Marine invert lecture exam 2
1/96
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Protozoa, porifera, ctenophora, and cnidaria
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
97 Terms
What are perisarcs and coenosarcs?
The perisarc is the structure that hydrozoan polyps attach to, and in some species grows around the polyp for them to retreat into to avoid predation. The coenosarc is a living structure, and serves as the direct attachment point between the perisarc and the polyp.
Classify this organism. What stage is it in?
This organism is in phylum Cnidaria, subphylum Medusozoa, class Hydrozoa, and order Anthoathecata.
It is the colonial polyp stage of fire coral Millepora
Match the image of typical Anthoathecata medusae
Match the image of the blue button Porpita, a floating coral polyp colony
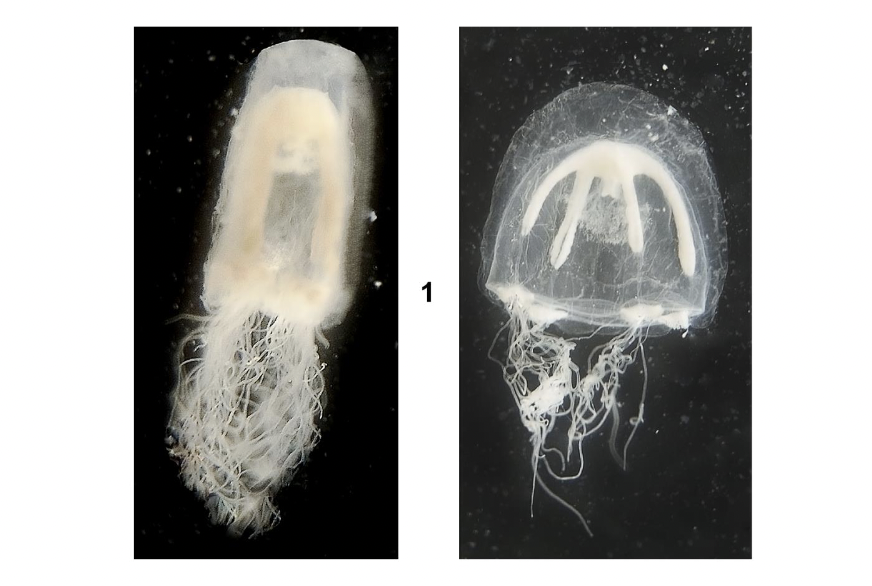
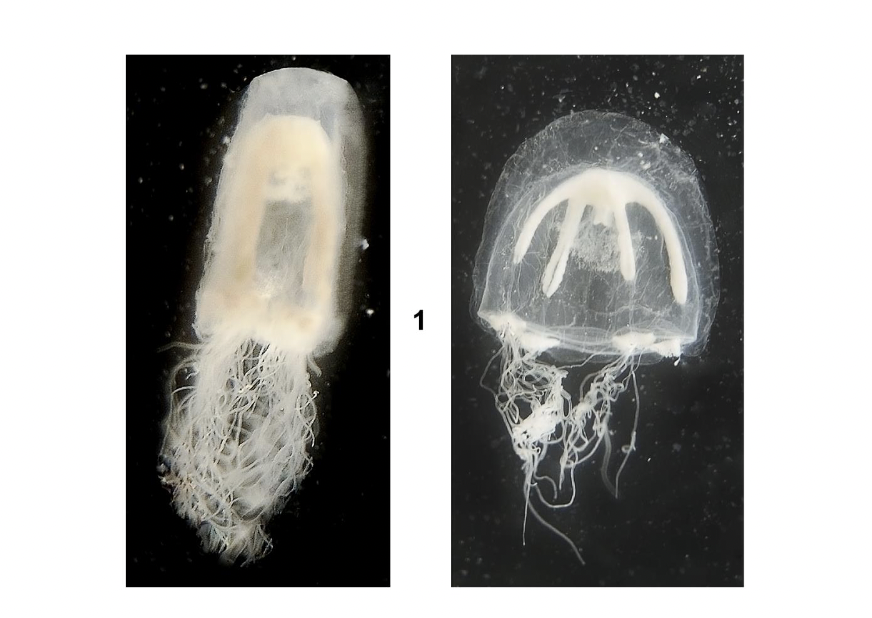
What phylum, subphylum, class, and order is this medusa? Describe their habitat and diet.
Phylum Cnidaria
Subphylum Medusozoa
Class Hydrozoa
Order Lepthothecata
Habitat: attached to structures as polyp, planktonic as medusa
Feeding: carnivore
Match this anthoathecatan medusa to the correct colonial polyp stage.

What phylum, subphylum, class, and order is this medusa? Describe their habitat and diet.
Phylum Cnidaria
Subphylum Medusozoa
Class Hydrozoa
Order Siphonophorae
Habitat: Planktonic
Feeding: Carnivore

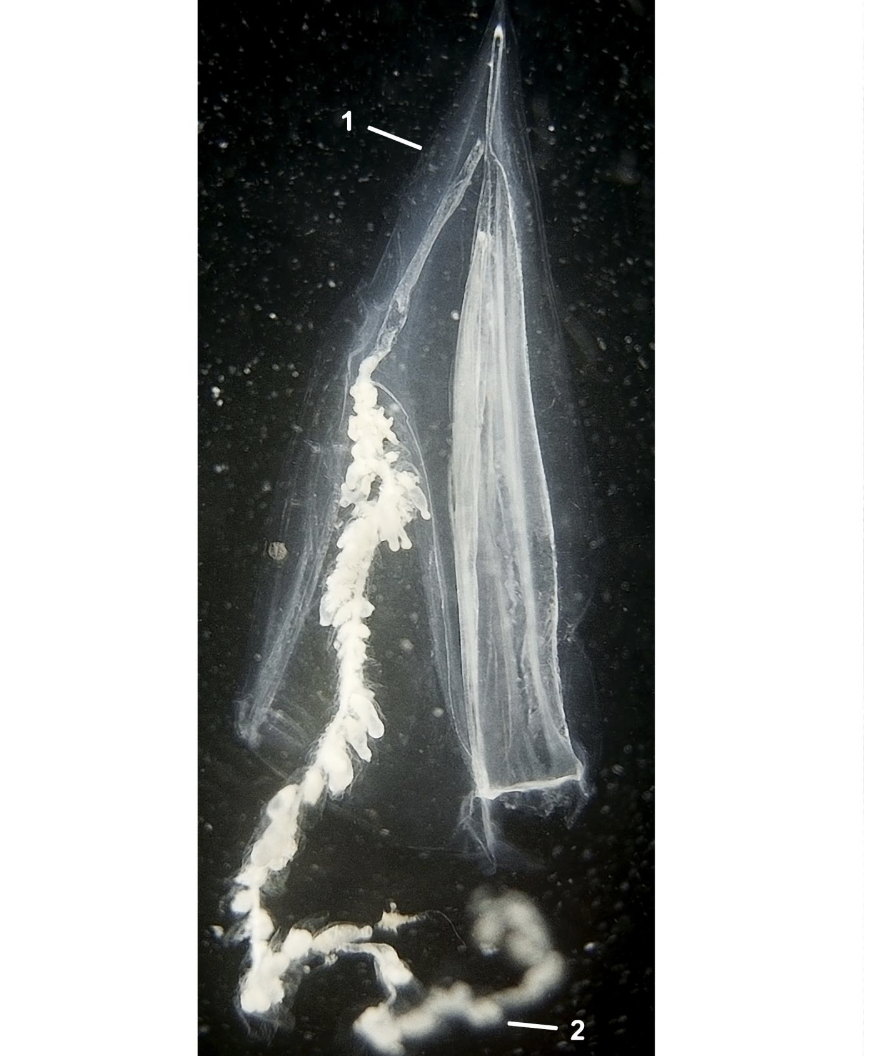
What phylum, subphylum, class, and order is this organism? Describe their habitat and diet.
Phylum Cnidaria
Subphylum Medusozoa
Class Hydrozoa
Order Siphonophorae
Habitat: Planktonic
Feeding: Carnivore

Correctly identify the two labeled parts in this image.
