Cartões: Lecture 12 Part 2: Properties of Enantiomers and Diastereomers | Quizlet
1/22
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
23 Terms
Physical properties of diastereomers are
different
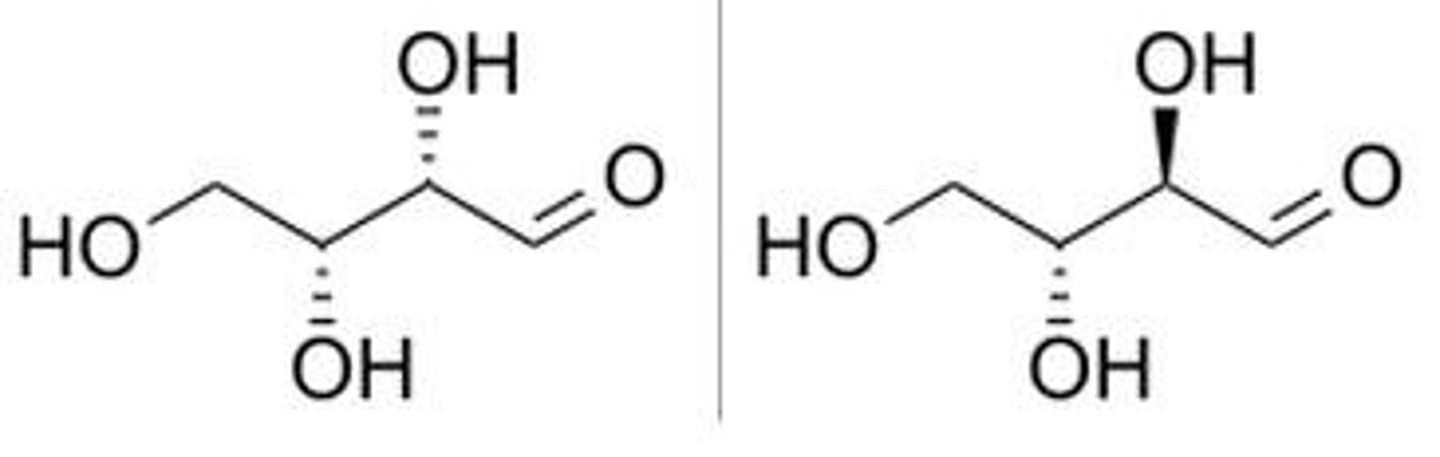
Physical properties of enantiomers are
the same except they rotate plane-polarized light equally but in opposite directions
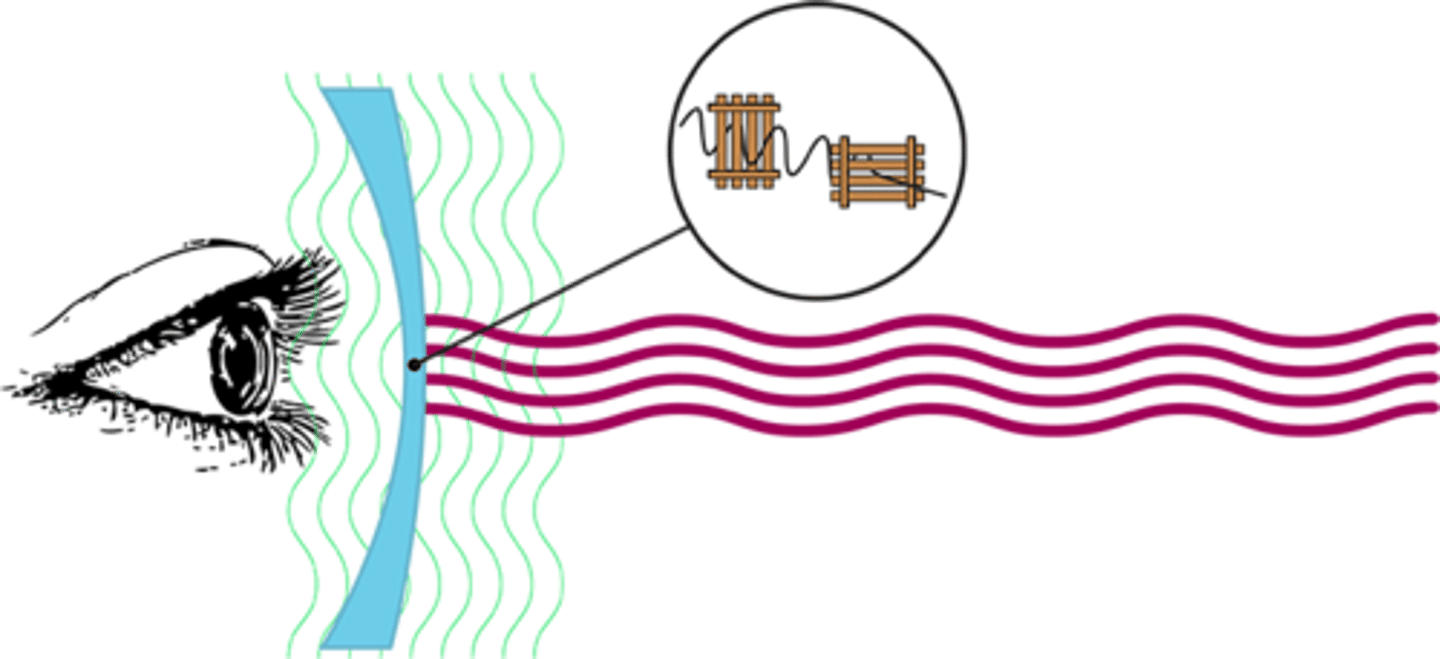
How do polarized glasses work?
