Microbiology Test 2
1/117
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
118 Terms
psychrophiles
cold-loving microbes, deep-ocean, 15 degree Celsius
psychtrophs
grow between 0 and 20-30 degrees Celsius cause food spoilage
thermoduric
can survive in elevated temps. for a short period of time
facultative halophiles
osmotolerant grow in hypertonic/isotonic, up to 15% of salt
neutrophiles
5.5-8 pH level
acidophiles
1-4.5 pH level
alkalophilic
greater than 8 pH level
enzymes that deoxify
superoxide free radicals and peroxide
superoxide dismutase
turns into hydrogen peroxide
catalase
hydrogen peroxide turns to water/gas
obligate aerobes
require oxygen
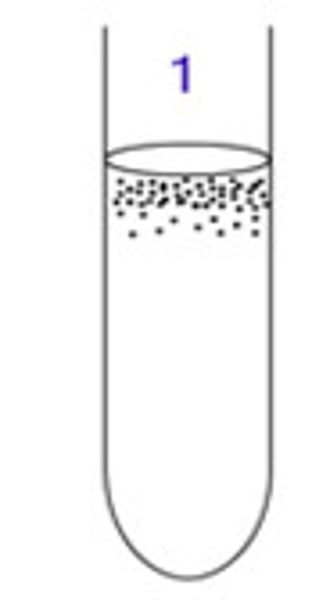
facultative anaerobes
can live with or without oxygen
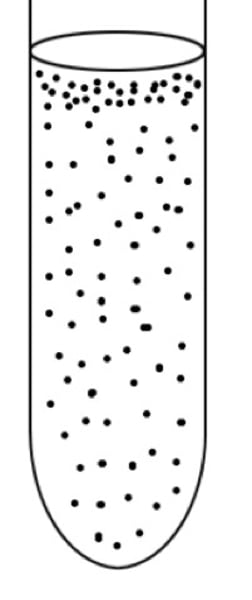
physical requirements for growth
temperature, pH, osmotic pressure
chemical requirements for growth
oxygen, carbon, trace elements
mesophiles
moderate temperature loving microbes (20-40C) medical
thermophiles
heat loving microbes (40-80 C) hot springs
hyperthermophiles
survive in high temperatures 95 degrees Celius
osmophiles
survive in hypertonic conditions
extreme halophiles
live in highly saline environments, dead sea
obligate anaerobes
organisms that cannot live where molecular oxygen is present
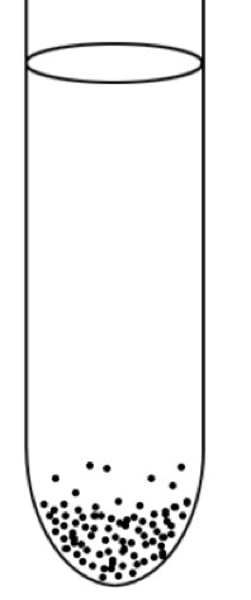
aerotolerant anaerobes
do not utilize oxygen but can survive and grow in its presence
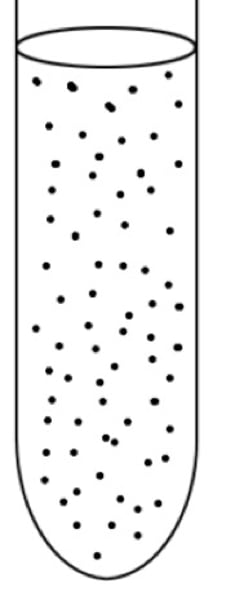
microaerophiles
require oxygen concentration lower than air
CO2
.03% of the atmosphere
capnophiles
grows best in 3-10% concentration of CO2
lag period
bacteria getting used to new environment, adjustment period
biofilms
aggregation of bacteria of many species embedded in gel-like matrixes
advantages of biofilms
-maintaining position in environment -protection from chemical control -increased resistance to immune system -cross feeding -quorum sensing
cross feeding
product oof one bacteria of metabolic process feed other bacteria
quorum sensing
enables microbes to detect cell density within a biofilm
autoinducer
molecule released by bacteria in biofilm, cause change in genetic expression
microbial growth
increase in number of cells, not cell size
binary fission
form of asexual reproduction, most common, DNA replication then cell division
generation time (doubling time)
time it takes to complete a fission cycle, depends on bacterial species and environmental conditions
lag phase
"flat" period of adjustment, enlargement; little growth
log phase
begin replication, ideal conditions and characteristics
stationary phase
growth rate=death rate, growth rate=0
death (decline) phase
growth rate
direct bacteria counting
quick, cells counted under light microscope , known quantity, cheap
plate counts
only counts viable cells, common way for bacteria are counted
serial dilution
samples can have very high bacteria concentration, must dilute to bring down total colonies
indirect bacteria counting
most probable number, useful in dilute samples, uses color change to detect microbial growth
pathology
study of disease
etiology
study of the cause of disease
pathogenesis
development of disease
infection
colonization of the body by pathogens
disease
an abnormal state in which the body is not functioning normally
Koch's Postulates
1. bacteria must be present in diseased but not in healthy individuals 2. bacteria must be isolated + grown on artificial media 3. test organism must replicate signs and symptoms of disease 4. bacteria must be reisolated + grown on artificial media
symptom
a change in a body function that is felt
sign
a change in a body function that can be observed
syndrome
a specific group of signs + symptoms that accompanies a disease
communicable
a disease that is spread from one host to another
contagious
disease that easily spread from one to another