Pneumatophore
Tentacle
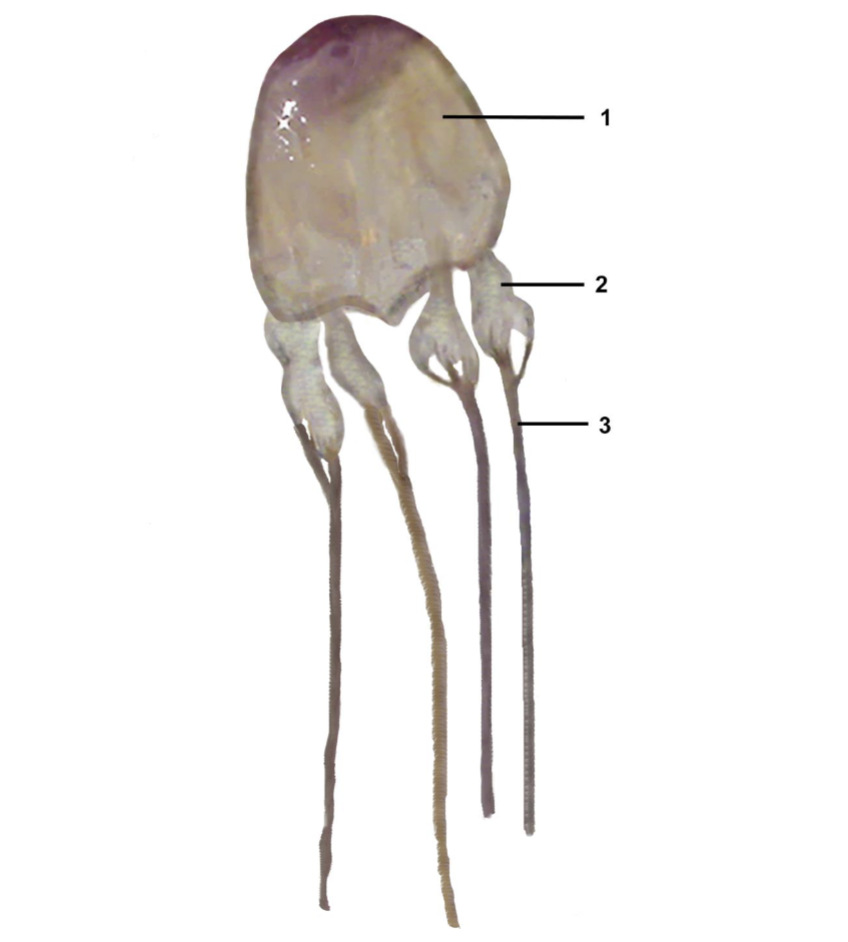
What phylum, subphylum, and class is this organism? Name all the labeled parts of this organism.
Phylum Cnidaria
Subphylum medusozoa
Class cubozoa
Exumbrella
Pedalia
Tentacles
If an organism is in class cubozoa, what phylum and subphylum is it? What habitat and feeding do they use?
Phylum Cnidaria
Subphylum medusozoa
Habitat: attached to structure as a polyp, planktonic as medusa
Feeding: carnivore
What are all the labeled parts to this organism?
Planula
Scyphula (planula just settled)
Scyphistoma (polyp)
Strobila
Ephyra
Lappet
Rhopalium
Oral arm
Manubrium and mouth
What are all the labeled parts to this organism?
Medusa
Exumbrella (bell)
Rhopalium
Tentacles
Oral arm
Gonads
Radial canals
Ring canal
