Midterm 1
1/95
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
96 Terms
What are the two formats of measure?
Count— number of cases affected with a condition in a population
Ratio— compares relative size of two quantities
What are three different types of ratios?
odds, proportions, rates
___________: numerator is not part of denominator. A/B. Not written as a percent
Odds
_____________: numerator is a subset of the denominator. A measure of risk or probability of a disease. A/(A+B). Written as a percent.
Proportion
What is the possible range of odds?
0 to infinite
What is the possible range of a proportion?
0-100
_________: denominator includes a measure of time (ex. animal-time). Ranges from 0 to infinite.
Rate


________=existing cases at a given time/population at risk
prevalence
_____________= new cases during a time period/population at risk at the beginning of the observation.
incidence
True or false: incidence and prevalence are both odds.
False: proportions
________________: prevalence at a single point in time.
Point prevalence
______________: prevalence over a specific period of time. Cases present at the period start and new cases during the follow up period.
period prevalence
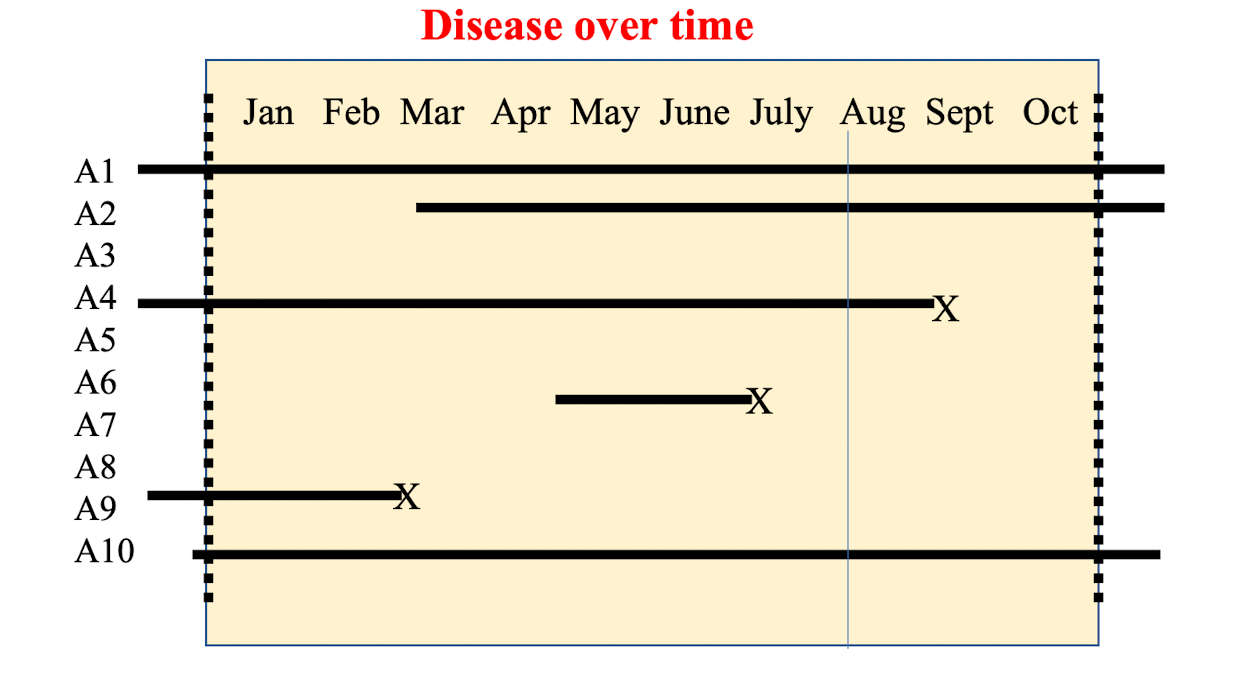
