L13 Molecular evolution
1/33
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
34 Terms
What processes does the rate of evolution depend highly on?
on processes at the population level, including
- Mutation rate (μ)
- Population size (genetic drift and fixation rate)
- Selection
How does evolution occur on the molecular scale?
- DNA → proteins → phenotype
Is DNA mutation proportional to time?
This is sometimes, but not always, proportional to time (i.e. a molecular clock)
What are mutations?
• Mutations are stochastic permanent physical changes
• Errors in DNA replication
- Most often they are changes in a single base
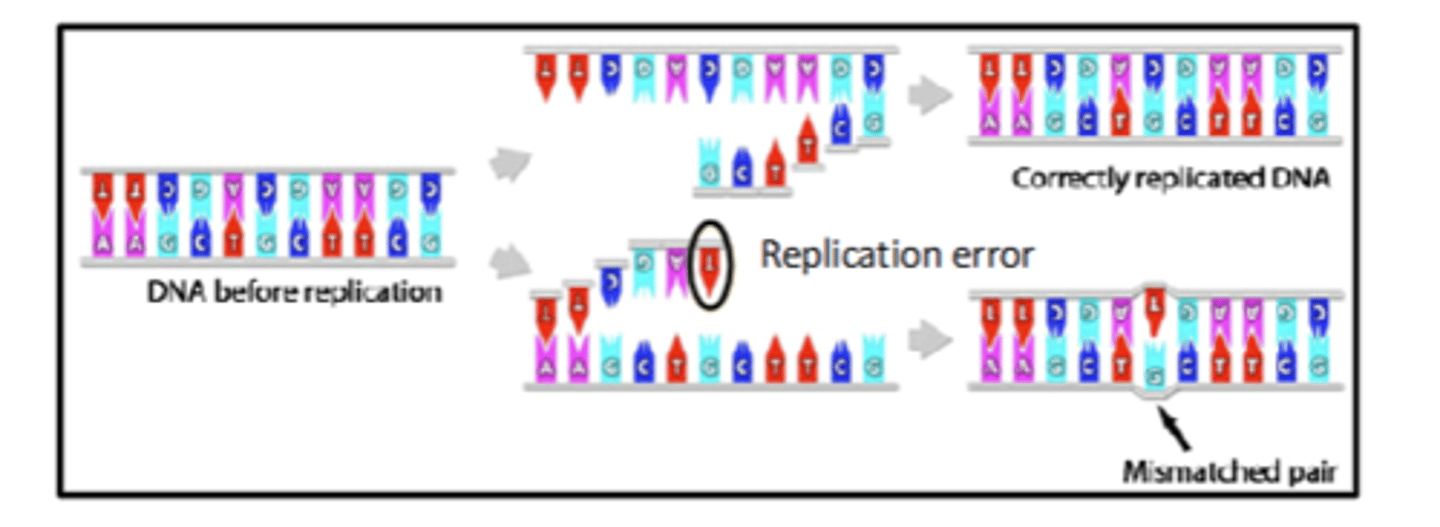
What type are mutations most often?
- Most often they are changes in a single base
but can be large scale
Can mutations be transmitted if they occur in sex cells?
Yes
Does mutation rate vary across species?
yes
- μ varies across species
