Chemotherapy Toxicities
1/23
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
24 Terms
Which drugs cause myelosuppression? Which don’t?
All chemotherapy drugs except bleomycin, pegasparagase, and vincristine
What is the nadir?
The lowest point that WBCs and platelets reach, usually occurs at 7-14 days
Cutoffs for neutropenia and severe neutropenia for ANC
Neutropenia <1000 cells/mm3
Severe neutropenia <500 cells/mm3
Granulocyte Colony-Stimulating Factors - MOA and Drugs and Dosing Frequency
Stimulate WBC production in the bone marrow.
Given prophylactically after chemotherapy to reduce the duration and severity of neutropenia
Filgrastim (Neupogen) - Daily
Pegfilgastrim (Neulasta) - Once per chemo cycle
Granulocyte Colony-Stimulating Factors - Side effects and Monitoring
Side effect: Bone pain, splenic rupture
Monitoring: CBC with diff, upper abominal pain
Store in refridgerator
Administer first dose no sooner than 24 hours AFTER chemo start
Febrile neutropenia diagnostic criteria
Fever: Temp >= 38.3C (101F) or 38C for 1 hour
Neutropenia: ANC <500
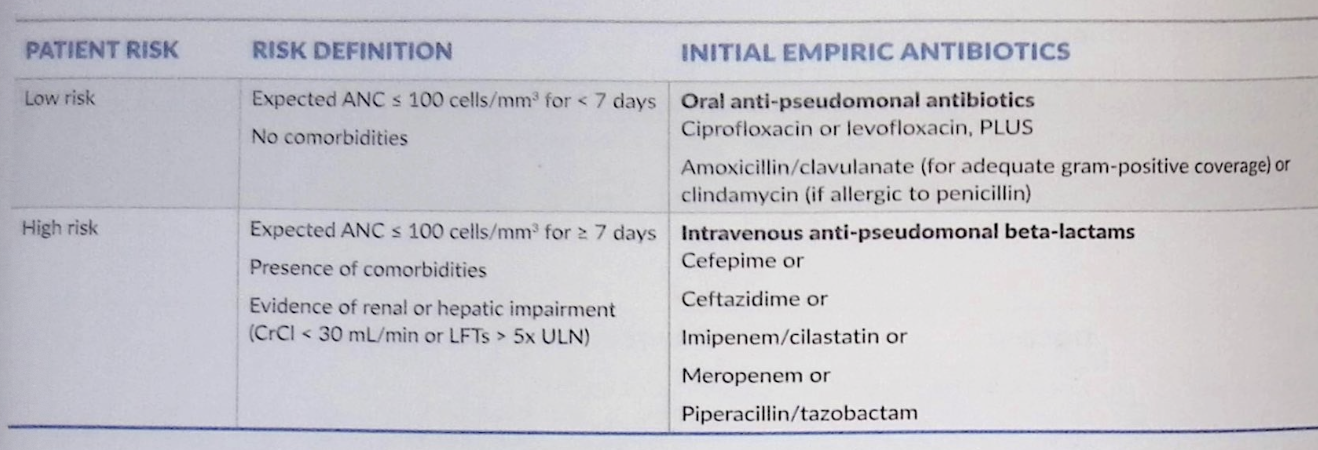
When to start empiric antibiotics for febrile neuotropenia?
For all patients with febrile neutropenia
When to give platelet transfusion for thrombocytopenia?
When platelets reach <10,000 cells/mm3
When to give erythropoiesis-stimulating agent (ESA)?
Patient has a non-myeloid malignancy (e.g., carcinoma, sarcoma) and anemia is due to the effect of myelosuppressive chemotherapy.
Hgb is < 10 g/dL and there is a minimum of two additional months of planned chemotherapy.
The lowest dose needed to maintain a Hgb level sufficient to avoid RBC transfusions is used.
ESA's can shorten survival and increase tumor progression —> not recommended in patients receiving chemotherapy with curative intent
What drugs most commonly cause chemotherapy-induced nausea and vomiting?
