Embryology – Early Human Development (Weeks 1-4)
1/92
Earn XP
Description and Tags
This set of vocabulary flashcards summarizes key terms and definitions from early human embryology (fertilization through week 4), covering cellular stages, germ layers, extraembryonic structures, neural and mesodermal development, pharyngeal apparatus, skull growth, and germ-layer derivatives.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
93 Terms
Gametogenesis
The process that produces haploid male (sperm) and female (ovum) gametes, each containing 23 chromosomes.
Fertilization
Fusion of sperm and ovum in the ampulla of the fallopian tube forming a diploid zygote.
Zygote
First diploid cell of the embryo formed after fertilization; contains 46 chromosomes (23 maternal, 23 paternal).
Pronuclei
Male and female haploid nuclei that migrate, fuse, and exchange chromosomes before the first mitotic division of the zygote.
Corpus luteum
Endocrine structure formed from post-ovulation follicle cells; secretes progesterone (and estrogen) to prepare endometrium.
Human chorionic gonadotropin (hCG)
Hormone from syncytiotrophoblast that rescues the corpus luteum if fertilization occurs.
Cleavage
Rapid mitotic divisions of the zygote producing smaller cells (blastomeres) within the zona pellucida.
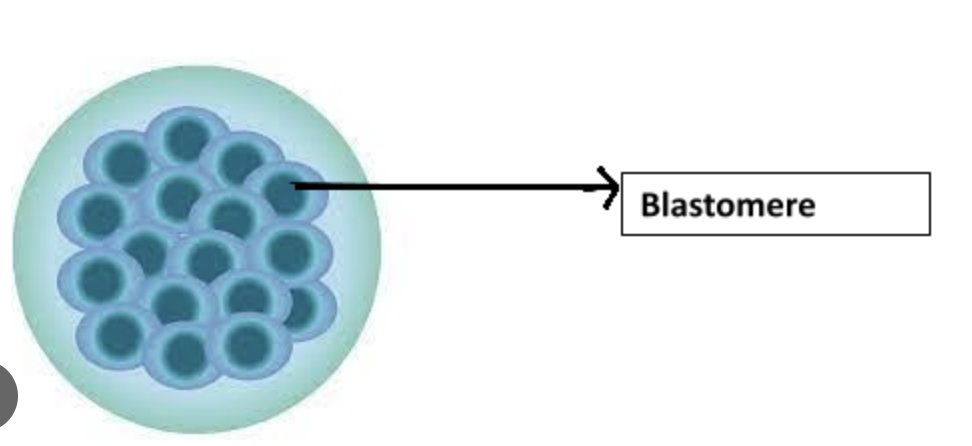
Blastomere
One of the smaller cells produced during cleavage of the zygote.
Morula
16-cell solid ball (about day 3) consisting of inner and outer cell masses.
Inner cell mass (Embryoblast)
Central cells of the morula that form the embryo proper.
Outer cell mass
Peripheral cells of the morula that form trophoblast and extraembryonic membranes.
Blastocyst
Structure formed when fluid enters morula creating the blastocele; consists of embryoblast and trophoblast.
Blastocele
The fluid-filled cavity inside the blastocyst.
Trophoblast
Outer layer of blastocyst that contributes to placenta; differentiates into cytotrophoblast and syncytiotrophoblast.
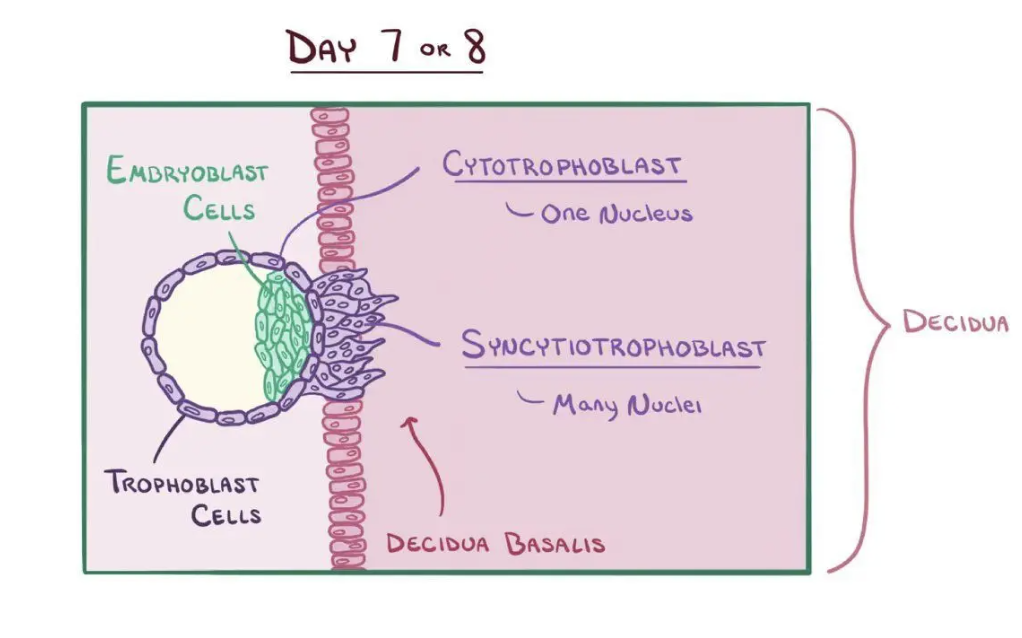
Cytotrophoblast
Inner cellular layer of trophoblast retaining distinct cell boundaries.