• Human μ = ~2.5 x 10-8 substitutions per site per generation
• One in every 250,000,000 bases will mutate each generation
• Genome size 3.2 GB (gigabases, or billion bases)
• 13 DNA changes per individual per generation
Are there more or less mutations in a larger population
more
Are There are more or less mutations over time if generation time is shorter?
More
What are other reasons mutation rate can change?
- pop size
- generation time
What is population size?
Population size (genetic drift and fixation rate)
- Fixation rate (of a neutral allele) is proportional to allele frequency
• Alleles will fix faster in small populations due to sampling effect
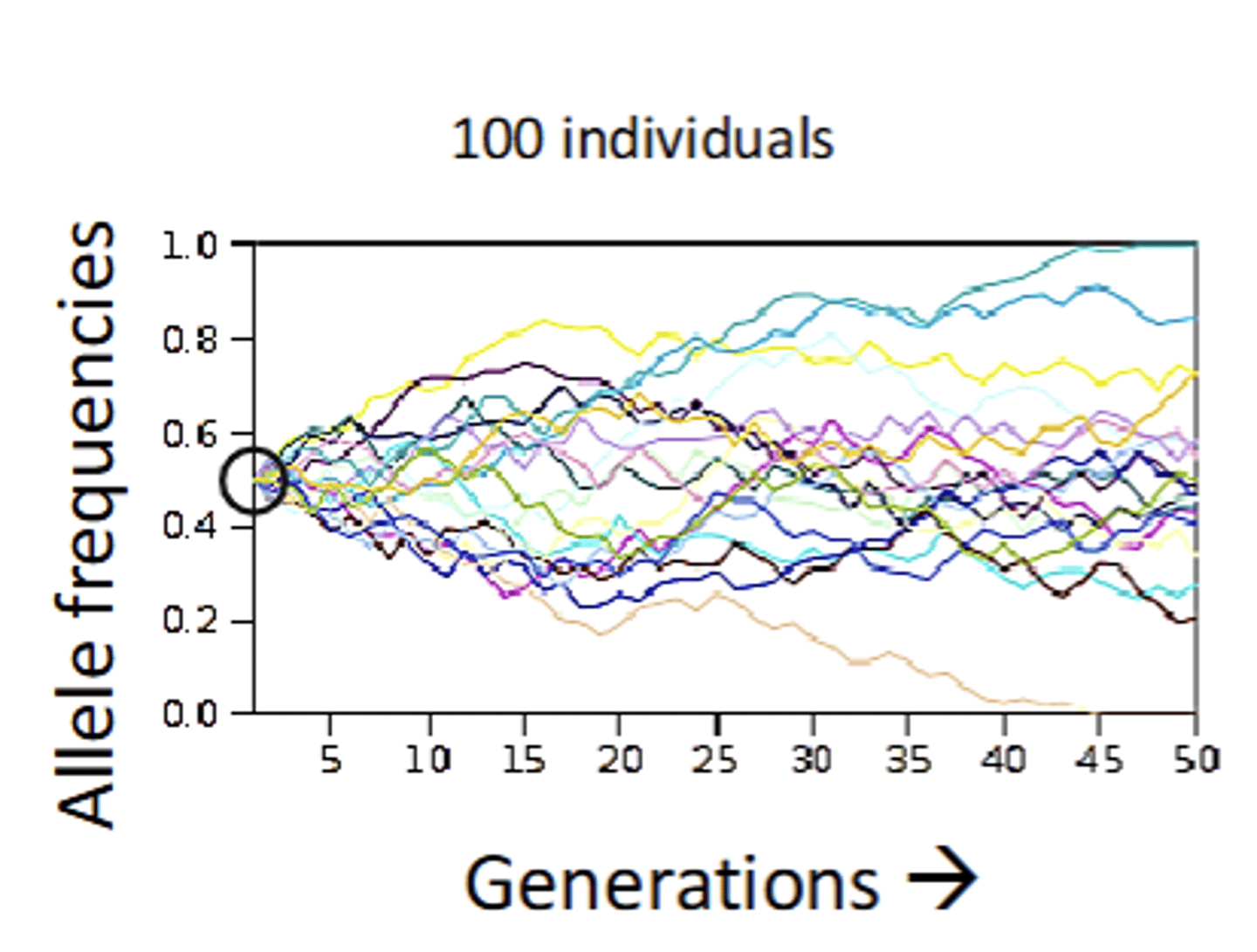
What would molecular evolution and drift look like in 100 individuals?
Some alleles lost, most still segregating
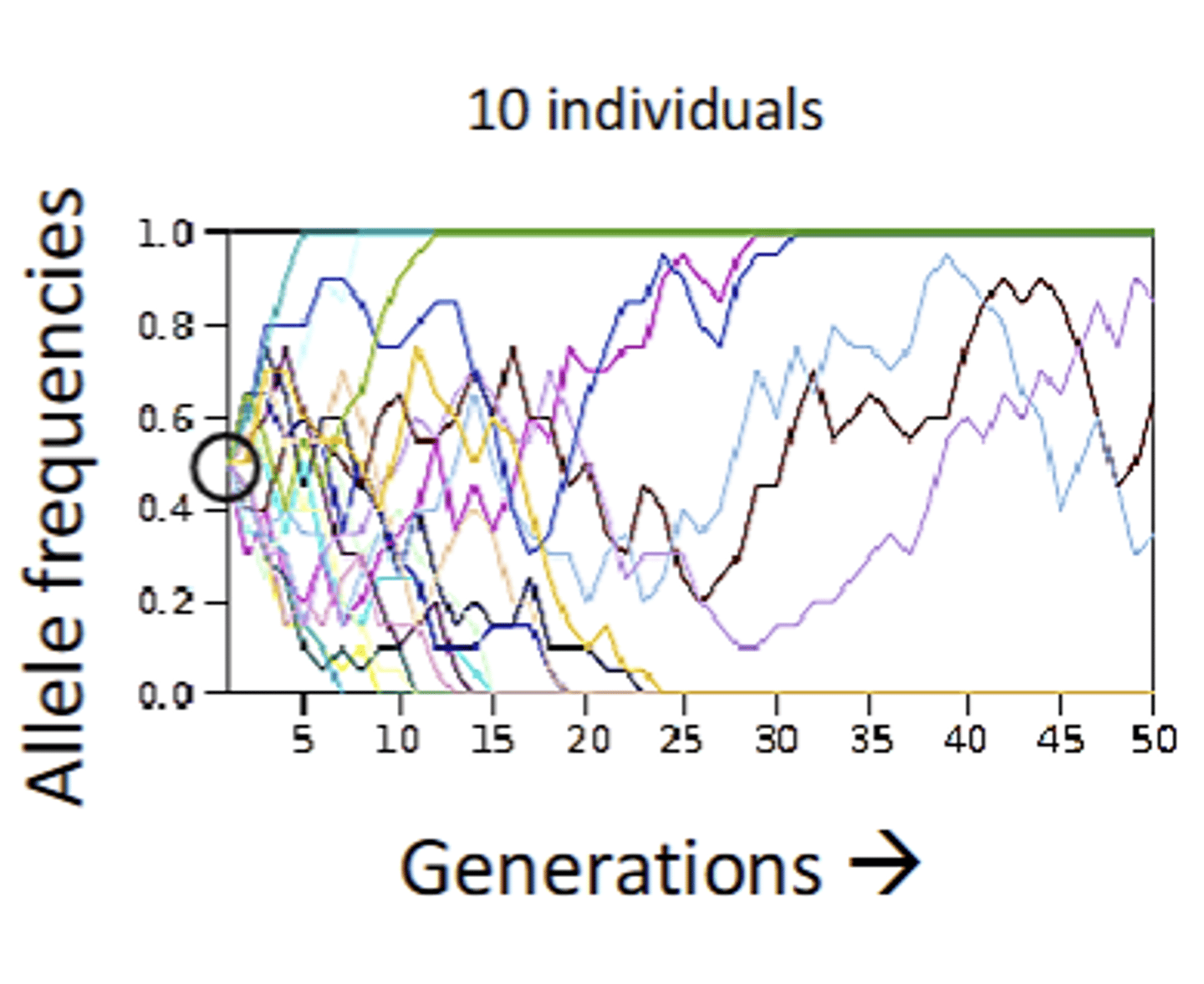
What would molecular evolution and drift look like in 10 individuals?
