601: Pterygopalatine Fossa
1/78
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
79 Terms
pterygomaxillary fissure
what structure leads to the pterygopalatine fossa?
pterygopalatine fossa
traveling medially from the pterygomaxillary fissure will place you in the:
inferior
The pterygopalatine fossa is ________to the apex of the orbit.
lateral
The pterygopalatine fossa is ________ to the sphenopalatine foramen
foramen rotundum
pterygoid canal
pharyngeal canal
what 3 foramen are located on the posterior wall of the pterygopalatine fossa?
sphenoplatine foramen
if you move a probe medially in the pterygopalatine fossa to get to the nasal cavity, you must go through the:
pterygomaxillary fissure
the lateral boundary of the pterygopalatine fossa is the:
pterygopalatine canal
the floor of the pterygopalatine fossa is the:
maxilla
the anterior wall of the pterygopalatine fossa is formed by the:
maxilla
sphenoid
palatine
what 3 bones make up the pterygopalatine fossa
sphenoid bone
the posterior wall and roof of the pterygopalatine fossa is formed by the:
palatine bone
the medial wall of the pterygopalatine fossa is formed by the:
pterygomaxillary fissure
inferior orbital fissure
name the 2 fissures associated with the pterygopalatine fossa:
foramen rotundum
sphenopalatine foramen
name the 2 foramen associated with the pterygopalatine fossa:
vidian canal/ pterygoid canal
pterygopalatine canal
pharyngeal canal
name the 3 canals associated with the pterygopalatine fossa:
inferior orbital fissure
what hole is located anterior and superior on the maxilla bone in the pterygopalatine fossa?
orbit
a probe from the pterygopalatine fossa through the infraorbital fissure, you would arrive in the:
inferior orbital fissure
if you wanted to go from the orbit to the pterygopalatine fossa, you'd take the
sphenopalatine foramen
what hole is located superiorly on the palatine bone?
nasal cavity
a probe from the pterygopalatine fossa through the sphenopalatine foramen, you would arrive in the:
sphenopalatine foramen
if you wanted to go from the nasal cavity to the pterygopalatine fossa, you'd take the
middle cranial fossa
a probe from the pterygopalatine fossa through the foramen rotundum, you would arrive in the:
foramen rotundum
what hole is located superiorly on the sphenoid bone?
foramen rotundum
if you wanted to go from the middle cranial fossa to the pterygopalatine fossa, you'd take the
nasopharynx
a probe from the pterygopalatine fossa through the pharyngeal canal, you would arrive in the:
pharyngeal canal
if you wanted to go from the nasopharynx to the pterygopalatine fossa, you'd take the
foramen lacerum
a probe from the pterygopalatine fossa through the vidian canal/ pterygoid canal, you would arrive in the:
vidian canal/ pterygoid canal
if you wanted to go from the foramen lacerum to the pterygopalatine fossa, you'd take the
oral cavity
a probe from the pterygopalatine fossa through the pterygopalatine canal, you would arrive in the:
pterygopalatine canal
if you wanted to go from the oral cavity to the pterygopalatine fossa, you'd take the
foramen rotundum
the maxillary division of CV inter the pterygopalatine fossa via the:
infraorbital n.
V2 after fibers pass through the infraorbital fissure is called the:
meningeal n. branch
which branch from V2 does NOT pass through the foramen rotundum?
meningeal n. branch
provides sensory innervation to the dura mater:
V2
meningeal nerve branch is a branch of:
middle meningeal a.
meningeal nerve branch travels with what structure?
