tester starts the test by _____ the hands slowly forward without jerking, trying to reach the farthest distance possible without bending the knees
bouncing or ____ movement is not allowed
do it ____
zero point
knees
centimeters
For the Partner - sit and reach
as the tester assumes the (2) position, position the ____of the tape measure at the tip of the middle fingers of the tester
see to it that the ____ are not bent as the performer slides the farthest distance that he could
record the farthest distance reached in _____
61; excellent
___cm and above
60.9; very good
46 to ____ cm
31; good
____ to 45.9 cm
16; fair
____ to 30.9 cm
15.9; needs improvement
0 to____ cm
cardiovascular endurance
ability of the heart, lungs, and blood vessels to deliver oxygen to working muscles and tissues, as well as the ability of those muscles and tissues to utilize oxygen
endurance
may refer to the ability of the muscle to do repeated work without fatigue
3-Minute Step Test
to measure cardiovascular endurance
step
stopwatch
drum, clapper, clicker, metronome with speaker or any similar device
equipment for step test
8 inches
elementary height of step
12 inches
secondary height of step
For the Tester
stand at least one foot away from the step or bench with trunk erect and eyes looking straight ahead
The first step of the sequence should be alternate. At the signa; “Go” step up and down the step/bench for 3 minutes at a rate of 96 beats per minute. One step consists of 4 beats - up with the left foot, up with the right foot, down with the left foot, down with the right foot for the first sequence. Then up with the right foot, up with the left foot, down with the right foot, down with the left foot for the second sequence. Observe proper breathing (inhale - nose, exhale - mouth)
immediately after the exercise, stand and locate your pulse and in 5 seconds, or at a signal, start to get the heart rate
don’t talk while taking the pulse beat
count the pulse beat for 10 seconds and multiply it by 6
For the Partner
as the student assumes the position in front of the step, signal, ready, and go, start the stopwatch for the 3-minute step test
after the test, allow performer to locate his/her pulse in 5 seconds
give the signal to count the pulse beat
let the performer count his/her pulse beat for 10 seconds and multiply it by 6
procedure for 3 minute step test
record the 60-second heart rate after the activity
scoring for 3 minute step test
strength
ability of the muscle to generate force against physical objects
push-up
to measure strength of upper extremities
exercise mats or any clean mat
equipment for push-up
shoulder width; parallel
straight
in contact
20
50; 25
For the Tester - Push-up
lie down on the mat; face down in standard push-up position: palms on the mat about _____, fingers pointing forward, and legs straight, _____, and slightly apart, with toes supporting the feet
