Chemical Substances and Mixtures - UNIT 1
1/25
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
26 Terms
Element
A pure substance made of only one kind of atom
Compound
A substance made of different types of atoms chemically bonded
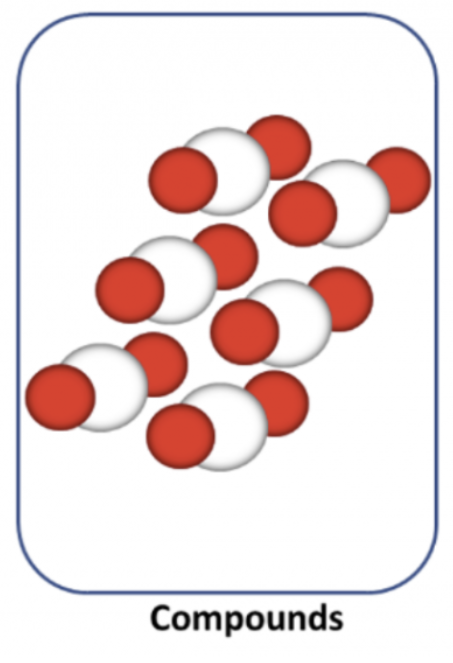
Mixture
A combination of two or more substances that are not chemically bonded
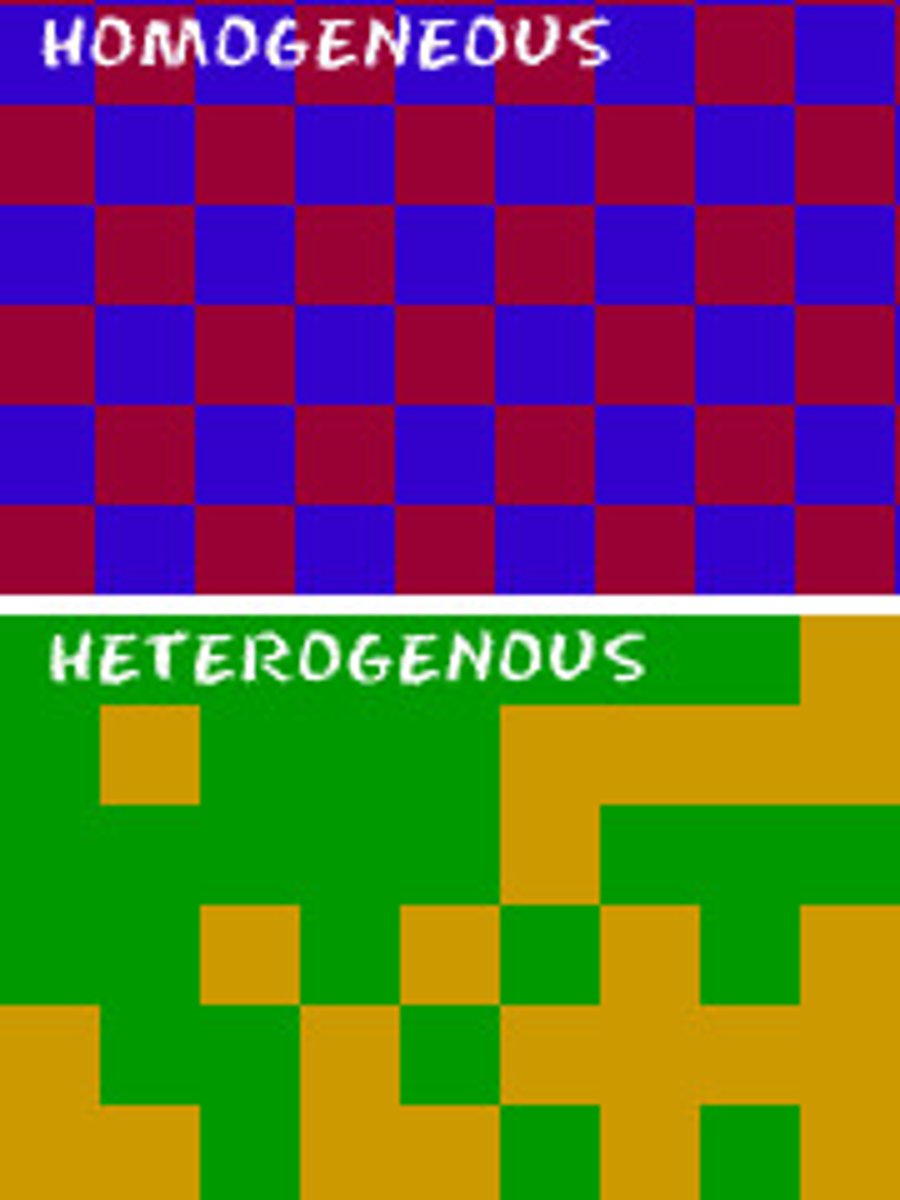

Homogeneous
Uniform composition no matter what part you chose to observe, like saltwater or sugar & water
Heterogeneous
Non-uniform composition, like a salad
What is the difference between homogenous and compounds?
