LESSON 3 SCADA
1/27
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
28 Terms
SCADA
communications can utilize a diverse range of wired and wireless media.
Monolithic or Early SCADA Systems
in the early first generation were limited to monitoring sensors in the system and flagging any operations in case of surpassing programmed alarm levels.
Distributed SCADA Systems
the sharing of control functions is distributed across the multiple systems connected to each other using Local Area Network (LAN).
Networked SCADA Systems
are generally networked and communicate using Wide Area Network (WAN) Systems over data lines or phone. These systems use Ethernet or Fiber Optic Connections for transmitting data between the nodes frequently
Internet of Things
are able to report state in real time by using the horizontal scale from the cloud computing facility; thus, more complex control algorithms can be implemented which are practically sufficient to implement on traditional PLCs
Instrumentation Layer
contains all the plant floor equipment that is responsible for acquiring information and controlling the process directly.
This layer would not talk to a SCADA directly. However, a SCADA system receives information from the PLC that will communicate with this layer.
PLC, RTU, and HMI Layer
understands the current state of the process by receiving information through inputs and makes decisions and controls the process through the use of outputs.
An HMI would send the information to the PLC and vice versa; it would not interact with the instrumentation directly.
SCADA Layer
An important infrastructure within this layer is the network. Although the PLC and HMI layers will require a network for data, the SCADA system would create an additional strain on the plant network due to the volume of data it will consume.
MES - Manufacturing Execution Systems Layer
Systems are used in manufacturing, distribution, supply chain operations and more.
ERP - Enterprise Resource
Planning Layer
The goal of these systems is to provide the data as well as accountability of the flow of operations. The ___ will create necessary information to manage shipping, receiving, transportation, purchasing and more.
PLCs
are the devices with which the SCADA will interact with the most; data will continuously flow between the two
SCADA zone
zone contains the HMI (Human Machine Interface) workstations which operators use to interact with the SCADA system
The process zone
contains systems responsible for communication with the substations
The SCADA DMZ zone
except from the process zone, the only zone connected to the SCADA zone. This means that it is acting as an intermediate zone for the data transfer between the SCADA zone and the Office zone.
Engineering zone
This is where the power system structure is defined. This definition is then fed into the SCADA system and will determine what operations that can be done to different parts of the power grid
Office LAN
is where the staff not working with operating the process is located.
Public DMZ
representing regular office communication with Internet and is in our model represented with a mail server.
DSO (Distribution System Operator)
is in this example representing a dedicated communication channel managed by the DSO.
Telecom Operator and Secondary Substation
For communication with secondary substations, the option of using a dedicated and DSO-owned
AMI Zone
for collecting readings of energy consumption from household and industrial end customers as well as allowing the office staff to query meter status and in some environments send switching commands to specific customers when needed

Energy supplier zones
represent systems related/belonging to an external power supplier, not part of the DSO system.
HW/SW vendor, TSO and Data hub zones
are related to the SCADA solution because they are fetching or delivering data to/from the Engineering Zone and/or the SCADA DMZ zone.