Many alleles lost, few still segregating(inbreeding depression?)
have more rapid changes in allele frequency and faster fixation
What is molecular evolution and drift?
Neutral mutations are prone to drift
- Kimura's (1968) 'neutral theory of evolution'
- Most mutations are neutral and therefore most genetic variation we see is due to genetic drift
Are most mutations considered to be good or bad?
Most of the situations we've discussed are about neutrality or negative selection
some can be beneficial
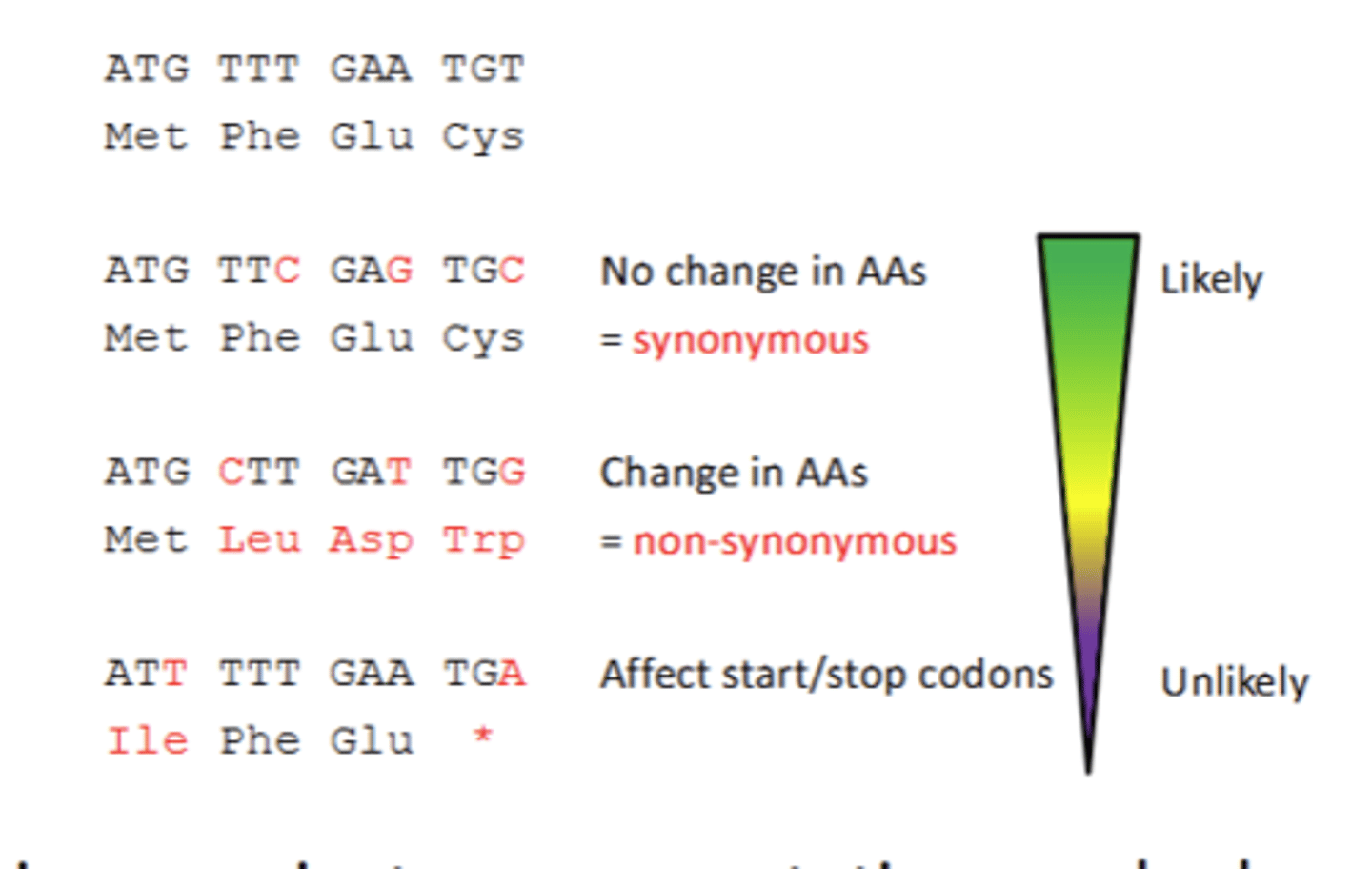
What can the effect of mutations be?
