Med Imaging - abdominal imaging (E2)
1/132
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
133 Terms
What is KUB?
kidneys, ureters, and bladder aka flat plate
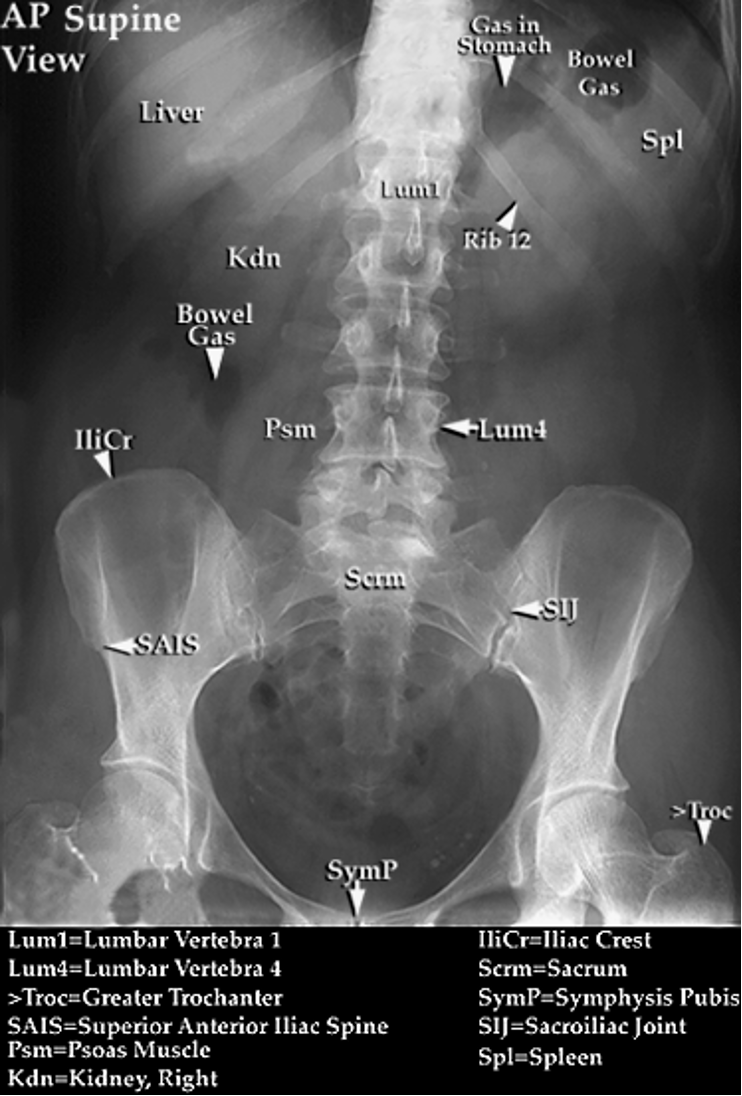
What does a KUB evaluate?
gas patterns, soft tissues and bony structures
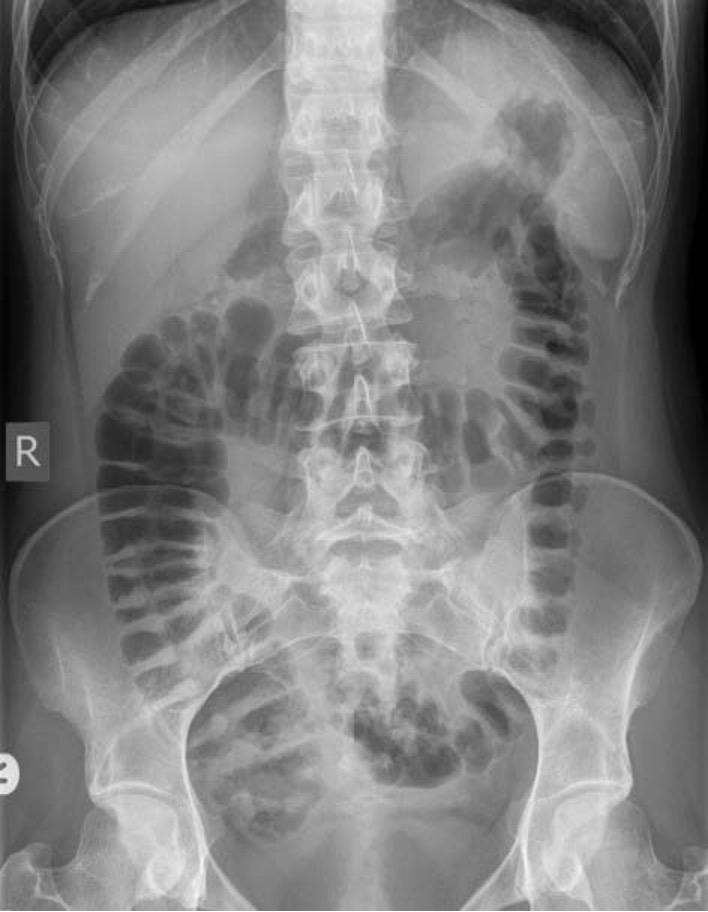
What does an abdominal upright film evaluate?
gas patterns and air fluid levels
What does a CXR evaluate?
free air under the diaphragm
(possible to see as little as 3-4 cc air)
How are the lateral psoas margins seen on KUB?
may or may not be seen bilaterally
How is the liver seen on KUB?
homogeneous soft tissue density in RUQ
How is the spleen seen on KUB?
homogenous soft tissue density in LUQ
What scans are the liver and spleen difficult to asses?
plain films- minimal to moderate enlargements are not well seen
KUB margins
superior poles of kidneys down to pubic symphysis
typically doesn’t include diaphragm
What air levels are normal in KUB?
stomach- almost aways air
small bowel- small amt, approx 2-3 loops
large bowel- varies, almost always air in rectum and sigmoid colon
What air levels are normal in upright KUB?
stomach- always
small bowel- 2-3 levels
large bowel- none
What is the 3-6-9 rule?
normal diameters of small bowel, colon, and cecum
What is normal diameter of small bowel?
< 3 cm
What is appearance of colon?
bubbly- mix of gas and fecal material; may see haustra
diameter- < 6 cm
what is normal diameter of cecum?
< 9 cm
What are you looking for in supine abdomen view?
bowel gas pattern, calcifications, masses
What are you looking for in upright abdomen view?
free air and air fluid levels
What are you looking for in upright chest view?
