CH 9-11 Environmental Science
5.0(1)
5.0(1)
Card Sorting
1/23
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Study Analytics
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
24 Terms
1
New cards
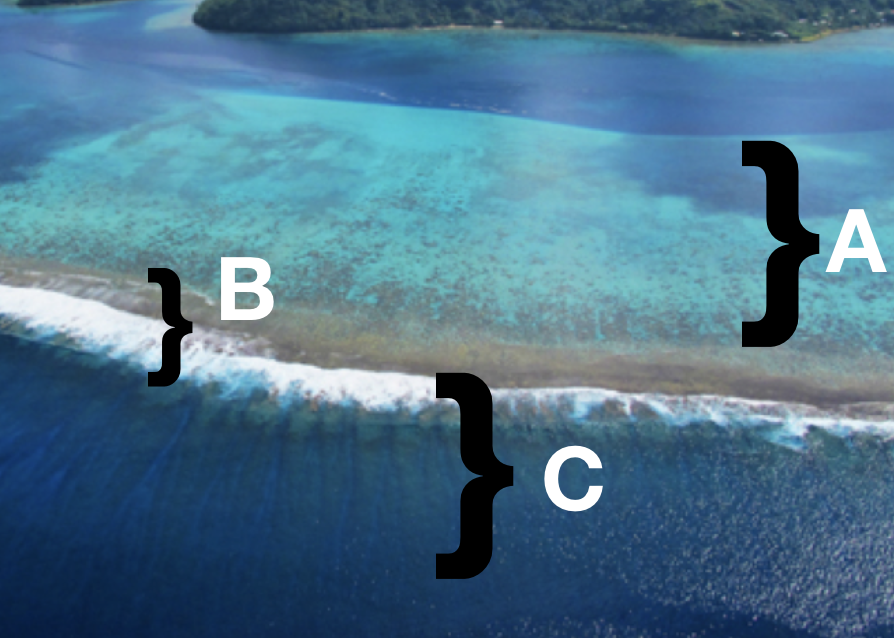
What are 3 parts of the reef?
(A)= Reef Flat (B)= Reef Crest (C)= Reef Front or Fore Reef
2
New cards
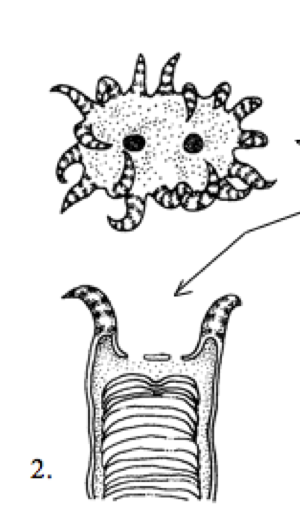
What type of growth is this?
Intratentacular growth
3
New cards
Reef flat
shallow part between the shore and the reef crust. Bottom is mostly sand and coral rubble, with nay reef framework filled in. Often see sea grasses and sea cucumbers. As water gets deeper, begin to see staghorn corals and damselfishes. (plants of the reef flat caulerpa, mastophora and hydroclathrus)
4
New cards
Reef Crest
where waves break at edge of reef, may be exposed at very low tide. live coral is essentially intertidal, so often has algae on the actual crest. is higher than the reef flat.
5
New cards
Reef Front or Fore Reef
coral slopes steeply into deep water. Often very productive, with lots of fishes.
6
New cards
Where does the sand from beaches, reef flats, and deep reef slopes come from?
1. Coral skeletons
2. Shells
3. Calcified and coralline algae (e.g. Halimeda)
4. Star sand (foraimiferans)
2. Shells
3. Calcified and coralline algae (e.g. Halimeda)
4. Star sand (foraimiferans)
7
New cards
Bio-erosion
wearing away of rock by grazing organisms (parrotfish, limpets, chitons . (takes place at sea level, so indicates where sea level used to be)
8
New cards
Corals are Colonial
Usually asexual reproduction. Share common "skin" and skeleton calcium carbonate. Growth of the colony occurs in 2 ways extratentacular growth(outside tentacles) and intratentacular growth(inside tentacles)
9
New cards
Ciguatera
a type of food poisoning that comes from eating reef fish. Is rarely fatal, but produces unpleasant and long-lasting digestive and neurological symptoms. The most distinctive symptom is a reversal of hot and cold sensations. the toxin comes from Gambierdiscus toxicus. Toxins dissolve in fats and lipids. Held in animal tissues.
10
New cards
Biological magnification
toxic concentration increases as you move higher up the food chain.
11
New cards
What is DDT?
Dichloro-diphenyl-trichloroethane (DDT) is a insecticide that caused a problem to populations of predatory birds, such as eagles, pelicans and hawks.
12
New cards
What are the values of reefs?
mnemonic aid(i.t.s.p.b.s)
1. Important fisheries
2. Tourism
3. Souvenirs
4. Protection from waves
5. Building materials
6. Sources of potential drugs
1. Important fisheries
2. Tourism
3. Souvenirs
4. Protection from waves
5. Building materials
6. Sources of potential drugs
13
New cards
What are the classifications of the open ocean?
1. The depth
2. How far from shore
3. Penetration of sunlight
2. How far from shore
3. Penetration of sunlight
14
New cards
3 types of hydrothermal vents
1. Black smokers (sea floor spreading)
2. White smokers (plate subduction)
3. Cold seeps
2. White smokers (plate subduction)
3. Cold seeps
15
New cards
Black smokers (sea floor spreading)
Release hot water (360-400 degrees Celsius) does not turn into steam because of pressure. Water is saturated with H2(Hydrogen), CH4 (Methane) and minerals. Cold seawater seeps into the crust and is superheated, dissolves minerals ( mostly sulfides and iron) and rises out the main chimney.
16
New cards
White smokers(plate subduction)
Release hot water (40-90 degrees Celsius) does not turn in steam because of pressure.
17
New cards
Hydrothermal vents ecosystems
depends on chemicals in the water for both energy and nutrients. Primary producers are bacteria. Both free-living and endosymbionts. Not all organisms are invertebrates (
18
New cards
What are the 6 major causes of extinction?
mnemonic aid (HOPNIC)
1.Habitat destruction
2. Overharvesting
3. Pesticides
4. Natural disasters
5. Invasive species
6. Climate change
1.Habitat destruction
2. Overharvesting
3. Pesticides
4. Natural disasters
5. Invasive species
6. Climate change
19
New cards
What are the 3 strategies in dealing with pest?
1. Biological control
2. Pesticides
3. Integrates pest management
2. Pesticides
3. Integrates pest management
20
New cards
Pests
plants, animals, or microorganisms ( diseases) that harm people value, such as crops or landscapes. (they rise rapidly, weeds for plants, plagues for if they are animals, and epidemics if they are diseases)
21
New cards
Chain of love (latana)
tendency to form impenetrable thorny leaves, invade pasture land, and compete with agricultural crops for water, nutrients, and light.
22
New cards
Biological control
to use a natural predator or diseases of the pest organisms to cut down the population.
23
New cards
Pesticides
essential to maintaining high agricultural productivity in mechanized, single crop agriculture. When sprayed, little of it gets to the target species. Much of it drifts onto other vegetation, people, and other nontarget species or washes into rivers and lakes.
24
New cards
Endangered species
Those whose populations have declined so low that they are in danger of becoming extinct.