- they only let in the vertical light, not horizontal
- polarized glasses reduce glare from the road
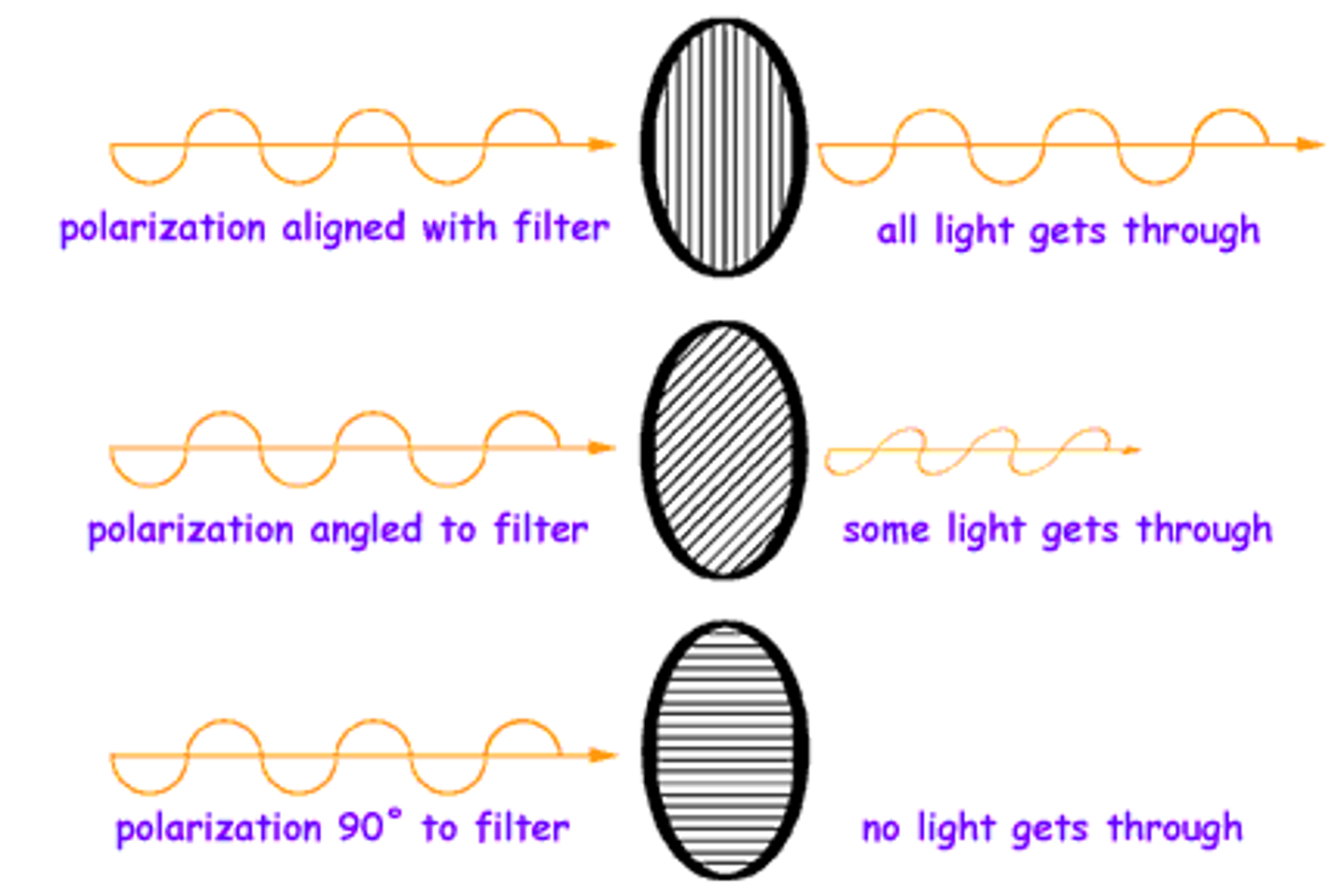
What does the polarizing filter do?
- A polarizing filter only lets waves through that are vibrating in a certain direction.
- only let through light in the same path of the vertical strip
- light goes in waves, so the wave will either go through the paper or the wave will not match the filter
