Pediatrics Exam 3
1/53
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
54 Terms
Life threatening GI symptoms/conditions?
Red flags for serious causes?
dehydration, infection, IBD, celiac
poor appetite, weight loss, poor growth, blood/mucous in stool, nocturnal symptoms, pain awakens from sleep
Most common abdominal pain in 6 y.o?
Constipation
Most common abdominal pain cause in 16 y.o?
functional abdominal pain (FAP)
**also think about pregnancy
what do you think about with vomitting in 2 m.o?
Pyloric stenosis
Pyloric stenosis: presentation/sx/exam/treatment
3-12 weeks old
non bilious projectile vomiting after feeds
hungry feeder
PE: olive shapped nontender mobile mass to R of epigastrium
US shows elongated and thick pylorus, upper GI shows string sign
Tx: surgical pyloromytomy
Functional constipation: presentation/sx/exam/treatment
most common cause of abdominal pain in kids
encopresisEncopresis: passage of stool into underwear under 4 y.o
Tx:
disimpaction/clean out (stimulant laxatives)
maintenacne: 3-6 m stool softener, lube, laxative, behavior, diet
weaning meds slow and continue good habits
Celiac Dz: presentation/sx/exam/treatment
sx: diarreah, stearrhea, Fe deficiency
autoimmune, fam hx
PE: short, abd distention, mouth ulcers
Dx: TTG IgA, upper endoscopy with SM biopsy
Tx: gluten-free diet
IBD: presentation/sx/exam/treatment
adolescent; sx: crampy abdominal pain, bloody diarrhea, extraintestinal manifestations
PE: possible perianal abscess/fistula
Dx: positive labs, upper and lower endoscopy w/ biopsy
Tx:
induction to induce remission Ex: exclusive enteral nutrition therapy
Maintenance to prevent inflammation and flares
possible colectomy for UC
Functional abdominal pain: presentation/sx/exam/treatment
most common cause of abdominal pain in adolescents
disorder of gut-brain interaction
Sx: altered bowl habits, abdominal pain relieved with defacation.
Dx: Rome IV criteria. NO + LAB RESULTS
Tx: stress management, psychosocial support, low FODMAP diet, supplements, meds for sx
mild, moderate, severe dehydration presentation and tx
normal PE, active alert, normal vitals, moist mucous membranes: oral rehydration (small sips/4 hrs)
irritable, alert, thirsty, dry mucus membranes: oral rehydration
lethagic, sick, vitals unstable, sunken frontanelle, severely reduced UO: IV fluids (isotonic saline/formula)
**Consider antiemetics (ondansetron) for nausea
GER vs GERD presentation and tx
GER
“happy spitter”
normal in 50% of infants less than 3 mo. peaks at 4m resolved at 12-24 m
Tx: sit upright 20-30 min after feed. smaller, more frequent feeds, avoid overfeed
GERD
irritability, poor feed, poor weight gain
Tx: protein-free milk, UGI imaging to r/o malrotation, 2 wk trial of H2 blocker (famotidine), peds GI
Migraines: presentation, treatment
4-72 hr unilateral/pulsating pain aggravated by activity. Looks sick, improves with sleep
N/V/photophobia
Fam Hx important!!!
association with mental and behavioral health conditions
Tx: CBT, encourage school attendance
#1: Ibuprofen
amitriptyline, topiramate, propranolol, triptans
Tension type HA: presentation, treatment
bilateral pressing/tight “band around head”
NOT aggravated by physical activity
association with mental and behavioral health conditions
Tx: CBT, encourage school attendance
#1: Ibuprofen
amitriptyline, topiramate, propranolol, triptans
Post concussive HA
Fatigue is most common followed by HA
increase risk for depression and anxiety
What is epilepsy? Risk factors? Treatment?
