Meteorology and Weather Recognition
1/80
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
81 Terms
What is an isobar?
An isobar is a line on a meteorologic chart that joins places of equal sea
level pressure.
What is an isotherm?
line joining places of the same mean temperat
specific heat capacity?
ability of a material to hold thermalJheat
Describe TAT.
total air temperature indicated on the air temperature instrument;
What is a temperature inversion/layer?
occurs when air closest to the ground, or even the ground itself, is cooler than the air above it, where temperature increases with height
inversion layer is the heighUaltitude where the air temperature changes from the temperature increasing with height (i.e., a temperature inversion) to a normal decrease in temperature with height state.
What is an isothermal layer?
air remains at the same temperature through a vertical section of the atmosphere
What is the adiabatic process?
heat is neither added nor removed from a system,
compressing air increases its temperature, and decompressing it (expansion) reduces its temperature.
What is ELR? Environmental lapse rate
rate of temperature change with height of the general surrounding atmosphere.
2°C per 1000 ft of height/ altitude gained.
What is DALR? and SALR? Dry/ Wet adiabatic lapse rate
dry air drop of 3°C per 1000ft of he ighValti tude gained.
wet air drop 1.5 per 1000ft
Explain humidity/relative humidity.
amount of water vapor present in a parcel of air compared with the maximum amount it can support
How does air temperature affect relative humidity?
warm air is able to hold more water
What is dewpoint?
air becomes saturated, relative humidity is 100 percent.
How is the height of a cloud base determined?
difference between the dewpoint temperature and the ground temperature divided by the appropriate lapse rate per 1000 ft

shape of cumulus clouds?
flat bases and round tops
How are cloud types classified?
1. Curriform, or fibrous
2. Cumuliform, or heaped
3. Stratiform, or layered
4. Nimbus, or rain-bearing
further subdivided with the following prefixed names according to the level of their base above mean sea level (MSL)
1. Cirro, or high-level cloud: (cloud base> 16,500-20,000 ft
2. Alto, or medium-level cloud: cloud base> 6500 ft
3. No prefix, for low-level clouds: cloud base < 6500 ft
If cumulus clouds were present in the morning, what would you expect later?
Cumulonimbus clouds (CBs).
What is mist and fog?
parcels of low-level air in contact with the ground that have small suspended water droplets
What are the different types of fog?
1. Radiation fog
2. Advection fog, including sea fog
3. Frontal fog, including hill fog
How is radiation fog formed
cloudless nights, high humidity, earth loose hear through radiation
How is advection fog formed
warm body of air moving horizontally to low lying areas.
frontal fog
forms in cold air ahead of a warm occluded front
What is dew, and how is it formed?
same as for radiation fog except for the lower or nil wind (needs 2 knots of light winds)
What is frost, and how is it formed?
frozen water cover on the earth's surface that is formed in the same manner as dew except that the earth's surface has a subzero temperature that causes the water droplets that have condensed out of the air to freeze on the ground.
What is virga?
rain that falls from the base of a cloud but evaporates at a lower level in drier warmer air before it reaches the ground. This is a sign of a temperature inversion,
Describe the formation of a thunderstorm.
DEVELOPING STAGE (updrafts)
1. A high moisture content in the air.
2. A trigger lifting action
a. Convection
b. Turbulence
c. Frontal
d. Orographic
3. Adiabatic cooling of the rising air.
4. A highly unstable atmosphere so that once the air starts to rise, it will continue rising.
MATURE STAGE (downdrafts)
water drops fall through
DECAYING STAGE (strong windshear)
end of thunderstorm marked by end of coninuous rain
How are thunderstorms a hazard to aviation?
severe windshear
severe turbulence
Severe icing, especially clear ice formed from supercooled water droplets
Airframe structural damage from hail
Reduced visibility
Lightning strikes,
Radio communication
When is lightning most likely to occur?
outside air temperature
(OAT) is + 10°C to -10°C
What is wind?
movement of air driven initially by a difference in pressure, then influenced further by rotation forces, temperature and surface friction
How is wind described or expressed?
Direction and speed (strength)
Describe a veering and backing wind.
when wind changes direction to clockwise or anti clockwise respectively
What is the pressure gradient force
natural force generated by a difference in pressure across a horizontal distance. EG gradient between 2 isobars
What is the coriolis force
the ‘change’ in direction of the wind due to the rotating earth surface.
What is the geostrophic wind?
parallel to straight isobars with a low-pressure system to its
left
What is a gradient wind?
wind that blows around the curved isobars common to circular low- or high-pressure patterns
What is a thermal wind, and how is it generated?
wind generated by a difference in temperature
What is a jetstream?
narrow bands of high-speed upper thermal winds at very high altitudes.
can find it when thermal gradients are high enough
Describe the characteristics of a surface wind.
wind weakens in strength comapred with the free air at 200gt
Describe the diurnal variation of the surface wind.
surface wind by day will resemble the gradient wind more closely than the surface wind at night
Why is the surface wind important to pilots?
effects aircraft during takeoffs and landings.