Not chemically bonded
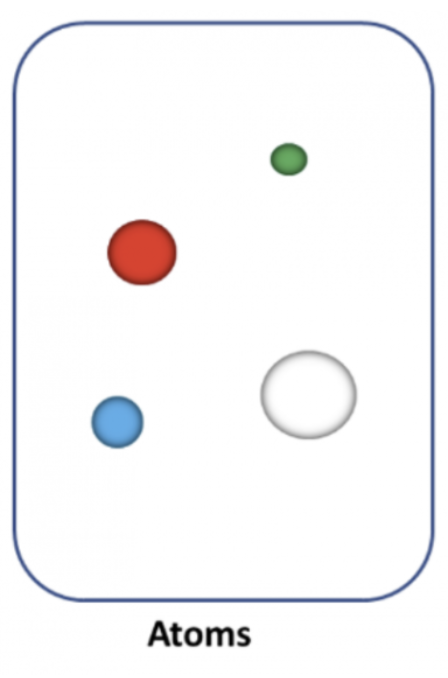
Atom
Smallest sample of matter, one atom & it isn't chemically bonded
Are atoms bigger than molecules?
NO
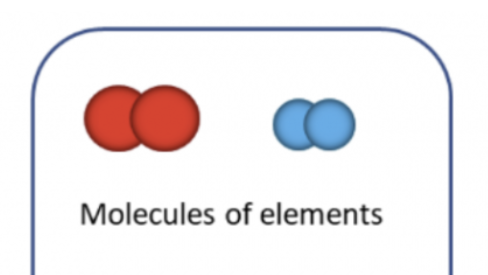
Molecule (of an element)
A group of atoms bonded together, at least two atoms chemically bonded together
Chemical Bond
A force that holds atoms together in a compound
Classification of matter
Matter is split up into two sections:
PURE SUBSTANCE & MIXTURES
Pure Substances: either elements & compounds
Mixtures: Homogenous & heterogenous
Pure substance
A substance made of only one kind of matter and having definite properties.
Ex. Water & gold
Pure substance are either element & compound
Elements: whose atoms all have the same number of protons Ex. H2, Cu ---> elements are then atoms or molecules
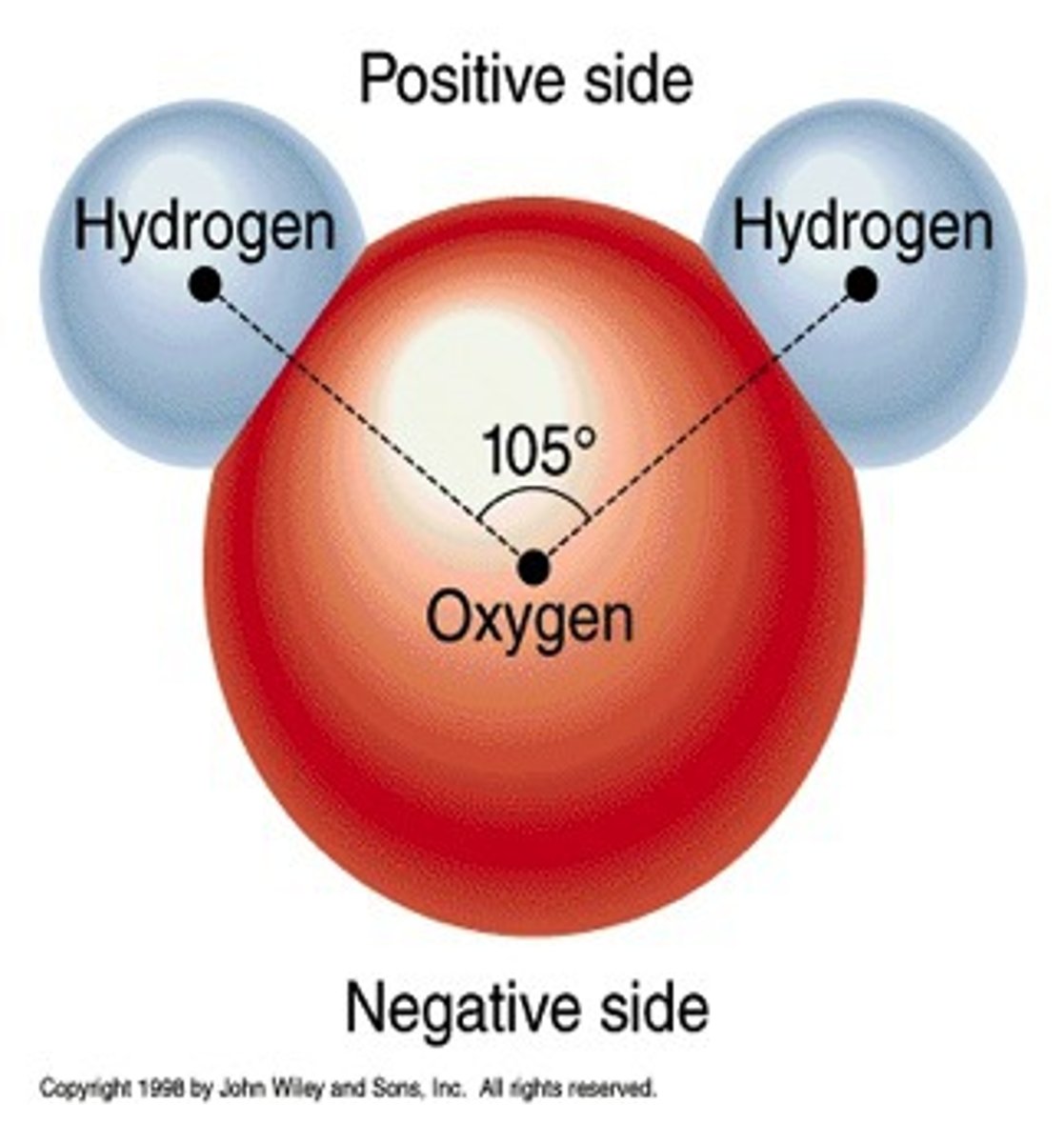
Compound: formed when two or more chemical elements are chemically bonded together. Ex. H2O, NaCl
Mixture
Heterogeneous & homogenous
Heterogeneous mixture: one in which the composition varies from one region of the mixture to another.
Example: a salad