2 unprovoked seizures, 1 unprovoked seizure with 2+ risk factors
Age <1 yr, abnormal PE, development, EEG, MRI and Fam Hx
Tx:
Generalized: Keppra (levetiracetam)
Focal: carbamazepine, oxcarbazepine
status epilepticus: midazolam
Infantile spasms (west syndrome): presentation, treatment
4-8 m
trunk and arm spasms. can lead to developmental regression and risks long term deficits
Tx: high dose steroids, vigabatrin
Lennox-Gastaut syndrome: presentation, treatment
infancy/toddler
mixed seizures that evolve and cause cognitive delay and are often refractory
tx: aggressive meds, diet, surgery, CBD
Benign focal epilepsy (BECTS, Rolandic Epilepsy): presentation, treatment
grade school (8-9 grade)
nocturnal unilateral facial parenthesis spread to ipsilateral arm and leg
usually outgrow
Absence Epilepsy: presentation, treatment
brief staring spells
childhood (5-7 yr): outgrow
juvenile (>10 yr): overlaps with juvenile myoclonic epilepsy TREAT!
Juvenile myoclonic epilepsy: presentation, treatment
most common cause of new onset GTC seizures in teens
Triggers: sleep deprivation, EtoH, menses, flashing lights, hereditary
often dont remit
Reflex epilepsy: presentation, treatment
triggered by stimulus: flashing lights, reading, music, video games
panayiotopoulos syndrome
4-5 yrs
occipital epilepsy
non-convulsive ictal sx: N/V, CV and thermal dysregulation
does NOT impact development
Febrile seizures: age, workup? management
6m-6y
only work up if complex: EEG, neuroimaging, referral to peds
support and monitor
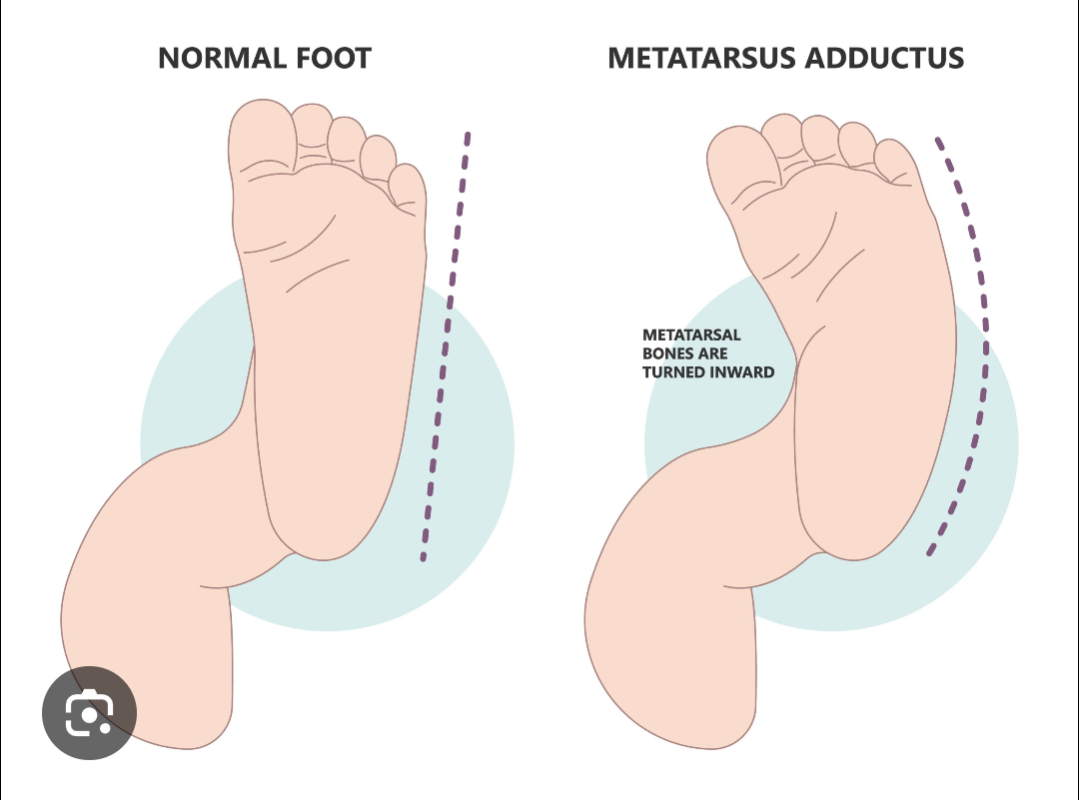
Metatarsus adductus: presentation, management
“packaging issue”
metatarsals leaning medially
PE: heel bisector line
often self correcting (flexible), but refer to ortho if rigid
congenital talipes equinovarus (clubfoot): presentation, management
CAVE (midfoot spin): Cavus/high arch, Adductus Varus/heel curl, Equinus/foot points downward
refer to ortho: serial casting (ponseti method), tenotomy, boots and bars. surgery is NOT first line due to development of OA
tibial torsion (shin bone twist): presentation, management
presents with in-toeing/out-toeing
brace,PT, orthotics DO NOT WORK
refer to surg if 10 yo and still tripping