- Detrimental (negative)
- Neither detrimental nor beneficial (neutral)
- Beneficial (positive)
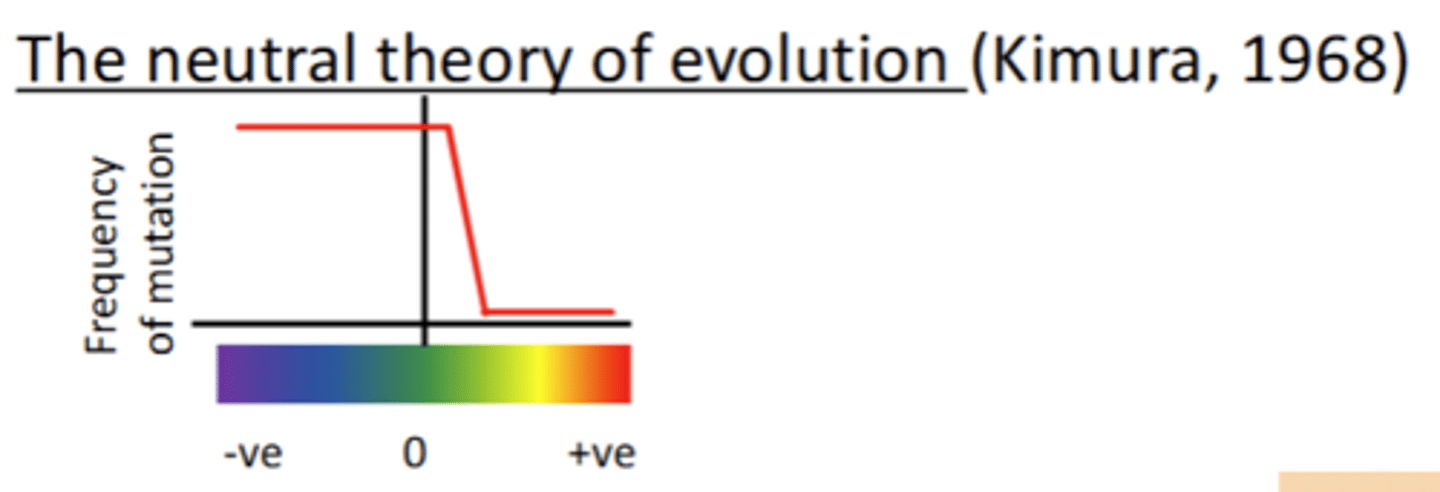
What is the neutral theory of evolution (Kimura, 1968)?
said:
- Positive selection is probably rare
- Negative mutations are removed by natural selection
- Molecular evolution is governed primarily by drift
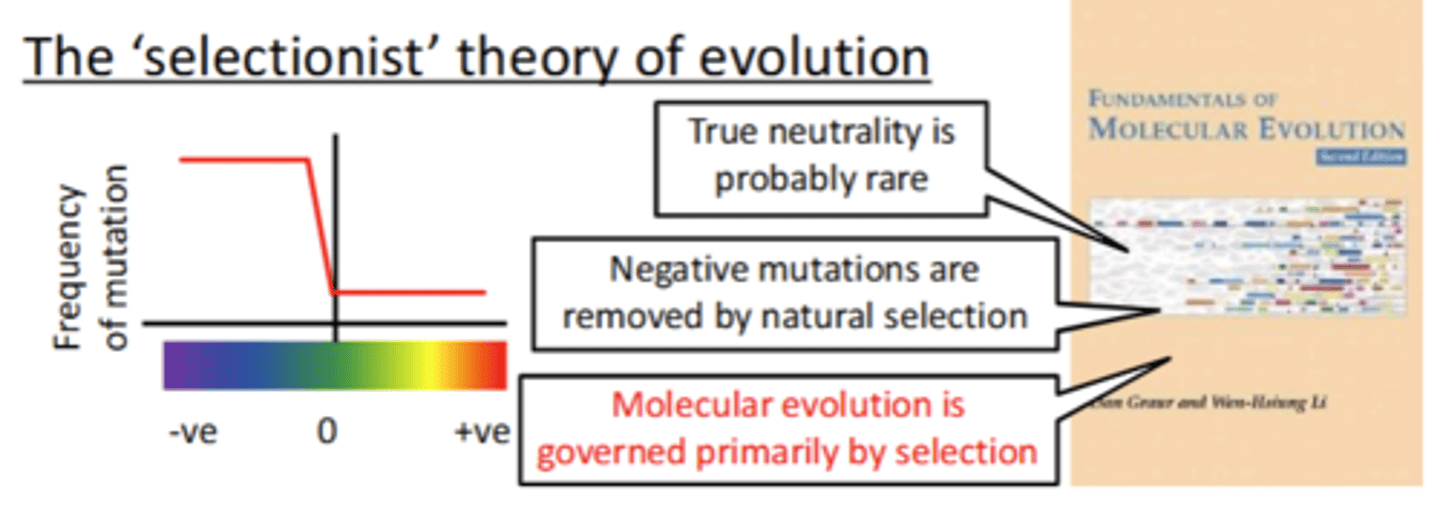
What is the selectionist theory of evolution?