Homogeneous mixture is one made of multiple substances but appears to be one substance. UNIFORM. The atoms or molecules that compose them mix uniformly.
Example: a salt and water mix or sugar & water
Molecular Elements (Diatomic Molecules)
Elements that have 2 atoms of the same type being chemically bonded
- H2, O2, N2, F2, Cl2, Br2, I2 (7 on periodic table)
2 polyatomic elements
P4, S8
Physical change key words
Boil, melt, freeze, crush, cut, dissolve, condense, bend
Chemical change key words
rust, oxidize, corrode, tarnish, ferment, burn, rot
Physical changes
stays as same substances but goes through different states of matter
ex. ice (solid w/ strong IMF) -> (liquid w/ weak IMF) -> (gas w/ no IMF) (melting to evaporation)
Chemical changes
4 H2 & 2 O2 -> electrolysis w/ electric current -> creates H2O
Units of measurement
Metric: used in most of the world
English system: United States
SI units: based on metric system
MUST KNOW CONVERSIONS
1 m = 100 cm
1 cm = 10 mm
2.54 cm = 1 inch
Metric system
Length: m
Mass: g
Volume: L
Temperature: Celcius
Time: seconds
Length:
km -> m
m -> cm
cm -> mm
mm -> nm
Mass
kg -> g
g -> mg
mg -> mcg
Volume
L -> mL
L -> dL
L -> cL
Temperature
Celsius -> Kelvin (K)
Celsius + 273.15 = K