Capital Budgeting
1/55
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
56 Terms
– long-term commitment of significant funds to meet certain objectives such as acquiring additional plant assets for business expansion.
CAPITAL INVESTMENT
– projects that are evaluated individually against predetermined corporate standard of acceptability.
INDEPENDENT CAPITAL INVESTMENT (for SCREENING DECISIONS)
MUTUALLY EXCLUSIVE CAPITAL INVESTMENT (for PREFERENCE DECISIONS) –
projects require choosing from among alternatives.
process of measuring, evaluating, and selecting capital investments.
CAPITAL BUDGETING
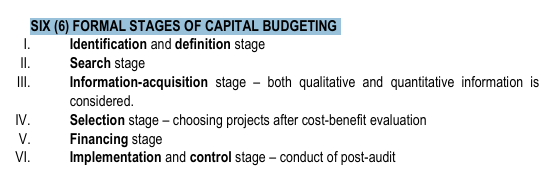
SIX (6) FORMAL STAGES OF CAPITAL BUDGETING
Identification and definition stage
search stage
information acquisition
selection stage
financing stage
implementation and control stage
Primarily computed for investment decision-making purposes.
Refer to COST (cash outflows) LESS SAVINGS (cash inflows) incidental to the acquisition of the capital investment projects.
NET INVESTMENTS
CAPITAL INVESTMENT FACTORS
Cost and savings
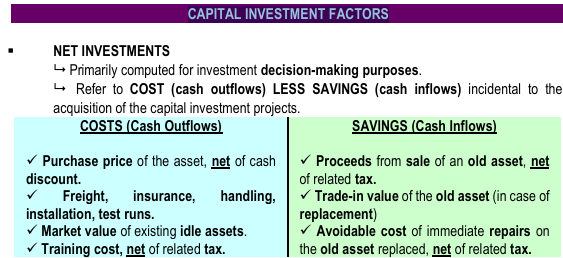
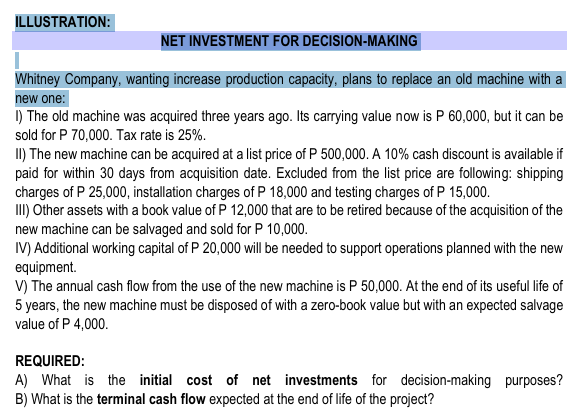
ILLUSTRATION: NET INVESTMENT FOR DECISION-MAKING
Whitney Company, wanting increase production capacity, plans to replace an old machine with a new one:
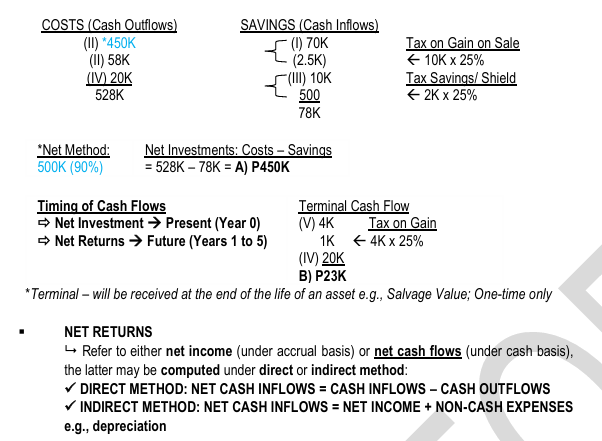
ILLUSTRATION NET RETURNS – INCREASE IN REVENUES
Mariah Cinema plans to install coffee vending machines costing P 200,000. Annual sales of coffee are estimated to be 10,000 cups to be sold for P 15 per cup. Variable costs are estimated at P 6 per cup, while incremental fixed cash costs, excluding depreciation, at P 20,000 per year. The machines are expected to have a service life of 5 years, with no salvage value. Depreciation will be computed on a straight-line basis. The company’s income tax rate is 30%.
REQUIRED: Determine the following:
A) The increase in annual net income.
B) The annual net cash inflows that will be generated by the project.
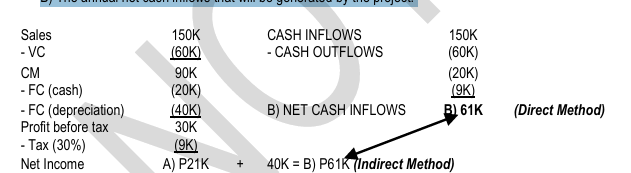
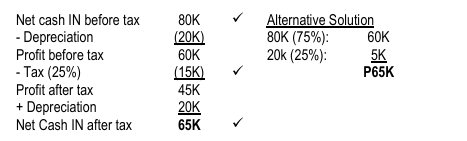
ILLUSTRATION NET RETURNS – COST SAVINGS
Celine Company is planning to buy a high-tech machine that can reduce cash expenses by an average of P80,000 per year. The new machine will cost P 100,000 and will be depreciated for 5 years on a straight-line basis. No salvage value is expected at the end of the machine’s life. Income tax rate is 25%.
REQUIRED: Determine the net cash inflows that will be generated by the project.
– used as a discount rate in discounted capital budgeting techniques like NPV and IRR.
COST OF CAPITAL
– measures the length of time required to recover the full amount of initial investment.
NON-DISCOUNTED TECHNIQUE
PAYBACK PERIOD
PAYBACK PERIOD =