Point-to-Point
Each field device has a communication device at the host
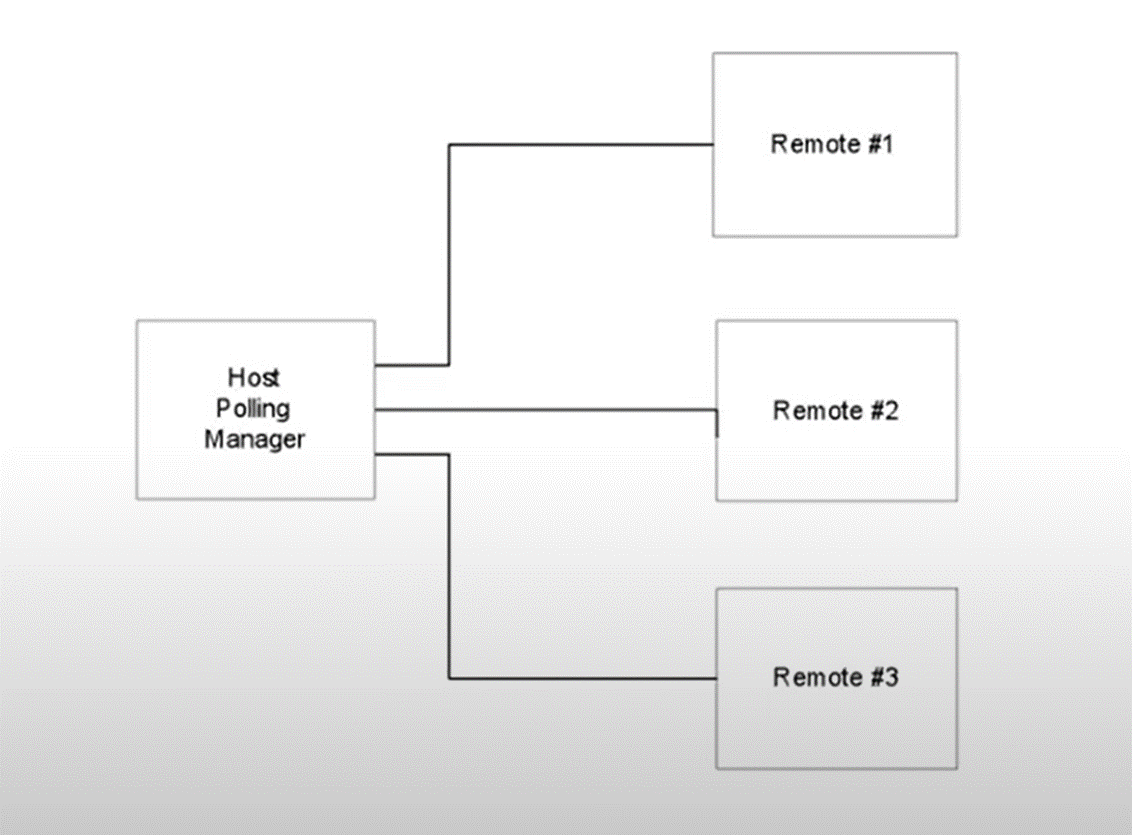
Point-to-Multipoint
Each communication device at the host addresses multiple field devices.
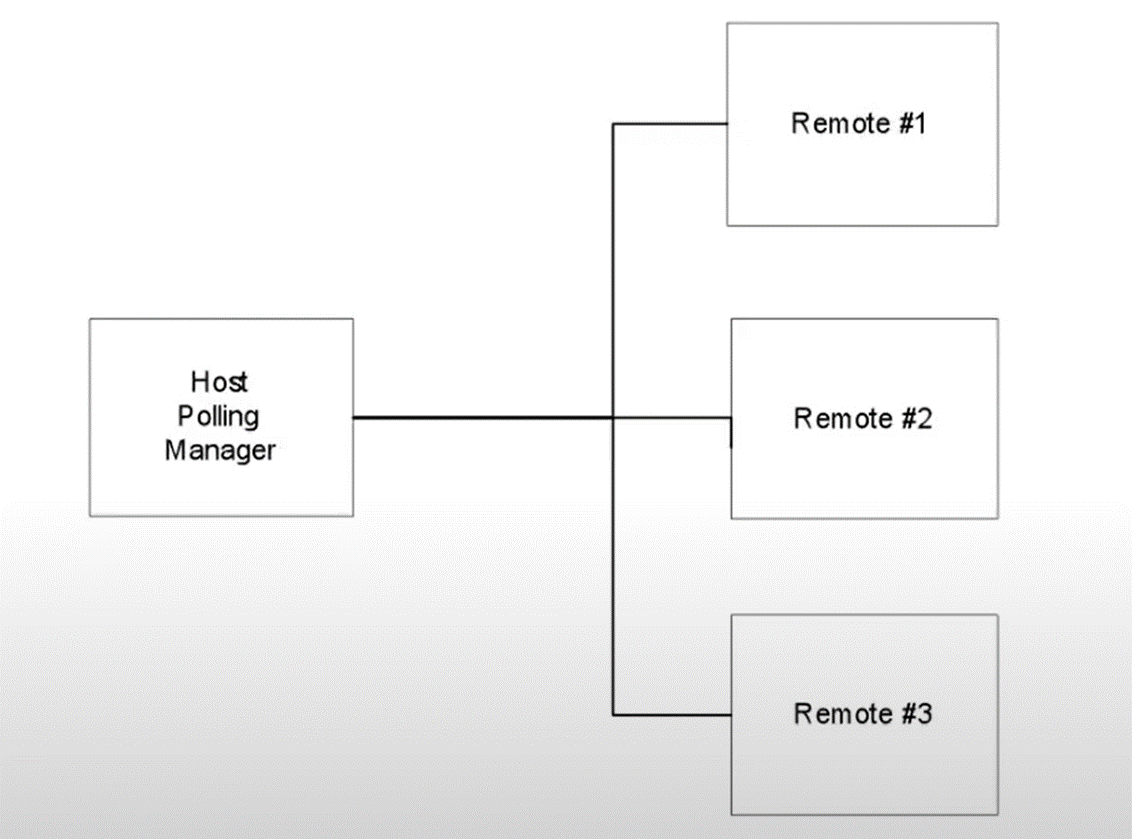
Point-to-Point-to-Point
§A communication device at the host addresses a field device that addresses additional field devices.
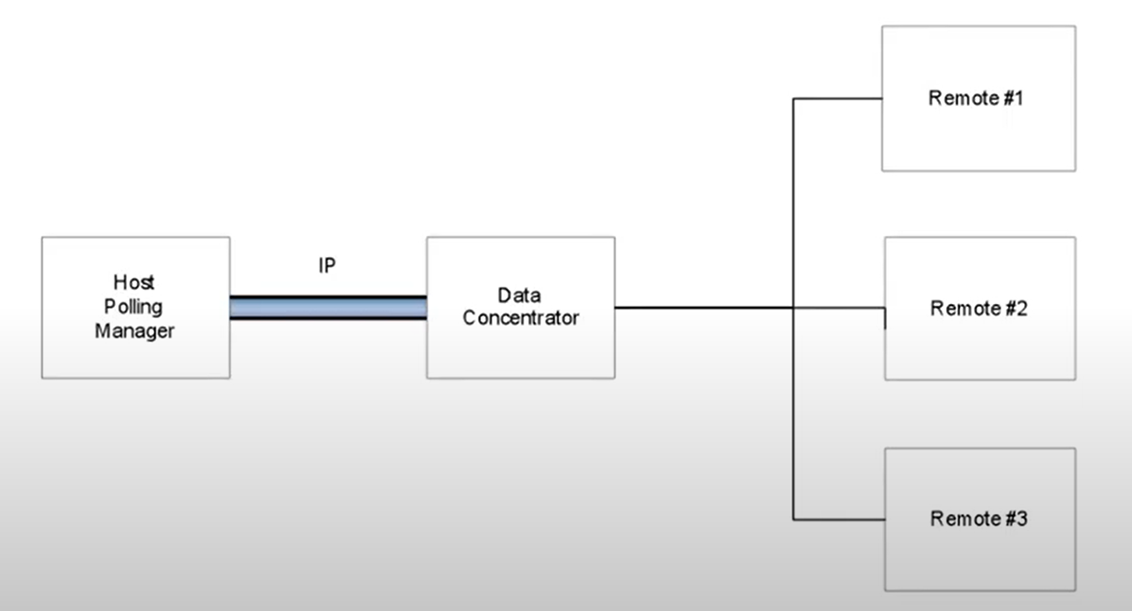
Multipoint-to-Point
Data is transmitted by one node, and all the other nodes have to wait for their turn. However, this topology is reliable since if one node fails, the rest of the network will function in a normal way.
Multipoint-to-Multipoint
§Enables users to interconnect their data center assets across many locations through a common network instead of requiring direct connections between individual locations.