Neural Information Processing and Brain Organization
1/25
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
26 Terms
What is the tiny space between the terminal boutons of the gifting neuron and the dendrites of the receiving neuron called?
Synapse.
What happens when a neuron fires?
It sends a message along its axon that either excites or inhibits receiving neurons.
What is released at the synapse that affects the receiving neuron?
Neurotransmitter chemicals.
What determines whether a receiving neuron increases or decreases its rate of firing?
The nature of the neurotransmitter released; excitatory connections decrease potential difference, while inhibitory connections increase it.
How does a receiving neuron compute its response to incoming signals?
It sums all positive potentials minus all negative potentials arriving at its dendrites.
What is the speed range of electrical activity propagation down an axon?
Between 0.5 m/s to 130 m/s.
What is the time it takes for communication to pass from one neuron to the next?
Around 10 ms.
How do computers and brains differ in representing information?
Computers represent information discretely in patterns of 0's and 1's, while brains represent it in terms of rate of firing.
What is the significance of increased firing rate in neurons?
Neurons that fire at a greater rate are more active and have a greater influence on downstream neurons.
What is required for permanent knowledge to be encoded in neurons?
Repeated use of a synapse to increase its strength.
What is the difference between a grandmother detector cell and distributed representation in the brain?
A grandmother detector suggests each neuron represents a distinct concept, while distributed representation indicates information is represented by patterns of activation across sets of interconnected neurons.
What do feature detectors in the brain respond to?
Specific features of stimuli, such as color receptors in the eye or line and angle detectors in the visual cortex.
What evidence did Haxby et al. provide regarding the representation of faces and objects in the brain?
Faces and objects are represented by distinct patterns of activation across a wide expanse of cortex.
What are the main planes from which the brain is viewed?
Medial pre-cortical hemispheric structures, sulcus, sulci, gyrus, gyri.
What is the thickness of the cerebral cortex?
About 3 mm thick.
What is the area of the cerebral cortex when unfolded?
About 2500 cm².
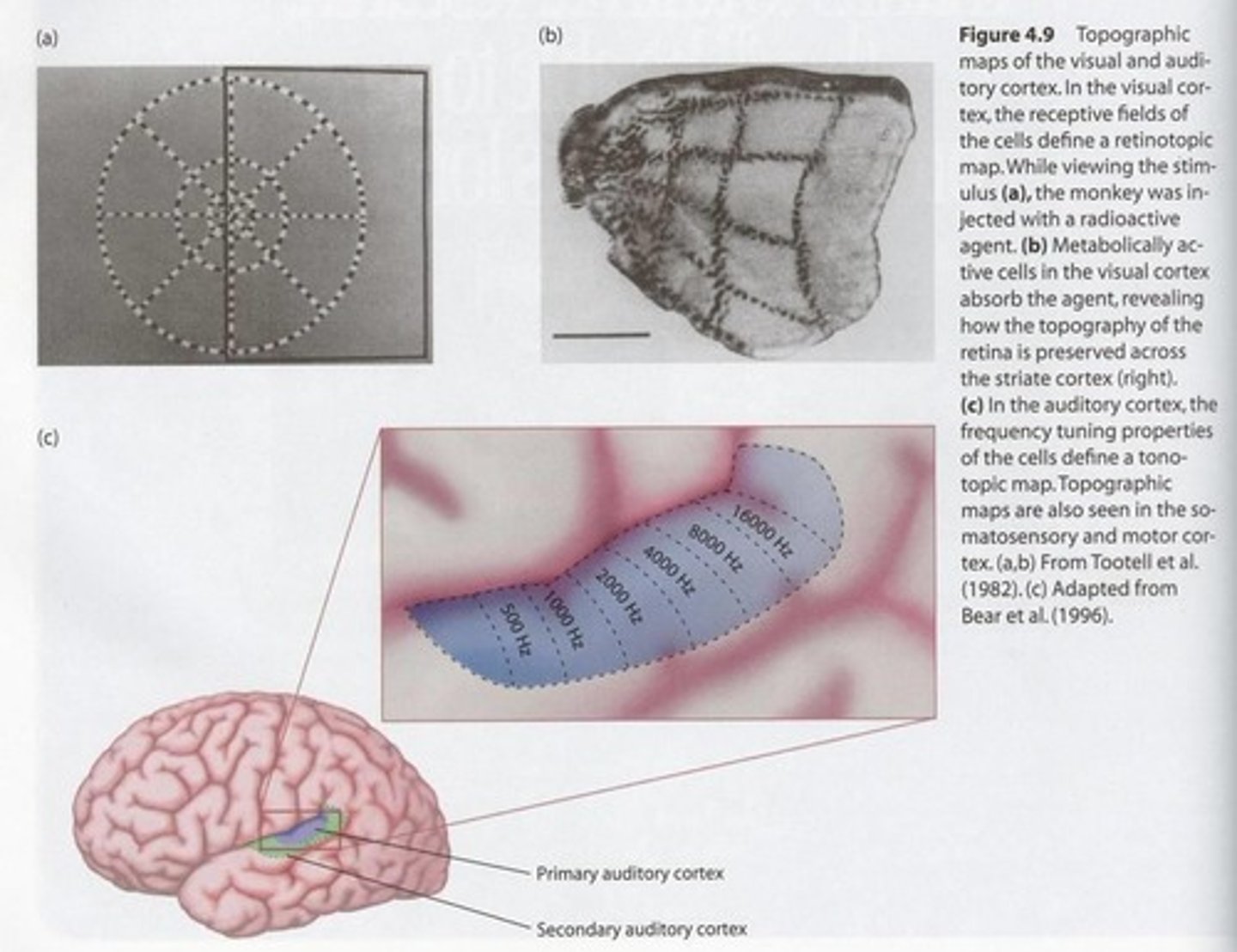
What is topographic organization in the brain?