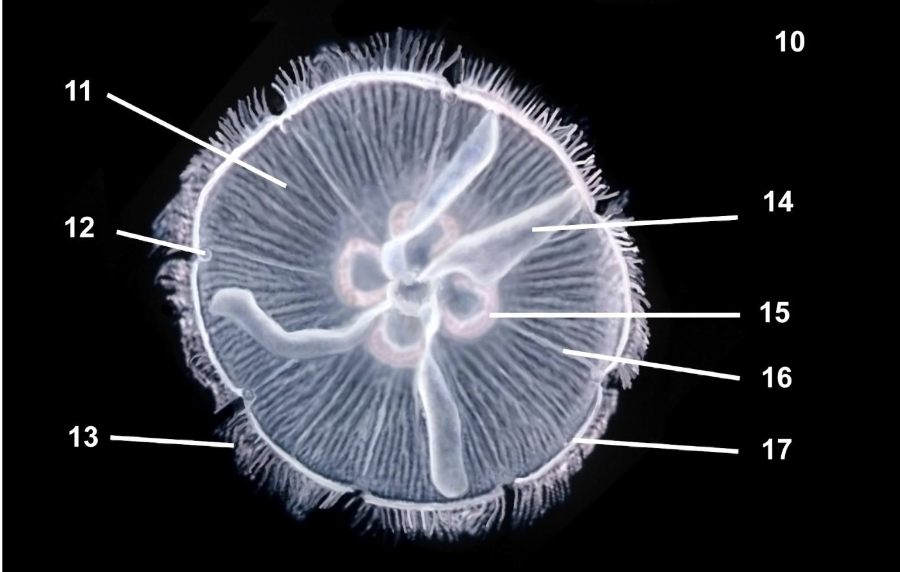
What phylum, subphylum, class, and subclass is this organism?
This medusa diagram is:
Phylum Cnidaria
Subphylum Medusozoa
Class Scyphozoa
Subclass Discomedusae

What phylum, subphylum, class, and subclass is this organism?
Phylum Cnidaria
Subphylum Medusozoa
Class Scyphozoa
Subclass Discomedusae
It is the same as this image.

Classify this organism:
Phylum: Cnidaria
Subphylum: Anthozoa
Class: Otocorallia
Order: Scleralcyonacea
If an organism is in subclass Discomedusae, what habitat and feeding does it have?
Habitat: attached to structure as polyp, planktonic as medusa
Feeding: carnivore
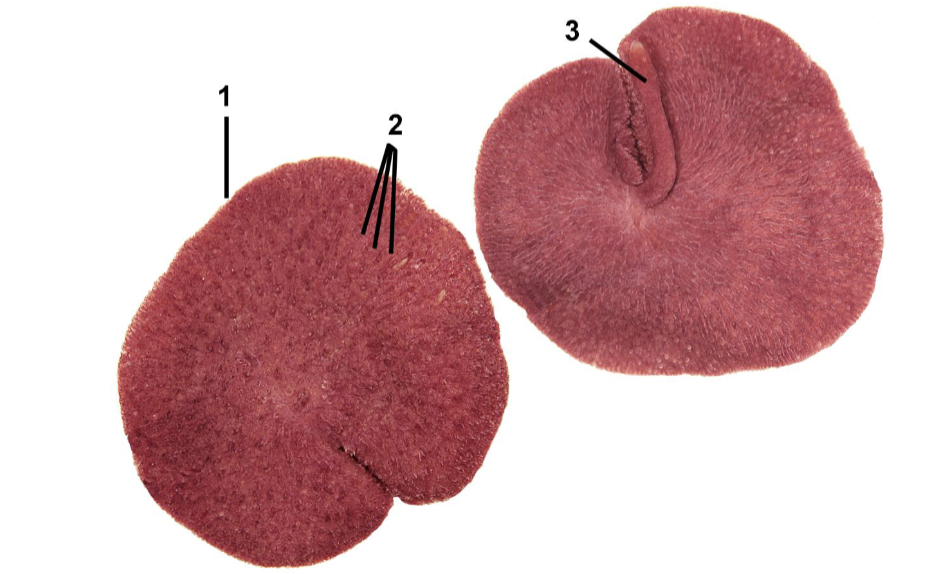
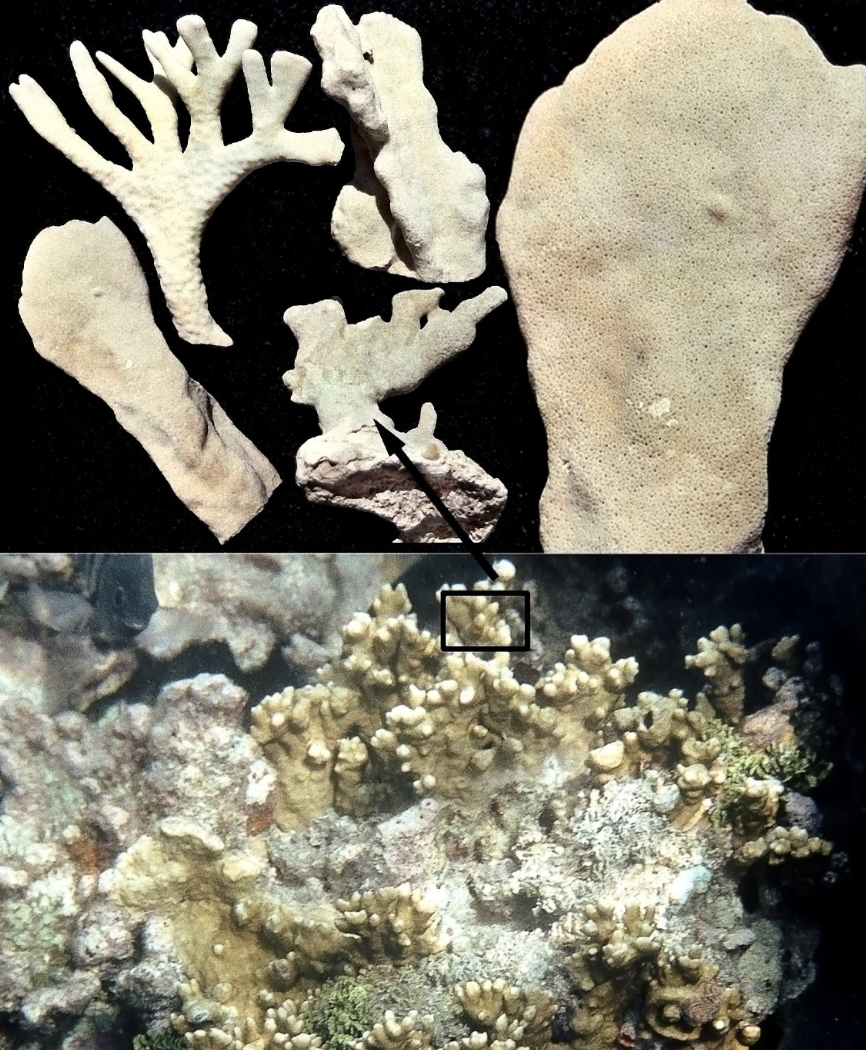
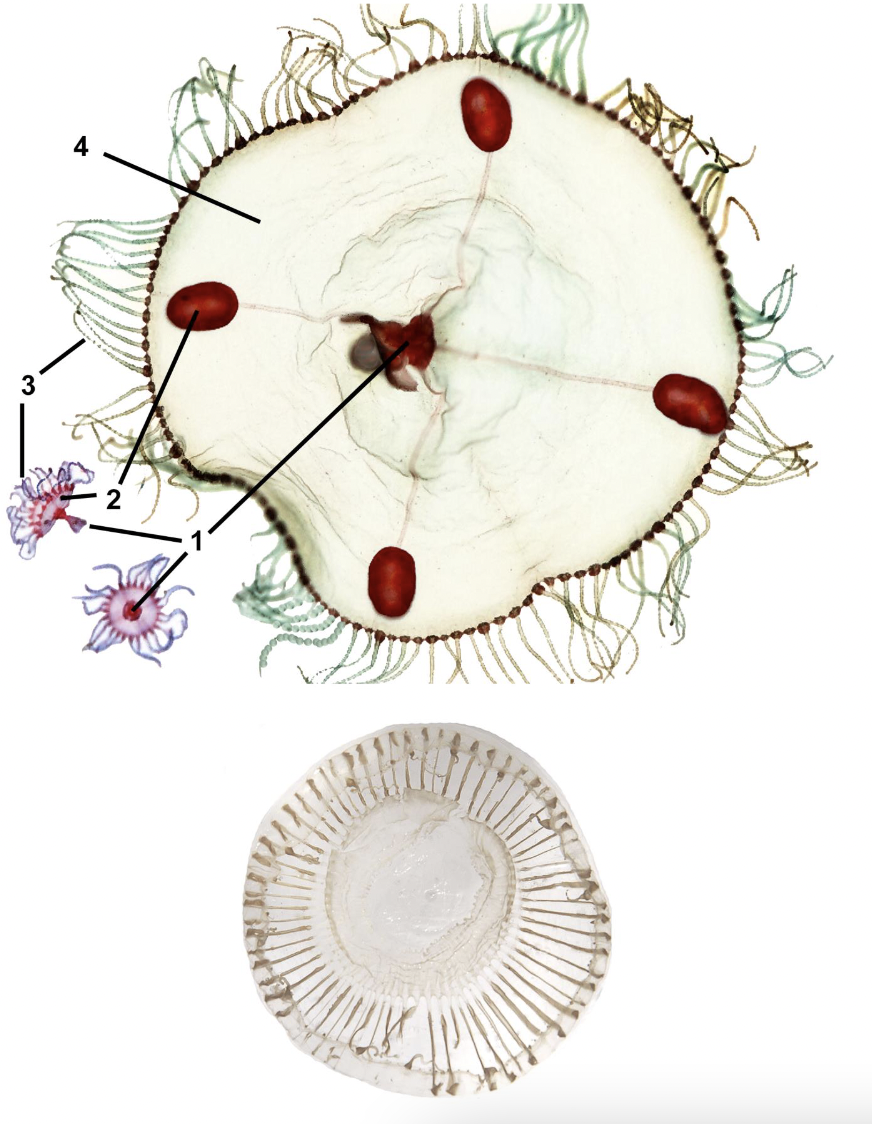
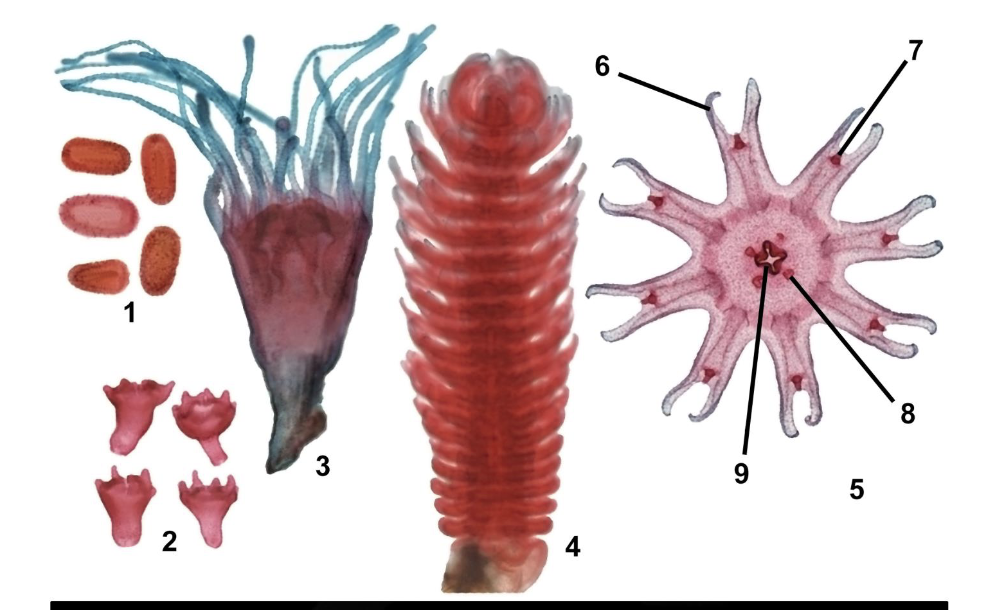