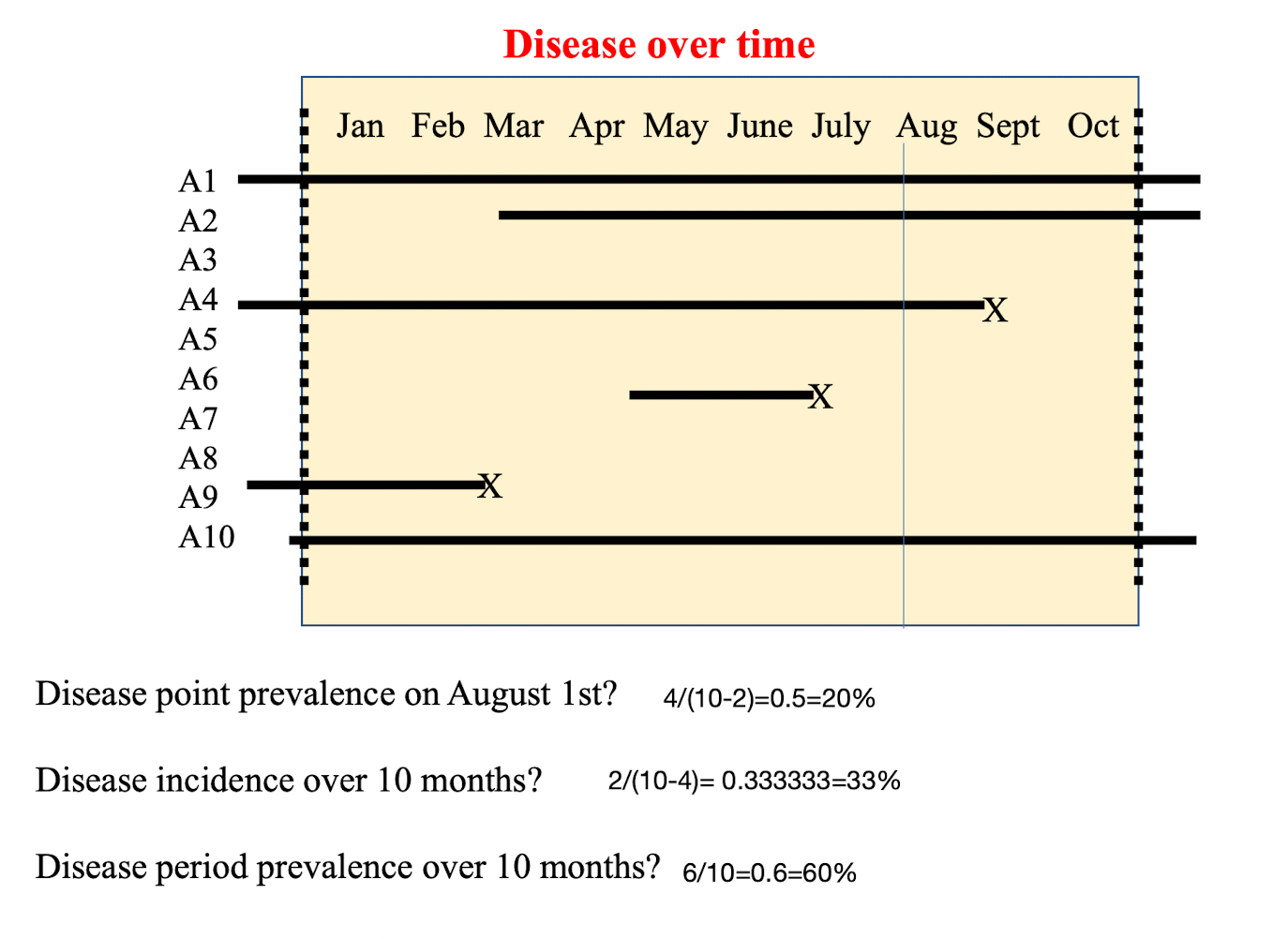
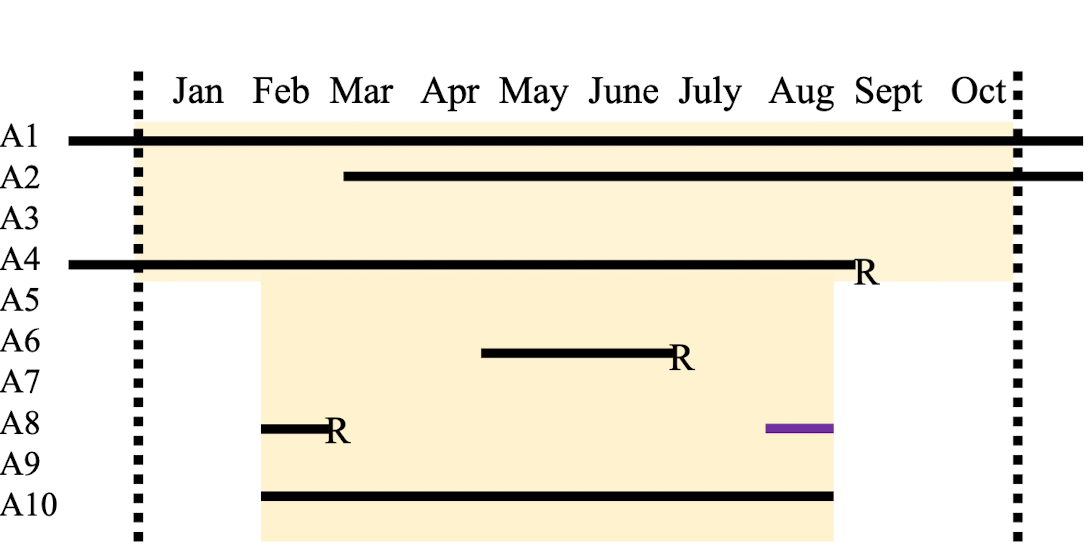
disease point prevalence on August 1st? Disease incidence over 10 months? Disease period prevalence over 10 months?
typo in pic: 50% for point prevalence

Case fatality rate? Mortality rate?
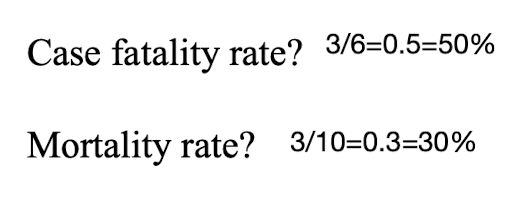
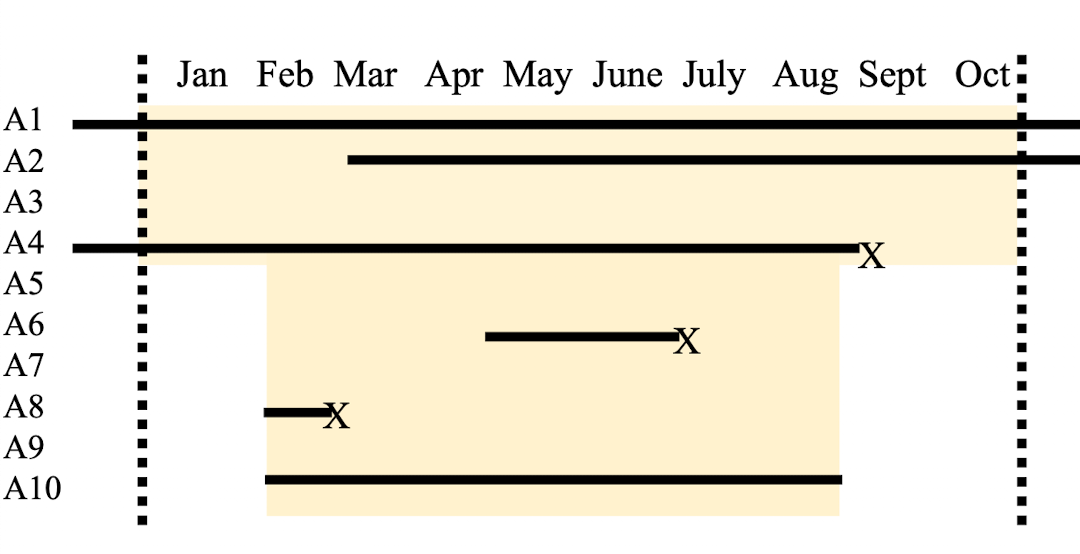
____________________: new cases/time of observation at risk. Accounts for re-infections.
Incidence rate
The time at risk for each animal only ends on what three conditions?

Incidence rate?
2 new cases per 35 animal months
Incidence rate?
3 new cases per 44 animal months.