Adjacent cells in the cortex tend to process sensory stimuli from adjacent areas of the body.
What is retinotopic mapping?
A type of topographic map that represents visual stimuli based on their spatial location.
What does functional magnetic resonance imaging (fMRI) measure?
The overcompensation in blood supply to high firing neurons, indicating areas of high activity.
What are some limitations of fMRI?
It can be expensive, noisy, and claustrophobic.
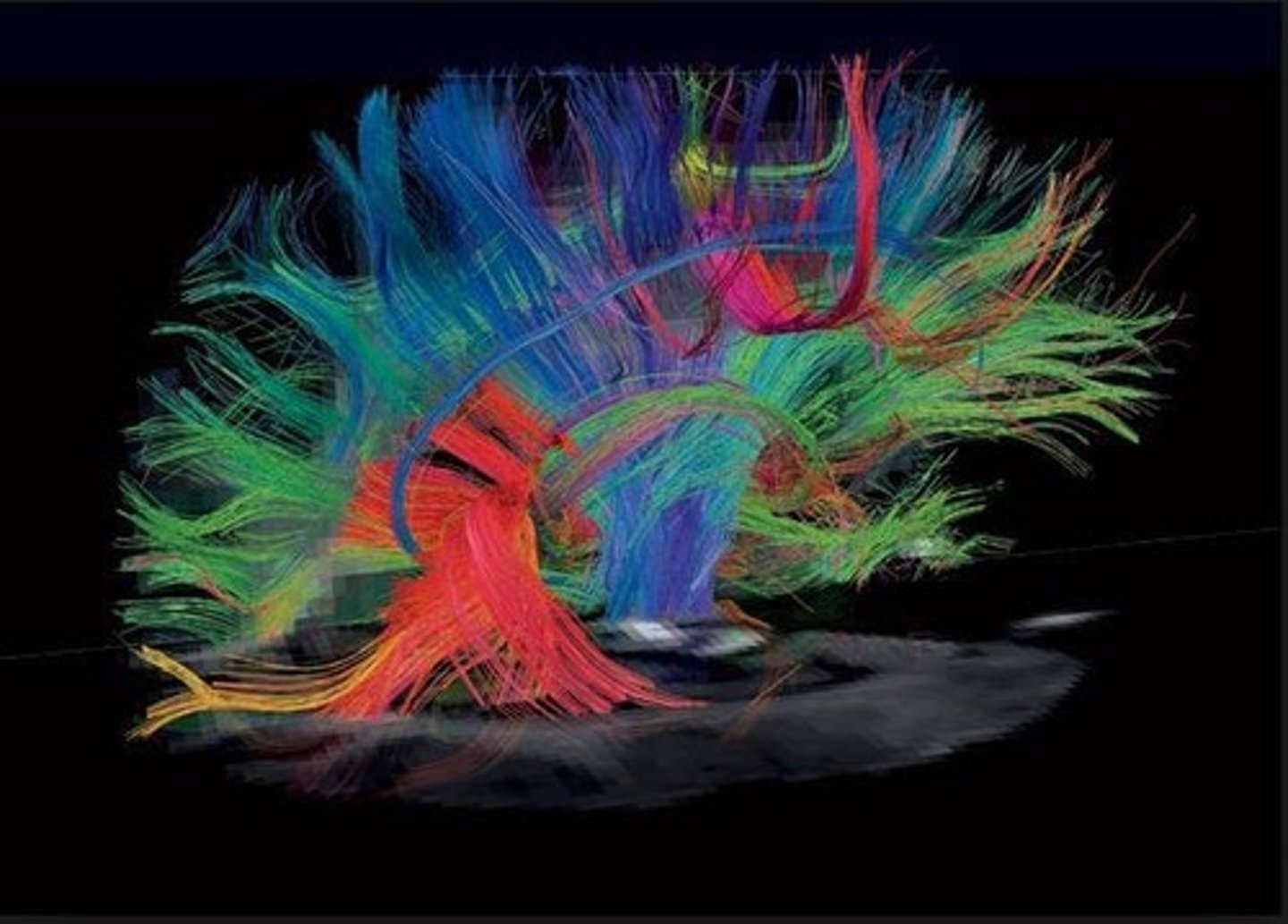
What does diffusion tensor imaging (DTI) track?
The movement of water molecules along nerve cell connections, revealing the brain's pathways.
What is the role of synaptic changes in neural representation?
Synaptic changes give permanence to representations by strengthening connections with repeated use.
What is the relationship between excitation and inhibition in neural communication?
Neurons interact by driving up the activation level of other neurons (excitation) or driving it down (inhibition).
What is the significance of the cerebral cortex in cognitive psychology?
The cortex performs most operations that give rise to intelligence and is of greatest interest to cognitive psychologists.
What is the time frame for neurotransmitter release to affect the receiving neuron?
It occurs within about 10 ms after a neuron fires.
How does the brain's organization contribute to its function?
The brain is organized into distinct areas that serve different functions, with newer structures coordinating with older parts.