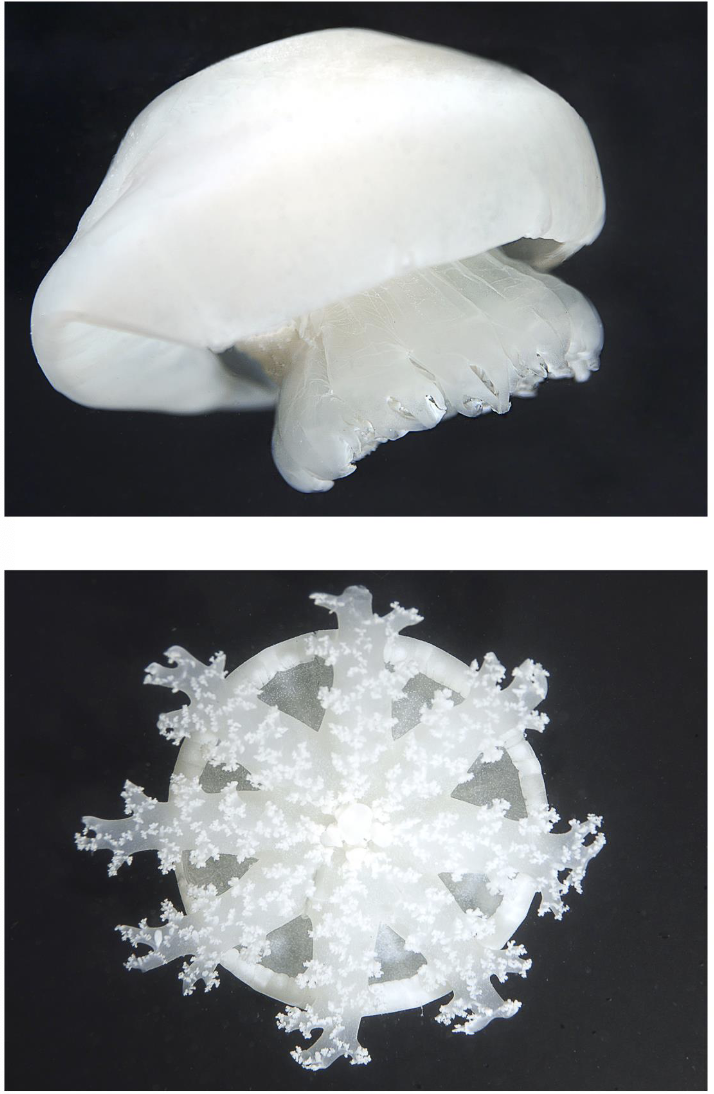
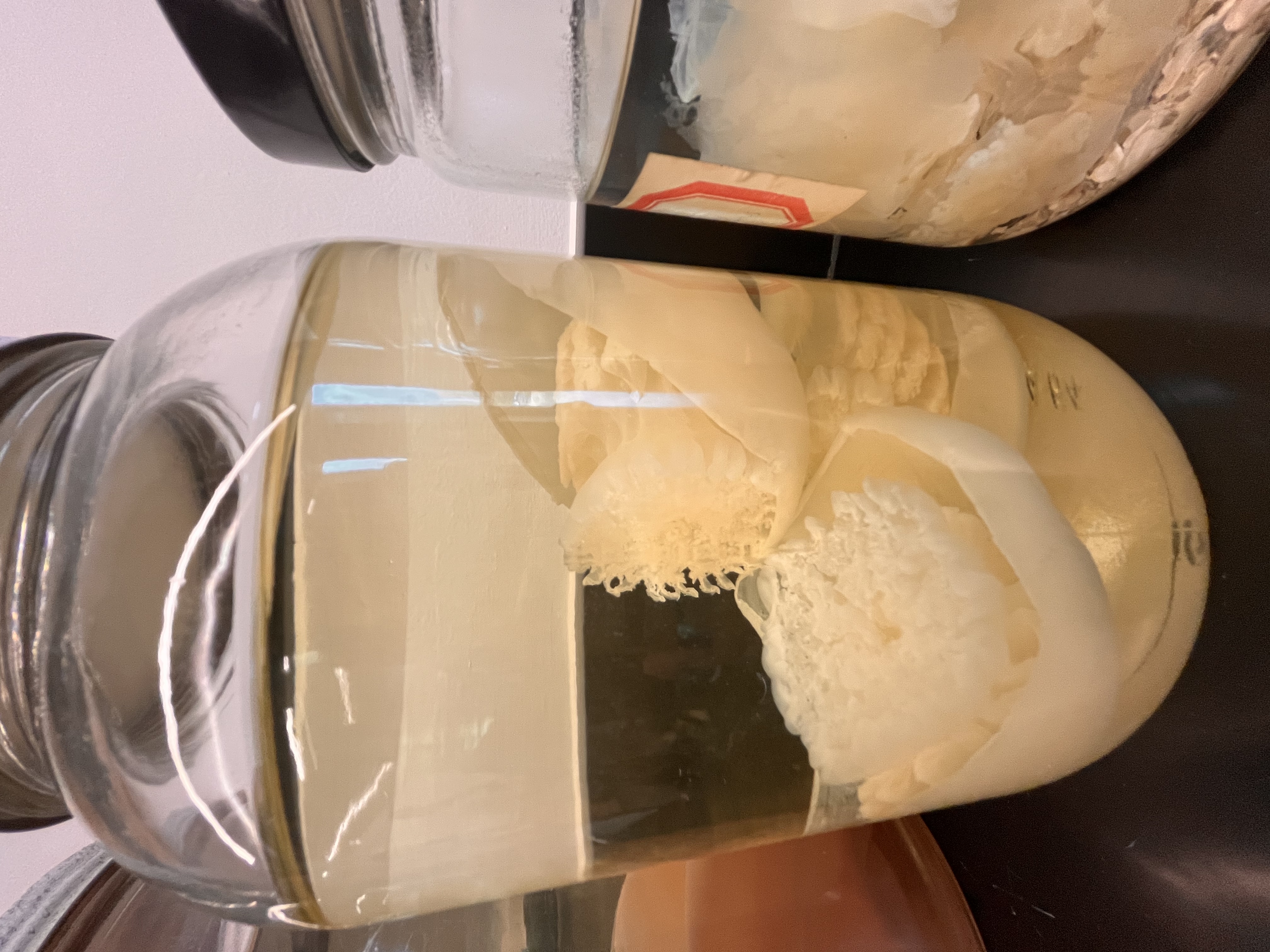
Classify this organism and identify the labeled parts
Phylum Cnidaria
Subphylum Anthozoa
Class Octocorallia
Order Scleralcyonacea
1. primary polyp; 2. secondary polyps; 3. sand anchor of primary polyp
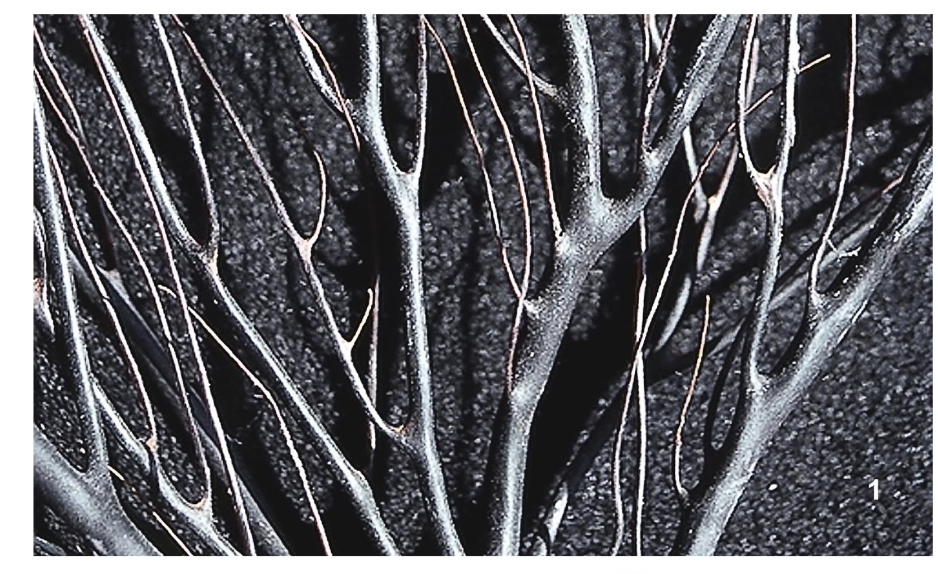

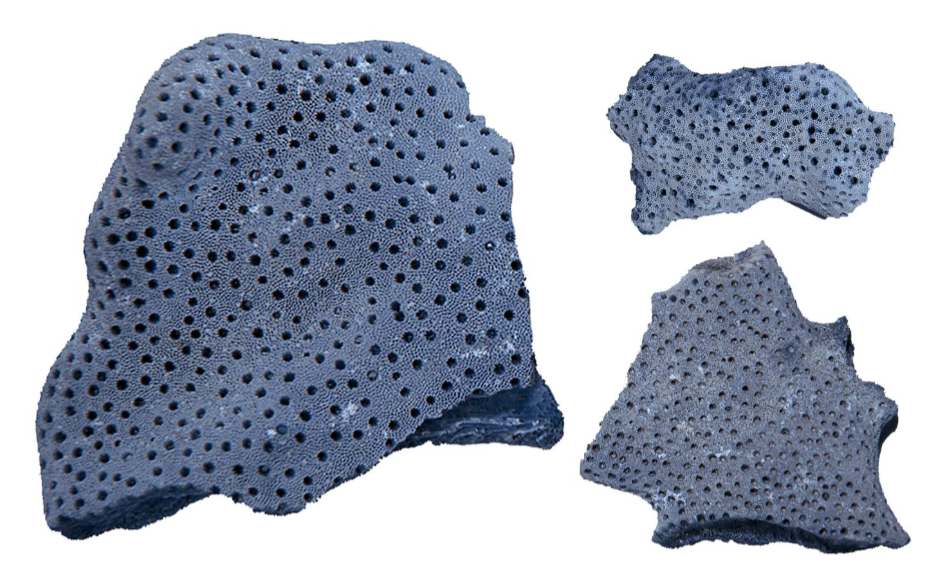
What is this?
Classified as: Cnidaria:Anthozoa:Octocorallia:Malacalcyonacea
It is a gorgonian protein skeleton forming axial rod (soft tissue removed)
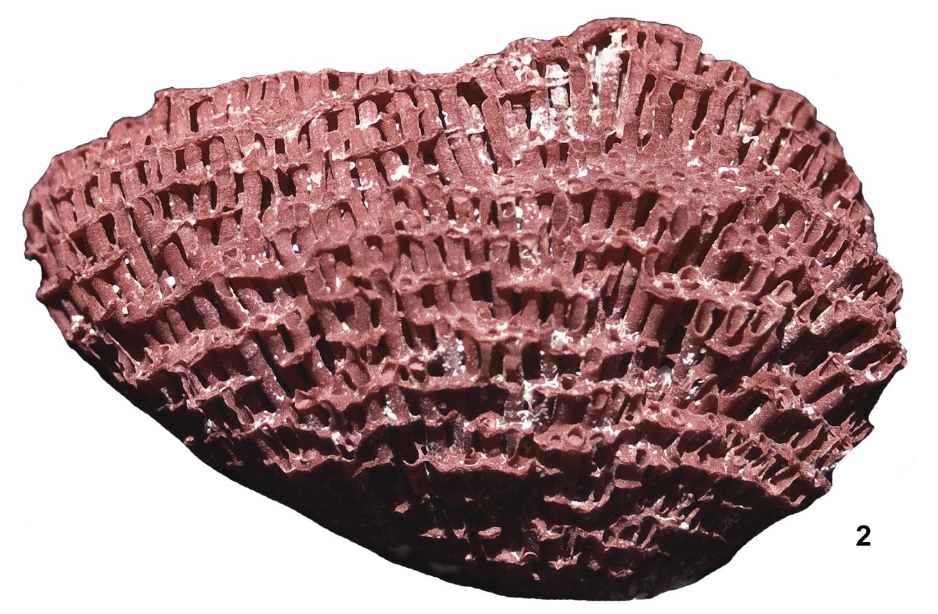
What is this?
Classified as: Cnidaria:Anthozoa:Octocorallia:Malacalcyonacea
It is the calcified skeleton of organ pipe coral
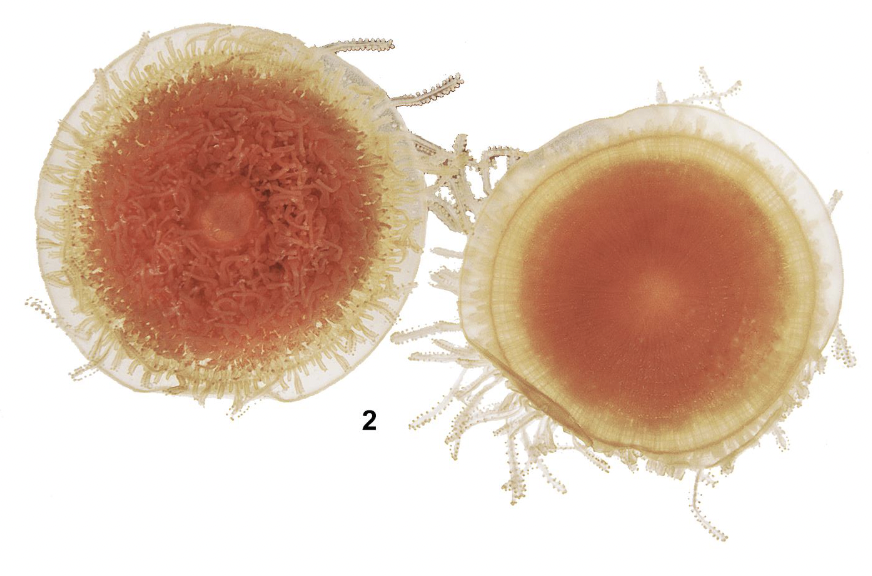
What is this? Identify the labeled parts.