Said:
- True neutrality is probably rare
- Negative mutations are removed by natural selection (agrees with Kimura)
- Molecular evolution is governed primarily by selection (+ve mutations)
What is an example of a beneficial mutation?
For example, in a novel environment the mutation causes the encoded protein to function better in a new environment
How can we see if a mutation would be beneficial?
We can look at DNA sequence alignments and search for positive selection
How can we detect selection?
We can look at DNA sequence alignments and search for positive selection
- A few mutations might be adaptive
• Non-synonymous changes (different amino acid)
- Most mutations we see are expected to be neutral
• Synonymous changes (same amino acid)
What is a synonymous change(DS)?
SNP in the coding region that doesn't change an amino acid or lead to a mutation (because of redundancy of the genetic code)
What is a non-synonymous change (DN)?
A SNP that is a mutation that changes a base in a coding region, which changes the amino acid sequence
If dN /dS < 1 what does this mean?
we have selection AGAINST change (few NS changes)
If dN /dS = 1 what does this mean?
we have neutrality (equal likelihood of NS and S changes)
If dN /dS > 1 what does this mean?
we have selection FOR change (many NS changes)
What is the red queen hypothesis?
the hypothesis that organisms are constantly struggling to keep up with one another in an evolutionary race between predator and prey species
• Parasite numbers increase as number of hosts increase
• More parasites means negative effect on host
• Host numbers go down
• Host evolves immunity
• Host numbers increase
• Parasites overcome host immunity.
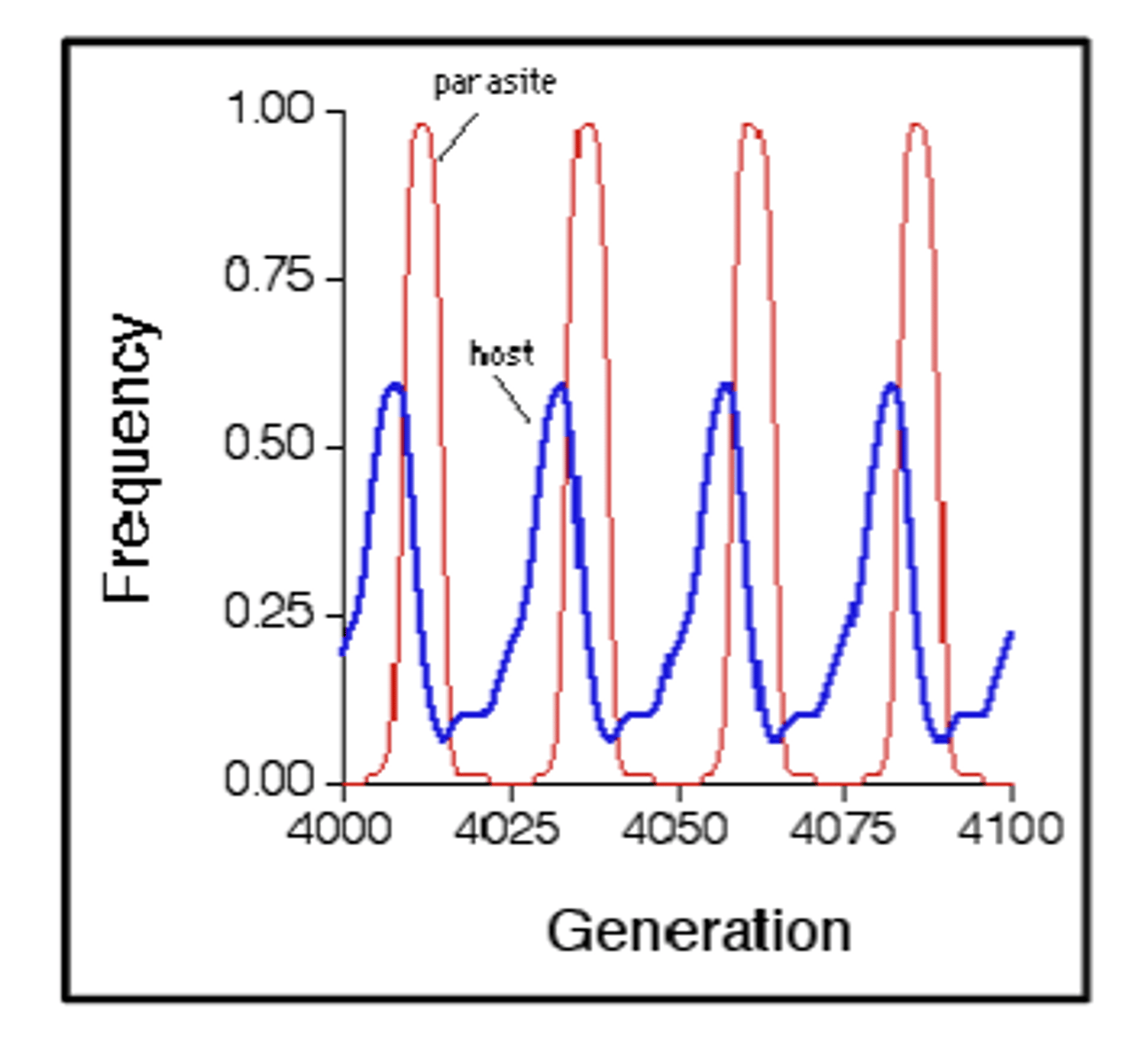
What does the red queen hypothesis mean about selection and immunity?
