cartilage, tissue, and bone cells
1/61
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
62 Terms
[ ] is a specialized form of connective tissue
cartilage
cartilage is [ ], has firm consistency, and is able to bear mechanical stress without permanent distortion
avascular
[ ], [ ], and [ ] are three types of cartilage where [ ] is the most common
hyaline, elastic, and fibrocartilage
hyaline
[ ] is responsible for long bone growth
hyaline
the temporary skeleton besides the brain in embryos that is replaced by bone is [ ]
hyaline
hyaline can be found in the skeleton of a fetus, walls of larger respiratory passages, and [ ]
epiphyseal plates of growing bones
articular surface of movable joints
hyaline is most abundant in the respiratory system in the [ ], [ ], [ ] and [ ]
nose, larynx, trachea, and bronchi
cartilage forms from mesenchyme » [ ] » chondrocytes » isogenous groups
chondroblasts
[ ] are completely covered by ground substance and fibers
chondrocytes
chondroblast are formed by differentiation of progenitor cells in the [ ]
perichondrium
[ ] sits in the lacuna, where it is only visible after tissue processing
chondrocytes
why is the lacuna only visible after tissue processing?
the chondrocytes shrink
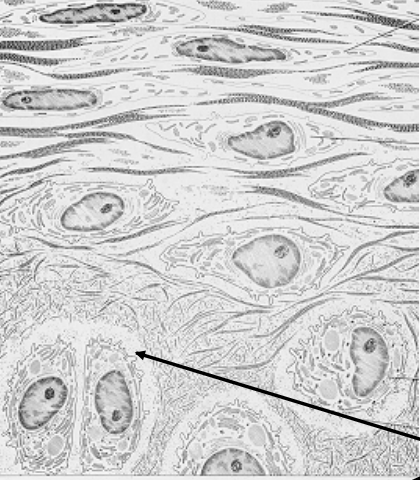
cell type?
structure?
cell type: chondrocyte
structure: lacuna
fibers are made out of [ ] collagen fibrils
type II
fibers contain a lot of [ ] and are [ ] (in terms of staining)
hydroxylysine
basophilic
the type of collagen that predominates bone formation is [ ]
type X collagen
chondroitin 4-sulfate, chondroitin 6-sulfate, keratan sulfate, and hyaluronic acid are all types of
GAGs
[ ] is a cart-specific proteoglycan
aggrecan
the cartilage extracellular matrix is [ ] and is composed of 60 - 80% water
hydrophilic
the [ ] acts as a shock absorber and cushioning
ground substance of cartilage extracellular matrix
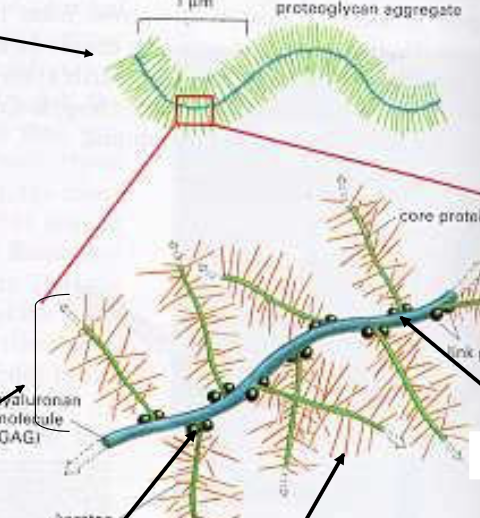
the arrows indicate which features of proteoglycan aggregates
(from left to right)
link protein, GAGs, hyaluronic acid
the [ ] is immediately around the cell and rich in GAGs but poor in collagen
territorial matrix
the [ ] has a darker stain while the [ ] has a lighter stain due to a more balanced ratio of collagen to GAG
territorial matrix, interterritorial matrix
the [ ] is made of type I cartilage
perichondrium
a layer of dense connective tissue surrounding the cartilage is called the [ ]
perichondrium
the [ ] synthesize dense CT where [ ] form chondroblast
fibroblast, progenitor cells
[ ] and [ ] do not contain a perichondrium
articular cartilage and fibrocartilage
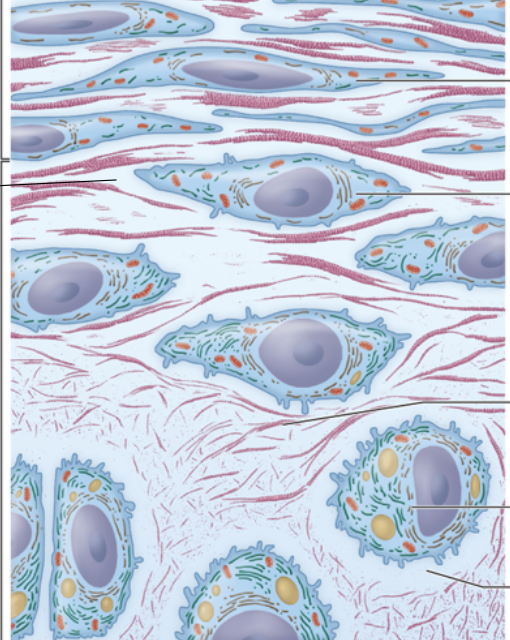
the top portion is called the ?
