Chapter 7, Lesson 1: Tissues and Organs of the Skeletal System
1/22
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Flashcards from Chapter 7, Lesson 1 of McGraw Hill Anatomy and Physiology, Ninth Edition, by Kenneth S. Saladin.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
23 Terms
Skeletal system
System of the body composed of bones, cartilages, ligaments, and tendons
Cartilage
Connective tissue that covers the surface of mature bones
Ligaments
Connective tissue that links bones at joints
Tendons
Connective tissue that ties muscles to bones
Skeleton functions
Support and protection of the body’s organs
Movement alongside muscles
Electrolyte and acid-base balance by leveling calcium, phosphate, and carbonate salt levels
Blood formation to support the immune system
Bone (osseous tissue)
The connective tissue hardened by calcium phosphate and other minerals
Minerlization (calcification)
The hardening of bone
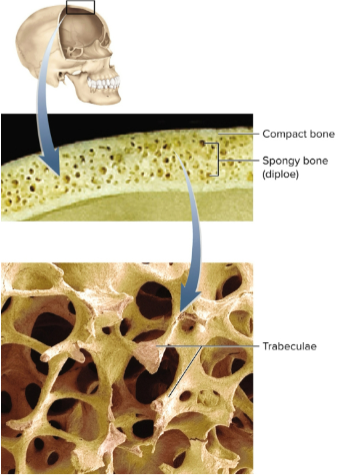
Flat bones
Thin, curved bones that protect soft organs
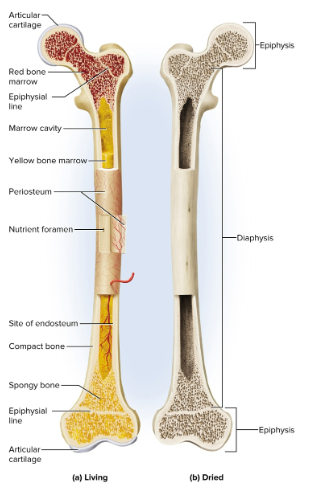
Long bones
Bones that are longer than they are wide and are acted upon as levers for movement by muscle
Short bones
Bones that are approximately equal in length and width that glide across one another in multiple directions
Irregular bones
Bone shapes that do not fit into other categories
Compact bone (dense or cortical)
The dense outer shell of the bone; 75% of the skeleton
Spongy bone
Loosely organized bone tissue found at the end of long bones; 25% of the skeleton
Diaphyses
The middle of long bones; it provides leverage and contains the marrow cavity
Marrow cavity
The space in the diaphysis of a long bone that contains bone marrow
Epiphyses
Enlarged ends of long bones, strengthening joints and anchoring ligaments and tendons
Articular cartilage
Layer of hyaline cartilage that covers the joint surface to allow movement
Nutrient foramina
The minute holes in the bone surface that allow blood vessels to penetrate
Periosteum
The external sheath covering most of bone made of collagen and bone-forming cells
Endosteum
The thin layer of reticular connective tissue inside the marrow cavity; helps dissolve and create osseous tissue as needed
Epiphysial plate (growth plate)
The area of hyaline cartilage that enables the growth in length in childrens’ bones and creates a scar in adults
Features of long bones
Epiphyses and diapheses
Compact and spongy bone
Marrow cavity
Articular cartilage
Perosteum
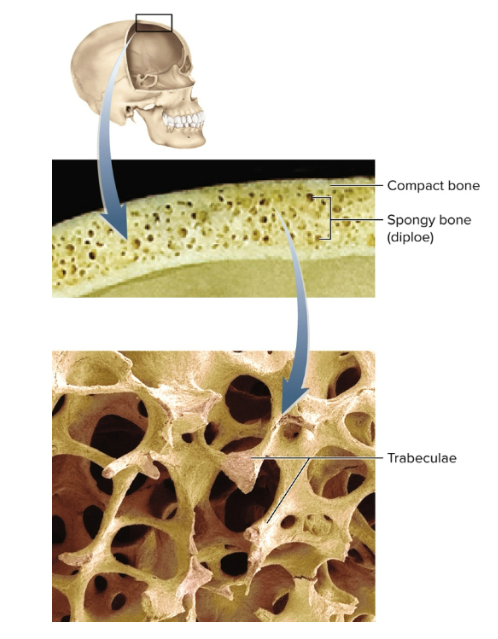
Features of flat bones
Sandwich-like construction of two layers of compact bone with a middle layer of spongy bone
Diploe, or the spongy middle layer that absorbs shock and has marrow spaces lined with endosteum