What are trade winds?
steady and predictable surface winds that rarely exceed 15 knots at the surface but can extend up to 10,000 ft
sea and land breeze?
sea in the day, land in the night
What is the fohn wind effect?
when air is cooled as it is forced to rise over
high ground
What is a katabatic/anabatic wind?
A katabatic wind is a local valley wind that flows down the side of a hill
An anabatic wind is a local valley wind that flows up the side of
a hill.
What is a pressure system?
circulating airmass that is classified as either a low or high, which relates to the direction of pressure change toward the center of the airmass at the surface, i.e., gets lower or higher.
Describe the characteristics of a low and high-pressure system.
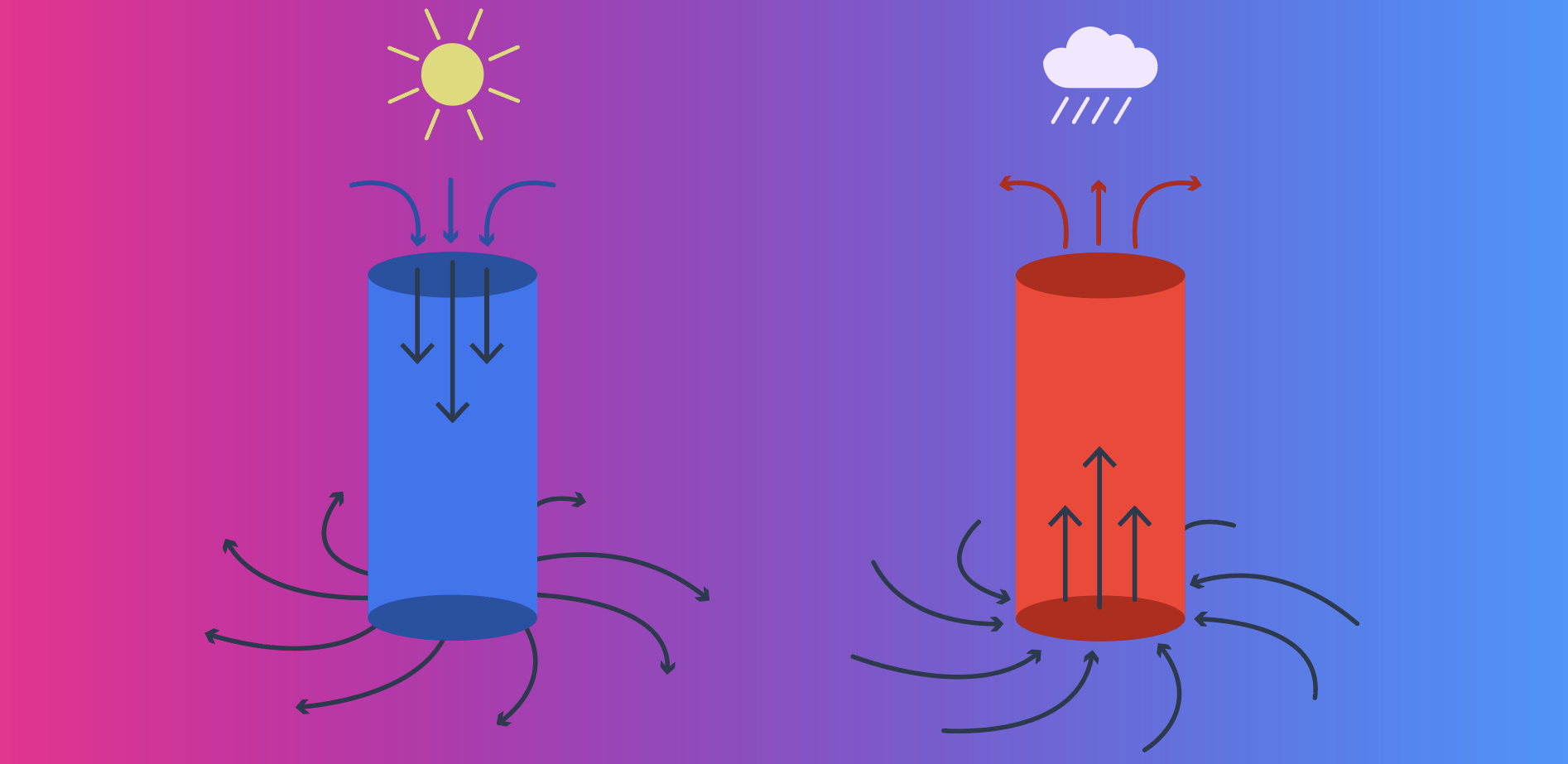
Describe the weather associated with a depression. (low pressure system)
1. Cloud formation
2. Visibility may be good
3. Moderate to strong winds are present.
4. Frontal weather is present because fronts are associated with lowpressure systems;
What is a trough?
line of extended low pressure
Describe the weather associated with a high-pressure system.