Classified as:
Phylum Cnidaria
Subphylum Anthozoa
Class Octocorallia
Order Malacalcyonacea
1. polyp; 2. tentacle; 3. axial rod; 4. gastrovascular cavity
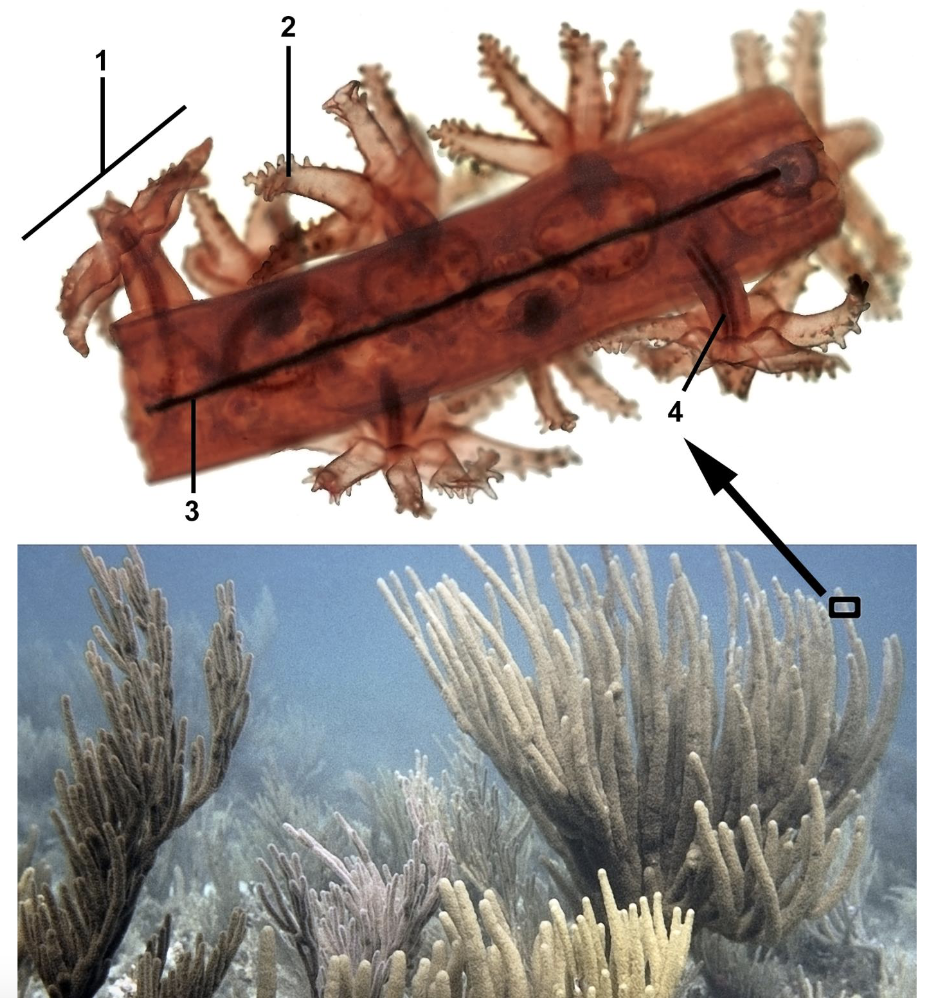
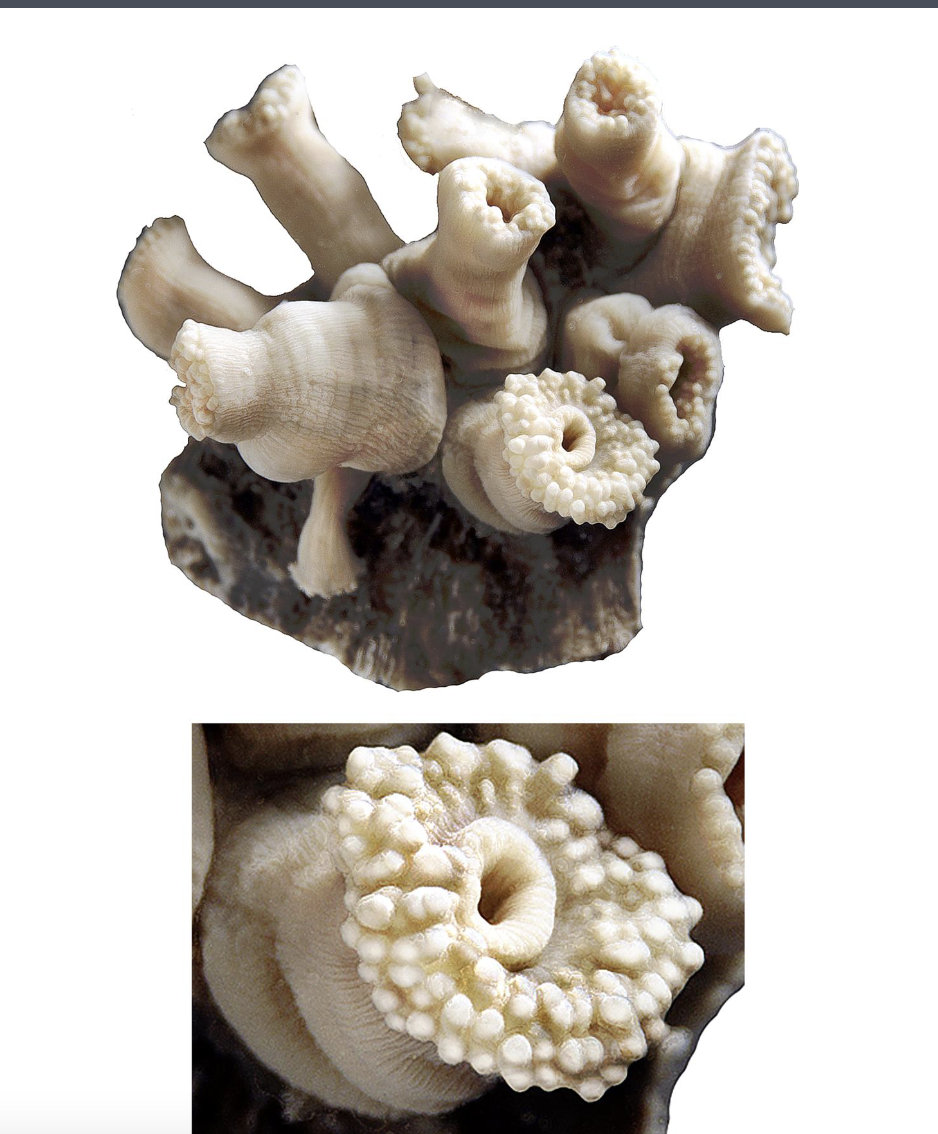
What are these?
Phylum Cnidaria
Subphylum Anthozoa
Class Hexacorallia
Order Zoantharia

What order is this organism?
