1.1 Energy Changes in a System & Energy Stores
1/68
Earn XP
Description and Tags
These flashcards are for Topic 1 - Energy in AQA GCSE Physics (Triple Higher). They cover specification points 4.1.1.1 - 4.1.1.4
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
69 Terms
What is a 'system' in the context of physics?
An object or a group of objects.
What is the principle of conservation of energy?
Energy can be transferred usefully, stored, or dissipated, but it can never be created or destroyed.
What defines a 'closed system'?
A system where no energy can enter or leave, resulting in no net change to its total energy.
Name the eight main energy stores.
Kinetic, Gravitational Potential, Elastic Potential, Thermal, Chemical, Nuclear, Magnetic, and Electrostatic.
What is the kinetic energy store?
The energy an object possesses due to its motion.
What is the gravitational potential energy store?
The energy stored in an object due to its position in a gravitational field, typically its height above a surface.
What is the elastic potential energy store?
The energy stored in an object when it is stretched or compressed.
What is the thermal energy store?
The total kinetic and potential energy of the particles within an object, related to its temperature.
Describe the main energy store changes when an object is projected upwards.
The kinetic energy store decreases as it is transferred to the gravitational potential energy store.
Describe the main energy store changes when a moving object hits an obstacle.
The kinetic energy store decreases, transferring energy to thermal and sound energy stores.
Describe the main energy store changes when bringing water to a boil in an electric kettle.
Energy is transferred from the chemical energy store of the fuel (at the power station) to the thermal energy store of the water.
State the symbol equation used to calculate the kinetic energy of a moving object.
Ek = ½ mv2
In the kinetic energy equation, Ek = ½ mv2, what does the symbol ‘m’ represent, and what are the SI units?
m is mass in kilograms (kg)
In the kinetic energy equation, Ek = ½ mv2, what does the symbol’ v’ represent, and what are the SI units?
v is speed in metres per second (m/s)
State the equation used to calculate the gravitational potential energy gained by an object
Ep = mgh
In the gravitational potential energy equation, Ep = mgh, what does the symbol ‘m’ represent, and what are the SI units?
m is mass in kilograms (kg)
In the gravitational potential energy equation, Ep = mgh, what does the symbol ‘g’ represent, and what are the SI units?
g is gravitational field strength in newtons per kilogram (N/kg)
What is the Earth’s gravitational field strength?
9.8 N/kg
In the gravitational potential energy equation, Ep = mgh, what does the symbol ‘h’ represent, and what are the SI units?
h is for height in metres (m)
State the equation used to calculate the elastic potential energy stored in a stretched spring
Ee = ½ ke2
In the elastic potential energy equation, Ee = ½ ke2, what does the symbols ‘k’ represent, and what are the SI units?
k is the spring constant in newtons per meter (N/m)
In the elastic potential energy equation, Ee = ½ ke2, what does the symbols ‘e’ represent, and what are the SI units?
e is the extension in metres (m)
What is the term for the amount of energy required to raise the temperature of 1kg of a substance by 1°C?
Specific heat capacity
State the equation that links change in thermal energy, mass, specific heat capacity, and temperature change.
ΔE = mcΔθ
In the equation ΔE = mcΔθ, what does the symbol ‘m’ represent, and what are the SI units?
m is the mass in kilograms (kg)
In the equation ΔE = mcΔθ, what does the symbol ‘c’ represent, and what are the SI units?
c is specific heat capacity in joules per kilogram per degree Celcius (J/kg°C)
In the equation ΔE = mcΔθ, what does the symbol ‘Δθ’ represent, and what are the SI units?
Δθ is the change in temperature in degrees Celcius (°C)
What is the formal definition of 'power'?
Power is the rate at which energy is transferred, or the rate at which work is done.
State the two equations used to calculate power
P = E / t
P = W / t
What are the SI units for power, energy transferred, work done, and time?
Power is in watts (W), energy and work done are in joules (J), and time is in seconds (s).
An energy transfer of 1 joule per second is equal to a power of _ _____.
1 watt
What piece of equipment is used to measure the mass of the material block in the specific heat capacity practical?
A balance
Why is insulation wrapped around the metal block in the specific heat capacity practical?
To reduce the transfer of thermal energy to the surroundings, minimising experimental error.
In the specific heat capacity practical, why might a few drops of water be added to the hole containing the thermometer?
To ensure good thermal contact between the thermometer and the block, leading to a more accurate temperature reading.
Which two electrical components are connected to the heater in RP1 to determine its power?
An ammeter connected in series and a voltmeter connected in parallel across the heater.
How is the power of the heater calculated in the specific heat capacity practical?
Power = Potential Difference × Current (P = VI)
How is the energy transferred by the heater (work done) calculated at each time interval in RP1?
Energy = Power × time (E = Pt)
What quantities are plotted on the x-axis and y-axis for the graph in the specific heat capacity practical?
Work done is plotted on the x-axis and temperature is plotted on the y-axis.
Why might the beginning of the temperature vs. work done graph be curved in RP1?
Due to thermal inertia, as it takes time for the block and heater to warm up initially.
How is the heat capacity of the metal block calculated from the graph of temperature against work done?
The heat capacity is the reciprocal of the gradient of the straight-line portion of the graph (1 / gradient).
What is the relationship between heat capacity, specific heat capacity, and mass?
Specific heat capacity is the heat capacity per unit mass.
How is the specific heat capacity of the block calculated using the gradient from the graph in RP1?
Specific heat capacity = (1 / gradient) / mass
What is a significant source of systematic error in the specific heat capacity experiment?
Thermal energy being transferred to the surroundings instead of heating the block.
How does unwanted thermal energy transfer to the surroundings affect the calculated value for specific heat capacity?