free air, lung pathology secondary to intra abdominal process
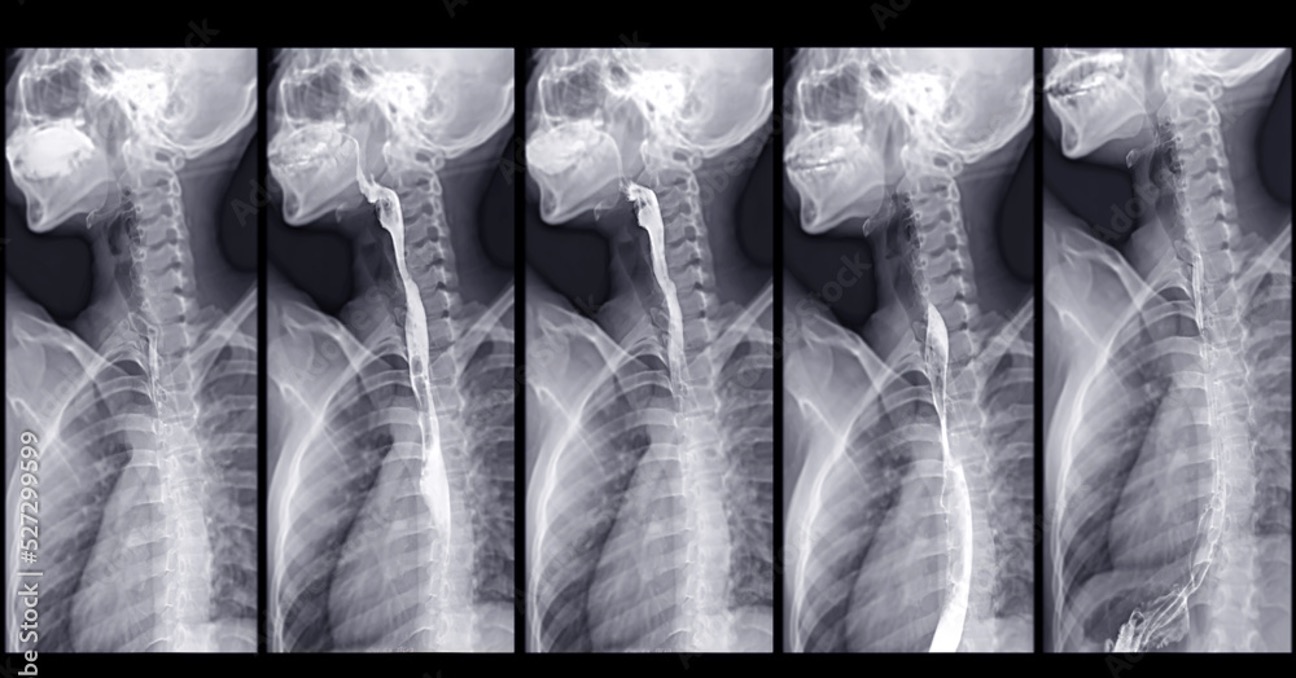
what does barium swallow evaluate?
esophagus
What does upper GI series evaluate?
stomach and duodenum
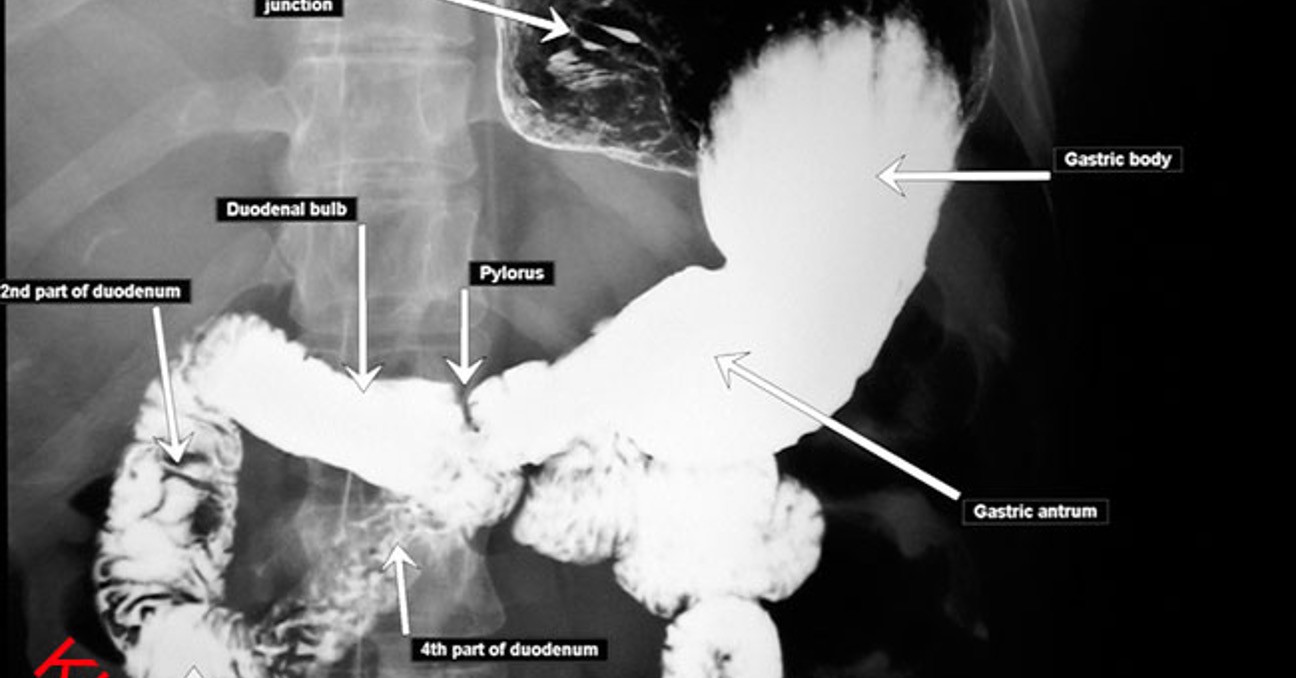
What does small bowel follow through evaluate?
small bowel (extension of UGI)
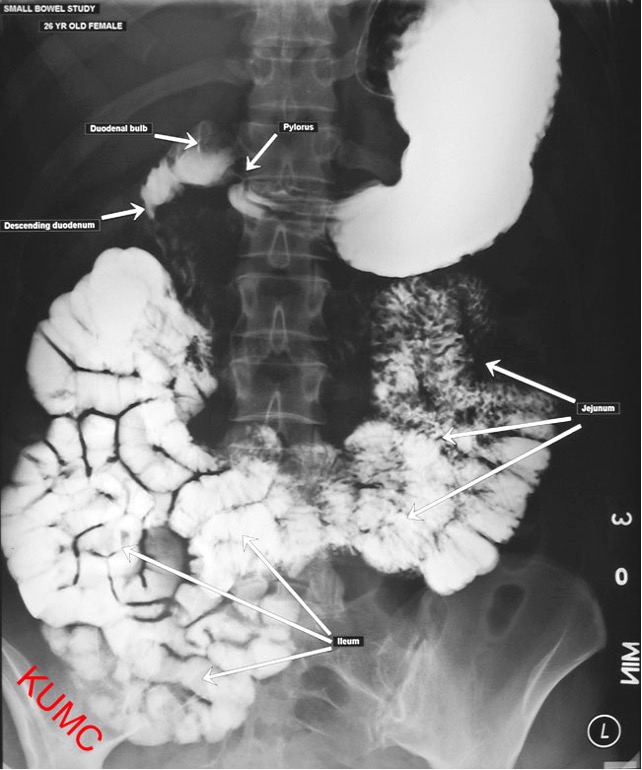
what does barium enema evaluate?
large bowel
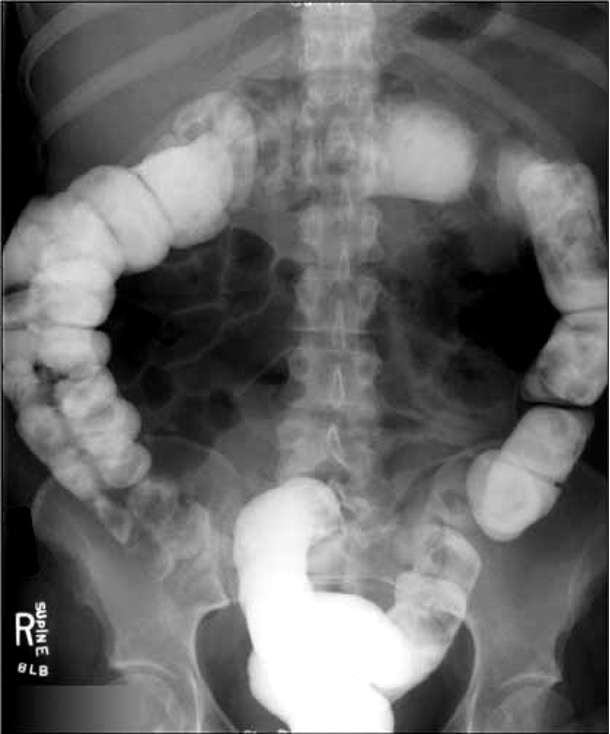
what is the most common test for abdominal pathology?