FOR BOYS: Straighten the arms, keeping the back and knees _____, then lower the arms until there is a 90-degree angle at the elbows
FOR GIRLS: With knees ______ with the floor, straighten the arms, keeping the back straight, then lower the arms until there is a 90-degree angle at the elbows
perform as many repetitions as possible, maintaining a cadence of _____ push-ups per minute (2 seconds going down and 1 second going up
a maximum of ____ push-ups for the boys and ____ push-ups for the girls
counting
correct
terminated
For the Partner - Push-up
as the tester assumes the position of push-up, start ____ as the tester lowers his/her body until he/she reaches 90-degree angle at the elbow. The partner should stand in front of the tester and his/her eyes should be close to the elbow to accurately judge the 90 degrees bend
make sure that the performer executes the push-ups in the ____ form
the test is _____ when the performer can no longer execute the push-ups in the correct form, is in pain, voluntarily stops, or cadence is broken

push up - boys elementary
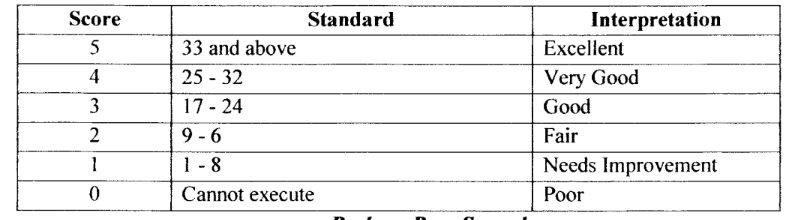
push up - boys secondary
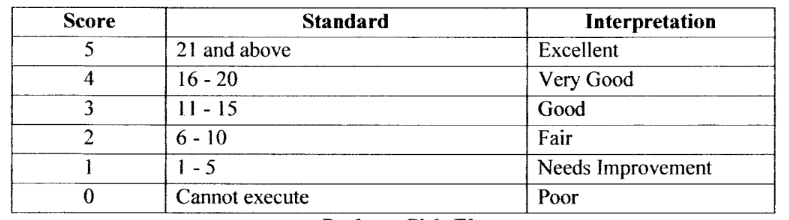
push up - girls elementary
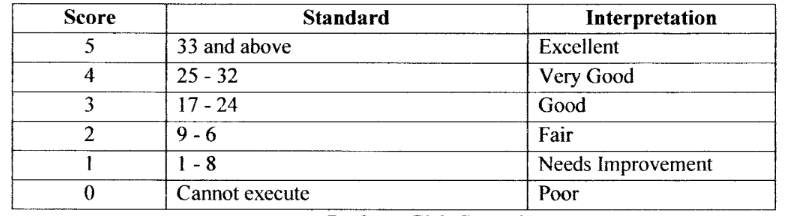
push up - girls secondary
basic plank
to measure strength/stability of the core muscles
exercise mats/any clean mat
stopwatch/time piece
equipment for basic plank
push-up; aligned
legs
back; straight
abdominals
For the Tester - Plank
assume a _____ position. Rest body on forearms with palms and finger flat on the floor. Elbows are ____with the shoulders
____ are straight with ankles, knees, and thighs touching together
support weight on forearms and toes; make sure that your ____ is flat. Head, neck and spine are in ____ line
Keep ____ engaged/contracted; do not let stomach drop or allow hips to rise
mat/smooth
start/go
head, neck, spine, ankles
2
90; unnecessary
For the Partner - Plank
ensure the availability of a _____ flooring or anything that can protect the forearms
give the signal ____ and start the time piece
make sure that the back of the ___, ____, ____, and ____are in a straight line
give___ warnings
stop the time when the performer can no longer hold the required position, or, when the performer has held the position for at least 90 seconds. Holding the plank position beyond ____ seconds is considered ____
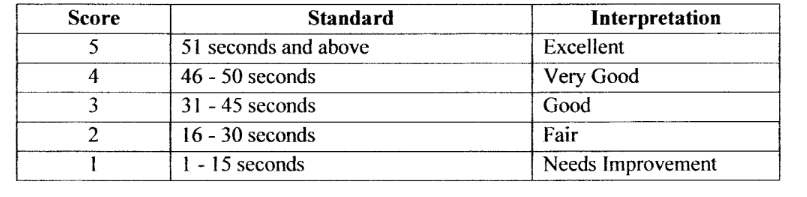
scoring for basic plank
shoulder-width
2; hamstring
1
fatigued
For the Tester - Squats
stand, feet _____ apart
squat down (__ seconds) and make your ____ parallel to the ground
immediately stand back up (__ second)
repeat this until you are ____
record the number of squats completed
repetitions
parallel
toes; knees
flat
For the Partner - Squats
count the number of _____
make sure that the hamstrings are _____ to the ground when going down
make sure that the direction of the _____ is similar to the direction of the _____ when lowering the body
make sure that the feet are planted ____ on the floor during the entire squat execution