It causes the calculated value to be higher than the actual value, as more energy input is recorded for the same temperature rise.
What determines how much kinetic energy a moving object has?
Its mass and its speed.
If two objects have the same mass, which one has more kinetic energy?
The one that is moving faster.
If two objects are moving at the same speed, which one has more kinetic energy?
The one with the greater mass.
What is the relationship between the extension of a spring and the force applied, provided the limit of proportionality is not exceeded?
The extension is directly proportional to the force applied.
What is the term for the energy required to raise the temperature of a substance by 1°C, which depends on its mass?
Heat capacity
What apparatus is used to measure the potential difference across the heater in RP1?
A voltmeter
What apparatus is used to measure the current flowing through the heater in RP1?
An ammeter
How should the voltmeter be connected in the circuit for RP1?
In parallel with the heater
How should the ammeter be connected in the circuit for RP1?
In series with the heater
The rate at which energy is transferred is the definition of _______.
power
Energy stored in an object at a height, such as a mug on a table, is known as ___________ potential energy
gravitational
A drawn catapult or a compressed spring are examples of objects with an _______ potential energy store
elastic
In the specific heat capacity practical (RP1), what is the independent variable?
The energy transferred to the block.
In the specific heat capacity practical (RP1), what is the dependent variable?
The temperature of the metal block.
Name two control variables in the specific heat capacity practical (RP1)
The mass of the metal block and the material of the block.
What is the purpose of a joulemeter in an experiment to find specific heat capacity?
To directly measure the amount of electrical energy that passes into the immersion heater.
If a student's calculated specific heat capacity is significantly higher than the accepted value, what is the most likely experimental reason?
A significant amount of thermal energy was lost to the surroundings, meaning the energy input measured was much higher than the energy that actually heated the block.
What is meant by the 'spring constant'?
A measure of a spring's stiffness; the force required to stretch or compress it by one metre.
Two motors lift the same weight through the same height. Motor A does this in 10 seconds, while Motor B does it in 20 seconds. Which motor is more powerful and why?
Motor A is more powerful because it transfers the same amount of energy in less time, meaning its rate of energy transfer is greater.
What happens to the total energy of a closed system when changes occur within it?
The total energy of the closed system remains constant.
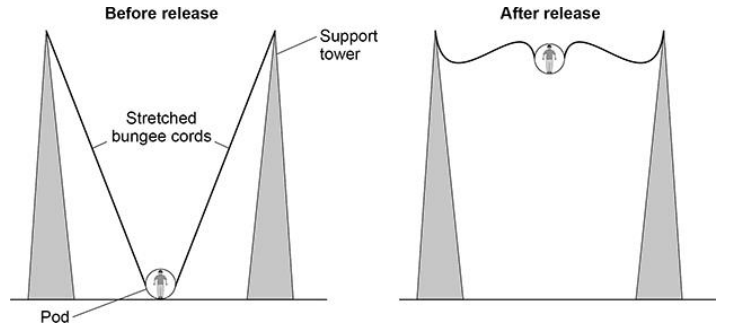
In a ride at a theme park, a person is strapped into a pod that is attached to two stretched bungee cords.
The bungee cords behave like springs.
The figure shows a person using the ride.
Which energy store increases as the bungee cords are stretched?
Elastic potential energy

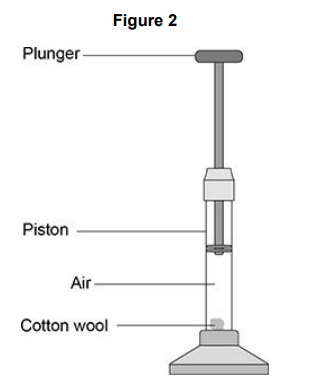
A fire piston is a special type of syringe that can be used to start fires.
Figure 2 shows a fire piston.
The plunger is pushed quickly downwards and compresses the air.
When the air is compressed quickly, the temperature of the air increases.
How does an increase in temperature affect the air particles inside the piston?
The mean kinetic energy of the particles increases.
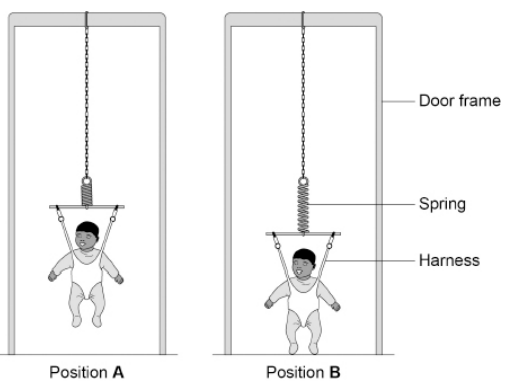
A baby bouncer is a harness attached to a spring that hangs from a door frame.
The figure shows a baby in a baby bouncer in two positions.
The baby bouncer should not be used with babies that have a mass greater than 12 kg.
Suggest one reason why.
The spring may become permanently extended.

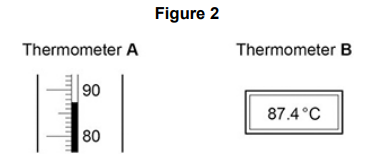
A student used two different types of thermometer to measure temperature changes.
Figure 2 shows a reading on each thermometer.
What is the resolution of thermometer B?
0.1 °C
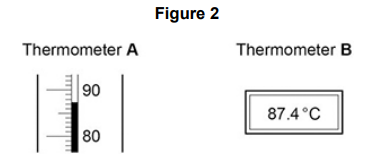
A student used two different types of thermometer to measure temperature changes.
Figure 2 shows a reading on each thermometer.
Thermometer A is more likely to be misread.
Give one reason why.
Parallax error