CT scan- usually w/ IV/GI (oral) contrast
fast and detailed exam of abdomen and pelvis
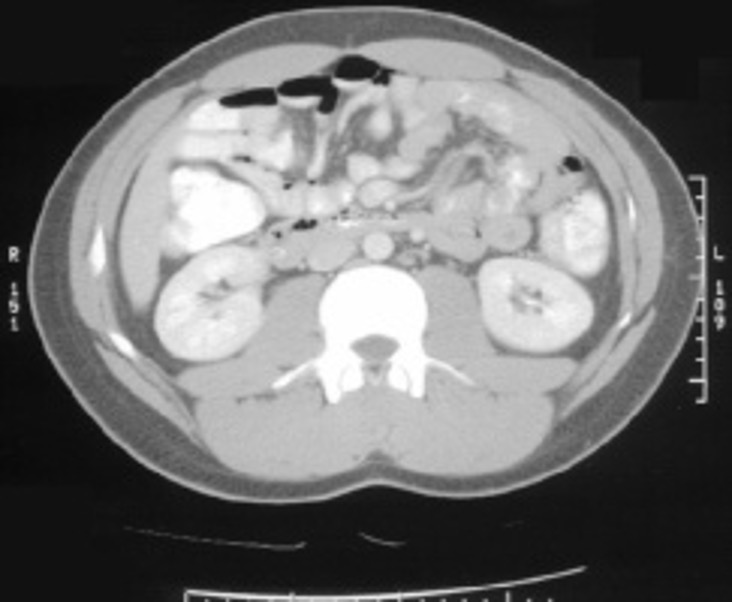
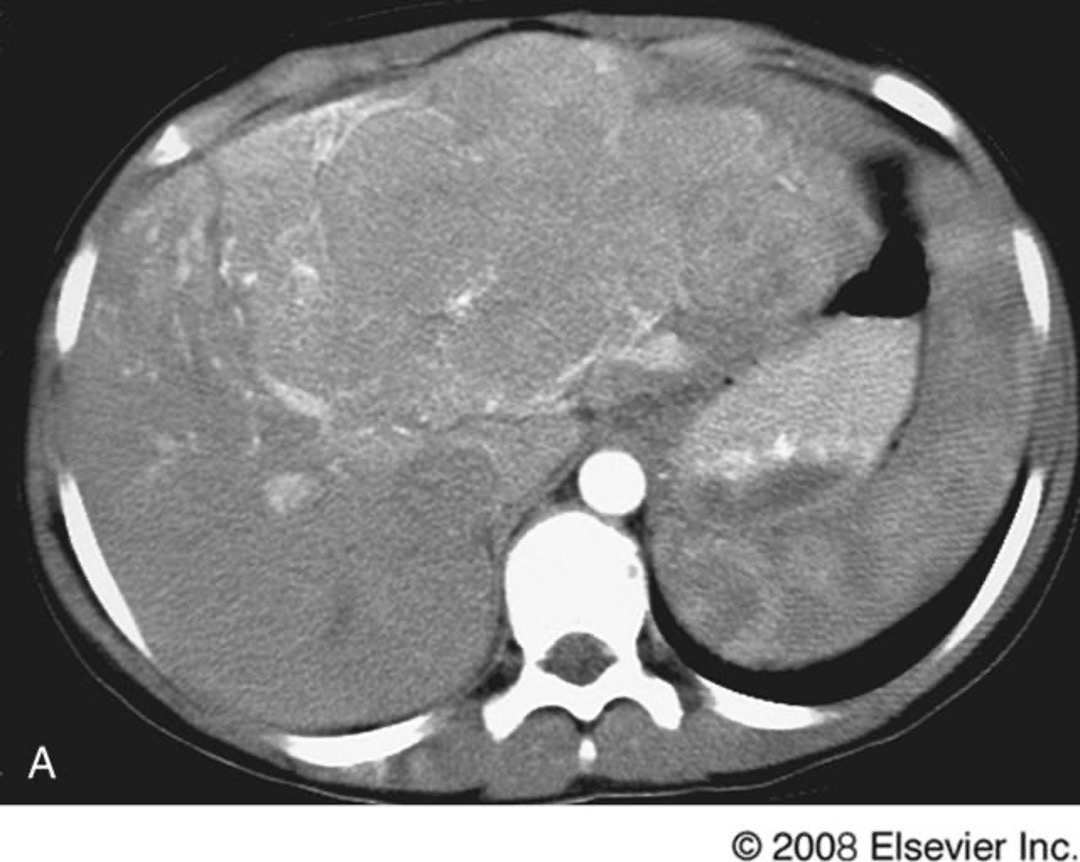
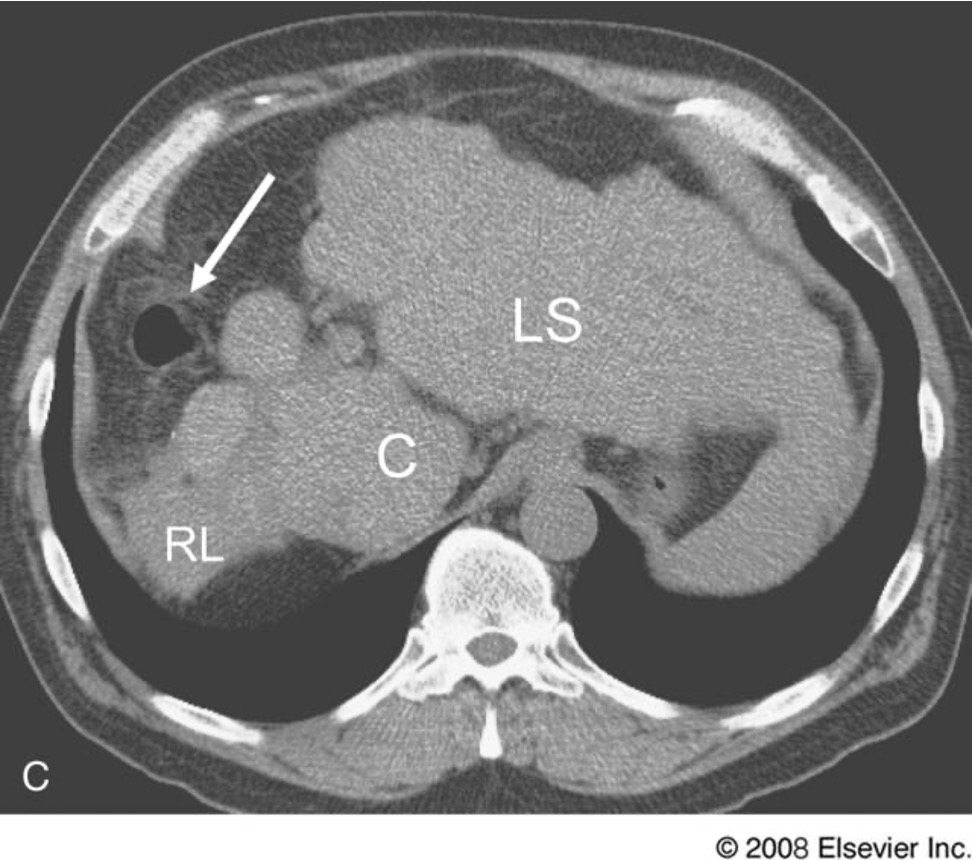
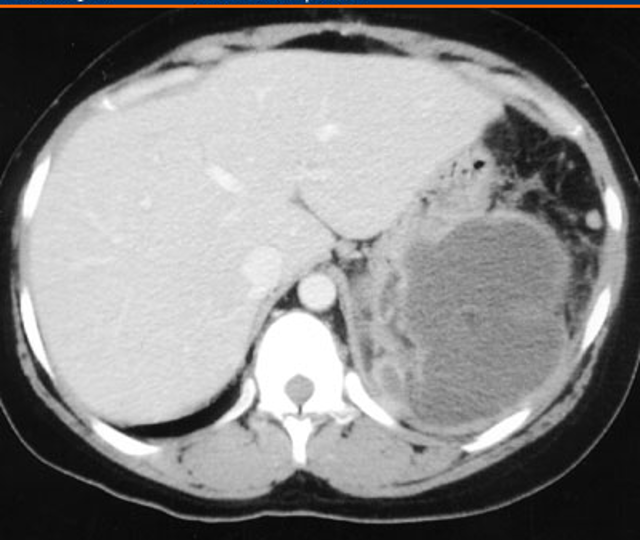
what is this
hepatocellular carcinoma
What is this?