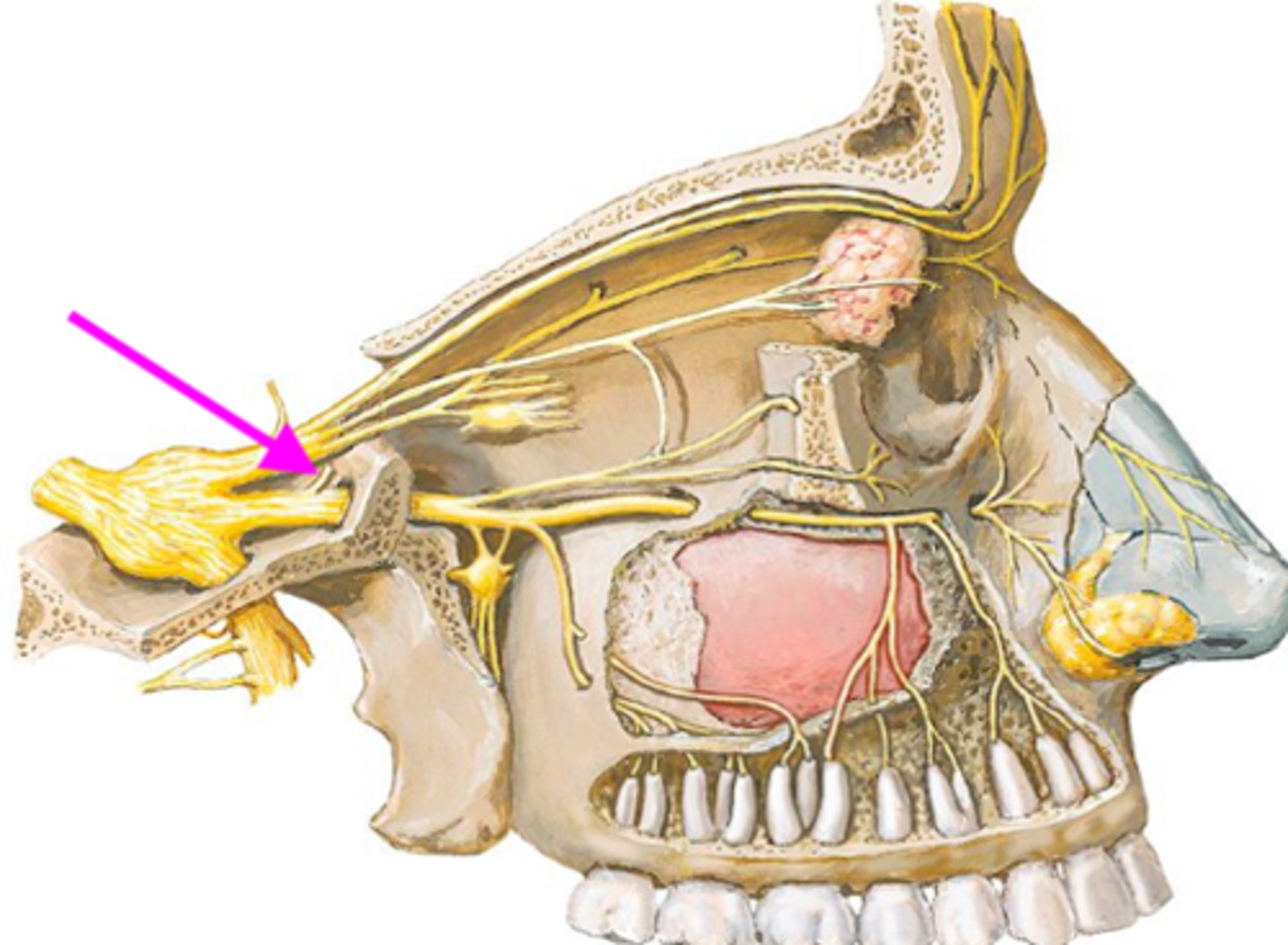
meningeal n. branch
identify the structure:
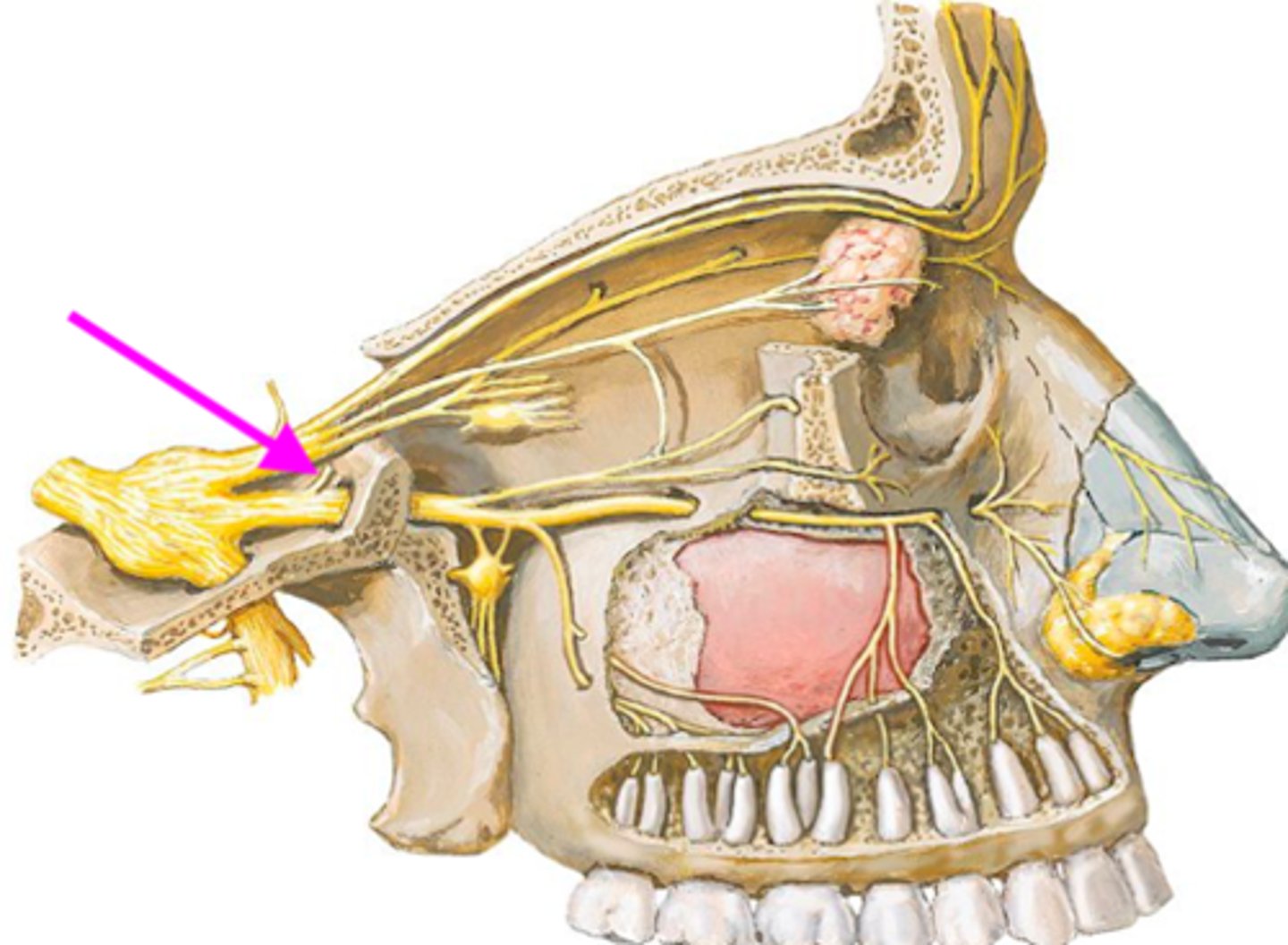
sensory innervation of dura mater
if this structure was lacerated, what function would be diminished
inferior orbital fissure
the zygomatic nerve enters leaves the pterygopalatine fossa and enters the:
zygomatico-facial n.
zygomatico-temporal n.