Order Corallimorpharia
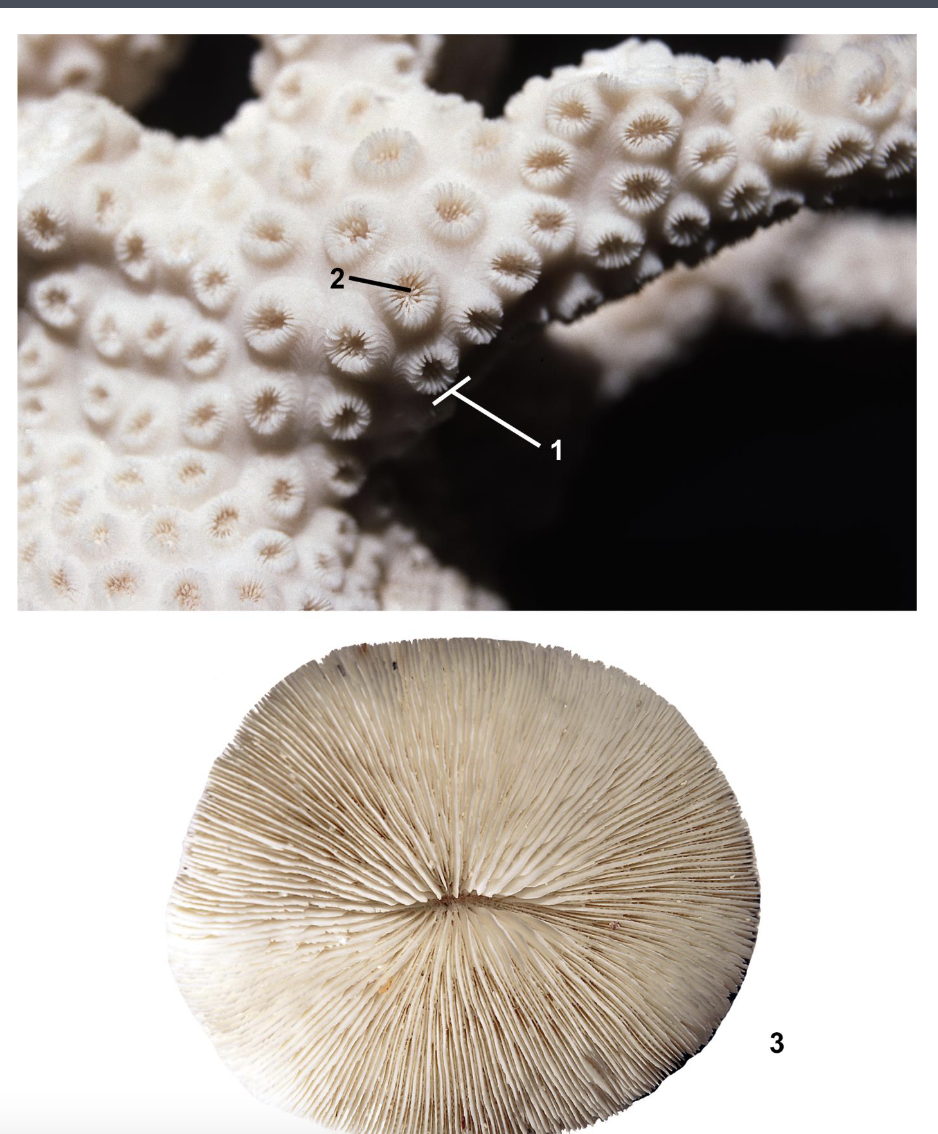

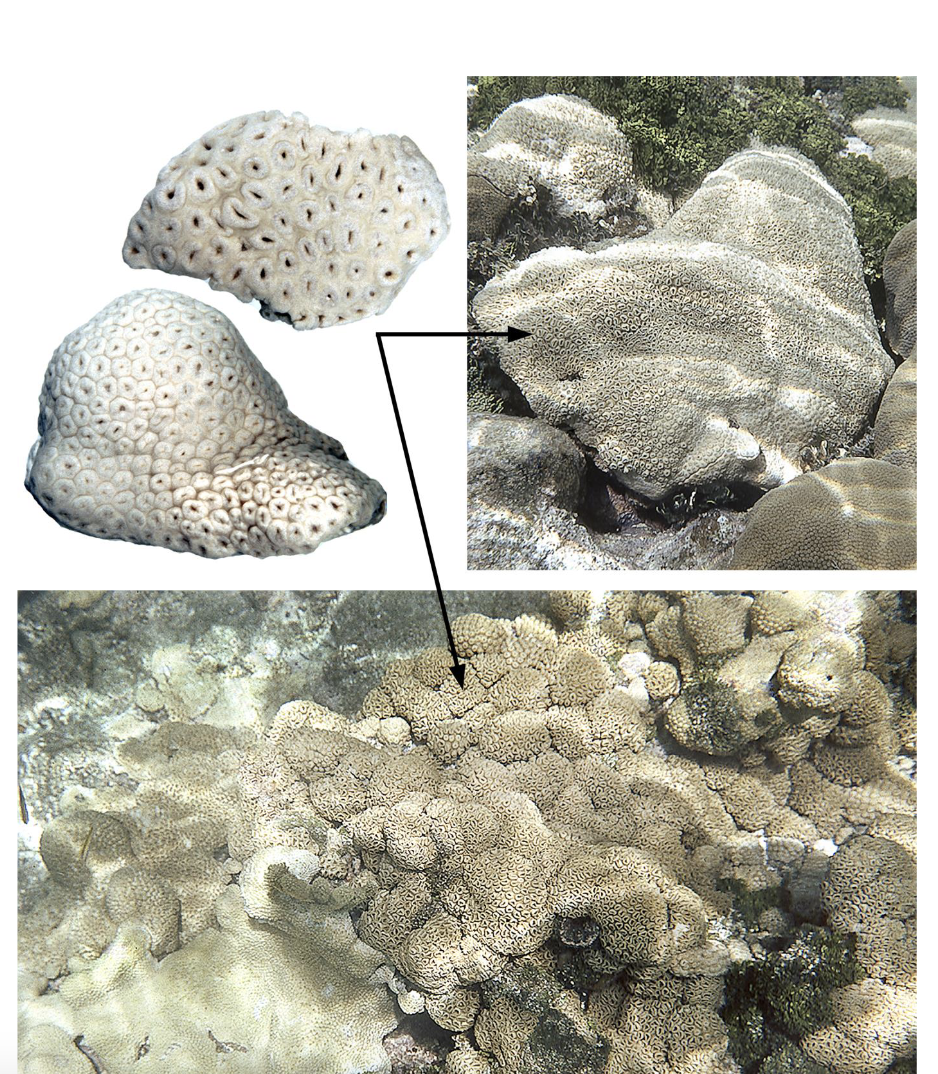
What class and order order is this organism? Identify the labeled parts.
Class Hexacorallia, Order Scleractinia
1. theca of colonial polyp; 2. sclerosepta; 3. solitary polyp
Approximately how many species are in Cnidaria?
~13,000 spp
What is the general body plan of a cnidarian?
Dipoblastic (2 of 3 germ layers)
Radial symmetry (sometimes bilateral)
Tentacles with cnidae
Epidermis: nerve net and muscles
Mesoglea: jelly of proteins, carbs, etc
Gastrodermis: digestive system, generates muscles
What life cycle do most cnidarians have?
Dimophic, meaning polyp and medusa stages
Diffusion serves what functions in cnidarians?
Excretion and respiration
What is the diet and digestion of cnidarians?
They eat plankton and small fish using a gastrovascular cavity
What modes of reproduction do cnidarians have? What are their larvae called?
Monoecious or dioecious
Planula larvae (asexual budding forms colony)
Describe the cnidarian nervous system
They have a nerve net, medusa may have ocelli and/or statocysts
What do ocelli and statocysts do?
Ocelli are light/dark detectors, statocysts are for orientation
What do hydrozoans do and don’t have?
DON’T have:
Cells within mesoglea
Cnidocytes in gastrodermis
Mesentaries
Phopalia
DO have:
Colonial polyps (usually)
Velum on medusa
Describe the life cycle of hydrozoans
Planula —>Actinula
What larval stage is unique to hydrozoans?
Actinula
Describe order trachymedusae within class hydrozoa
NO POLYP
Size range: a few cm
Thick rings of tissue on bell with nematocysts (bell can sting)
Tentacles on bell margin
Margin not lobed
Statocyst present on medusa
Gonads on radial canals
Deep water
Describe order narcomedusae within class hydrozoa
Usually no polyp
Few cm size
Tentacles on BELL, not margin
Bell margin- lobed
Statocyst ARE present
Gonads on manubrium
Deep water
What are the differences between the hydrozoans in narcomedusae vs.trachymedusae?
Narcomedusae: tentacles on bell, bell margin IS lobed, gonads on manubrium
Trachymedusae: tentacles on bell margin, margin NOT lobed, gonads on radial canals
Describe order actinulida
Simplified medusa (reduced bell with tentacles)
Size: few mm
Interstitial (too small to be infauna)
How is order stauromedusae classified?
Phylum Cnidaria—> Subphylum Medusozoa—>Class Staurozoa —> Order Stauromedusae
Describe order stauromedusae
Mesoglea with cells
Gastrodermis with cnidocytes
Solitary polyp (benthic)
Cold water (deep or shallow)
Minor part of food web, unique morphology
Describe a stauromedusae medusa
Benthic (attached)
Finger-shaped bell looks like polyp
~cm
8 lobes
Capitate (ball shape) tentacles
What is the life cycle of a stauromedusae?
Planula larvae —> stauropolyp —>medusa
Describe class scyphozoa
Mesoglea with cells
Gastrodermis with cnidocytes
Habitat: all oceans
Polyp and medusa
Medusa planktonic without velum, rhopalia sensory structure
Describe the life cycle of scyphozoans
Planula larvae—> Scyphistoma/Polyp (benthic)—> undergoes strobulation to form Strobila —> ephyra —> adult medusa
How are organisms of order coronate classified?
Phylum cnidaria—> Class scyphozoa —> Subclass Coronamedusae —> Order Coronatae
Order coronatae is the only order in coronamedusae
What is unique about jellies in order coronatae?
They have a bell with a coronal groove
Also have pedalia
What distinguishes subclass discomedusae?
They have a bell without a coronal groove AND lack pedalia
Describe class cubozoa
Mesoglea with cells
Gastrodermis with cnidocysts
Polyp = solitary and benthic
Medusa = planktonic 4-sided bell
Velarium
Pedalia
Rhopalia present
Eyes with lens
Very dangerous sting
Describe the life cycle and habitat of cubozoans
Life cycle: planula—> polyp —> medusa
Habitat: tropical shallow water
What famous cubozoan has a very dangerous sting?
Chironex fleckeri
What is used to identify order caroybdeida?
They have unbranched pedalia with a single tentacle attached
What is used to identify order chirodropida?
Pedalia ARE branched, with multiple tentacles attached to each.
What subphylum are myxosporeans in? Describe them
Subphylum endocnidozca
Intracellular parasites, form capsules
Life cycle:
infective actinospores (polychaete host)
infective myxospores (vertebrate host)
Describe subphylum anthozoa
Mesoglea with cells
Gastrodermis with cnidocytes
Polyp: solitary or colonial, internal mesentaries
NO MEDUSA STAGE- only planula larvae and polyp
Habitat: benthic, all oceans
What are the defining features of octocorallians?