liver cirrhosis
Ascites is easily seen on what scan?
ultrasound
What are ultrasounds used to evaluate?
aorta, pancreas, liver, spleen, kidneys, gallbladder, common bile duct, appendix (± value pf study)
does not penetrate bone or air- air in bowel may interfere w/ study
What is a HIDA scan?
radioactive tracer injected in to vein, bile producing cells take it up, travels w/ bile into gallbladder, bile ducts, and small intestine
helps in dx of cholecystitis, bile duct obstruction, biliary atresia, bile leaks/fistulas, assessment of liver transplant
What is the best evaluation of GI tract?
endoscopy
What is an endoscopy used to evaluate?
most of the tubular GI tract except small bowel
provides direct visualization of tissue and allows for bx, cauterization, or injection of contrast/dye
What are disadvantages of endoscopies?
often requires sedation, is invasive and expensive
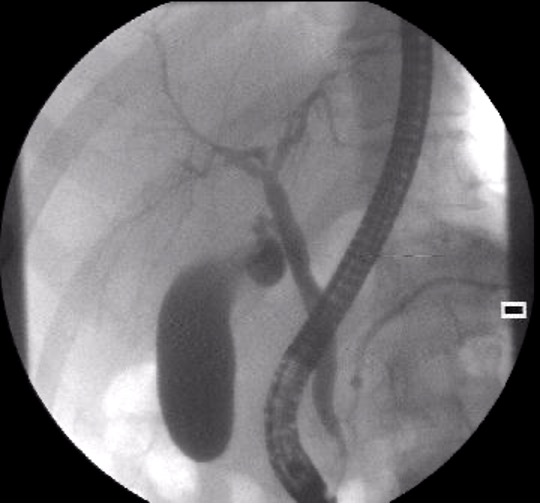
What is endoscopic retrograde cholangiopancreatography (ERCP)?
used to identify presence of stones, tumors, or narrowing in biliary and pancreatic ducts
What is capsule endoscopy?
disposable video camera that is swallowed; takes thousands of high quality digital images as it passes through entire length of small intestine
images are transmitted to data recorder worn by pt and is returned after 8 hours for processing and analysis
What previously difficult to detect disorders of the small bowel has capsule endoscopy significantly improved?
ulceration of jejunum and ileum, Crohn’s dz, small tumors, A-V malformation
What are indications for capsule endoscopy?
obscure GI bleeding, detection of Crohns dz, small tumors, malabsorption disorders such as celiac
Where does bright red blood rectal (BRBPR) usually come from?
rectal or colonic lesion
What is melena (black tarry stools) from?
bleeding in upper GI tract
in patients under 40, where does GI bleeding usually involve?
upper GI tract
what is the study of choice for bright red rectal bleeding?
colonoscopy
what is the study of choice for Melena?
EGD
what is the best study to evaluate for pneumoperitoneum?
CXR
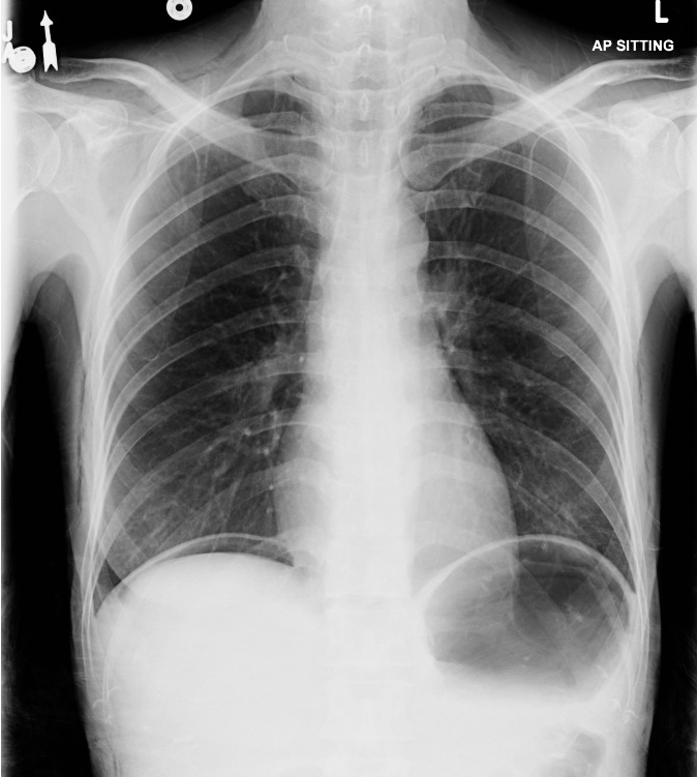
what is the most common cause pneumoperitoneum?
bowel perforation
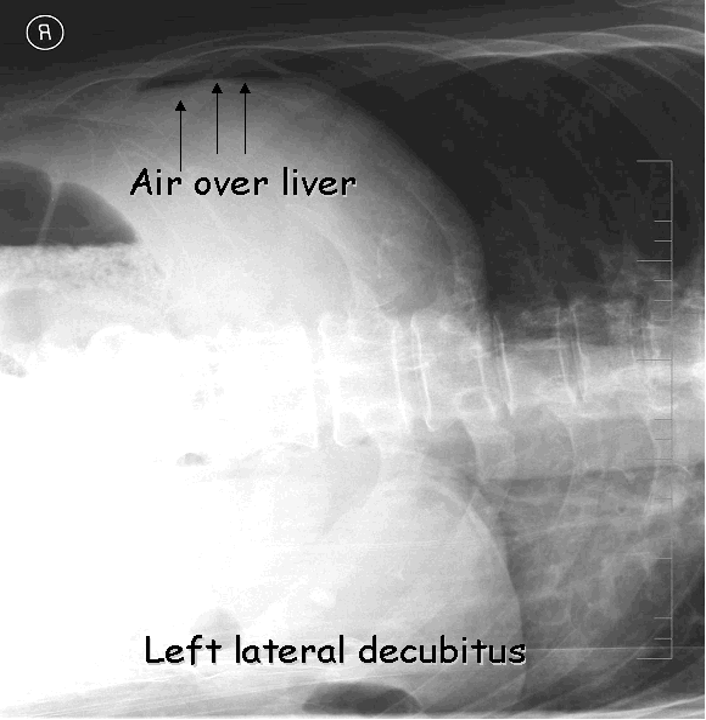
What kind of scan can be done for pneumoperitoneum patients that are unable to stand?
left lateral decubitus- look for liver air sign
what is the test of choice for suspected abdominal or pelvic abscess?