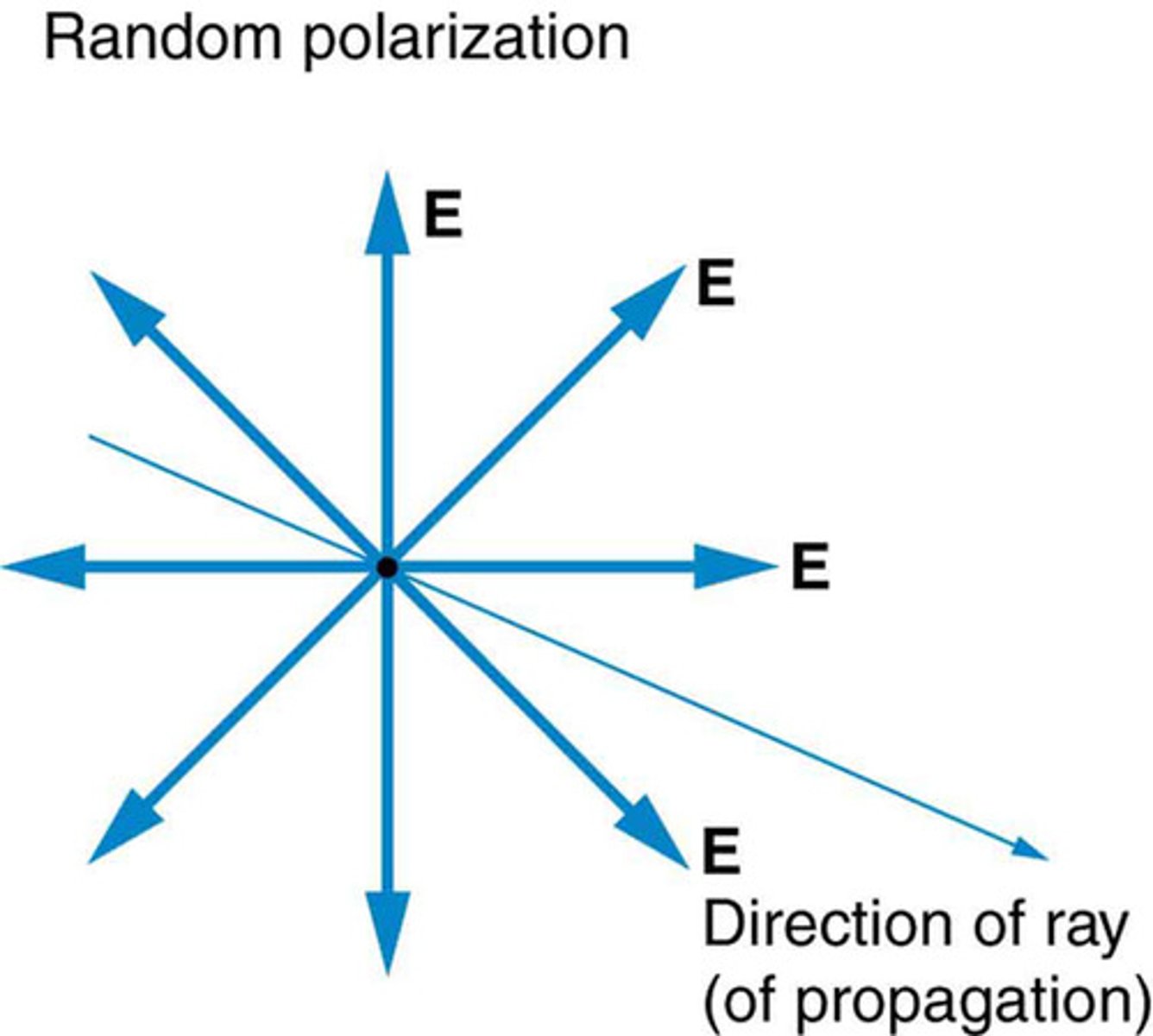
What is "unpolarized light"?
- A light wave that is vibrating in more than one plane
- no specific orientation of oscillation
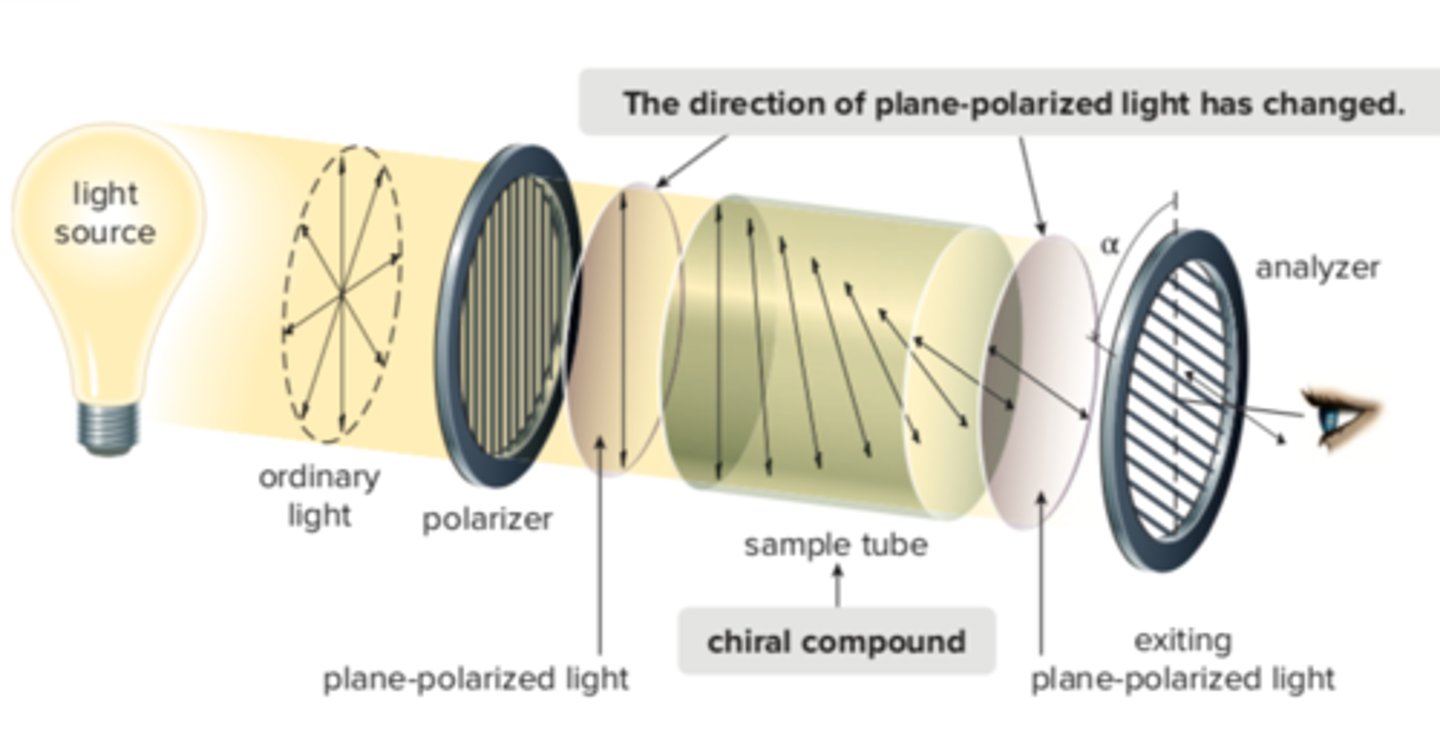
Can achiral and meso compounds rotate plane-polarized light?
- NO, achiral and meso compounds can not rotate plane-polarized ("optically inactive")
*only chiral compounds can rotate plane-polarized light
