Hydrocarbons
0.0(0)
Card Sorting
1/32
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Last updated 3:10 PM on 11/5/25
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
33 Terms
1
New cards
Why are alkanes generally unreactive?
* C-C and C-H bonds have a fairly high bond enthalpy and therefore require a lot of energy to overcome
* The difference between electronegative of C and H small so it is resistant to reactions with polar reagents
* The difference between electronegative of C and H small so it is resistant to reactions with polar reagents
2
New cards
What is chemical equation for the complete combustion of ethane
C2H6 +3 1/2O2 → 2CO2 + 3H2O
3
New cards
Write an overall for the substitution reaction of ethane and chlorine
C2H6 + CL2 →(UV light) C2H5Cl + HCl
4
New cards
What are the three steps of free radical substitution?
1. Initiation
2. Propagation
3. Elimination
5
New cards
What is crude oil a source of?
Aliphatic and aromatic alkanes
6
New cards
What is cracking?
The process which large alkanes are broken down into smaller more useful molecuels
7
New cards
Conditions for cracking
* Hydrogen
* Nickel/platinum catalyst
* 150°C
* Nickel/platinum catalyst
* 150°C
8
New cards
Write the equation for the hydration of ethene
C2H4 + H2O → C2H5OH
H3PO4 Catalyst
9
New cards
Conditions for the hydration of alkenes
* Presence of steam
* H3PO4 (phosphoric acid) catalyst
* 300°C
* 60-70 atm
* H3PO4 (phosphoric acid) catalyst
* 300°C
* 60-70 atm
10
New cards
What is Markovnikov’s law?
In electrophilic addition of hydrogen halide an asymmetric alkene, they hydrogen atom bond to the carbon that is already bonded to the most hydrogens
11
New cards
State the equation for the hydration of ethene
C2H4 + H2O → C2H5OH
12
New cards
How are carbocations classified?
Primary
Secondary
Tertiary
Secondary
Tertiary
13
New cards
What is the trend in stability of carbocations?
Stability increases
Tertiary carbocation is the most stable
Tertiary carbocation is the most stable
14
New cards
In terms of carbocation stability, what will be the major product in the addition reaction between hydrogen halide and an unsymmetrical alkene?
The major product will be the one whose carbocation intermediate is the most stable
15
New cards
How can alkenes be oxidised to give a diol?
Manganate (VII) ions are a strong oxidising agent
When cold, dilute and acidified, the ions change from purple to colourless
When cold, dilute and acidified, the ions change from purple to colourless
16
New cards
Give the equation for the oxidation of ethene
C2H4 + H2O + \[O\] → (CH2OH)2
17
New cards
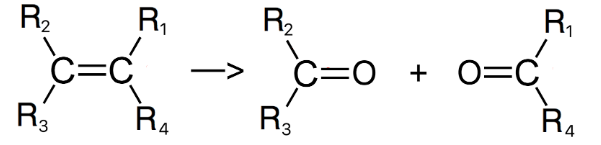
What happens when an alkene is oxidised with, hot concentrated acidified potassium manganate?
The C=C double bond is broken and replaced with 2 X C=O bonds
What happens next is based on whether the R groups are alkyl groups or hydrogen atoms
What happens next is based on whether the R groups are alkyl groups or hydrogen atoms
18
New cards
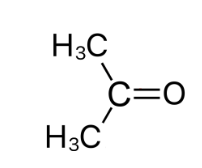
After an alkene has been oxidised using hot concentrated H+/Cr2O72-, both R groups of one the products are alkyl groups. What happens to this product?
The alkene was split into a ketone (both R groups are alkyl groups and another carbonyl)
Ketones cannot be oxidised further so no further reaction occurs
Ketones cannot be oxidised further so no further reaction occurs
19
New cards
After an alkene has been oxidised using hot concentrated H+/Cr2O72-, both R groups of one the products has the following R groups: an alkyl chain and a hydrogen chain. What happens to this product?
The alkene was split into an aldehyde ( with an alkyl group and a hydrogen atom as the R groups) and another carbonyl
The aldehyde is further oxidised to form a carboxylic acid
The aldehyde is further oxidised to form a carboxylic acid
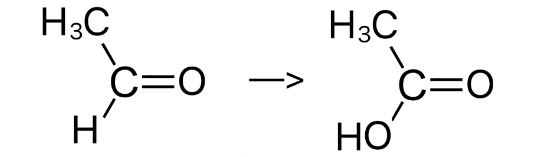
20
New cards
After an alkene has been oxidised using hot concentrated H+/Cr2O72-, both R groups of one the products are hydrogen atoms. What happens to this product?
The alkene was oxidised to form methanal (with 2 hydrogen groups as R groups) and another carbonyl
Methanal will be completely oxidised form CO2 and H2O
Methanal will be completely oxidised form CO2 and H2O
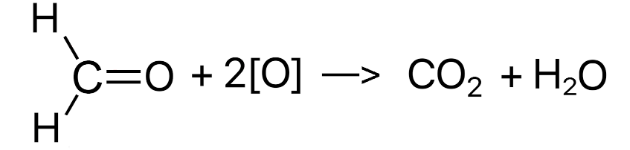
21
New cards
What is addition polymerisation?
The joining together of unsaturated alkene monomers to form a polymer (atom economy is 100%)
22
New cards
How do alkenes undergo addition polymerisation?
The π bond breaks and each electron goes towards forming a σ bond with an adjacent monomer unit
23
New cards
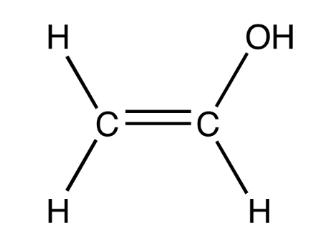
Deduce the repeat unit of the addition polymer formed from the monomer below
Turn the C=C bond into C-C
Add and extend the bonds out from the side of the carbon atoms
Add in square brackets around the molecule
Add and extend the bonds out from the side of the carbon atoms
Add in square brackets around the molecule
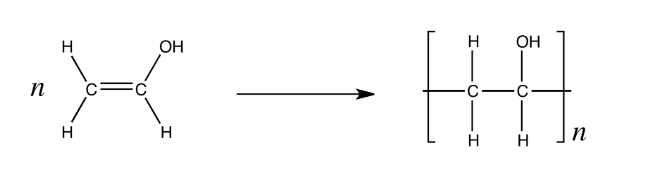
24
New cards
Why polymers difficult to dispose of?
They are non-biodegradable
Their combustion releases harmful compounds
Their combustion releases harmful compounds
25
New cards
Why are alkanes suitable as fuels?
High standard enthalpy change of combustion ( releases a lot of energy)
26
New cards
Problems with CO
Poisonous
Irreversibly binds to haemoglobin
Cells may become deoxygenated - leading to death
Irreversibly binds to haemoglobin
Cells may become deoxygenated - leading to death
27
New cards
Why are amphoteric oxides of nitrogen pollutants?
Nitrogen monoxide reacts with chemicals that can cause acid rain
Nitrogen dioxide can also contribute to photochemical smog
Nitrogen dioxide can also contribute to photochemical smog
28
New cards
Describe how a catalytic converter works
* Nitrogen monoxide is formed in car engines: N2 + O2 → 2NO
* Catalytic converter removes majority of NO so it isn’t released into the atmosphere: 2NO + 2CO → N2 + CO2
* Ceramic honeycomb structure is coated in a thin layer of metal catalysts like platinum and rhodium
* Catalytic converter removes majority of NO so it isn’t released into the atmosphere: 2NO + 2CO → N2 + CO2
* Ceramic honeycomb structure is coated in a thin layer of metal catalysts like platinum and rhodium
29
New cards
What are the environmental consequences of unburnt hydrocarbons?
They absorb infrared radiation, causing the greenhouse effect
30
New cards
What the environmental effects of greenhouse gases?
* Electromagnetic radiation from the sun passes through the atmosphere, some radiation is absorbed and the earths temperature rises
* Heat is radiated from the earth as infrared radiation which is absorbed by greenhouse gases in the atmosphere causing bonds in the molecules to vibrate
* As a result the atmosphere warms up more
* Heat is radiated from the earth as infrared radiation which is absorbed by greenhouse gases in the atmosphere causing bonds in the molecules to vibrate
* As a result the atmosphere warms up more
31
New cards
How is infrared spectroscopy used to monitor air pollution?
IR spectroscopy identifies particular bonds in a molecule
Different pollutants will have different patterns of absorption as they contain different bonds
It is also possible to measure the concentrations of the different pollutants
Different pollutants will have different patterns of absorption as they contain different bonds
It is also possible to measure the concentrations of the different pollutants
32
New cards
How does the halogen carrier generate the electrophile when benzene reacts with a halogenoalkane?
Halogen carrier reacts with halogenoalkane to generate electrophile: AlCl3 + C2H5Cl → AlCl4- + C2H5+
AlCl4- reacts with proton expelled from the intermediate to regenerate the halogen carrier:
AlCl4- + H+ → AlCl3 + HCl
33
New cards