CT scan w/ GI (PO)
What is second choice test for abdominal/pelvic abscess?
Ultrasound- good for liver, pancreas, appendix; not very good for bowel lesions
What is sudden abdominal pain due to?
bowel perforation, ruptured ectopic pregnancy, ruptured ovarian cyst, aneurysm, ischemic bowel
What is gradually increasing and localizing abdominal pain due to?
appendicitis, cholecystitis, bowel obstruction
What dictates the choice of study for abdominal pain?
patient history and physical exam
What is indicated for acute abdominal pain?
PA CXR, supine abdominal film (flat plate) and upright abdominal film
What is indicated for suspected gallbladder, obstetrical, or gyn disease?
ultrasound
what is indicated for appendicitis, pancreatitis, diverticulitis, small bowel obstruction, suspected abscess or tumor, or trauma?
CT scan
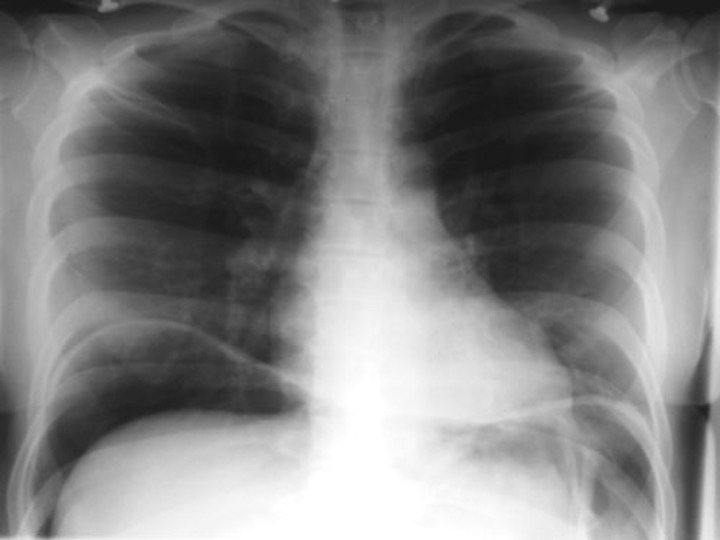
what is this CXR diagnostic of?
bowel perforation
What imaging studies are indicated for acute gastroenteritis?
none- unless there is blood in the stool, then colonoscopy
Where do abdominal masses usually NOT grow?
pelvis
Where do pelvic masses often grow?
up into the abdomen
What are RUQ calcifications usually due to?
kidney stones or gallstones (U/S will distinguish)
What are LUQ calcifications usually related to?
spleen
Where are pancreatic calcifications usually?
horizontal at the L1-L2 level (CT scan more sensitive than abdominal film)
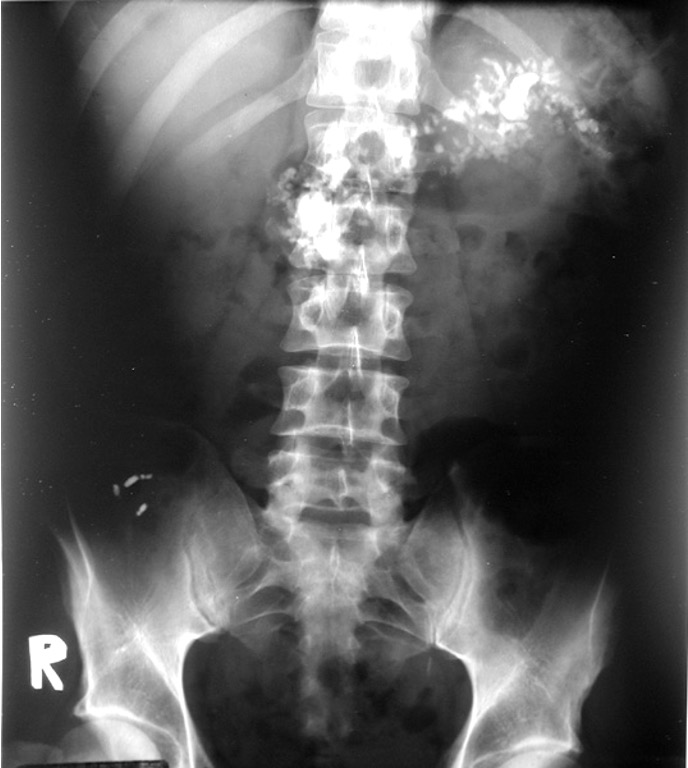
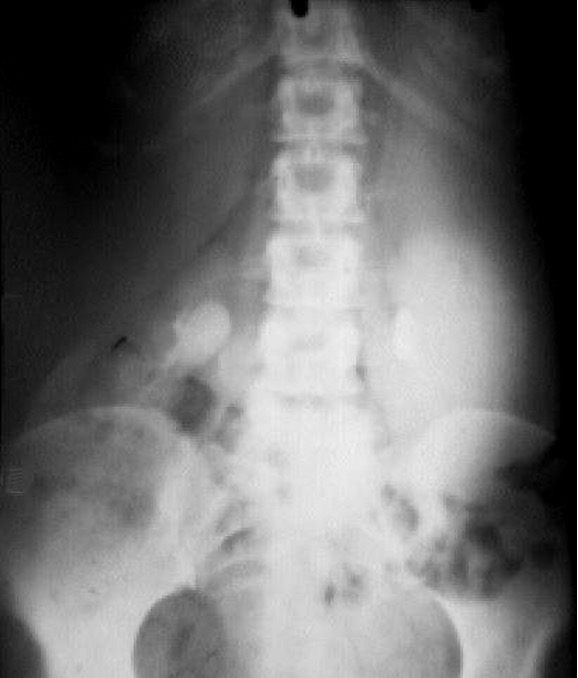
Whaat are these?
mesenteric lymph nodes- popcorn shaped calcification
benign and usually from previous infx
What is an appendicolith?