- Interactions between hosts and parasites cause very strong selection
- If you're not immune you die
- If a mutation arises that means you don't die you are at a much greater fitness advantage
- Immune-related (and virulence-related) genes are therefore a good place to look for positive selection
In interspecific comparisons, what may genes with dN/dS > 1 correspond with?
might correspond to the species differences
How can we use interspecific comparisons?
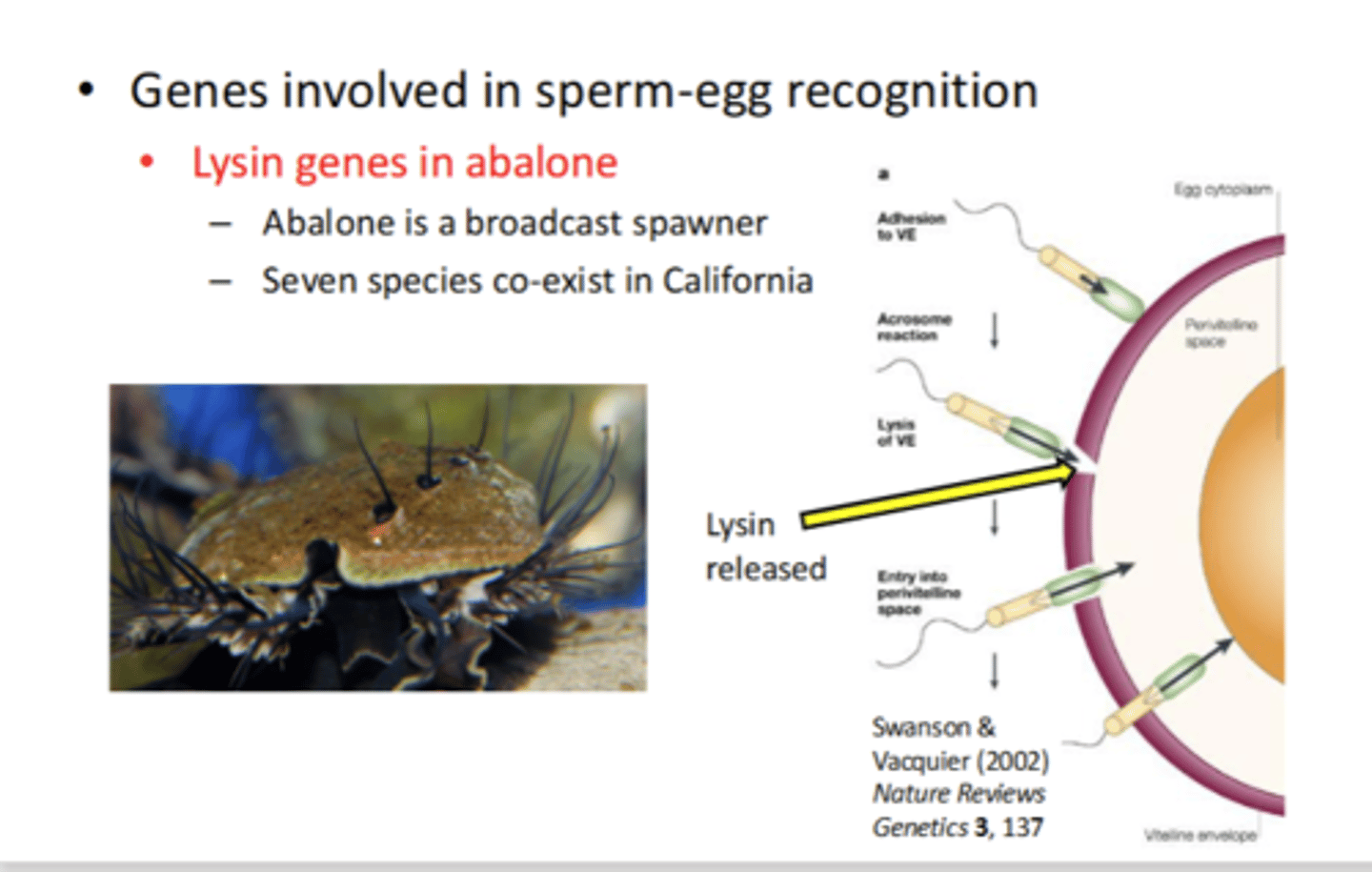
• Genes involved in sperm-egg recognition
• Lysin genes in abalone
- Abalone is a broadcast spawner
- Seven species co-exist in California
• Many DNA sequence comparisons have dN/dS > 1
• For the species to co-exist there must be 1:1 recognition between lysin and the vitelline envelope.