Os Good Shlatter: presentation, management
painful tibial tubercle in adolescent and resolves after growth
Tx: streatching/quad flexibility, NSAIDS, ice, patellar tendon strap
can continue to play spots
Patellofemoral syndrome : presentation, management
vague diffuse pain and timing, C sign. Cant localize with one finger
Developmental dysplasia of hip: sx, tx
instability/loosness of hip joint.
Risk factors: Female, first born, fam hx, frank breech
sx: +ortolani'/barlow, hip click/clink when diapering, leg length discrepancies, limited hip motion, gait abnormalities
Tx: pavlik harness <6m spica cast >6m surgery if late presentation
leg calve perthes: sx, tx
idiopathic avascular necrosis of femoral head, progressive
Boys 4-7 yo with painless limp
hip/knee pain worse with activites
semiurgent referrel
Slipped capital femoral epiphysis (SCFE): sx, tx
displacement of femoral head through growth plate “ice cream fallen off the cone”
painful limp, often knee pain
during adolscence, male, obese
surgical emergency: scew to stop progression
Scoliosis Who? screen?
F 10-22 y, M 13 yr
adams forward bending test, Cobb angle scoliosis vie x ray
Nursemaids elblow
pull injury
annular ligament subluxation,
Tx: reduce
Croup: caused by? sx, presentation, dx, tx
6m-3y
acute laryngotracheitis (upper airway inflammation)
parainfluenza virus
barking cough, stridor, worse at night, steeple sign on xray
Tx: dexamethasone, neb epi, cool air
Acute bronchitis: sx, presentation, dx, tx
inflammation of large airways, viral cause
acute cough, normal exam (r/o other things)
Tx: supportive (expect lingering cough)
Bronchiolitis: caused by? sx, presentation, dx, tx
infection of small airways. 3-6m.o
RSV
increased respiratory effort
Tx: supportive, hydration, resp support, suction, antipyretics, monitor status (admit if low O2)
Community acquired pneumonia: sx, presentation, dx, tx
leading cause of death in kids under 5
strep pneumo
fever, cough
Tx: amoxy, azithro if atypical, vaccine, f/u in 2-3 d to ensure improvement
Urinary incontinence over 5 yo management
behavioral
enuresis alarm
desmopressin (DDAVP)
contraindications to circumcision? Advantages?