stone in appendix
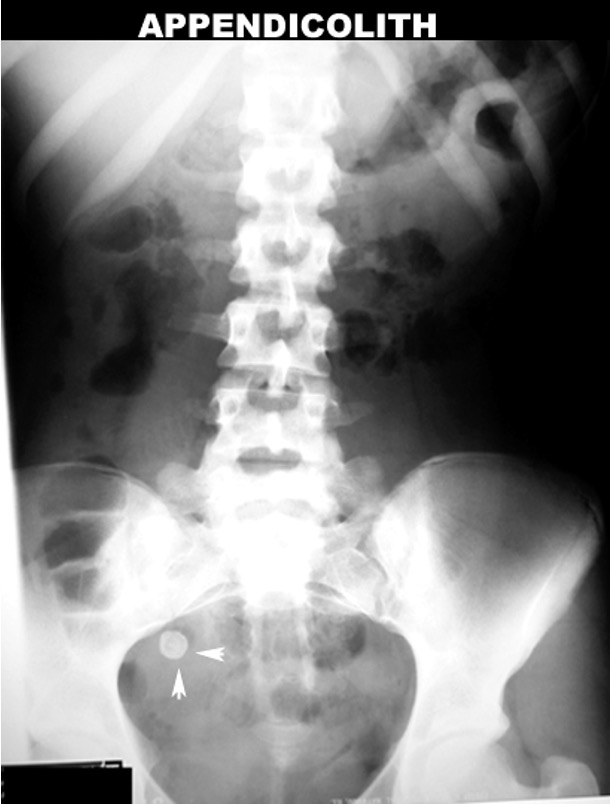
What does RLQ pain + appendicolith indicate?
appendicitis
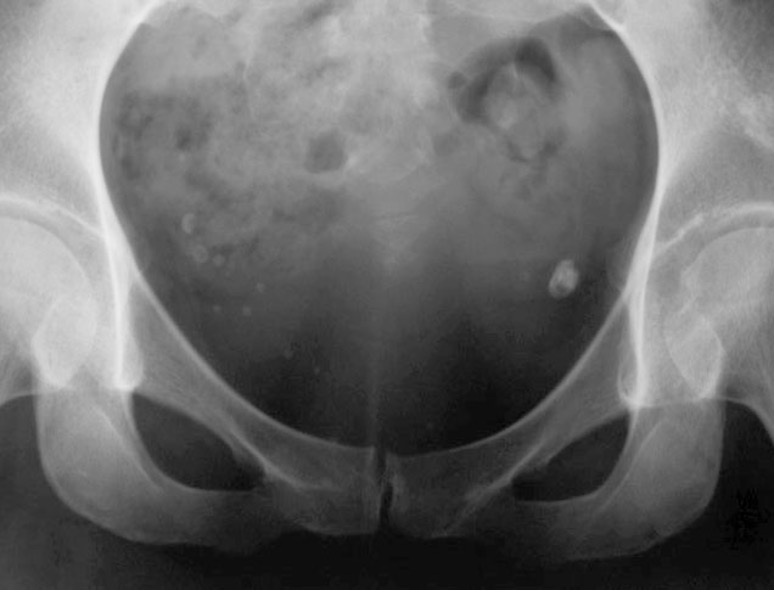
What are phleboliths?
calcification w/in pelvic venous system- no clinical significance
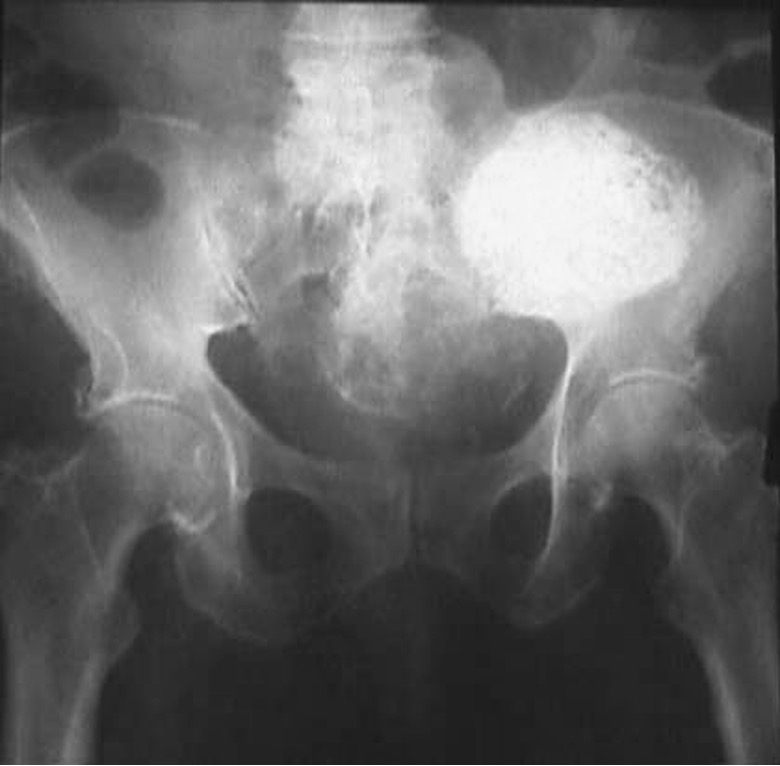
What are uterine fibroids (leiomyomas)?
calcification of uterine fibroids; located in pelvis
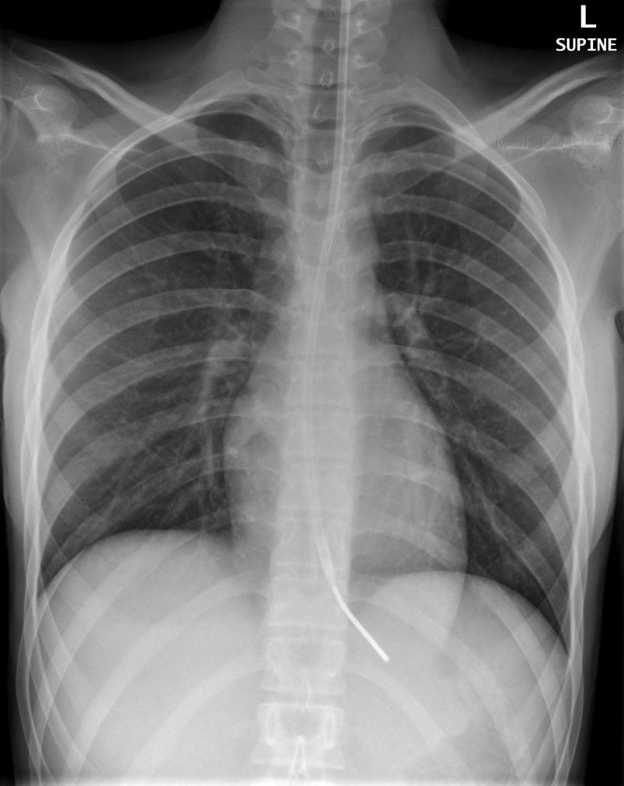
What is nasogastric tube?
used to decompress stomach; end of tube should be in the stomach and to the left of the spine
What is a feeding tube?
used to provide enteric feedings
end of tube should be in distal duodenum or jejunum- pass from left through duodenum then back right, finally back to left into jejunum
What does esophagus normally look like?
smooth lining w/ 2 indentations on left side - aortic arch and left mainstem bronchus
What is the most common cause of dysphagia?
hiatal hernia w/ GERD
What is the most common cause of odynophagia?
infection or esophagitis
When is an EGD indicated for GERD?
systems persist or worsen after trial of medication
What is indicated w/ severe dysphagia or odynophagia?
