Exam 3 OB
1/41
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
42 Terms
Purpose of Lost at Sea exercise
Compare decisions made by individuals with decisions made by teams
Consensus Decision Making
The decision is acceptable to all group members
Achievement Motive
Concern for making the most effective decision
Power Motive
Concern for getting one's own point of view accepted
The Power Motive leads to...
the Process of Division
The Achievement Motive leads to...
the Process of Consensus
Advocacy
stating one's views
Inquiry
asking questions
Factors that harm consensus building
o Domination
o Withdrawal
o Quick decision making
o Avoiding confrontation
Factors that facilitate consensus building
o Concern for others
o Listening
o Discussing reasoning and logic
o Identifying and using resources
o Checking for consensus and disagreement
o Process orientation
Synergy
The concept that the total amount of work produced by a team is greater than the amount of work produced by individual members working independently
Raising the White Flag Behaviors
· Behaviors that involve team members giving up and withholding effort. Term comes from a white flag being recognized as a symbol of surrender in war. Include social loafing (free-riding), self-censorship, and the Abilene Paradox.
Social loafing (also called free-riding)
a phenomenon wherein people put forth less effort when they work in teams than when they work alone
Self-censorship
when team members don't speak up due to concerns about upsetting others or about others viewing what they have to say negatively
Abilene Paradox
Team members agree to a course of action that none of them wants, because each member assumes that the others want it
Groupthink
a psychological phenomenon in which members of a cohesive group go along with the group consensus rather than offering their own opinions
Psychological safety
the shared belief held by team members about whether it is safe enough to trust each other well enough to take risks
Psychological safety can...
reduce self-censorship
Teams
engage in interdependent, collaborative, and cooperative work on a common project or shared goal
Group
members work more independently
Programmed Decisions
automatic responses to routine and recurring situations
Non-Programmed Decisions
responses to new or non-routine problems with no proven solutions
Complete Rationality
We consider and evaluate every single option on every single criterion
Bounded Rationality
We are restricted by a variety of constraints when making a decision. We instead apply a limited number of criteria (select benchmarks) and then evaluate a smaller subset of options meeting those key benchmarks
Maximizing
Aiming to make the best decision
Satisficing
Aiming to make an acceptable decision
Maximizers are...
unhappier with outcomes
Heuristics
shortcuts or "rules of thumb" that allow us to make judgments and decisions quickly and efficiently
Anchoring and adjustment heuristic
a process whereby people base their decision on the first piece of information they are given without taking other numbers and probabilities into account. EX: original vs sales price
Representativeness Heuristic
a shortcut that bases a decision on our existing mental prototype and similar stereotypes.
Availability Heuristic
a rule of thumb for making judgments on examples and events that immediately spring to mind. EX: being scared of tragic deaths because they're more vivid.
Framing effect
How we portray something or what aspects we highlight affect how something is perceived. Two logically-equivalent alternatives portrayed differently can be perceived differently. EX: 80% fat free or 20% fat.
Sunk cost bias
the decision to continue an unwise investment based on past investments of time, effort, and/or money
Escalation of commitment
the increased commitment we may make to a decision despite receiving negative information about the consequences
Creativity
The generation of meaningful ideas by individuals and teams
Innovation
The creation or development of a new product or service
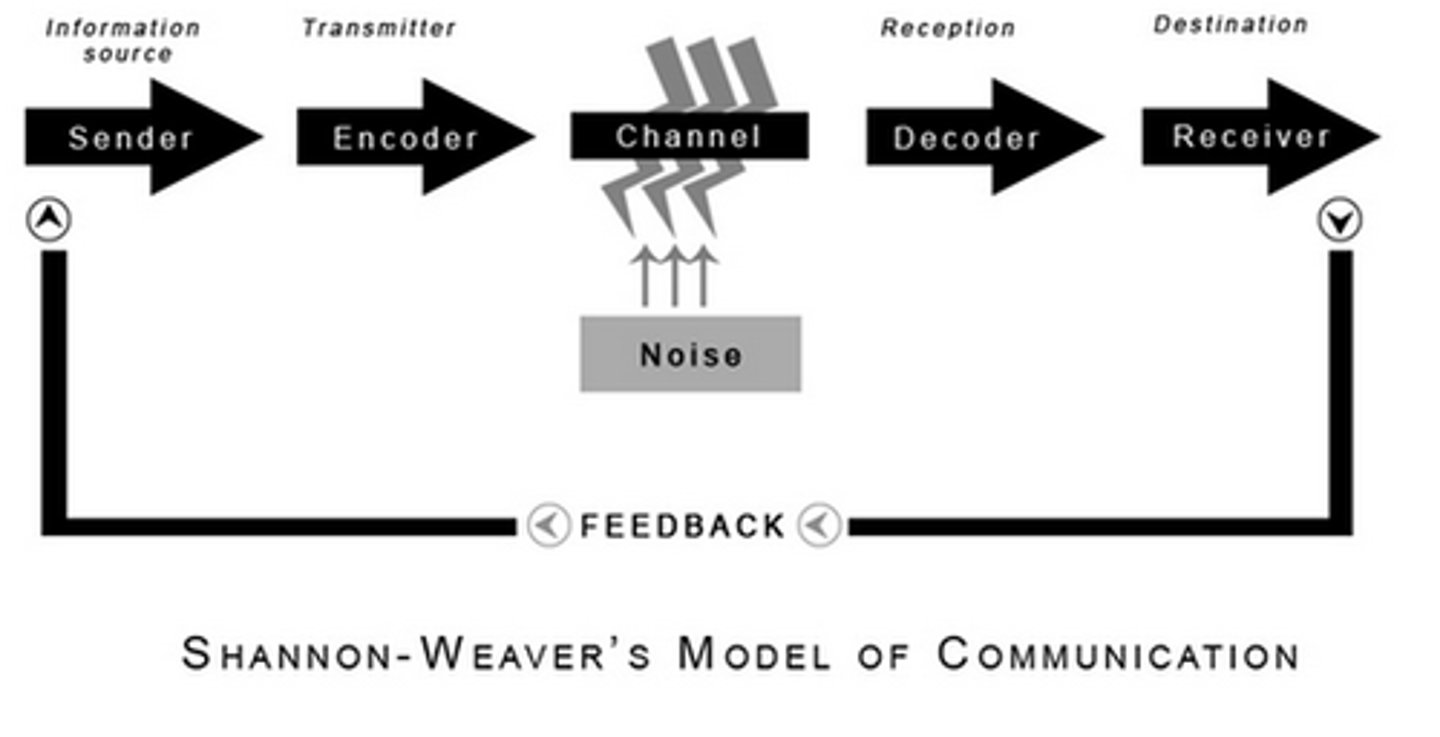
Shannon-Weaver Communication Model
Source --> Encoder --> Noise (interference with message during transmission) --> Decoder --> Receiver --> Feedback
Oral communication
the exchange of information, ideas, and processes verbally, either one-on-one or as a group
Written communication
the use of the written word in the form of reports, memos, and letters to communicate messages
Electronic communication
the transmission of messages through various types of electronic media
Nonverbal communication
the transmission of wordless cues between people. EX: gestures, facial expressions
Elevator speech (elevator pitch)
a short (30 seconds) speech that pitches an idea or concept, such as why a prospective employer should hire you. It's called an elevator speech because it lasts about as long as an elevator ride