• As new species evolve so must lysin
When may selection on genes involved in adaptation be involved?
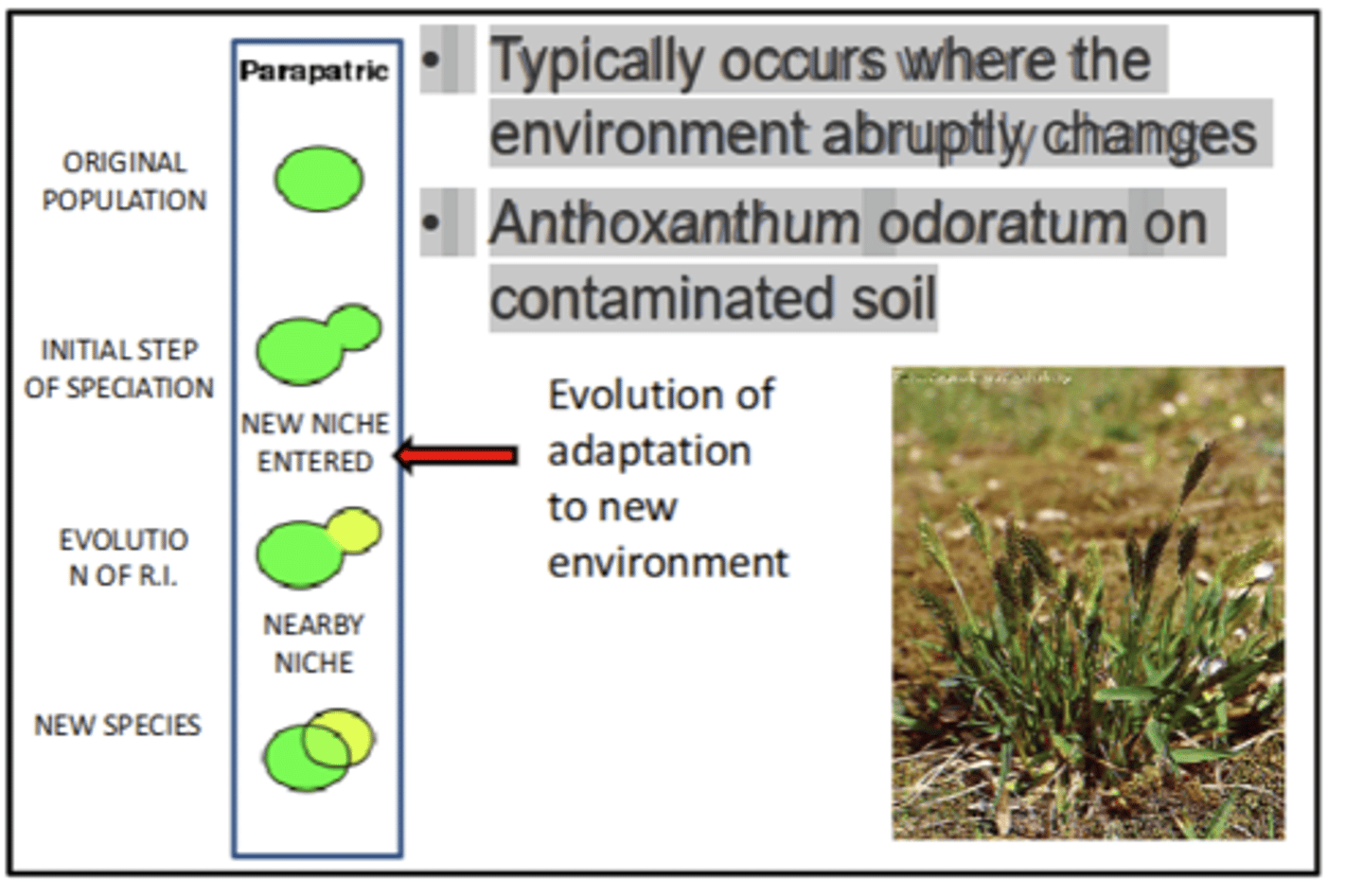
in early stages of speciation
• Typically occurs where the environment abruptly changes
• Anthoxanthum odoratum on contaminated soil
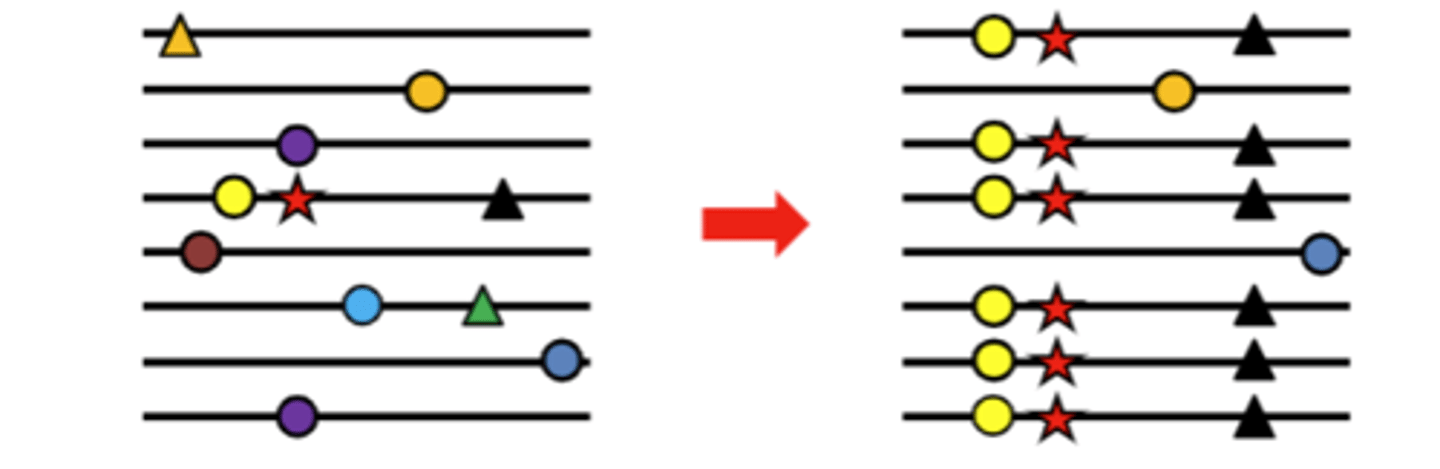
What are selection sweeps?
