Polarity
1/33
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
34 Terms
* decreases down a group
* the less electronegative atom has a slight positive charge
* as a result a charge separation occurs across the bond (dipole)
* resulting in the formation of a negative ion from the most electronegative atom gaining an electron
* this is known as an ionic bond
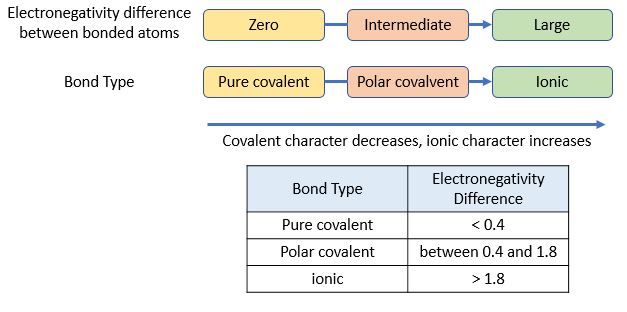
* electrons are shared equally
* electrons shared unequally between atoms
* one atom donates its valence electrons to the other
* ions are formed resulting in an ionic bond
* the way the polar bonds are arranged
* more than one type of atom bonded to the central atom
* causes the liquid polar substance to deflect towards a charged object
* non-polar liquids flow without deflection past charged objects
(water and rod test)
* the large electronegativity difference between hydrogen and oxygen atoms produces strong attractive forces between the molecules
substances that contain polar molecules
hydrogen chloride HCl
phosphorus trichloride PCl3
ammonia NH3
water H2O
dichloromethane CH2Cl
substances that contain non-polar molecules
carbon dioxide CO2
oxygen O2
hydrogen H2
nitrogen N2
methane CH4
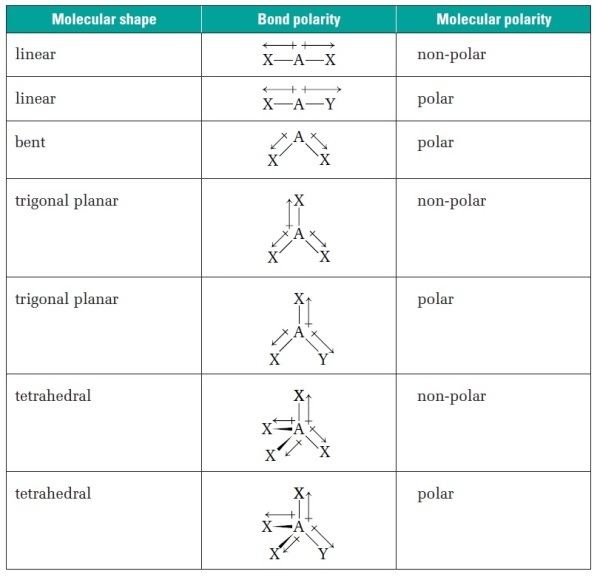
polar shapes and why
bent and v-shaped
trigonal planar
asymmetrical shapes, dipoles don’t cancel → polar molecules
non-polar shapes and why
tetrahedral
linear
symmetrical shapes, dipoles can cancel if equal and opposite → non-polar molecules
what makes a polar molecule
different electronegativity values between Z and X
not arranged symmetrically around the central atom due to shape
effect of dipoles is not cancelled
what makes a non-polar molecule
bonds are arranged symmetrically around the central atom in a certain shape
the effect of any dipoles formed by the different electronegativity of the X-Z bond is cancelled
what is the solubility rule of “like dissolves in like”
polar molecules can dissolve in polar liquid
non-polar molecules dissolve in other non-polar molecules but not in water