Which measure of disease frequency is being described?
prevalence
Annual proportions of cows becoming lame range from 5.5 to 68.8 per 100 cows. Which measure of frequency is being described?
incidence

What measure of disease frequency?
period prevalence

A) prevalence
B) mortality rate
C) case fatality rate
C
Of a population of 100 horses, 5 died in march 2022. Prevalence? Mortality rate? Case fatality rate?
Mortality rate
What are the two measures of strength?
risk ratio and odds ratio
What are the two measures of effect in exposed?
risk difference and attributable fraction
What are the two measures of effect in population?
population attributable risk and population attributable fraction

What measure of strength was used?
relative risk

What kind of measure of strength was used?
Odds ratio
____________________________________
Risk of disease among the exposed that is attributable to exposure = If we removed the exposure, the risk of the outcome among the exposed would decrease by x cases per 100
Risk difference or attributable risk = RE+ - RE-
_____________________
Proportion of disease among the exposed that is attributable to exposure = If we removed the exposure, risk of the outcome among the exposed would decrease by x%
Attributable fraction = RD / RE+
_______________________
→ Risk of disease in the population that is attributable to exposure = If we removed the exposure, the risk of the outcome in the population would decrease by x cases per 100
Population attributable risk = RT – RE-
_______________________
→ Proportion of disease in the population that is attributable to exposure = If we removed the exposure, the risk of the outcome in the population would decrease by x%
Population attributable fraction=PAR / RT
What are the purposes of using risk difference? (3)
• Excess disease risk in the exposed compared to the unexposed
• Risk in the exposed that can be attributed to the exposure
• Amount of disease prevented in the exposed if exposure removed
If they had not been treated with antimicrobials, the risk of MRSP+ among dogs who received antimicrobials would be reduced by 25 cases per 100 dogs. What kind of measures of effect in exposed was used based on the wording?
Risk difference
If we had not given antimicrobials, the risk of MRSP+ in dogs that received antimicrobials would be reduced by 83%. What kind of measures of effect is being used here?
attributable fraction
If antimicrobials would not be given to dogs, MRSP+ cases in the dog population would decrease by 50%. What kind of measure of effect was used here?
Population attributable fraction
What are the three components of the epidemiologic triad?
Pathogen (agent)
host
environment
_____________ - ability of organism to penetrate and reproduce in a host; does not imply disease
• Proportion of individuals exposed to the agent that become infected (infected/exposed)
Infectivity
__________ - ability of organism to cause disease
• Proportion of infected individuals that develop clinical disease (diseased/infected)
Pathogenicity
________ - ability of organism to cause severe disease or death
• Proportion of diseased individuals that develop severe disease (severely diseased/diseased)
Virulence
__________:Capable of becoming infected with the agent; disease may occur
host
_________ host – does not normally transmit the agent
Dead-end
_________ host – supports rapid multiplication of the agent
Amplifier
What are the 5 essential elements of infectious disease transmission?
• Agent
• Host
• Reservoir
• Escape from reservoir
• Portal of entry into host
_____________
• Where the infectious agent normally lives and multiplies
• Serves as a common source of infection
Reservoir
NOTE: can be a host
What are the two types of vertical routes of transmission?
• Trans-placental transmission
• Born with the infectious agent
What route of transmission is this describing? — Spread through direct contact with open wounds, mucous membranes, or abraded skin contacting an infected animal or its tissues or fluids (e.g., blood, saliva, urine).
Direct contact
What are the three main types of indirect contact?
vehicle
vector
airborne
What are the three categories of vehicle transmission? Explain them.
• Fomite — Spread of pathogens through contact with inanimate objects, contaminated by an infected individual
• Oral — Ingestion of disease-causing agents from contaminated food or water
• Biological products (e.g., blood, organs, semen)
_________ vector
• No multiplication or development of the agent
Mechanical
_________ vector
• Multiplication or development of the agent occurs
• Typically biting arthropods: mosquitos, ticks, lice, fleas, mites, blood sucking flies/bugs (e.g. midges)
Biological
What are the two main types of vectors?
mechanical and biological
________ (small particle)
• Travel large distance (> 3 m)
• Can remain suspended in air for extended period
• Enter respiratory tract
• Infrequent route of disease transmission in veterinary medicine
Airborne
What is the period before a patient is infectious?
latent period
What is the period called between initial infection and clinical disease?