– is a payback method wherein cash recoveries include not only the annual net cash inflows but also the estimated salvage value realizable at the end of each year of the project life.
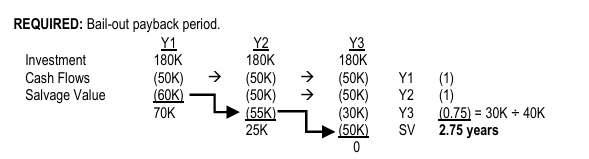
BAILOUT PAYBACK PERIOD
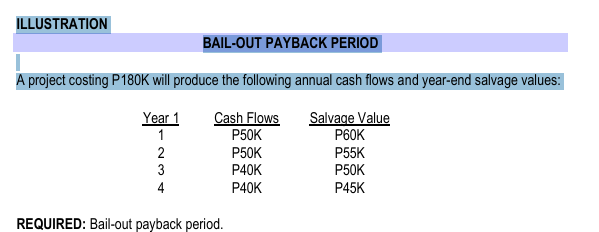
ILLUSTRATION BAIL-OUT PAYBACK PERIOD A project costing P180K will produce the following annual cash flows and year-end salvage values:
– measures the capital project’s profitability from accounting standpoint by relating the required investment to the annual net income.
NON-DISCOUNTED TECHNIQUE
OTHER NAMES: Book Rate of Return, Simple Rate of Return, Unadjusted Rate of Return, Financial Statement Rate of Return, Return on Capital Employed (ROCE)
ACCOUNTING RATE OF RETURN
ACCOUNTING RATE OF RETURN (ARR) =

ILLUSTRATION PAYBACK PERIOD & ARR (EVEN CASH FLOWS)
Lady G Company plans to replace its old equipment. The cost of the new equipment is P 90,000, with a useful life estimate of 8 years and a salvage value of P 10,000. The annual pre-tax cash savings from the use of the new equipment is P 40,000. The old equipment has zero market value and is fully depreciated. The company uses a cost of capital of 25%.
REQUIRED: Assuming that the income tax rate is 40%, determine:
A) Payback period
B) Accounting rate of return on original investment
C) Accounting rate of return on average investment

