Metabolism
1/23
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
24 Terms
Metabolism
The totality of an organism’s chemical reactions; all anabolic and catabolic rxns in the body
Metabolic Pathway
Begins with a specific molecule and ends with a different product; each step is catalyzed by a specific enzyme
Catabolic Pathway
Release energy by breaking big molecules down to small molecules
Anabolic Pathway
Consume energy by building big molecules from smaller molecules
Forms of Energy
Kinetic Energy
Heat/Thermal Energy
Potential Energy
Chemical Energy
First Law of Thermodynamics
Energy can not be created or destroyed; conservation of energy
Second Law of Thermodynamics
Every energy transfer or transformation increases the disorder (entropy) of the universe (High Entropy = High Disorder)
Spontaneous Reaction
During a spontaneous change, free energy decreases and the stability of a system increases
Biological Order and Disorder
Entropy may decrease in an organism, but the universe’s total entropy increases
Free Energy (ΔG)
Free energy that can do work
Gibb’s Free Energy
-ΔG = Shift Towards Reactants
+ΔG = Shift Towards Products

Exergonic Reaction
Release of Energy; Spontaneous
Endergonic Reaction
Absorbs Free Energy; Nonspontaneous
Energy Coupling
The use of exergonic processes to drive endergonic ones
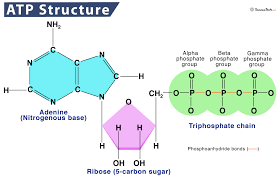
ATP (Adenosine Triphosphate)
The bonds between the phosphate groups of ATP’s tail can be broken via hydrolysis
Energy is released when the terminal phosphate bond is broken
Release of energy comes from the change to a state of lower free energy
Phosphorylated Intermediate
The molecule that receives the phosphate from ATP
Enzyme
A catalytic protein (speeds up a rxn without being consumed)
Activation Energy (Ea)
The initial energy needed to start a chemical reaction; Often supplied in the form of thermal energy that the reactants absorb from their surroundings
Enzyme Activity is Affected By
Temperature (98.6°F (37°C)
pH (Physiological pH = 7.4)
Inhibitors
Cofactors
Inorganic Nonprotein enzyme helpers (Ex: Metals like Mg2+)
Coenzymes
Organic Cofactors (Ex: Vitamins)
Allosteric Regulation
Activators stabilize the active form of an enzyme
Inhibitors stabilize the inactive form of the enzyme
Cooperativity can amplify enzyme activity
Feedback Inhibition
The end product of a metabolic pathway shuts down the pathway
Enzymes for cellular respiration are located in the
Mitochondria