Incubation period
_____– first case identified
______ – the case that brings the infection into a population
_______ – infected by a primary…
_______ – infected by a secondary
Index
Primary
Secondary
Tertiary
True or False:
Agents with short infective periods require rapid contact with susceptible
True
____________:Collective immunological status of a population
herd immunity
________________________ : mean number of individuals directly infected by an infectious case through the total infectious period, when introduced into a susceptible population
Basic reproductive number (R0 , called “R-naught”)
What proportion of the population needs to be immune to prevent an epidemic if R0 is 2? 4?
• If R0 is 2, then R < 1 if the proportion of immune, p, is > 0.50
• If R0 is 4, then R < 1 if the proportion of immune, p, is > 0.75
Infection will…
disappear, if R __1
become endemic if R__1
become epidemic, if R __ 1
<
=
>
What are the three types of descriptive studies?
Case report
case series
Descriptive studies based on rates/ frequencies, Surveys
________________:
•Describe (often unusual) clinical course of cases of a condition of interest – 5W - who, when, what, where, why
•May provide information on prognosis if cases are representative of all cases •May have exposure and disease info
• Peculiar to the cases? Hypothesis generating only
case series
_______________________:
Estimate the frequency and distribution of outcomes or exposure
-Eg. Incidence or Prevalence of disease
•Care to design well –Random sampling –Question design
Descriptive studies
What are the advantages (2) and disadvantages (3) of descriptive studies?
Disadvantages:
•Variable real-world relevance?
•Often low selection control
•No comparison group or lack info on D+ or E+
Advantages:
•Low level of difficulty
•Early interface between clinical medicine and epidemiology - Can describe treatment and success for cases - May lead to questions or new hypotheses about health hazards in both human and veterinary medicine
An animal behaviorist publishes a paper about 5 cases of unusual behavior in parrots that she observed after the owners of the parrots brought a newborn (human) baby into the family. What type of study?
Case series
Researchers visit 100 chicken farms and take dust samples to report the frequency of Salmonella species in the samples. What is the type of study?
Descriptive study
What are the two general categories of analytic studies?
observational and experimental
________________ study: Participant selection not based on exposure or outcome!
cross sectional
_________________ study: Initial participant selection/classification based on outcome!
case control study
_______________ studies: Initial participant selection/classification based on exposure!
cohort studies (can be retrospective or prospective)
What are pros and cons for cross-sectional studies?

What are pros and cons of case-control studies?
and hard to distinguish temporality
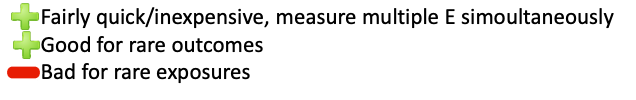
What are some pros (3) and cons (2) of cohort studies?

A questionnaire was administered to 200 dairy farmers in Canada asking them about their stress levels in the past month and the type of milking system they have in place. The researchers’ hypothesis was that a milk robot is associated with lower stress levels compared to the conventional milking system.
What type of study?
cross sectional
Researchers recruited 100 horses that had undergone surgery for colic. They also collected risk factors including whether or not the surgery lasted for more than 2 hours. The horses were followed for 3 months to record survival rates.
What type of study?
Cohort— prospective
Researchers obtained records of 100 horses that had undergone surgery for colic in 2017. Simultaneously, they also received information on risk factors including whether or not the surgery lasted for more than 2 hours. The researchers then reviewed the survival rates for these horses and determined which horse had died within 3 months of the surgery.
What type of study?
Cohort— retrospective
Researchers enrolled 100 dogs with aggression in their study and 100 dogs without aggression. They then asked the owners to fill out questionnaires including the dog’s breed and past dog training.
What is the type of study?
Case control
What are the two control options in controlled trials?