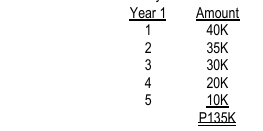
ILLUSTRATION PAYBACK PERIOD & ARR (UNEVEN CASH FLOWS)
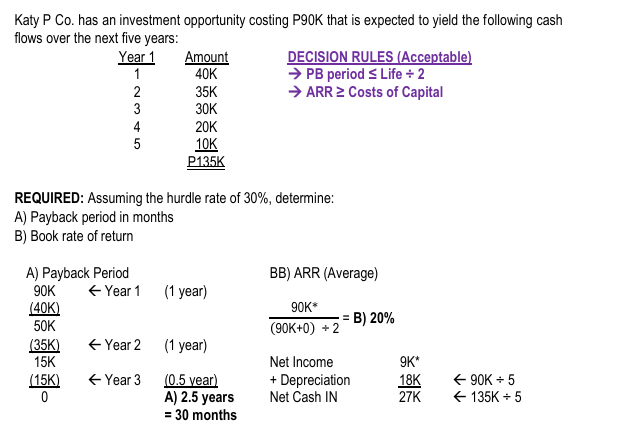
Katy P Co. has an investment opportunity costing P90K that is expected to yield the following cash flows over the next five years:
REQUIRED: Assuming the hurdle rate of 30%, determine: A) Payback period in months B) Book rate of return
– provides a reasonable estimate of the internal rate of return (IRR) provided that the following conditions are met:
PAYBACK RECIPROCAL
PAYBACK RECIPROCAL =
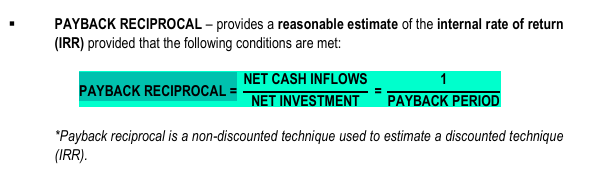
ILLUSTRATION X Co. is planning to buy an equipment costing P640K with an estimate life of 30 years and is expected to produce after-tax net cash inflows of P128K per year.
REQUIRED: Without using present value factors, what is the best estimate of the IRR?
Payback period: 640K ÷ 128K = 5 years
Payback reciprocal: 1 ÷ 5 years = 20%
Payback reciprocal is a reasonable estimate of the internal rate of return (IRR) provided that the following conditions are met:
Payback period is at most half of the economic life of the project [i.e., 5 years ≤ (30 ÷ 2)]
![<p><strong>Payback period: 640K ÷ 128K = 5 years </strong></p><p><strong>Payback reciprocal: 1 ÷ 5 years = 20% </strong></p><p>Payback reciprocal is a reasonable estimate of the internal rate of return (IRR) provided that the following conditions are met: </p><p> Payback period is at most half of the economic life of the project [i.e., 5 years ≤ (30 ÷ 2)]</p><p></p><p></p>](https://knowt-user-attachments.s3.amazonaws.com/7011c738-24c9-45a9-bb4b-5fb3c6c73ec9.png)
– measures the difference between the present value of cash inflows generated by the project and the amount of initial investment.
NET PRESENT VALUE
NPV =
NPV = PRESENT VALUE OF CASH INFLOWS – PRESENT VALUE OF CASH OUTFLOWS
CASH INFLOWS – include annual net cash inflows and any cash realizable at the end of the project life e.g., salvage value, return of working capital requirements
CASH OUTFLOWS – based on the net investment cost required at the inception of the project.
Expresses the present value of the cash benefits as to an amount per peso of investment in a capital project.
Used as a measure of ranking projects in descending order of desirability.
PROFITABILITY INDEX
PROFITABILITY INDEX =

Equates the present value of cash inflows to present value of cash outflows.
OTHER NAMES: Time-Adjusted Rate of Return, Discounted Cash Flow Rate of Return, Sophisticated Rate of Return, Break-Even Cash Flow Rate or Return.
INTERNAL RATE OF RETURN (IRR)
IRR is the discount rate at which the NPV is _____
Zero
IRR must be distinguished from CROSSOVER RATE (NPV Point of Indifference, Fisher Rate), which is the discount rate at which NPV of two capital investment projects are _____
Equal

ILLUSTRATION CROSSOVER RATE – NPV POINT OF INDIFFERENCE Olivia Co. has a weighted average cost of capital of 12% and is evaluating two mutually exclusive projects (Newton and Rodrigo), which have the following projections:
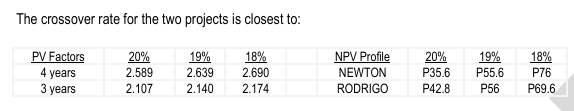
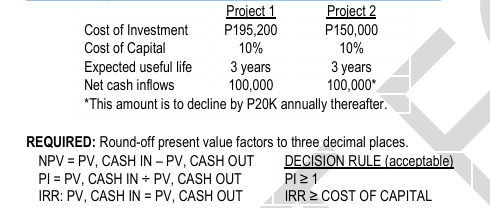
ILLUSTRATION NPV, PROFITABILITY INDEX & IRR (EVEN & UNEVEN CASH FLOWS) Madonna Co. gathered the ff. data on two capital investment opportunities:
– length of time required to equalize the discounted cash flows (using the cost of capital as a discount rate) and initial investment of a capital project. OTHER NAME: Break-Even Time
DISCOUNTED PAYBACK
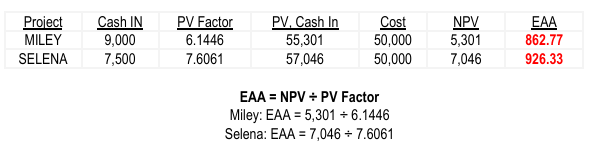
– an NPV-based technique used to compare capital investment projects with unequal lives. OTHER NAME: Annualized NPV
EQUIVALENT ANNUAL ANNUITY (EAA)
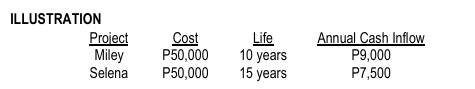
REQUIRED: Assuming a cost of capital of 10% (round-off factors to four decimal places): Based on the equivalent annual annuity, which project is more attractive?
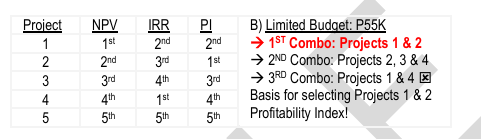
– is, given a constraint on capital budgets, the selection of investment proposals that would maximize the over-all NPV of the firm.
CAPITAL RATIONING
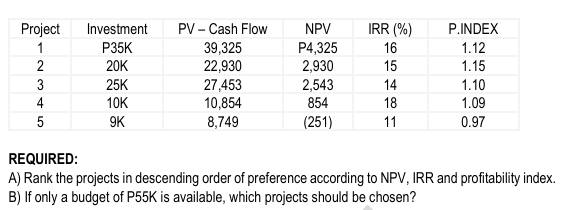
ILLUSTRATION
J-Lo Co. is considering five investment opportunities. The cost of capital is 12%.
– alternative actions that become available over the life of a capital investment.
REAL OPTIONS