Can chiral compounds rotate plane-polarized light?
- chiral compounds can rotate plane-polarized light
*achiral and meso compounds can NOT ("optically inactive")
What type of compounds can rotate plane-polarized light?
chiral compounds can rotate plane-polarized light
*achiral and meso can NOT ("optically inactive")
Are enantiomers chiral?
YES
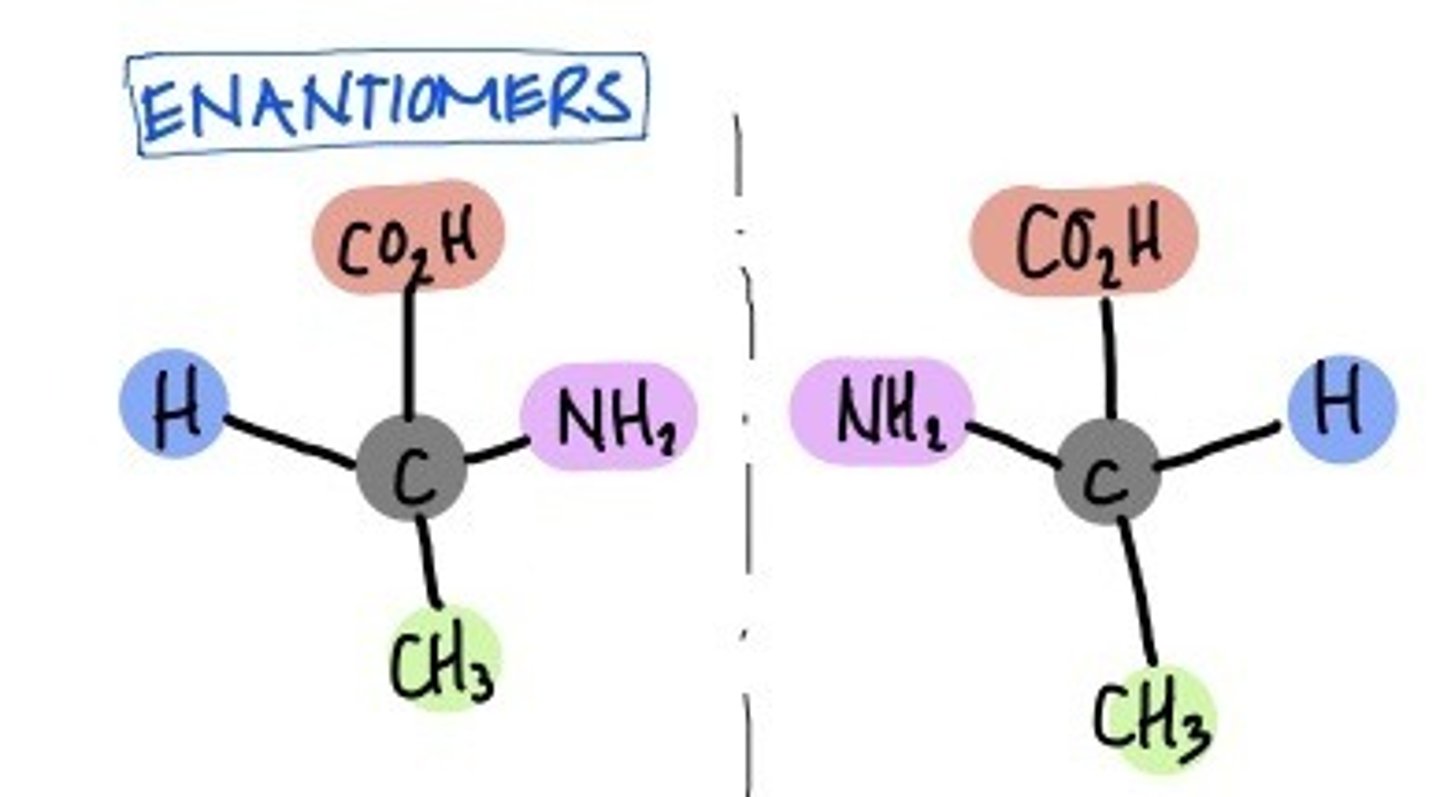
A pair of enantiomers will rotate plane polarized light _______, but in _______ directions.
a pair of enantiomers will rotate plane polarized light equally, but in opposite directions
Dextrorotatory vs Levorotatory
1. Dextrorotatory (+) = "right"
2. Levorotatory (-) = "left"

What are the 2 names for enantiomers based on direction?
(remember: in a pair of enantiomers, each will rotate light equally, but in opposite directions)
1. Dextrorotatory (+) = "right"
2. Levorotatory (-) = "left"

In a pair of enantiomers, each will rotate light equally, but in opposite directions. Therefore, we call them dextrorotatory (+) for right, and levorotatory (-) for left.
1. Is there a relationship between R/S and +/-?
2. Can we predict +/- from the structure alone? What about R/S?
1. No, there is no relationship between R/S and +/-
2. Can't predict +/- from the structure alone (but can assign R vs S from paper)
What is a racemic mixture?