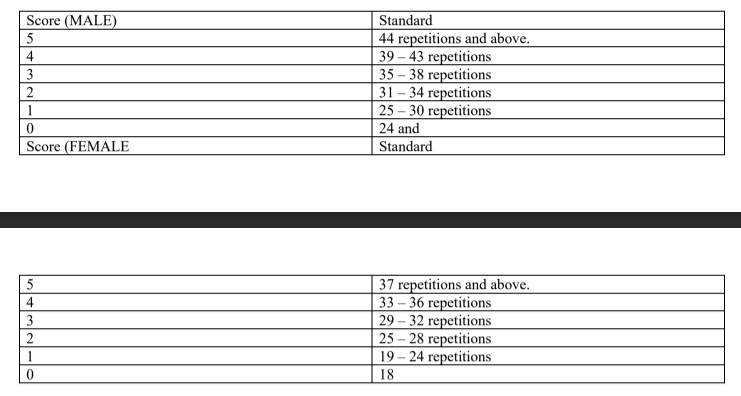
scoring for squat
Frequency
Intensity
Type
Time
FITT Principle
frequency
basic configuration of training and resting days
intensity
intensity of the exercise based on physiological indicators
type
type of exercise, could be bone and muscle strengthening (resistance training) or Aerobic training
time
duration of training and intervals based on training-to-rest ratio
Specificity
Progressive Overload
Reversibility
Rest & Recovery
Variability
Individualization
Adaptation
SPORRVIA Training Principle
specificity
specific training targets a specific goal
progressive overload
gradual increase in training intensity should be implemented for continuous improvement
reversibility
acquired level of fitness can regress if training stops
rest & recovery
there should be an allowance body to recover or repair itslef
variability
patterns of routine and types of exercise must be altered to maintain an individual’s enjoyment and motivation
individualization
people are different in terms of their fitness level and fitness needs
[HRR X (% Effort) +RHR]
% Effort = % of MHR
RHR = Resting Heart Rate
MHR = 220BPM - AGE
HRR = Heart Rate Reserve = MHR - RHR
formula for Target Training Heart Rate (TTHR)
50%
zone 0: lower your heart rate from ____ the better
100%
zone 5: the closer you are to ___ of your MHR the better
middle
zone 1-4: the closer you are to the ___ of the given ranges the better
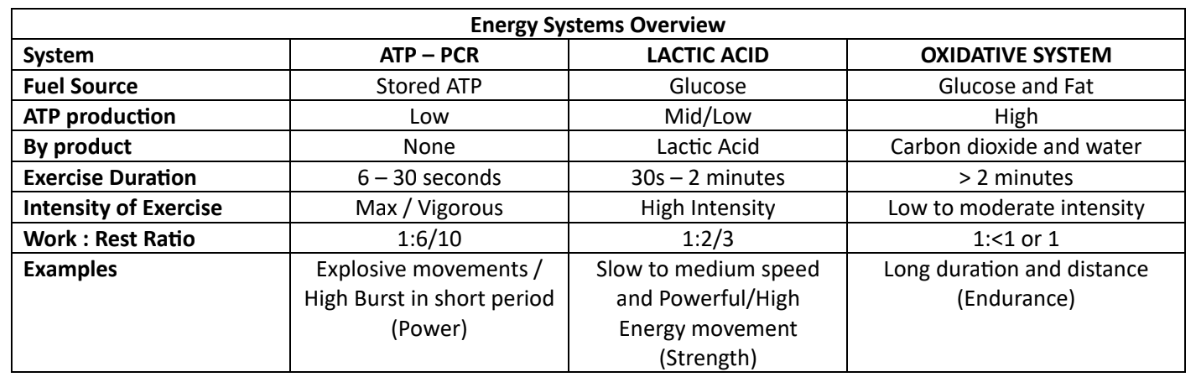
energy systems overview
functional fitness
health related fitness
athletic ability
skill related fitness
circuit training
type of training that alternates the use of muscle groups in short bursts or intensity
stress
body’s response to changing stimuli or stressors
stressors
challenges/demands
eustress
positive reaction
energizes and motivates us to make a change
distress
stress that negatively affects you
acute stress
results from body’s reaction to a new or challenging situation
short term
ex.: approaching deadline, narrowly avoid being hit by a car, ride on a roller coaster
episodic acute stress
acute stress that happens on a frequent basis
causes: repeatedly tight work deadlines, frequent high-stress situations
chronic stress
result of stressors that continue for a long-period of time
feels never-ending
difficulty to improve or change the situation that causes this
adrenaline
cortisol
both chemicals suppress non-essential body functions for surviving, everything needed for fight-or-flight
adrenaline
acute effect
cortisol
prolonged systemic effect
dopamine
movement, motivation, reward
reinforcer of action
endorphins
feel good chemical
natural painkiller
oxytocin
love or bonding hormone
serotonin
regulating chemical
warm up
stretching
physical activity/training/exercise
cooldown
stretching
best progression before engaging in physical activities
hyperthermia
abnormally high body temperature
hypothermia
abnormally low body temperature