Cisplatin, carboplatin, cyclophosphamide, and anthracyclines
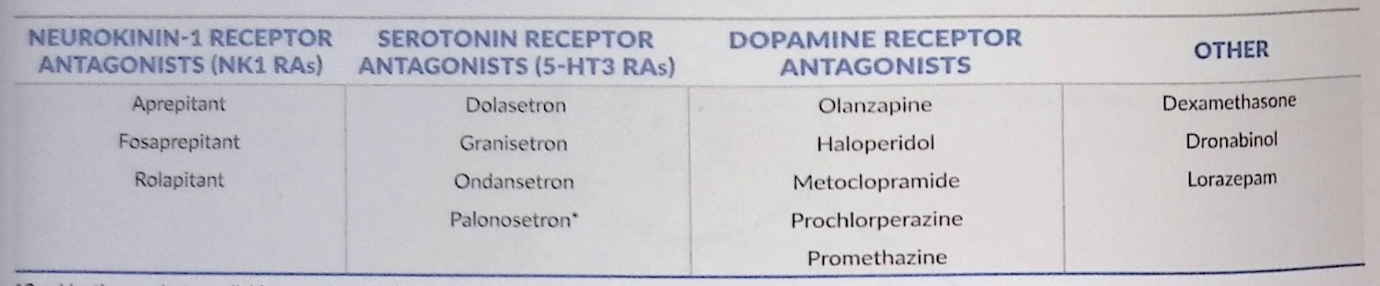
Classes of antiemetics for CINV
Antiemetic regimens for: High emetic risk (cisplatin, antracycline, and cyclophosphamide)
3-4 drugs
Preferred: NK1 RA + 5-HT3 RA + olanzapine + dexamethasone
OR NK1 RA + 5-HT3 RA + dexamethasone
OR Palonosetron + olanzapine + dexamethasone
NK1 RA example (aprepitant)
Antiemetic regimens for: Moderate emetic risk
2 or 3 drugs
NK1 RA + 5-HT3 RA + dexamethasone
5-HT3 RA + dexamethasone
Palonosetron + olanzapine + dexamethasone
Antiemetic regimens for: Low emetic risk
1 drug
5-HT3 RA (dolasetron, granisetron or ondansetron)
Dexamethasone
Metoclopramide
Prochlorperazine
Substance P/Neutokinin01 Receptor Antagonists (NK1 RAs) - Drugs
Aprepitant (Emend)
Fosaprepitant (Emend) - IV
5-HT3 Receptor Antagonists - Drugs, Warnings, Side effects
Ondansetron (Zofran)
Ganisetron (Sancuso)
Palonestron (Aloxi)
Warnings: Dose dependent QT prolongation (limit IV Zofran to 16 mg); Serotonin syndrome
Side effects: Headache, constipation
Dopamine Receptor Antagonists - Drugs
Olanzapine (Zyprexa)
Prochlorperazine
Promethazine
Metoclopramide (Reglan)
Haloperidol (Haldol)
Cannabinoids - Drug and extras
Dronabinol
Marinol capsules C3
Syndros solution C2
Extravasation management - Anthracyclines
apply cold compresses and administer dexrazoxane or topical dimethyl sulfoxide (DMSO)
Extravasation management - Vinca alkaloids
apply warm compresses and administer hyaluronidase
Vaccination notes
Avoid all vaccinations during chemotherapy
When planned, vaccination should precede chemotherapy by 2 or more weeks
What problems can tumor lysis syndrome cause?
Hyperkalemia - arrhythmias
Hyperphosphatemia
Hypocalcemia - anorexia, nausea, seizures
Hyperuricemia - Can damage kidneys
Acute renal failure - due to hyperuricemia or phosphate accumulation
Drugs used for prevention of TLS? How to treat?
Allopurinol (higher doses than gout (400-800 mg/day))
Febuxostat
Rasburicase if severe
Treatment of hypercalcemia of malignancy and MOA
Hydration with NS
IV bisphosphates - inhibits bone reporting by stopping osteoclast function
Zoledronic acid - inhibits bone reporting by stopping osteoclast function
Pamidonate - inhibits bone reporting by stopping osteoclast function
Calcitonin (Miacalcin - inhibibs bone resorption, increase renal calcium excretion
Denosumab (Xgeva) - RANKL