the zygomatic nerve divides into two branches:
V2
the zygomatic n. is a branch of:
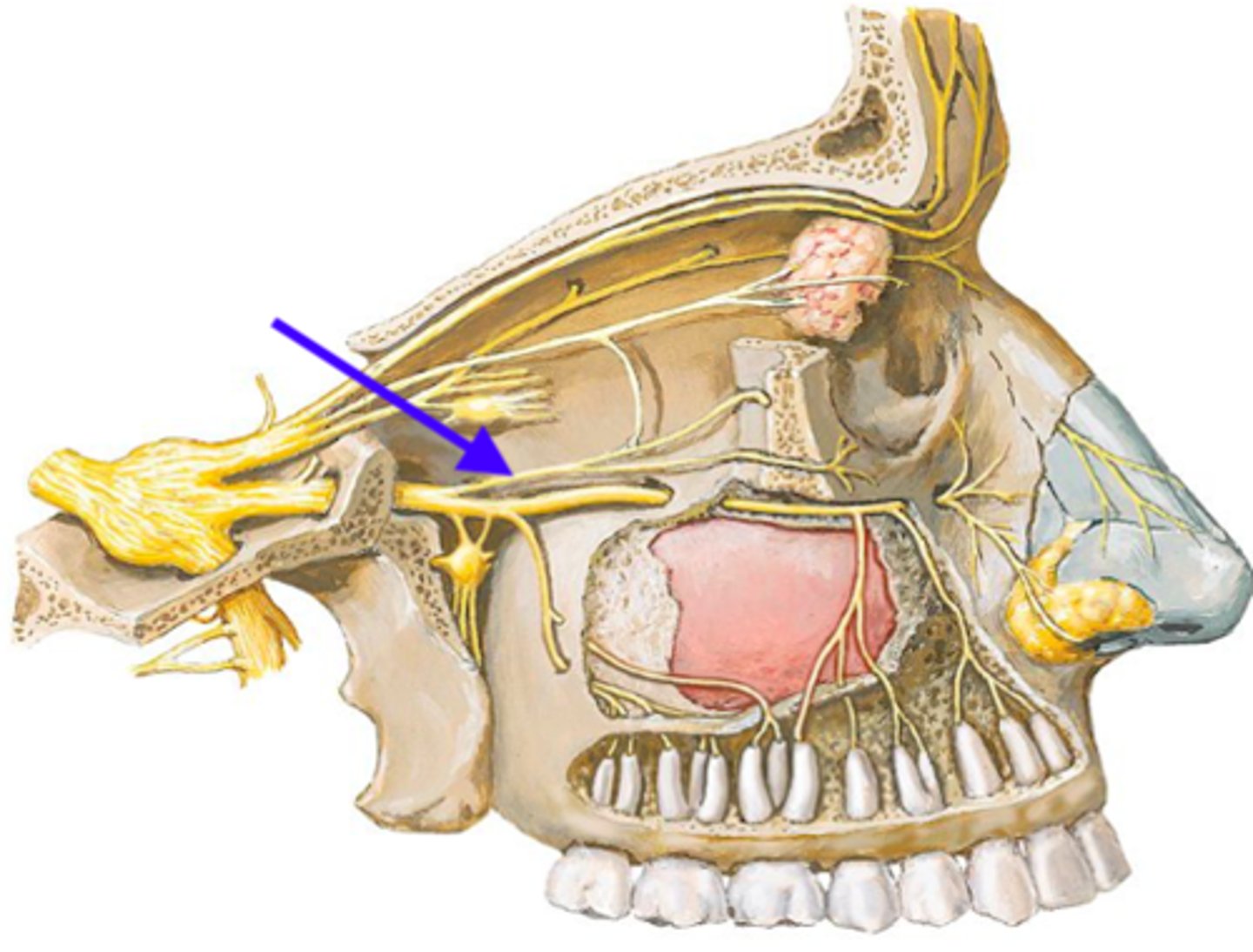
zygomatic n.