- a racemic mixture contains equal amounts of both enantiomers
- (+-) symbol
- an equal mixture of 2 enantiomers (50%/50%)
- physical properties of racemic mixtures are different enantiomers
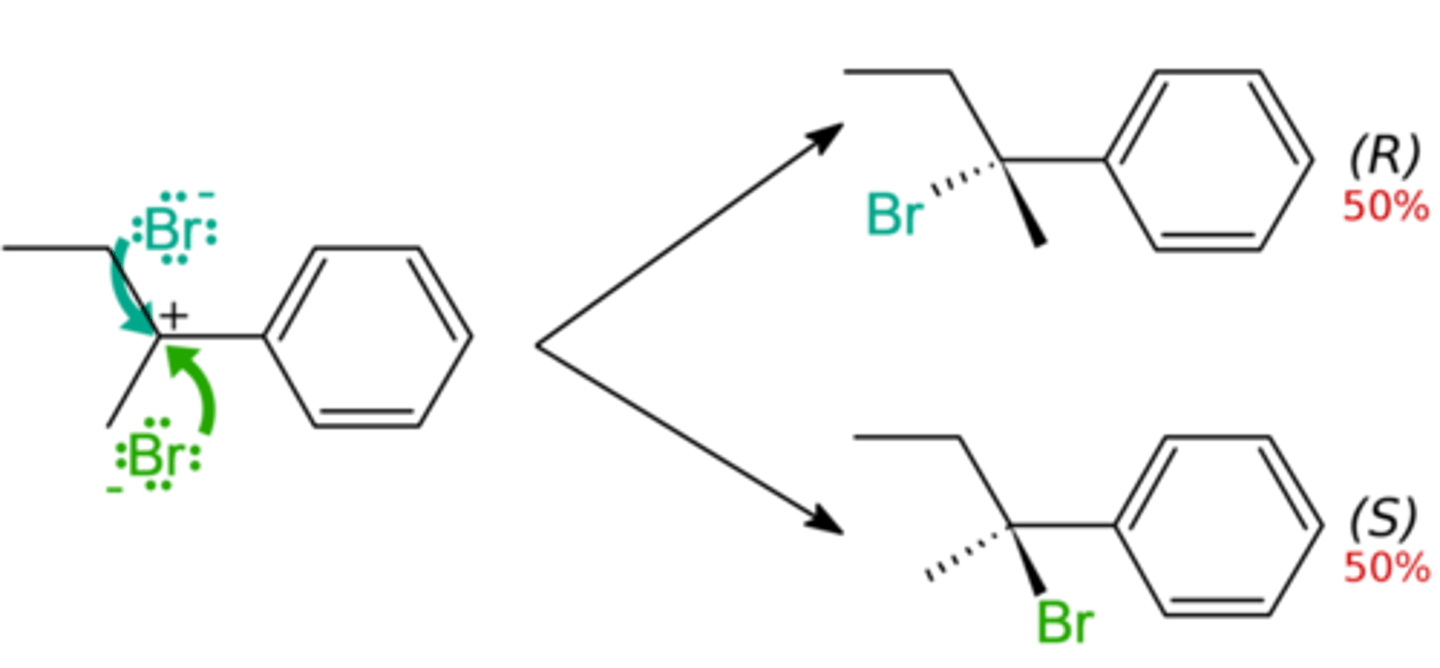
Physical properties of racemic mixtures are ___ enantiomers?
physical properties of racemic mixtures are different enantiomers
- mp and bp different because have 2 molecules, 1 right handed and 1 left handed
What does specific rotation mean?
