Individual Differences
1/31
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
32 Terms
Genetics
If 2 people have the same previous experience, amount of practice, level and amount of instruction, and motivation to perform a skill, then why would they possess different levels of proficiency?
abilities
genetic traits that determine the success, or achievable potential, for the performance of a skill
- all individuals possess all _____, and they cannot be measured
- stable and cannot be changed
- each motor skill requires specific motor abilities to successfully perform it
50
how many motor abilities has research identified?
static strength, stamina, reaction time, hand-eye coordination, and dynamic balance
name 5 motor abilities
limit
abilities are the building blocks of skills and limit the level that a particular skill can be obtained. However, if someone is weak in a particular motor ability that is required for a particular motor skill, they can still learng the motor skill and demonstrate improved performance, however, their weakness in that particular ability will ____ the ultimate level of their performance
reaction time
brief time lag between when the stimulus is presented and the response is initiated
increase
how does this affect reaction time? (increase/decrease)
- more response choices
increase
how does this affect reaction time? (increase/decrease)
- more uncertain
decrease
how does this affect reaction time? (increase/decrease)
- more consistent warning (foreperiod consistency)
increase
how does this affect reaction time? (increase/decrease)
- psychological refractory period
- e.g. the person has an ____ in RT due to still processing the first (fake out)
increase
how does this affect reaction time? (increase/decrease)
- stimulus response compatability (are things naturally related)
- EX: green means stop
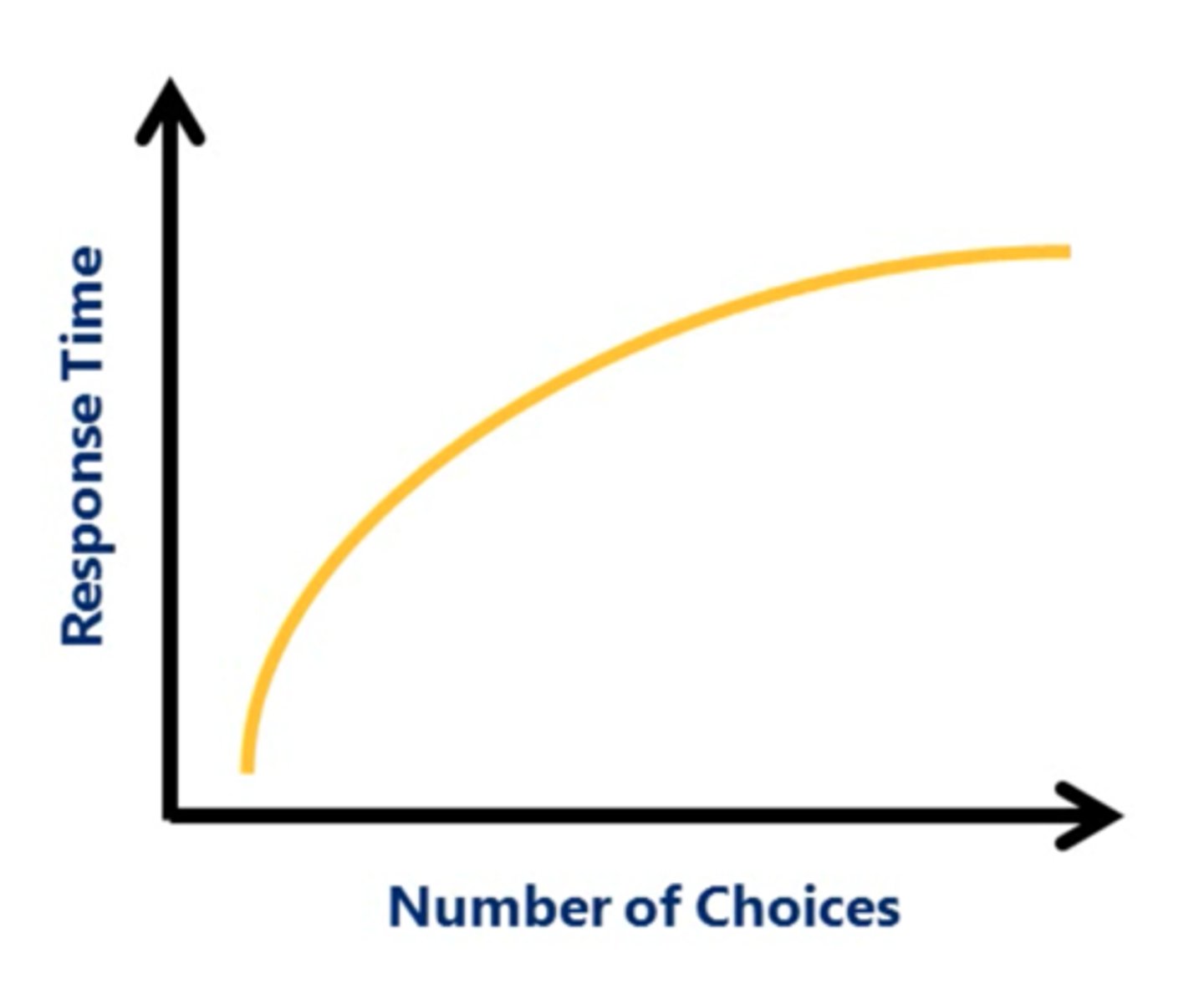
hick's law
a law of human performance stating that RT will increase logarithmically as the number of stimulus-response choices increases
simple
____ reaction time
- one signal, one movement
choice
____ reaction time
- different signals, each one associated with a specific response
discrimination
_____ reaction time
- different signal, only one response
true
T/F: reaction time is the time between stimulus and initiation of movement
movement time
from the initiation of movement to completion of movement
response time
reaction time + movement time
- stimulus presentation to completion of movement
limited
attention is a ____ resource
- we only have so much
attentional capacity
theories of attention are based on the assumption that we have a limited _____ _____
- they help explain why we can or cannot perform multiple tasks simultaneously
quality of output or speed will suffer
what happens when demands on our attention exceed our resources?
kahneman's attention theory
the amount of attention capacity available for a specific performance situation determined by the person's arousal level
enduring dispositions
an automatic influence where people direct their attention
- people spend more attention on new/meaningful tasks
momentary intentions
allocate attention according to instructions
completion of at least one task, enduring dispositions, and momentary intentions
what are the 3 rules on how people allocate attention according to Kahneman's attention theory
low arousal
attentional focus is too broad
not able to pay attention to relevant cues
optimal arousal level
attentional focus narrows and the person can concentrate on task-relevant cues
attentional focus
selectively attending to or concentrating on specific environmental information
ironic effects
phenomenon in which the action an individual was trying to avoid is carried out
internal focus of attention
focus on own body movements (pain, the way the movement feels, etc.)
external focus of attention
focus on movement effects (was the goal achieved)
externally
attentional focus should be ____ focused
- give an action goal rather than a movement goal
- requires less mental effort
- can be verbal cueing or nonverbal (metronome, music, pacing)