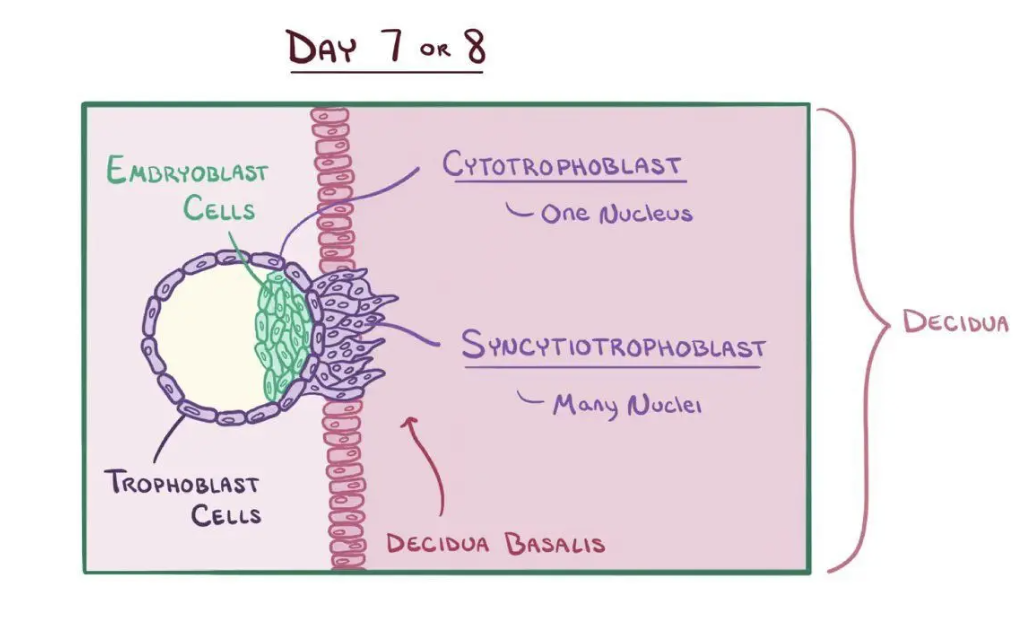
Syncytiotrophoblast (and what does it produce?)
Multinucleated outer trophoblastic layer invading endometrium; produces hCG.
Implantation
Adhesion and invasion of blastocyst into endometrial lining (~day 6).
Amniotic cavity (and what day is it formed?)
Fluid space forming between embryoblast and trophoblast (~day 8).
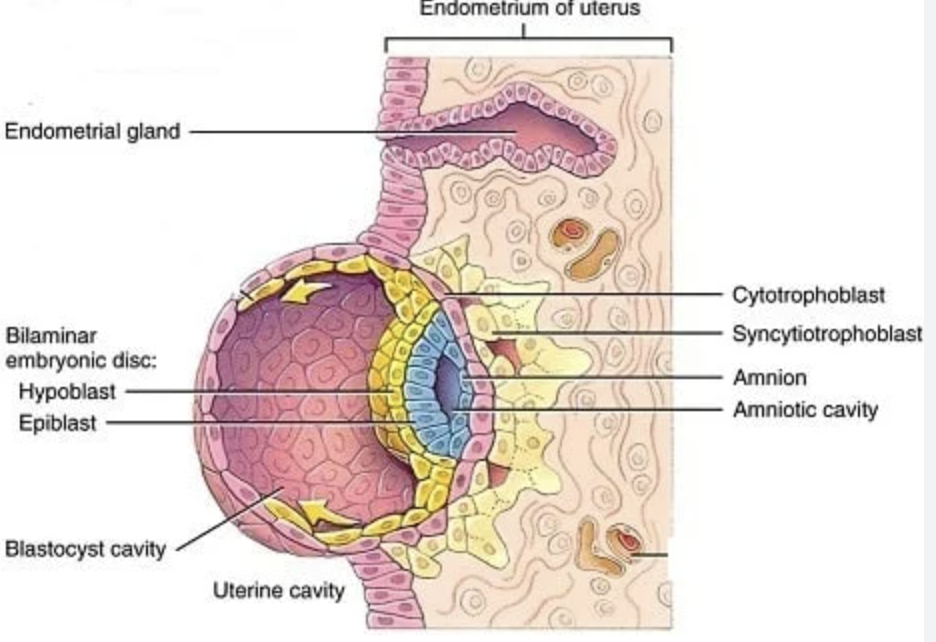
Epiblast
Columnar cell layer of embryonic disc facing amniotic cavity; forms ectoderm and contributes to mesoderm.