1. Clear upper skies with little or no low-level cloud formation and pre-cipitation.
2. Light winds. because weak pressure gradient
3. Possible poor visibility at low levels. becuase descending air may bring particles down
What is a ridge?
U-shaped extension to a high-pressure system.
What is a front?
boundary between two different air masses.
What is a warm front?
where the warmer, less dense air mass rises up and replaces at altitude (slides over) the colder air mass at the surface.
What is a cold front?
colder, denser air mass undercuts and replaces the wanner preceding air mass from the surface upward (slides under).
Why does a warm front move slower than a cold front?
because of the tendency of the wann air (in the wann front) to rise up and slide over the cold, more resistant, denser air (mass) in front of it.
What is an occluded front?
cold front moves faster than the warm front, and therefore, the cold front inevitably will catch up with the warm front.
What is turbulence?
eddy motions in the atmosphere, vertical gusts
The two main forms of vertical turbulence
1. Convection turbulence, caused by solar radiation heating the ground and producing rising thermal currents
2. Obstruction and orographic (terrain-generated) turbulence
horizontal turbulence?
1. J etstreams
2. Wake turbulence
What causes surface turbulence?
surface wind being blown over and around surface obstacles
What is windshear
variation of wind speed and/or direction
Where do you find windshear?
low levels, i.e., below 3000 ft.. eg low-level windshear (wind shear on final approach)
What is a microburst?
severe downdraft, i.e., vertical wind, emanating from the base of a cumulonimbus cloud during a thunderstorm.
5 km across, and often centered in the middle of a thunderstorm,
severe form of windshear.
What are the indications of a microburst?
1. Mature cumulonimbus clouds with thunderstorm activity
2. Roll cloud formation around a cumulonimbus cloud
3. Virga rain. Rain that evaporates before it reaches the ground absorbs latent heat out of the surrounding air
What do lenticular clouds indicate?
(lens-shaped) clouds indicate standing (mountain) wave
clear air turbulence (CAT).
What is wake turbulence?
phenomenon of disturbed airflow; i.e., wing-tip vortices
serious hazard to lighter aircraft following heavier aircraft.
What is sublimation?
turning water vapor immediat.ely into ice
when the dewpoint/actual temperature is less than O°C. (a type of icing)
What are supercooled water droplets (SWDs)?
small liquid water drops well below the normal freez-ing point of water (O°C).
freeze only partially on contact with a colder, subzero surface
it in turn freezes progressively. This can cause long trails of ice to build up on and from the leading edges,
What conditions present an icing risk?
water drops that are present in clouds and as rain
What hazards to aviation does icing cause?
1. Adverse aerodynamic performance effects.
2. Control surface effects.
3. Increase in aircraft weight effects.
4. Reduced engine power
5. Vent blockage effects.
6. Degraded navigation and radio communication effects.
What is carburetor icing?
Ice formation can occur in the engine induction system and in the carburetor of piston engines, particularly in the venturi and around the throttle valve, where the air acceleration produces drop by abour 25°C
What is smog, and how is it formed?
combination of smoke (and/or other airborne particles) and fog.
What is the thermal equator?
position of the maximum thermal temper-ature around the earth's surface
What is the ITCZ?
converging air masses meet near the thermal equator.
What are tropical revolving storms?
deep, intense depressions, i.e.,lows, found in equatorial regions around the intertropical convergence zone (ITCZ).
What is an AIRMET?
Textual advisory of weather less hazardous than sigmet
A. Sierra (see) - IFR conditions, mountain obscurations
B. Tango (turbulence) - Moderate turbulence, low level wind shear, winds 30kts>
C. Zulu - Icing & freezing level heights
What are METARs?
Surface observation reports
1. Special, any time, critical info/ aircraft mishaps/ rapid weather (SPECI)
2. Routine, hourly report
What is a SIGMET?
Significant meteorological report 4rs
a. Severe icing, not related to thunderstorm
B. severe turbulence not related to thunderstorm
C. widespread dust storms lowering visibility
D. volcanic ash (valid 6hrs)
E. valid up 4hrs
What are SPECIs?
Special, any time, critical info/ aircraft mishaps/ rapid weather
What is ATIS?
Automatic Terminal Information Service (ATIS)
What is VOLMET?
continuous broadcast on a VHF/HF frequency
1. The actual weather report
2. The landing forecast
3. A forecast trend for the 2 hours following
4. A SIGMET
What is a TAF?
coded routine weather fore- cast for an aerodrome.
METAR but forecasted
go and learn the metar codes
go and learn the metar codes