Negative control = no treatment (s) – (e.g., placebo, saline)
Positive control(s) = standard practice(s)
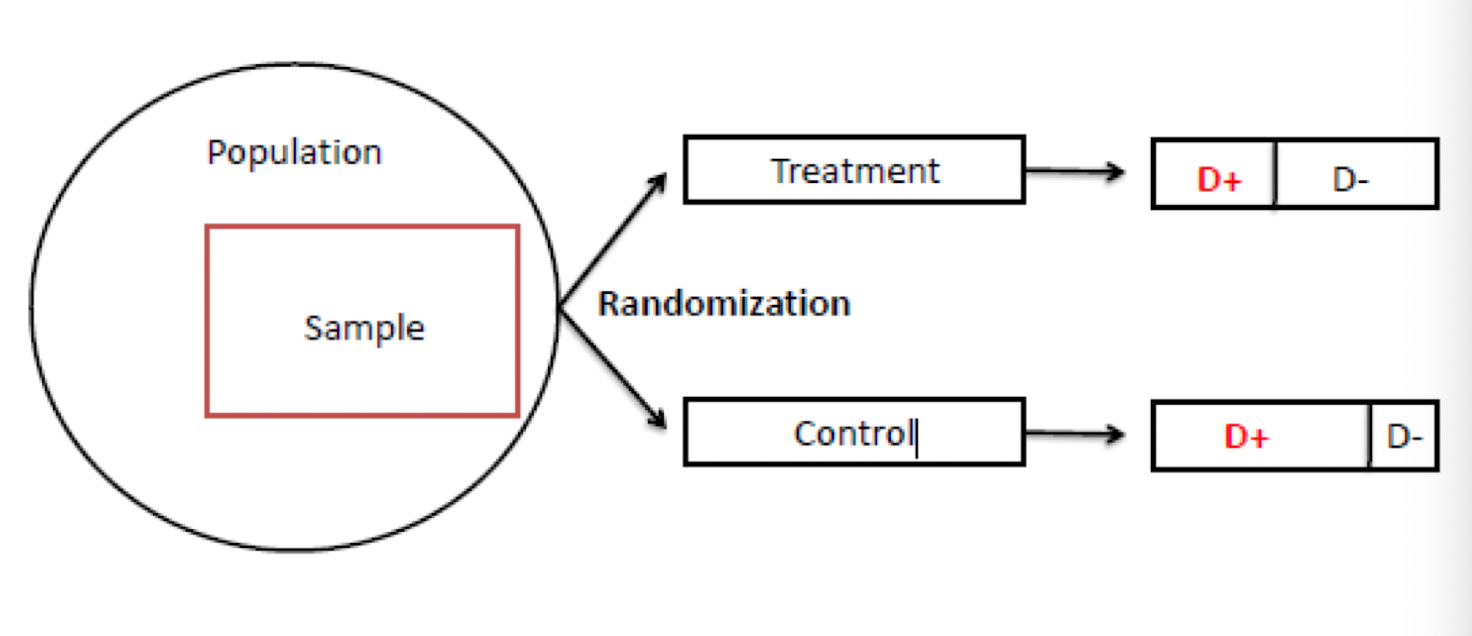
What kind of trial?
regular randomized controlled trial design
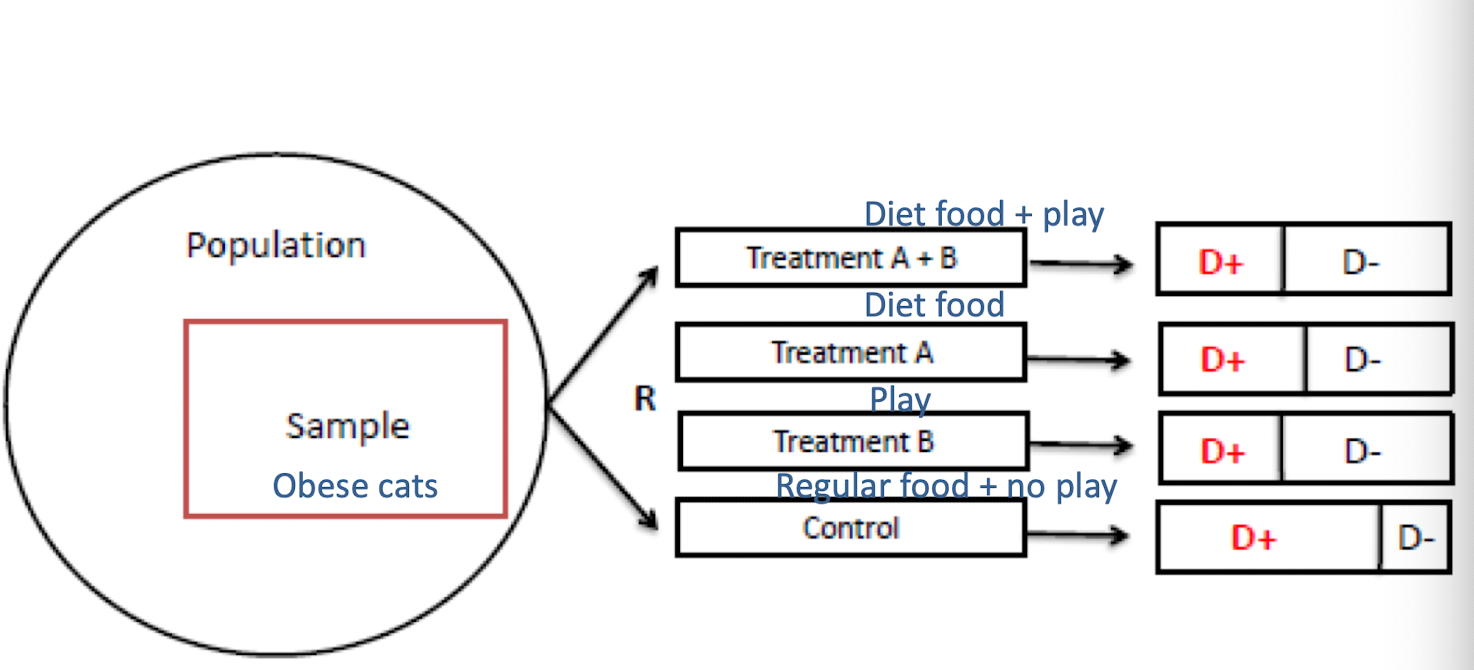
What kind of trial design?
Factorial randomized clinical trial design
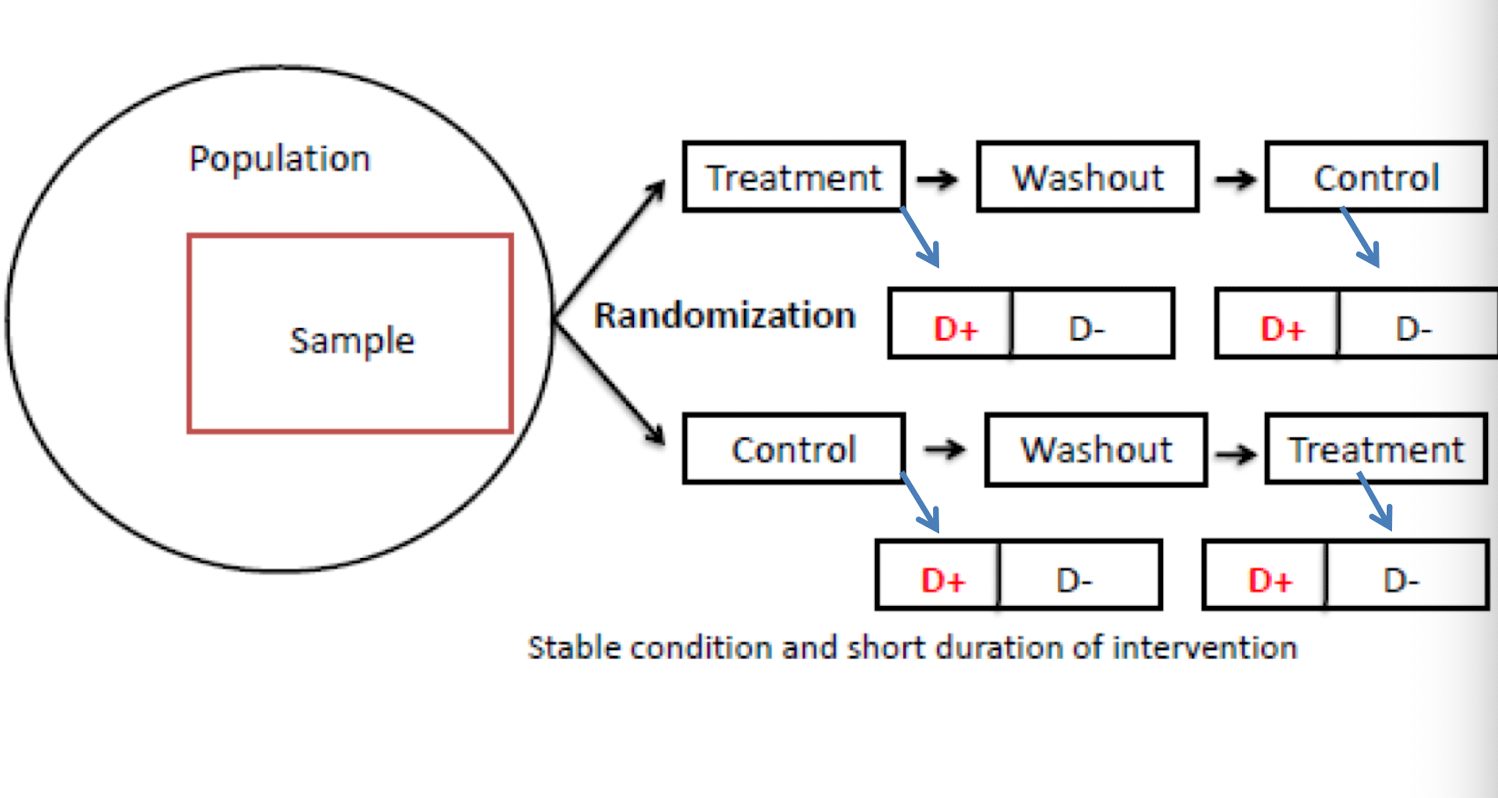
What kind of clinical trial?
Crossover randomized clinical trial
What are the two main advantages of crossover randomized clinical trials?
increases effective sample size
each subject serves as their own control
How many phases are there in clinical pharmaceutical research?
4
Phase ___:
“Formulation” or “Target animal safety (TAS)” trials
•Evaluation of safety in target species
–Test new drug on small group of healthy subjects (20-80) to evaluate safety
–Determine safe dosage range
–Identification of side effects
•Unblinded and uncontrolled
1
Phase ___:
Evaluation of safety and efficacy in target population –i.e. sick individuals (may not be representative)
•Evaluate different dosage formulations/regimens
–Document activity and safety, including side effects