hypospadias, buried penis, hydroceles
reduced risk of cancer, STI, and UTIs (treat with cephalexin, Augmentin, TMP/SMX)
Varicella: sx, presentation, tx
“dew drops on a rose petal”
1-2 day flu prodrome→rash→resolves in 7-10d
vescicles on erythematous base face to extremeties. in different stages
Tx: acycolvir, anti inflammatory, antihistimines, calamine
Meales: caused by? sx, presentation, tx
paramyxovirus
COUGH, CORYZA, CONJUNCTIVITIS
URI prodrome, high fever, koplik spots then rash
maculopapular morbilliform brick red rash. resolves in 7-10d
supportive care
Erythema infectiosum (5th dz): caused by? sx, presentation, tx
Parvovirus
“slapped cheek appearance”
nonspecific prodrome, fever→rash 1-3 weeks to resolve
red flushed face with circumoral pallor→lacy reticular rash on body
Supportive care
Roseola infantum: caused by? sx, presentation, tx
HHV6-7
3 days high fever→rash when fever stops
pink maculopapular blancable rash starts on trunk/extremeties→face
Supportive care
Hand, foot, mouth: caused by? sx, presentation, tx
coxsackie
fever and URI prodrome
painful vesicular lesions on reddened base with erythmatous halo in oral cavity→lesions on hands, face, feet, genitals, including palms and soles
supportive care
Diaper dermatitis: what is it? what causes it? presentation? complication? management?
Irritant contact dermatitis occurs on convex surfaces in contact with the diaper. spare skin folds
caused by moisture, friction, fecal enzymatic activity
mild asymptomatic papule to severe extensive erythema, erosions, nodules
could lead to candida if not treated
Management:
frequent change, air, clean, powder
barrier ointment for mild to moderate
1% hydrocortisone for severe
candida (beefy red plaques w/ satellite papules involving skin folds): clotrimazole
Neuroblastoma: age, presentation, dx,
0-2 y
abnormal neural crest cells from adrenal medulla and sympathetic ganglia
const sx, blueberry muffin rash, horner syndrome, racoon eyes
Dx: urine metabolites MRI, biopsy
acute lymphoblastic leukemia (ALL): age, presentation, dx, tx
2-5 yo
pancytopenia, fever, bruise, pallor, hepatosplenomegaly, lymphadenopathy
dx: bone marrow biopsy
tx: chemo
osteosarcoma: age, presentation, dx, tx
adolescent
metaphysis of long bone (distal femur)
sx:localized bone pain, worse at night, joint swell
sunburn appearence on x ray
Dx: biopsy
Tx: chemo→surg→chemo
Ewing sarcoma: age, presentation, dx, tx
adolscent
diaphysis of long bone (proximal femur)
bone pain, swell, systmic sx
onion peel appearence on x ray
Tx: chemo→surg if possible
Hodgekins lymphoma: age, presentation, dx, tx
asymptomatic painless lymphadenopathy, mediastinal mass, B symptoms
Reed-Sternberg “owl eye” cells
dx: lympth node biopsy
Tx: chemo
long term sequelae of childhood cancer?
neurologic
cardiac
endocrine: imparied growth, obesity, thyroid dys, fertility issues
secondary malignancies
cystic fibrosis: patho, manifestations, dx, management
autosomal recessive in CFTR gene leads to abnormal Cl and H2O transport across exocrine glands, causing thick, viscous secretions
GI: pancreatic insufficiency, steatorrhea, rectal prolapse, prolonged jaundice of infancy,
Reproductive: sterility (m), congenitcal absence of vas deferens, decrease f fertility with thicker cervial mucus
Increased salt in sweat
Resp: bronchiectasis, recurrent pulm infx, sinisitus, nasal polyps
Dx: elevated sweat Cl test
Management: high fat diet, with fat soluble vitamins (ADEK), pancreatic enzyme replacement, airway clearance, inhaled meds, systemic antibiotics for pneumonia, (CFTR protien modulators)
Childhood poverty knock it off. How to mitigate?
21% of kids live below the poverty line
Medicaid, free clinics, supplemental nutrition assistance program, section 8 vouchers for housing, earned income tax credit, paid fam leave
limitations of the federal poverty level?
outdated! does not account for the regional cost of living diff, changes in food, other resources