• Very strong selection will remove all (or most) alleles except the 'fittest'
• We look across many individual for the 'signature of selection'
• This gene is 'swept' of diversity
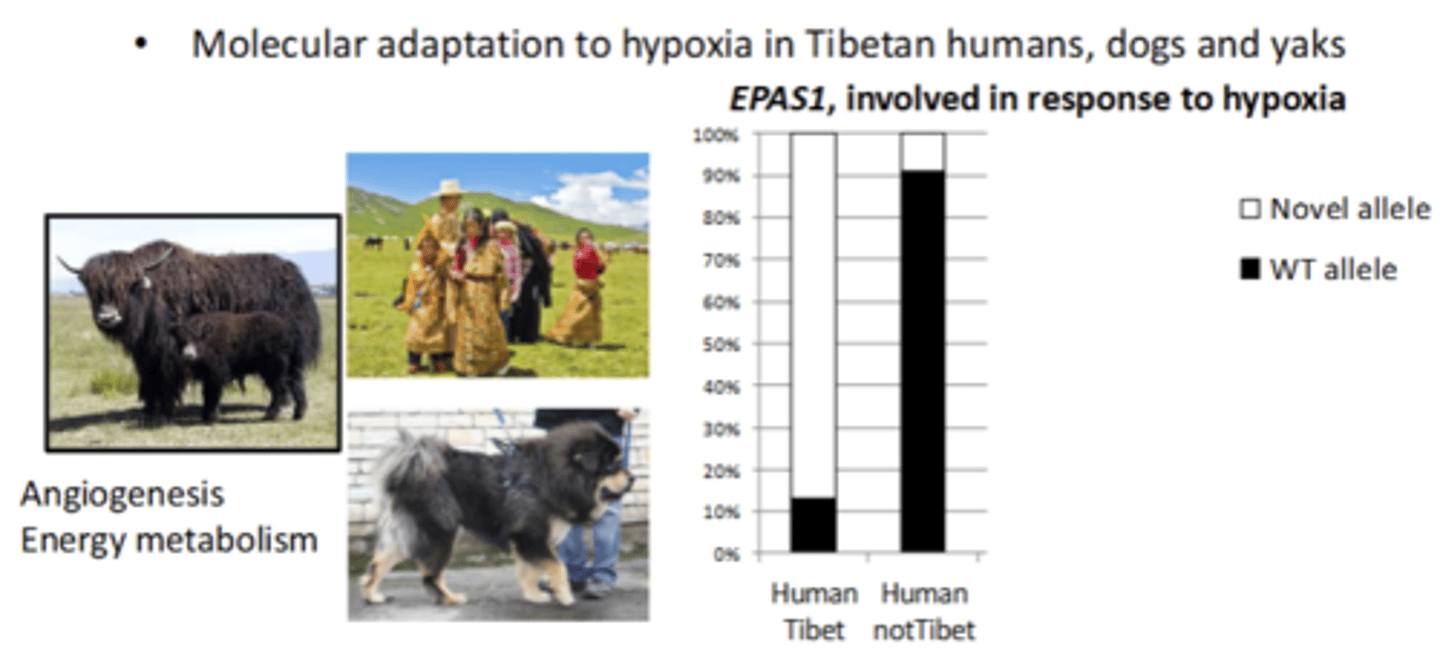
Waht have Tests for selection (based on dN/dS and/or selective sweeps) shown?
• Molecular adaptation to hypoxia in Tibetan humans, dogs and yaks
showed very different frequencies in tibet and not in tibet
- Molecular adaptation to poor soils in plants
- Molecular basis of wing patterns in butterflies
- Molecular adaptation to freshwater in sticklebacks
How can positive selection be detected?
through sequence comparisons