•Larger group of individuals (100 -300)
•May not be a randomized controlled trial –eg.
Before/after comparisons among sick anima
II
Phase___:
•Large-scale studies to determine efficacy of the drug in a typical clinical population and typical dosage
–Compare drug to placebo or other available (standard) treatments –Monitor for safety, side effects
–Larger group of subjects
•Randomized and controlled
III
Phase___:
•Post-marketing/post-registration
•Collect information about effect in various populations
•Very large group of individuals (Thousands)
• Drug/Treatment might be banned if risks/side effects outweigh benefits
4
What are 4 things that phase IV of clinical research can tell us?
1. Evaluate long-term risks and benefits
2. Compare to common treatments
3. Determine alternate ways of using the product in real world
4. Monitor rare side effects
Based on clinic records, a veterinarian enrolls cats with and without diabetes in her study. For both groups she then calls the owners asking them about specific risk factors such as the cat’s diet. What type of study design?
Case-control study
A research team enrolls 100 dogs with separation anxiety in their study. They then assign 50 dogs to undergo behaviour training, while the other 50 dogs do not receive any training. After a few weeks, the researchers follow up to assess whether or not the training has reduced separation anxiety. What type of study design?
controlled/clinical trial
A veterinary practitioner specialized in birds is interested in whether or not a rare disease in canary birds is associated with whether they get to fly outside the cage daily. What type of study design should be used?
case control
A veterinary researcher wants to investigate if cows that are left with their calf are more or less prone to mastitis postcalving compared to cows that have their calf removed within 24 hours after birth. Resources are limited. What type of study design should be used?
prospective cohort (possibly cross sectional too)
A research team wants to record all possible negative outcomes of secondhand smoke in dogs. Time and money are no issue. What study design should be used?
prospective cohort (not clinical because ethics)