identify the structure:
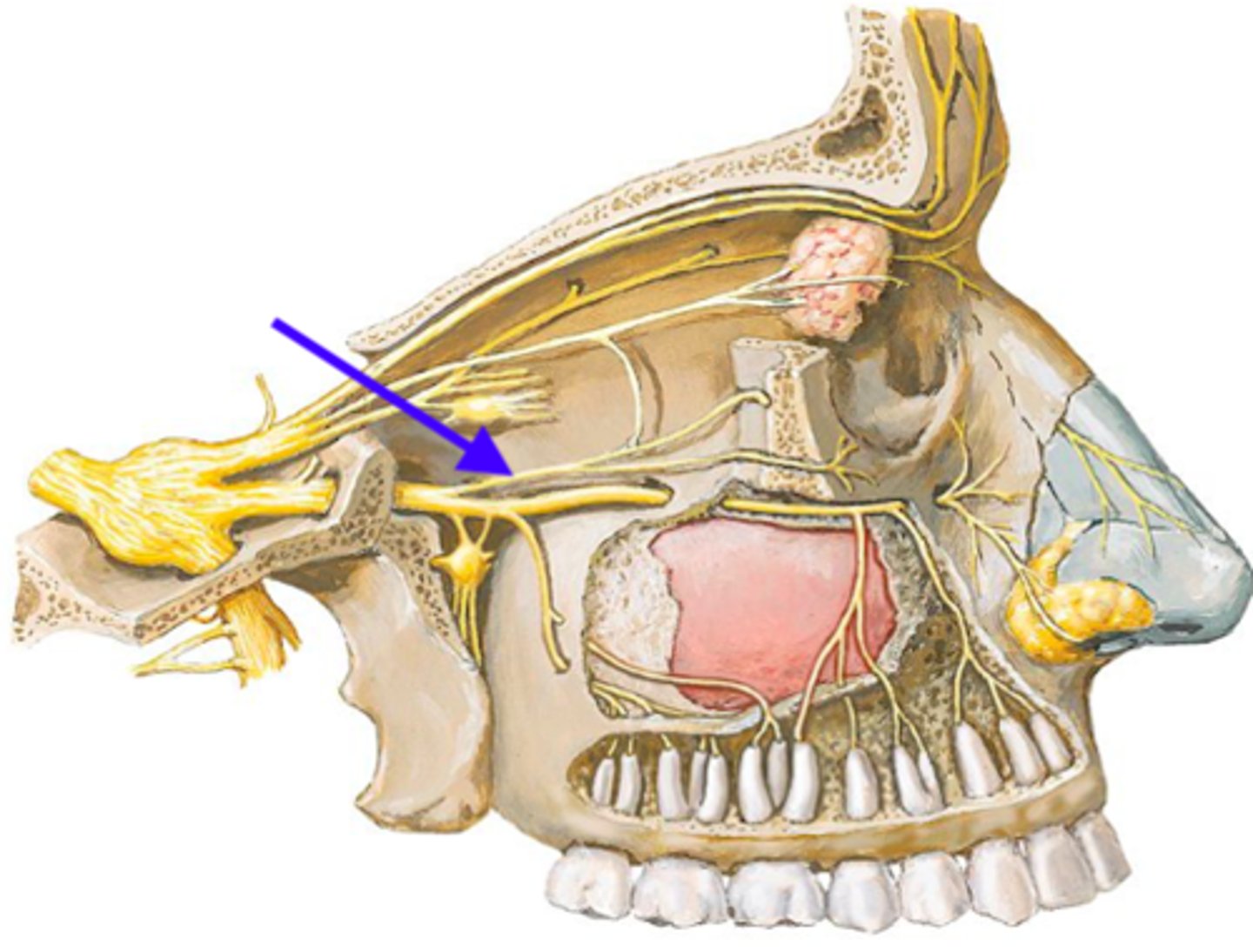
cutaneous sensation from skin over anterior temporal region and skin anterior to zygomatic bone
if this structure was lacerated, what function would be diminished
zygomaticotemporal n.
which V2 nerve communicates with V1's lacrimal n. in the orbit?