the lower portion?
perichondrium, cartilage
[ ] cartilage has to be stained to see
elastic
[ ] is more flexible than hyaline cartilage and appears yellow in fresh tissue
elastic cartilage
the external ear, walls of external auditory canal, eustachian tubes, and epligottis all contain [ ]
elastic cartilage
elastic fibers are differentiated from reticular fibers because?
they are long, straight, thin, and branched
the intermediate between dense connective tissue and hyaline cartilage is [ ]
fibrocartilage
type [ ] and type [ ] collagen make up fibrocartilage fibers
I and II
collagen fiber form [ ] bundles between chondrocyte groups that are aligned [ ] to stresses acting on fibrocartilage
irregular, parallel
fibrocartilage merges with [ ][ ][ ] and or [ ][ ] for nutrients
dense connective tissue, hyaline cartilage
[ ] [ ]and [ ] [ ]are two places we find fibrocartilage
intervertebral discs and pubic symphysis
the intervertebral disc is composed of two layers [ ][ ] and [ ][ ]
annulus fibrosus and nucleus pulposus
annulus fibrosus contains an overlapping laminae of [ ]
fibrocartilage
the [ ] [ ] provides disk with resilience to withstand stress of vertebrae
annulus fibrosus
the [ ] [ ] has cells embedded in amorphous, viscous fluid
nucleus pulposus
the nucleus pulposus is rich in [ ] [ ]
hyaluronic acid
cartilage is limited in size due to [ ] [ ]
nutrient diffusion
chondrocytes have lots of [ ][ ][ ] which help facilitate metabolic exchange
cell surface projections
interstitial growth is ?
the division of pre-existing chondrocytes
[ ][ ] is the differentiation of progenitor cells leading to growth in girth
appositional growth
in young children, cartilage [ ] but in adults, there’s [ ][ ]
regenerates, limited repair
[ ] are the structures that attach one bone to another
joints
there are two classifications of joints [ ] and [ ]
synarthroses and. diarthroses
bone united by bone is called [ ] and results in no movement
synostosis
bone joined by hyaline cartilage and/or fibrocartilage is [ ] and results in limited movement
synchondrosis
bones joined by dense CT is called [ ]
syndesmosis
[ ] unites long bones and allows for great mobility
diarthrosis
diarthrosis joints have three components [ ], [ ], and [ ]
articular cartilage, capsule, and synovial membrane
the [ ][ ] contains phagocytic cells that clear debris
synovial membrane
[ ][ ] contains nutrients, oxygen, hyaluronan, and proteoglycans
synovial fluid
[ ] is the abnormality of a joint
arthritis
the loss of articular cartilage from reduced proteoglycans and erosion of matrix is [ ]
osteoarthritis
rheumatoid arthritis is characterized by ?
chronic inflammation of joint
fibrous ingrowth into joint
erosion of cartilage and bone
pituitary dwarfism is caused by a lack of [ ][ ]
growth hormone
gigantism is caused by an excess of [ ][ ]
growth hormone
epiphyseal cartilage over stimulated
a mutation in type II, IX collagen, FGFr causes [ ]
chondrodysplasia