EGD (barium swallow or UGI can be done first if the wait is prolonged)
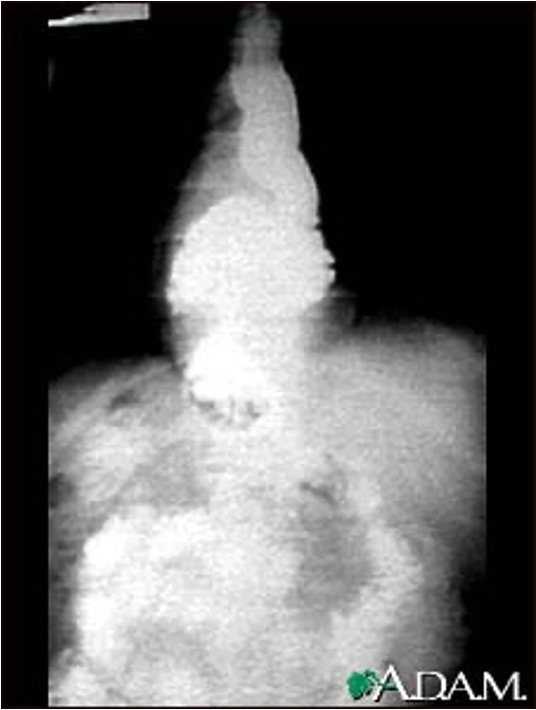
what is this?
hiatal hernia
What must all strictures be evaluated by to r/o malignancy?
EGD and biopsy
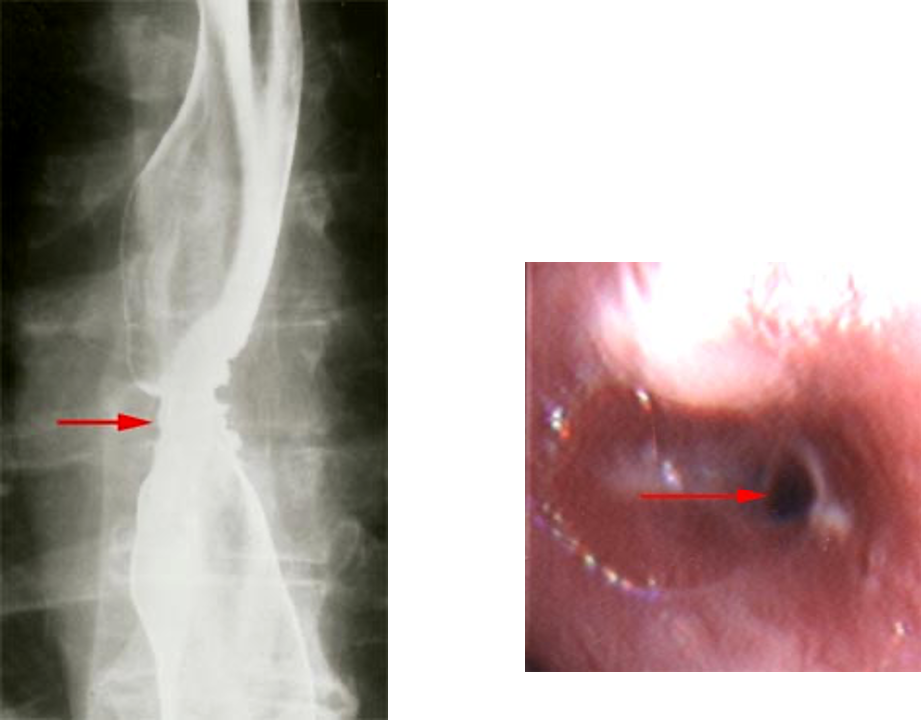
What is achalasia?
gastroesophageal sphincter fails to relax and esophagus becomes massively dilated and loses elasticity; usually no sx until GERD
What disease can look similar to achalasia?
chagas (infectious dz caused by parasite bite)
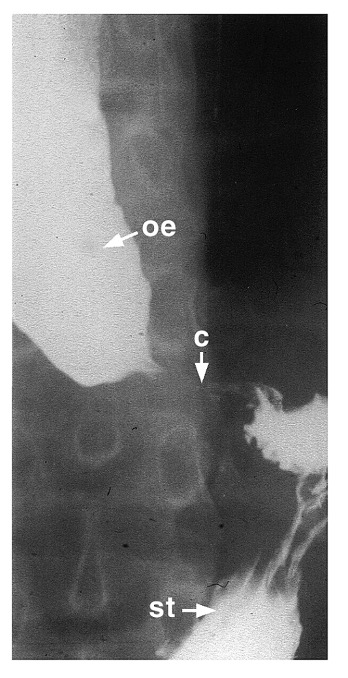
What is this?
achalasia - dilated and tortuous esophagus (oe) w/ narrowing at cardia © and esogastric junction, and normal stomach (st)
What is scleroderma?
collagen vascular dz that affects smooth muscle → esophagus dilates moderately and loses all contractions; may have sx of GERD
What is Boerhaave’s syndrome?
spontaneous perforation of esophagus due to pressure changes; severe epigastric pain and dyspnea; pt’s crash hard and fast
What might a CXR show in Boerhaave’s syndrome?
pneumomediastinum, pneumothorax, or left pleural effusion
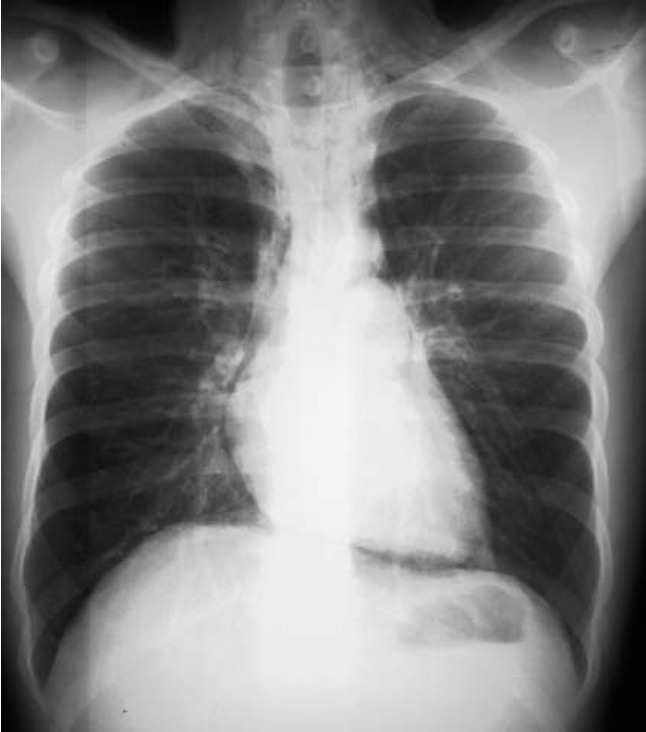
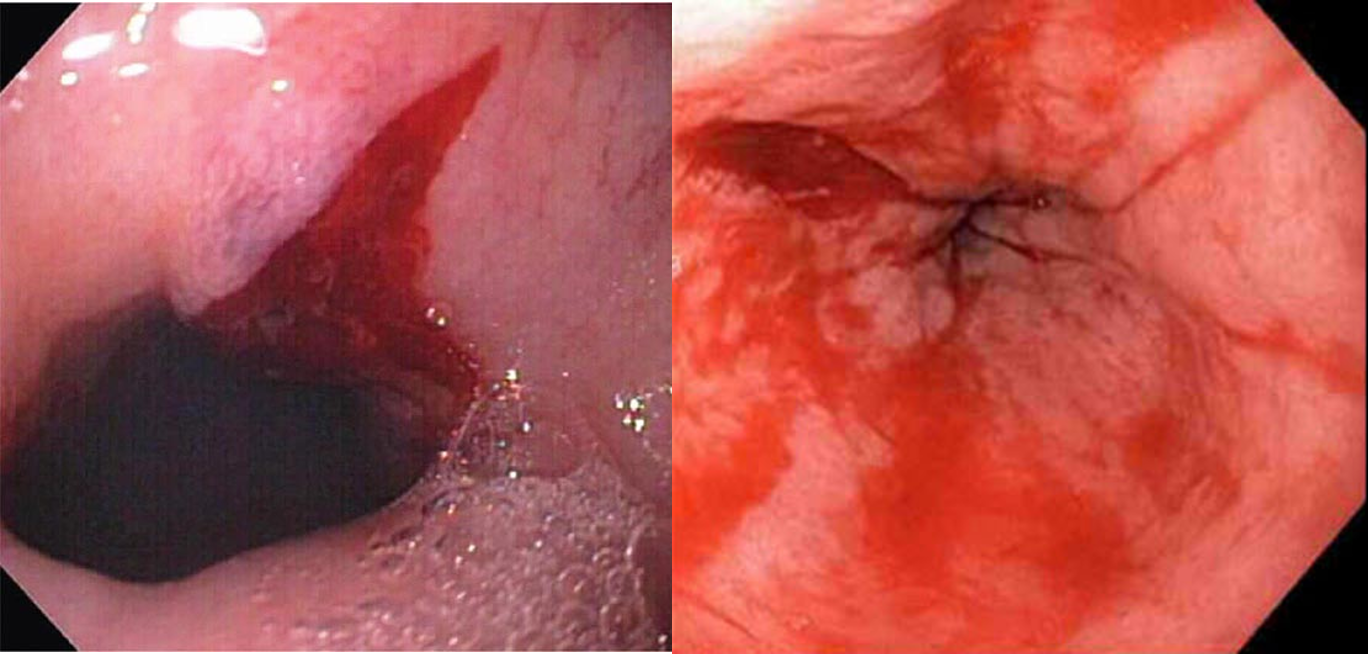
What is mallory-weiss tear?