noncommunicable
a disease that is not transmitted from one host to another
incidence
fraction of a population that contracts a disease during a specific time
prevalence
fraction of a population having a specific disease at a given time
endemic disease
established within geographical region (flu)
sporadic disease
disease doesn't naturally occur in location, new cases are random (ebola in the US)
epidemic disease
endemic disease that exceeds the number of cases for that time period, outbreak at a lower scale (ebola in Africa)
pandemic
epidemic at a global level (COVID)
herd immunity
number of individuals in a population which must acquire immunity to a disease in order to slow or stop spread
R(0)
number of individuals likely to be infected by a transmitting case
acute
symptoms develop rapidly
chronic
disease develops slowly
latent
disease within a period with no symptoms when causative agent is inactive
local infection
pathogens are limited to a small area of the body
systemic infection
an infection throughout the body
focal infection
systemic infection that began as a local infection
sepsis
toxic inflammatory condition arising from the spread of microbes
bacteremia
bacteria in the blood
septicemia
growth of bacteria in the blood
toxemia
toxins in the blood
viremia
viruses in the blood
primary infection
acute infection that causes the initial illness
secondary infection
opportunistic infection after a primary (predisposing) infection
subclinical infection
no noticeable signs or symptoms
human reservoirs
main reservoir, transmits actively or passively, s+s or latent infections
animal reservoirs
zoonoses, direct contact, airborne, consuming infected animal product
nonliving reservoirs
environmental sources, soil, water, environment
contact transmission
direct contact- vertical vs. horizontal, droplet, indirect-nonliving fomite
vehicle transmission
transmission by an inanimate reservoir, waterborne, airborne, foodborne
nosocomial infections
acquired in hospital, nursing home, or prison, 8th leading cause of death, compromised host through skin +mucous membrane and suppressed immune system
resident microbiota
microbes that are always there
transient microbes
microbes who colonize the body + may be present for days, weeks, or months
factors affecting distribution + composition
- nutrients, bodily fluids, diet, dead cells - physical + chemical factors - defenses of host - mechanical factors
microbial antagonism
when one microorganism kills, injures, or inhibits the growth of another microorganism
virulence factors
mechanisms that pathogens us to invade the immune system and cause infection
skin
most easily colonized area of body due to size + location, diverse environment, oily areas
gastrointestinal tract
bacteria reside in the lumen or attached to mucus epithelium, nutritional availability high
mouth
most diverse collection of microbes, aerobic bacteria survive within gumline and plaque build up
dysbiosis
an alteration of species composition in of microbiota, environmental changes responsible for change from mostly symbiotic bacteria
large intestine
highest density, contains most complex + important microbial interaction with host
genitourinary tract
sexual organs kept sterile through physical barriers, estrogen stimulates release of glycogen which encourages lactobacillus bacteria
probiotics
live culture microbes beneficial to developing human microbiota
prebiotics
a substrate that is selectively utilized by host microorganisms
portal of entry
the way a pathogen gets into your body
direct portal of entry
-gain access + adhere -avoid or penetrate host defense -damage tissue
indirect portal of entry
build up of waste/toxin
pathogenicity
the ability to cause disease
virulence
the extent of pathogenicity
stages of pathogenicity
1. exposure to host
2. adhesion
3. invasion
4. infection