- observed rotation under standard conditions
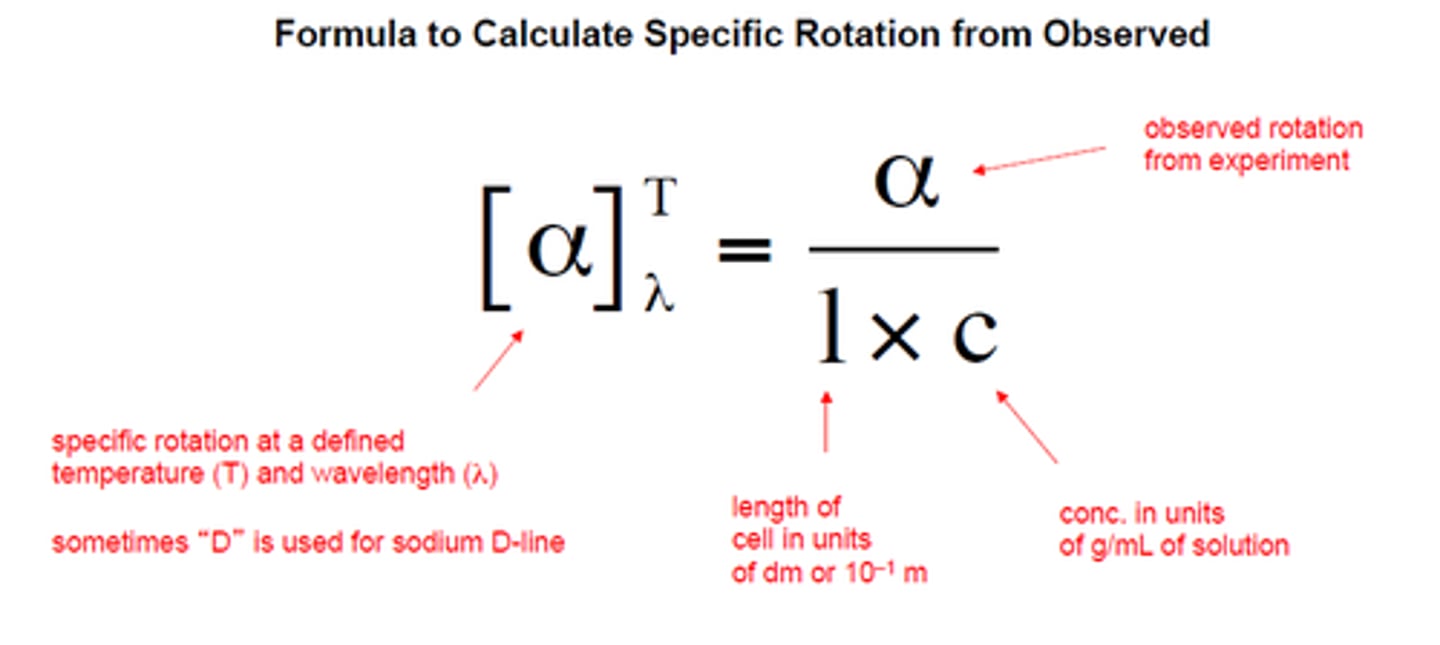
In a racemic mixture of 2 enantiomers, what is the observed optical rotation?
0 degrees
50% (+) + 50% (-)
*equal amounts so their optical rotations cancel
In any other mixture of 2 enantiomers (not racemic), what does the observed rotation depend on?
- in any other mixture of two enantiomers, observed rotation depends on which enantiomer is in excess, and by how much
- i.e. 20%(+) + 80%(-) --> 20%(+) + 20%(-) + 60%(-) excess
Example: What is the enantiomer excess?
20%(+) + 80%(-) -->
20%(+) + 80%(-) --> 20%(+) + 20%(-) + 60%(-) excess

What is enantiomeric excess (ee or %ee)?
- the amount of one enantiomer that is "not cancelled" in the mixture
Ex. 20%(+) + 80%(-) --> 20%(+) + 20%(-) + 60%(-) excess
Ex. if 5% (+) + 95% (-) -> 90% ee of (-)
Example: What is enantiomer excess (ee or %ee)?
if 5% (+) + 95% (-) ?
Ex. if 5% (+) + 95% (-) -> 90% ee of (-)

Ex. The specific rotation of (-)-cholesterol is -31.5 degrees. For a mixture of 25% (-)-cholesterol and 75% (+)-cholesterol, what is the %ee?
25% (-) + 25% (+) + 50% (+) -> 50% ee of (+)
Ex. The specific rotation of (-)-cholesterol is -31.5 degrees. For a mixture of 25% (-)-cholesterol and 75% (+)-cholesterol, what is the %ee and what is the observed optical rotation of the mixture?
1. 25% (-) + 25% (+) + 50% (+) -> 50% ee of (+)
2. 15.8 degrees
50% ee (+) -> 50% of max rotation observed
(0.5)(+31.5 degrees) = 15.8 degrees
*only the "excess" portion rotates light (rest cancels out)