in capital budgeting attempts to measure the likelihood of the variability of future returns from the proposed investment.
RISK ANALYSIS
Technique that adjusts the discount rate upward as investment becomes riskier.
RISK-ADJUSTED DISCOUNT RATE
Assumes a higher discount rate in later years of a project’s life to uncertainties (e.g., inflation)
TIME-ADJUSTED DISCOUNT RATE
Considers multiple possible outcomes to determine the overall expected outcome based on weighted average of all possible outcomes.
SCENARIO ANALYSIS
Uses forecasts of may NPVs under various “what-if” assumptions to see how sensitive NPV is to changing conditions.
SENSITIVITY ANALYSIS
Computer-based analysis that considers uncertainties and probability distributions for inputs and uses random number of inputs to map range of possible outcomes.
MONTE CARLO SIMULATION
Probability-based technique used when management needs to decide through a series of “if then” scenarios that describe how the firm might react based on future events.
DECISION TREE
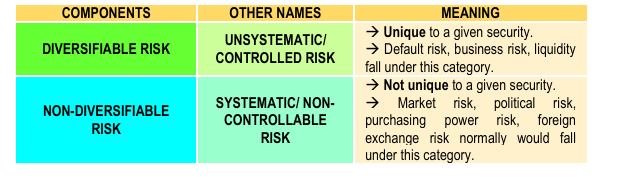
- possibility that actual investment returns will differ from expected return, which could result to either gain or loss.
OTHER NAMES: Security Risk & Speculative Risk
INVESTMENT RISK
Components of investment risk
Measure of dispersion of potential returns from average returns.
Commonly used to quantify risk of investment.
The higher the SD, the higher the risk of an investment.
STANDARD DEVIATION (SD)
Always smaller than SD.
Measures how far a sample mean (e.g., expected return) deviates from the actual mean of a population.
STANDARD ERROR OF THE MEAN
When comparing investments that have different expected returns, the more appropriate measure of investment’s relative risk is the COEFFICIENT OF VARIATION, a measure of risk per unit of return.
What is the formula?
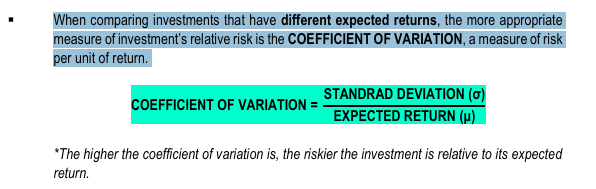
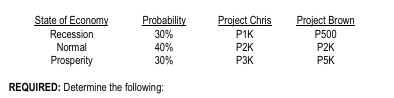
ILLUSTRATION CAPITAL BUDGETING UNDER RISK: COEFFICIENT OF VARIATION
Rihanna Co. considers to invest in one of two mutually exclusive projects: Project Chris vs. Project Brown. Depending on the state of the economy, the projects would provide the following cash inflows in each of the next 5 years. Consider the following probability distribution:
Determine the following:
Expected Return
Standard Deviation
Coefficient of Variation
Assuming Rihanna is a conservative, risk-averse type of investor, which project is likely to be chosen?
Payback period formula and decision rule
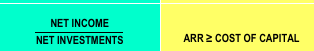
ACCOUNTING RATE OF RETURN (ARR) FORMULA DECISION RULE ( ACCEPTABLE)
NPV Decision rule:
PV, CASH IN – PV, CASH OUT
Decision rule: NPV ≥ 0
Profitability Index decision rule

IRR Formula and Decision Rule
PV, CASH ON = PV, CASH OUT
Decision Rule: IRR ≥ COST OF CAPITAL