AP Biology Unit 3- Cellular Energetics Vocab
5.0(1)
Card Sorting
1/51
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Last updated 2:05 PM on 11/3/22
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
52 Terms
1
New cards
Enzyme
macromolecules that catalyze (speed up) reactions by lowering the activation energy
2
New cards
Substrate
the substance that is acted upon by an enzyme
3
New cards
Enzyme-Substrate Complex
a substrate that is bound into the enzyme
4
New cards
Active Site
an area for substrate to bind to in the enzyme
5
New cards
Activation Energy
the amount of energy that is needed for a reaction to occur
6
New cards
Catalyst
a substance that initiates or accelerates a chemical reaction without itself being affected
7
New cards
pH
a measure of the acidity of a solution
8
New cards
Denature
destroy the characteristic properties of a protein by heat, acidity, or other effects that change its shape
9
New cards
ATP
molecule that organisms use as a source of energy to perform work
10
New cards
Kinetic Energy
energy associated with motion
11
New cards
Potential Energy
stored energy
12
New cards
Free Energy
used to determine the likelihood of reactions in organisms, or if the reactions are energetically favorable
13
New cards
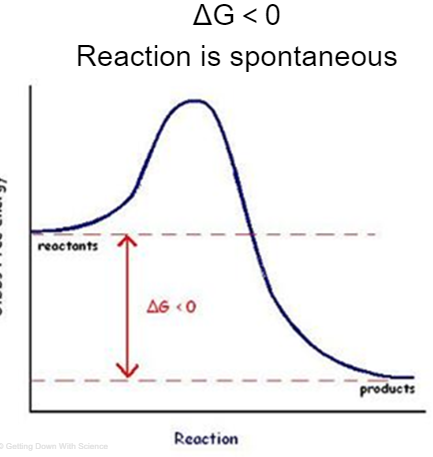
Exergonic Reaction
reactions that release energy
ΔG<0
reaction is spontaneous
ΔG<0
reaction is spontaneous
14
New cards
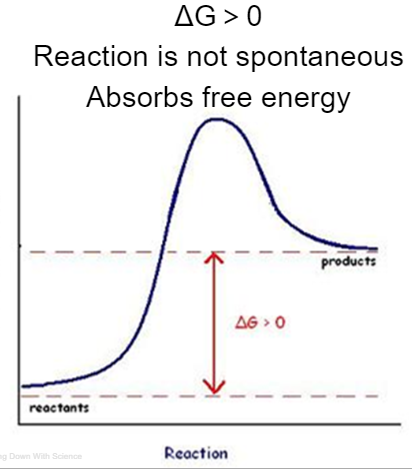
Endergonic Reaction
reactions that absorb energy
ΔG>0
Reaction is not spontaneous
ΔG>0
Reaction is not spontaneous
15
New cards
Catabolic Pathway
Pathways that release energy by breaking down complex molecules into simpler compounds
16
New cards
Anabolic Pathway
Pathways that consume energy to build complicated molecules from simpler compounds
17
New cards
Entropy
the measure of disorder in the universe
18
New cards
Energy
the ability to do work
19
New cards
First Law of Thermodynamics
Energy cannot be created or destroyed. Energy can be transferred or transformed
20
New cards
Second Law of Thermodynamics
Energy transformation increases the entropy (disorder) of the universe
21
New cards
C4 Plant
Plants that have their stomata collect and fix carbon to be delivered to the bundle sheath cells and used in photosynthesis.
22
New cards
NADPH
Electron carrier molecule that is used in photosynthesis
23
New cards
Stomata
pores in leaves that allow CO2 in and O2 out
24
New cards
Stroma
aqueous internal fluid of the chloroplast
25
New cards
Thylakoid
form stacks known as grana
26
New cards
Chlorophyll
green pigment in thylakoid membranes
27
New cards
Redox Reactions
reaction involving complete or partial transfer of one or more electrons from one reactant to another
28
New cards
Oxidation
loss of e-
29
New cards
Pigments
molecules that are able to absorb visible light
30
New cards
Photosynthesis
the conversion of light energy to chemical energy
31
New cards
Photons
particles of energy that make up light
32
New cards
Reduction
gain of e-
33
New cards
Heterotrophs
Organisms unable to make their own food so they live off of other organisms
34
New cards
Calvin Cycle
cyclic electron flow that produces G3P
35
New cards
Light Reactions
Converts solar energy to chemical energy
36
New cards
Chloroplast
organelle for the location of photosynthesis
37
New cards
Photosystems
protein complexes found in the thylakoid membrane that contain chlorophyll to collect energy from the sun
38
New cards
Mesophyll
the cells that make up the interior tissue of the leaf
39
New cards
Photorespiration
On very hot days plants close their stomata to stop water loss
40
New cards
G3P
a 3 carbon sugar that is produced during photosynthesis and can be turned into glucose
41
New cards
CAM Plant
Open stomata at night and close during the day then carbon dioxide is incorporated into organic acids and stored in vacuoles
42
New cards
Cellular Respiration
Cells harvest chemical energy stored in organic molecules and use it to generate ATP
43
New cards
NAD+
Electron acceptor molecule that is used in cellular respiration. Used in Glycolysis and Krebs Cycle
44
New cards
FADH+
Electron acceptor molecule that is used in cellular respiration. Used in Krebs Cycle
45
New cards
Glycolysis
-Starting point of cellular respiration
-Occurs in the cytosol
-Splits glucose (6C) into 2 pyruvates (3C)
-Occurs in the cytosol
-Splits glucose (6C) into 2 pyruvates (3C)
46
New cards
Pyruvate Oxidation
If oxygen is present, the pyruvate enters the mitochondria (eukaryotic cells) where it is oxidized into acetyl-coA
47
New cards
Krebs Cycle (Citric Acid Cycle)
-Occurs in the mitochondrial matrix
-Turns acetyl CoA into citrate
-Releases CO2
-ATP synthesized
-Electrons transferred to NADH and FADH2
-Turns acetyl CoA into citrate
-Releases CO2
-ATP synthesized
-Electrons transferred to NADH and FADH2
48
New cards
Chemiosmosis
H+ ions flow down their gradient through ATP synthase and produce ATP molecules
49
New cards
ATP Synthase
Protein imbedded in the inner membrane of the mitochondria that uses the power from chemiosmosis to produce ATP
50
New cards
Anaerobic Respiration
generates ATP using an ETC in the absence of oxygen
-The final electron acceptors: sulfates or nitrates
-The final electron acceptors: sulfates or nitrates
51
New cards
Fermentation
generates ATP without an ETC or oxygen. It is an extension of glycolysis.
52
New cards
Autotroph
Organisms that produce their own food (organic molecules) from simple substances in their surroundings