Primarily colonial
8 mesentaries
8 pinnate tentacles
1 siphonoglyph
Describe order scleralcyonacea (within class octocorallia)
Branching colonial polyp
CaCO3 central axial support
Some polyps are dimorphic
Some external skeleton
Habitat: attached to strucutre (reefs)
a few sand specialists (sea pens)
Describe class hexacorallia
Solitary or colonial
6-fold symmetry
Non-pinnate tentacles
How is order ceriantharia categorized?
Phylum cnidaria —> Subphylum Anthozoa —> Class Hexacorallia —> Order cerantharia
Describe order cerantharia
“tube anemones”
Solitary, several cm
Build tubes with sand, mucus and ptchocysts
Tentacle formation = double whorl
outer whorl - long and thin
inner whorl - short
Unpaired mesenteries
Siphonoglyph- 1 (small)
Support - hydroskeleton (no spicules/axial rod)
Habitat: sand and mud
What is a ptychocyst?
A type of cnidocyst
Describe order antipatharia (hexacorallia)
black corals
body: colonial, cm-mm, branched
single whorl of 6 tentacles
unpaired mesentaries
1 siphonoglyph
Axial hard protein support rod
deep reefs
Describe order actiniaria
Solitary
mm- several cm
Single whorl of tentacles
Paired mesentaries
2 siphonoglyphs
hydroskeleton support
benthic
asexual budding (clones break off and walk away)
mucus keeps them wet in intertidal
Describe order zooantharia (Class Hexacorralia)
“mat anemones”
Colonial (thin)
2 whorls of tentacles
Paired mesentaries
1 siphonoglyph
Hydroskeletal support
Glue sand grains to outside for protection
Attached to surfaces, epizoic
Describe order corraliomorpha (class hexactinellida)
Colonial or solitary body
mm-cm in size
Multiple whorls of capitate tentacles
paired mesentaties
NO siphonoglyph
Hydroskeleton
Attached to hard surfaces
Describe order scleractinia (class hexacorallia)
- Colonial
- Colony size a few cm to multiple m depending on age
- Tentacles are single whorl, variety of shapes
- Paired Mesentaries
- Siphonoglyphs- NONE
- Supoort- CaCO3 skeleton, forms theca with individual polyps separated by sclerosepta
What does it mean if a cnidarian is ahermatypic?
- Ahermatypic = non reef building
- Most are solitary
- Usually without zooxanthellae
- Shallow or deep water
What does it mean if a cnidarian is hermatypic?
- Hermatypic = reef building
- Most reefs are these guys
- Usually colonial
- Usually have zooxanthellae
- Shallow, clear water
- Mass spawning- most inverts spawn with the coral
What is the center of origin for corals, at a species level?
The pacific, specifically the indo-pacific
What is the main problem for corals in the Indo-Pacific?
Deforestation, which results in sediment runoff
What parts are fringing reefs comprised of?
Patch reef (near shore)
Main reef
Bank reef (deep offshore)
The fringing reef may not have all 3 of these components.
True or False: Any circular reef can technically be considered an atoll.
True, but many people define atolls by volcanic activity
What are the reef zones?
Shoreline/beach
Lagoon (between shoreline and start of reef)
Grass beds
Hardpan (gorgonians, fans)
Nursery
Patch reef
Back reef (rubble from damage, inverts, stony corals)
Reef crest (dry at low tide)
Forereef (spur/groove, most diverse)
Sand channel (mostly CaCO3 shells)
Bank reef (70-80 ft)
Deep reef (-90 ft, black corals)
Wall (dropoff)
How much more diverse are pacific reefs than caribbean reefs?
10 times more (species diversity)
What is the scientific name for elkhorn coral?
Acropora palmata
What do corals and anemones exposed at low tide do to protect themselves?
They secrete a mucus that covers them and protects them.
When were the first signs of coral bleaching? When did big bleaching events start to happen?
First evidence: 1980s and 1990s
Big bleaching: 1990s and 2000s
Bleaching events are more drastic in shallow water
How does sedimentation affect coral? How about eutrophication?
Sedimentation: cuts out light and smothers coral
Eutrophication: lowers light and affects nutrients
What is cyanide fishing? How does it affect coral?
Cyanide fishing occurs mainly in the Pacific, and happens when bottles of cyanide are squirted into a reef to flush out fish. This is mostly done to catch fish for the aquarium trade, but results in death for fish too close and for corals.
Why is dynamite fishing controversial?
It often results in people blowing themselves up and dying (karma tbh)
What items can physically damage coral reefs?
Lost fishing gear
Anchors
Ships
unethical tourism (“death by a thousand cuts”)
What does tripoblastic mean?
3 germ layers
Describe Phylum Chaetognatha
13 spp
Habitat: all oceans, planktonic (one benthic)
Digestion:
Flow-through
Carnivores (eat copepods)
Diffusion for respiration and excretion
Reproduction- monoecious, direct
Nervous: ganglia in head, nerve net, ocelli, cillia
Circulation: sinuses
Ecology: predators on plankton
Describe the body plan of chaetognatha
5-100 mm
Arrow shape
Head- spines
Trunk: long part of the body, under head
Fins: most cases tail fin (some trunk)
Muscles: longitudinal and circular
Describe phylum cycliophora
Species example: Symbion pandora
Body: feeding stage main part of life cycle
350-500 um
Adhesive disk
Trunk
Buccal funnel
Habitat: epizoic
Digestion: u-shaped gut (eat small particles)
Circulation: none
Diffusion for excretion and respiration
Reproduction: pandora larva
Nervous system: ganglia and nerve cords
Commensalism in lobster mouth
Explain the life stages of Cycliophorans
Pandora larva (asexual) = feeding stage
Colonizes the same lobster when reproducing
Prometheus larvae (male) attache to feeding stage larvae
Chordoid larvae move to other lobsters when shed during molt
Describe Phylum Platyhelminthes
20,000 spp
Many parasitic (know free-living spp)
Benthic (some can swim, not long)
Digestion: pharynx and gut, not complete
Carnivores
Circulation- none
Respiration: diffusion
Excretion: Protonephridia
Reproduction: monoecious, direct development
Nervous system: ganglia, ladder nerves, ocelli near ganglia
some have statocyst
Regeneration
What are protonephridia?
It is the adapted excretion system platyhelminthes worms use to speed up diffusion. Literally, it means “first kidney”
Describe the body form of platyhelminthes worms
Acoelomate (no body cavity)
mm-cm in size
Multiciliated epidermal cells
Rhabdite glands
Longitudinal and circular muscle tissues (long)
Mouth in middle of body
Describe Phylum Gnathostomulida
100 spp
Body: 300 um - 3 mm, elongate shape
big jaws, plate-like
Monociliated epidermal cells
Long and circular muscle layers
Habitat: Interstitial anoxic mud
Digestion: pharynx and gut (incomplete)
Circulation: absent
Excretion: protonephridia
Respiration: diffusion
Reproduction: monoecious, direct development
Nervous: ganglia, net, 2 cords
ciliary pits, bristles
Ecology: feed on bacteria
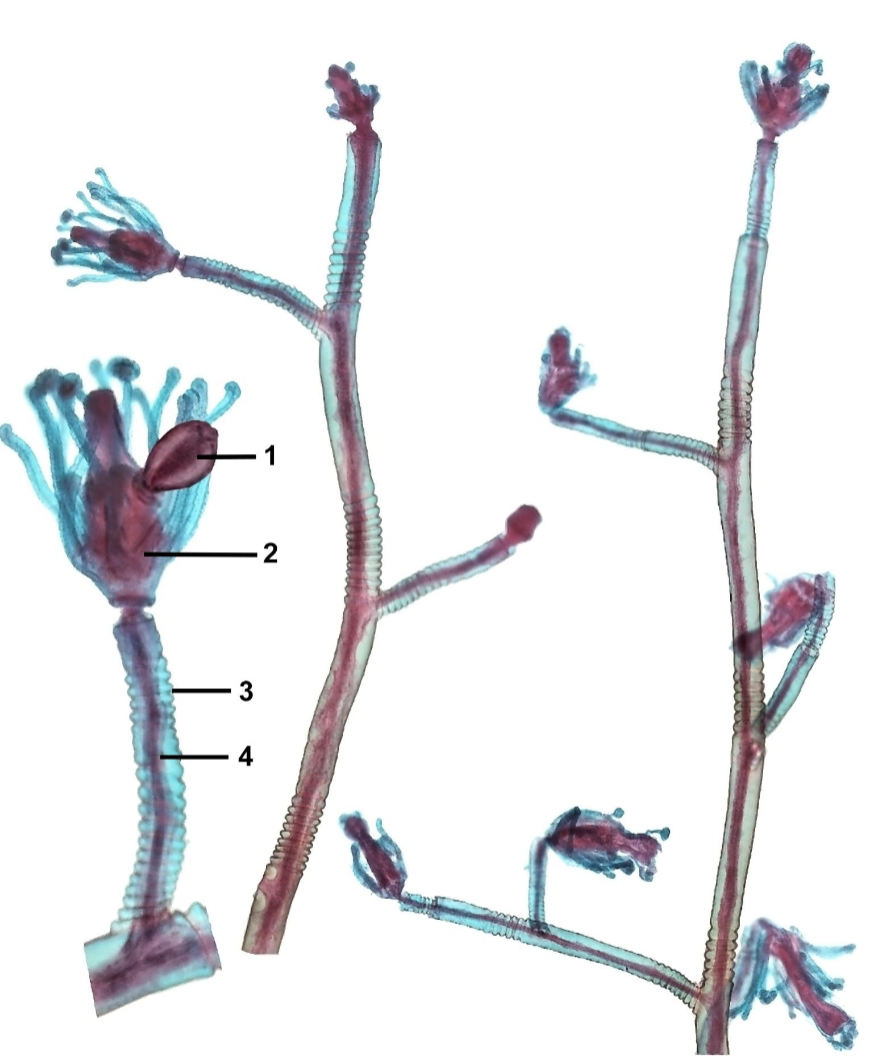
Describe order anthethocata. What class is it in?