longitudinal tear near gastroesophageal junction; not transmural but causes hematemesis
EGD indicated for dx and tx
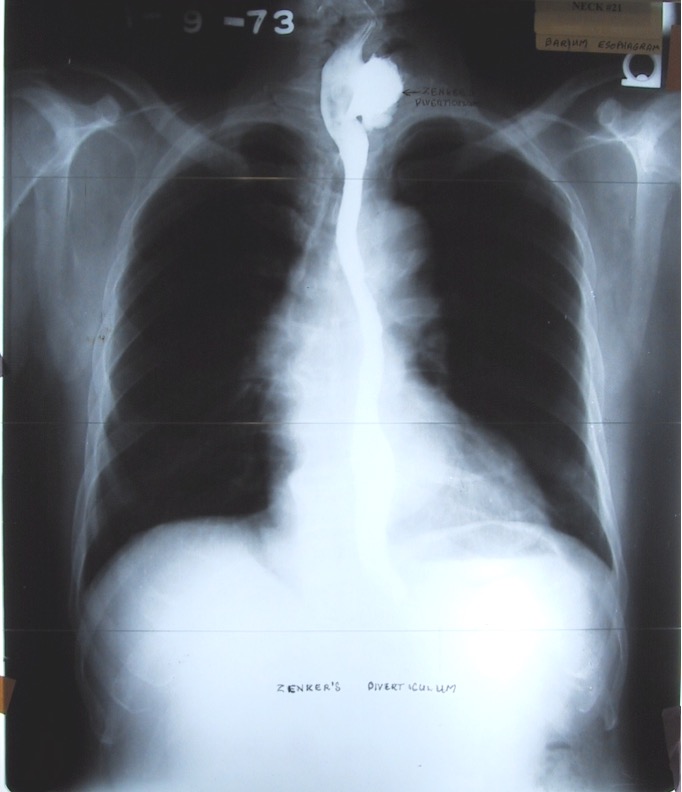
What is zener’s diverticulum?
out pouching of cervical esophagus that results form weakness in muscular wall; causes dysphagia
What is the most common esophageal foreign body found in children?
coins
What is the most common esophageal foreign body found in adults?
inadequately chewed meat
where do FB usually get stuck?
just above anatomical narrowing of esophagus due to aortic arch
what Is study of choice for esophageal FB?
EGD
What are the stomach and duodenum best visualized by?
UGI or EGD
what should you use instead of barium if perforation is suspected in stomach/duodenum?
gastrografin
what is the most common cause of gastritis and ulcers in the stomach and duodenum?
NSAIDs and H. pylori
what is the best study for gastritis and ulcers in stomach/duodenum?
EGD for visualization and biopsy but you can test for H. pylori first
What is the most sensitive test available to detect duodenal ulcers?
EGD
describe gastric ulcers
95% benign; malignant lesions have thickened irregular wall and dec peristalsis
describe duodenal ulcers
proximal- benign 90% of the time
bulbar/distal- malignant until proven otherwise
what is gastric outlet obstruction
can be caused by neoplasm, diabetes/gastroparesis, or narcotic addiction
enlarged stomach may be seen on plain films
UGI or EGD can be used
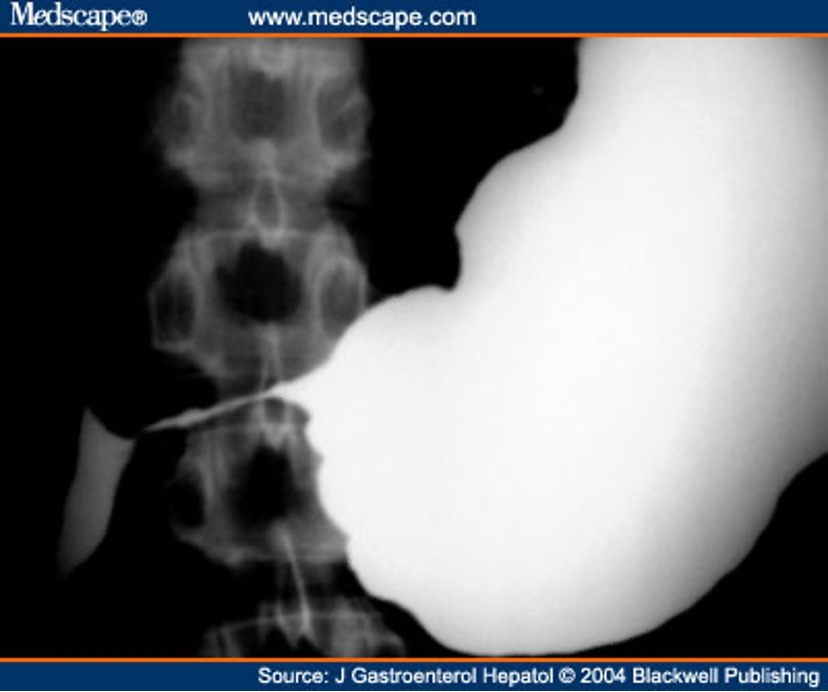
what is the most common imaging method for evaluating the liver?
CT scan
what is the most common imaging method for evaluating gallbladder and biliary system?
ultrasound
what is the most commonly injured intrabdominal organ in penetrating injury?
liver
what is the most commonly injured organ in blunt trauma?
spleen (liver is second)
what is the most common benign hepatic tumor?
cavernous hemangioma
what is the most common primary malignant hepatic tumor?
hepatoma- hepatocellular carcinoma HCC
What is the best image study for abscess suspected anywhere in abdomen?
CT w/ IV and GI (PO) contrast
BX to r/o malignancy
what is indicated by RUQ pain, fever or elevated WBCs and positive Murphy’s sign?
acute cholecystitis and acute cholangitis