2 short pterygopalatine nn.
these fibers suspend the pterygopalatine ganglion:
V2
the branches of the ganglion are branches of:
trigeminal ganglion
the post ganglionic fibers of the branches of the ganglion 's cell bodies are located in the:
posterior superior alveolar nn.
what nerve provides sensory innervation to maxillary third molar, second molar, palatal and distobuccal roots of first molar, associated buccal gingiva and maxillary sinus
infraorbital n.
anterior and middle superior alveolar nerves are branches of the:
posterior superior alveolar nn.
which nerve that provides sensory innervation to the maxillary teeth does not travel through the inferior orbital fissure?
anterior superior alveolar nn.
which nerve branching from the infraorbital nerve has branches that will innervate the floor and lateral wall of the nasal cavity?
infraorbital n.
what nerve provides cutaneous sensory innervation to the muscles of facial expression, lateral nose and upper lip?
orbital branches of the ganglion
provide sensory innervation from periosteum of orbit, sphenoidal sinus and posterior ethmoidal air cells
medially
the pharyngeal n. lies _______ to the vidian/pterygoid canal
nasopalatine n.
provides sensory innervation for septum, mucoperiosteum of anterior hard palate
posterior superior lateral nasal n.
provides sensory innervation for superior turbinate, superior meatus, middle turbinate
orbital branches
what nerves of the ganglia travel anteriorly?
nasopalatine n.
posterior superior lateral nasal n.
what nerves of the ganglia travel medially?
palatine n.
-greater and lesser palatine nn.
-posterior inferior lateral nasal n.
what nerves of the ganglia travel inferiorly?
pharyngeal n.
pterygoid/vidian n.
what nerves of the ganglia travel posteriorly?
pterygoid/vidian n.
which nerve of the ganglia is the only one that does not transmit V2 sensory fibers?
CN VII
parasympathetic fibers from which cranial nerve pass through the pterygopalatine fossa?
superior salivatory nucleus
preganglionic parasympathetic cell bodies for CN VII are located in the:
pterygopalatine ganglion
postganglionic parasympathetic cell bodies for CN VII are located in the:
preganglionic parasympathetic
the greater petrosal n. carries ____ _____ fibers:
internal acoustic meatus
parasympathetic fibers of CN VII will first travel through the ____ to enter the temporal bone:
hiatus of facial canal
parasympathetic fibers of CN VII will leave the temporal bone via the:
greater superficial petrosal n.
parasympathetic fibers of CN VII after leaving the hiatus of facial canal turn into the:
vidian canal/ pterygoid canal
the greater superficial petrosal n. will join the deep petrosal n. at the:
V2
parasympathetics of VII heading to the lacrimal gland after jumping on the 2 short pterygopalatine nn. will travel on:
2 short pterygopalatine nn.
parasympathetics of VII heading to the lacrimal gland after synapsing will travel on the:
zygomatic n.
parasympathetics of VII heading to the lacrimal gland after jumping onto V2 will travel on the:
zygomaticotemporal n.
parasympathetics of VII heading to the lacrimal gland after jumping on the zygomatic n. will travel on the:
communicating branch
parasympathetics of VII heading to the lacrimal gland after jumping on the zygomaticotemporal n. will travel on the:
lacrimal n.
parasympathetics of VII heading to the lacrimal gland after jumping on the communicating branch from zygomaticotemporal n. will travel on the ____ to reach its destination
IML T1-T3
preganglionic cell bodies of sympathetic fibers of CN VII are located on:
superior cervical ganglion
preganglionic sympathetic fibers of CN VII synapse at:
internal carotid a.
post ganglionic fibers of CN VII ride along what structure to reach its destination
postganglionic sympathetic
the deep petrosal nerves is made of _____ ______ fibers: