Neural Communicaton
1/9
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
10 Terms
Neural Transmission
The process by which neurons communicate with each other through electrical and chemical signals. Ex: Neural transmission in neurons is like sending a message through a series of relay runners in a relay race.
Threshold
The level of stimulation required to trigger an action potential in a neuron. It is the minimum amount of stimulation necessary to produce a response.
Action Potential
A brief electrical impulse that travels along the axon of a neuron. Ex: When you flip the switch on, electricity flows through the wires and the light turns on.
All-or-Nothing Principle
States that once a neuron reaches its threshold of excitation, it will fire an action potential at full strength. EX: This principle is like firing a gun: once the trigger is pulled and a critical pressure is applied to the firing pin, the bullet is discharged with a consistent force.
Depolarization
This is the phase when the inside of the neuron becomes less negative than usual.
This happens because positive electrical signals enter the neuron, making it more likely to activate or "fire."
Refractory Period
Brief period following an action potential during which a neuron is unable to generate another action potential. Ex: like waiting to flush a toilet again after it's been flushed once.
Resting Potential
The stable, negative electrical charge that exists across the cell membrane of a neuron when it is not actively transmitting signals. Ex: Just like a battery holds stored energy when not in use.
Reuptake
Process in which neurotransmitters that have been released into the synapse are reabsorbed by the presynaptic neuron from which they were originally released. Ex: Just like recycling bins collect and reuse materials.
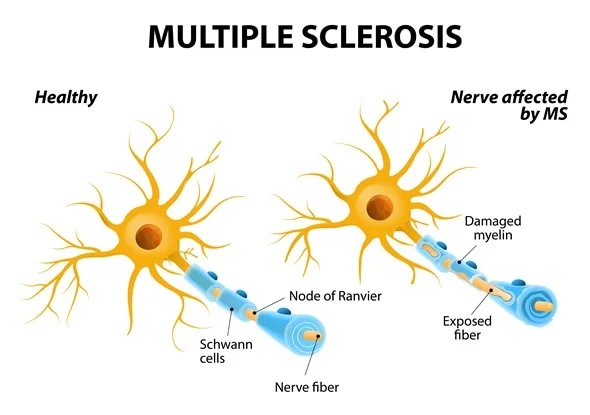
Multiple Sclerosis “MS”
chronic autoimmune disease that affects the central nervous system, including the brain and spinal cord. It occurs when the immune system mistakenly attacks the protective myelin sheath.
Myasthenia Gravis
chronic autoimmune disorder that affects the neuromuscular junction, where nerve impulses are transmitted to muscles.
It occurs when the immune system produces antibodies that block or destroy the receptors for acetylcholine, a neurotransmitter that stimulates muscle contraction.