Polyp = benthic and colonial
Athecate (perisarc stops at polyp)
Specialized zooids:
Dactylzooid - defense
Gonozooid - produces medusa
Gastrozooid - digestion
Medusa:
taller than wide
planktonic
tentacles on margin
margin NOT lobed
No statocyst
gonads on manubrium
They are in class Hydrozoa.
Describe order Leptothecata. What class is it in?
Polyp = benthic, colonial
Thecate - perisarc covers polyp
Medusa:
Sometimes absent
Wider than tall
Tentacles on margin
Margin not lobed
Statocyst present
Gonads on radial canals
Class Hydrozoa
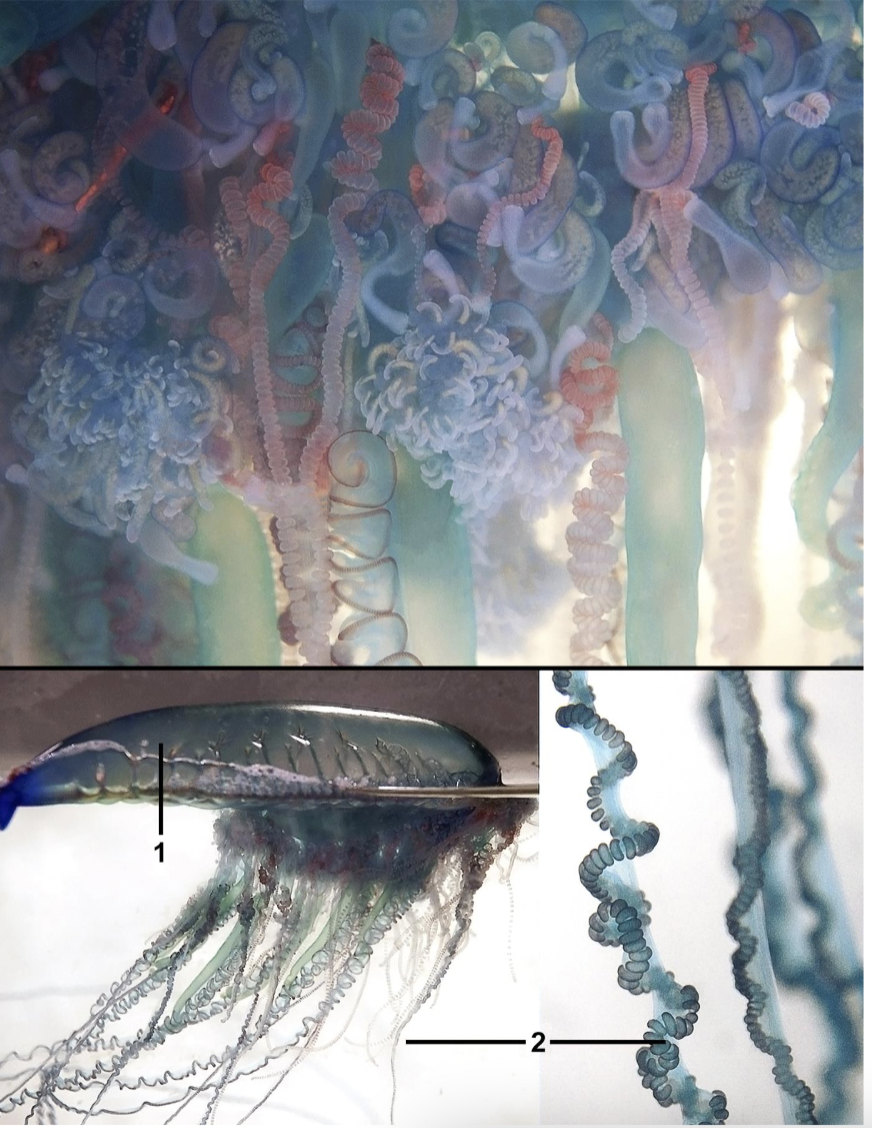
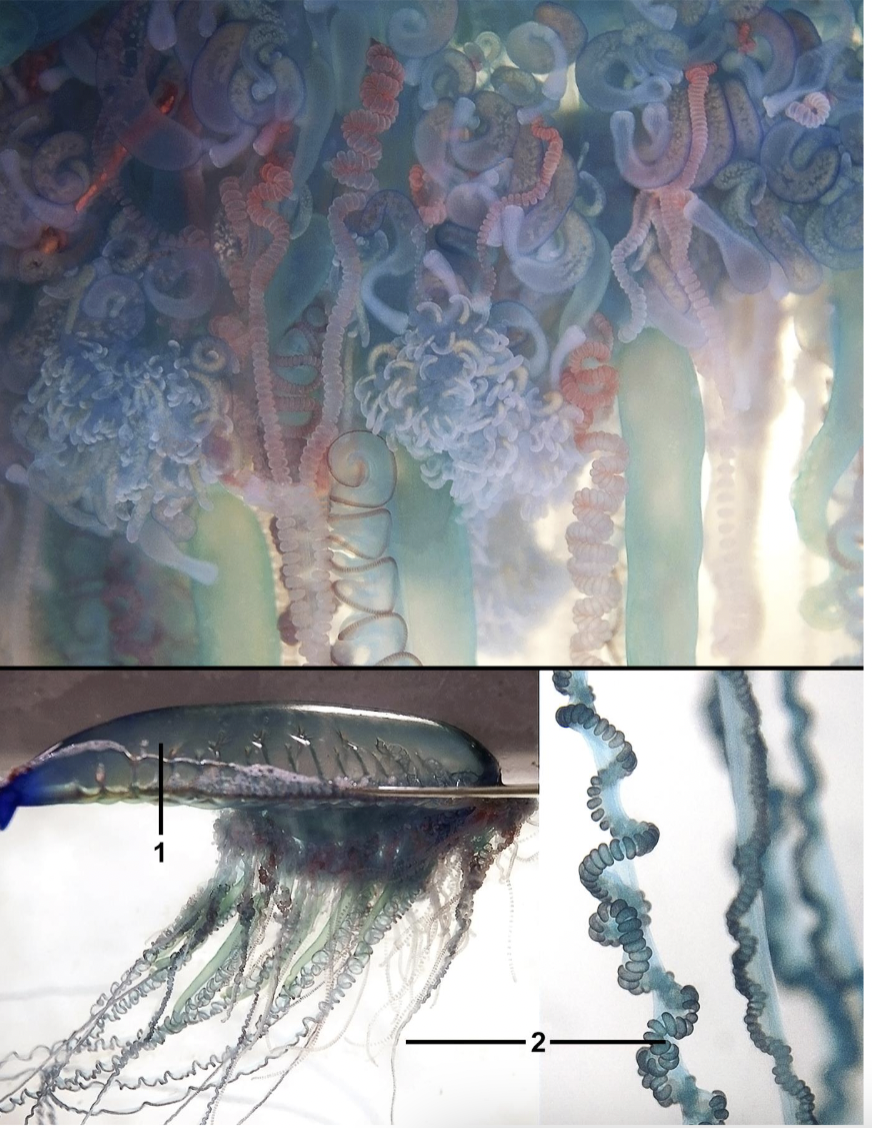
Describe order Siphonophorae within Class Hydrozoa
Polyp and medusa present
Colonial
Swim/float
Up to several m
Zooids (repeating units)
Gastrozooid - feeding
Tentacle has branching called tentilla
Palpons - internal water/food movement
Gonozooids - produce medusa
Bracts - protection
Nectophore/nectosome - swimming bell
Pneumatophore - float
Larva = siphonula
Describe suborder cystonectae. How is it classified?
Phylum Cnidaria —> Subphylum Medusozoa —> Class Hydrozoa —>Order Siphonophorae —> Suborder Cystonectae
Nectosome absent
Pneumatophore present
Bracts absent
Describe suborder codonophora. How is it classified?
Phylum Cnidaria —> Subphylum Medusozoa —> Class Hydrozoa —>Order Siphonophorae —> Suborder codonophora
Nectosome present
Pneumatophore small or absent
Bracts present
Big size range
Describe order stauromedusae. How is it classified?
Phylum Cnidaria —> Subphylum Medusozoa —> Class Staurozoa —> Order Stauromedusae
Mesoglea with cells
Gastrodermis with cnidocytes
Polyp = benthic, solitary
Medusa:
Benthic (attached)
8 lobes
Capitate tentacles
Few cm
Life cycle: planula—>stauropolyp—>medusa
Ecology: minor food web
What is cephalization?
When organs and structures are concentrated on the anterior portion of the body, forming a “head”