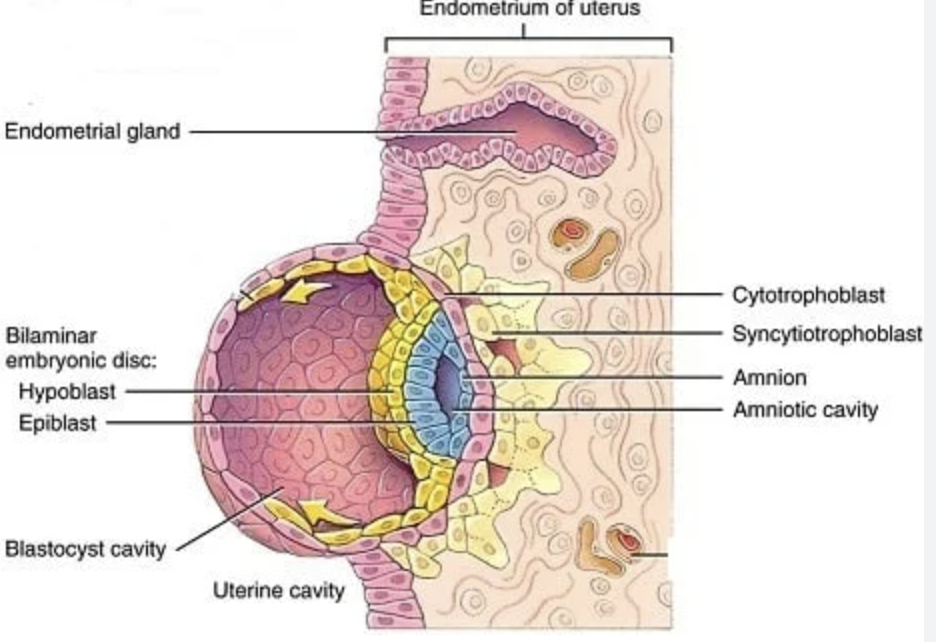
Hypoblast
Cuboidal cell layer facing blastocele; forms primitive endoderm lining yolk sac.
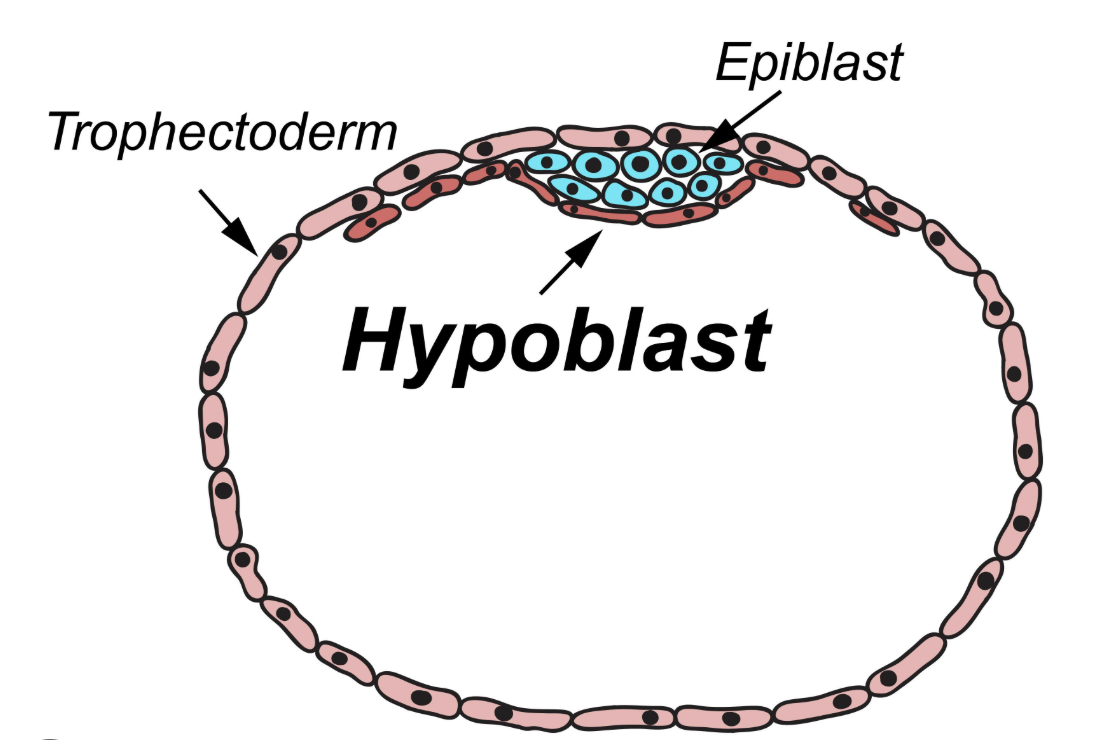
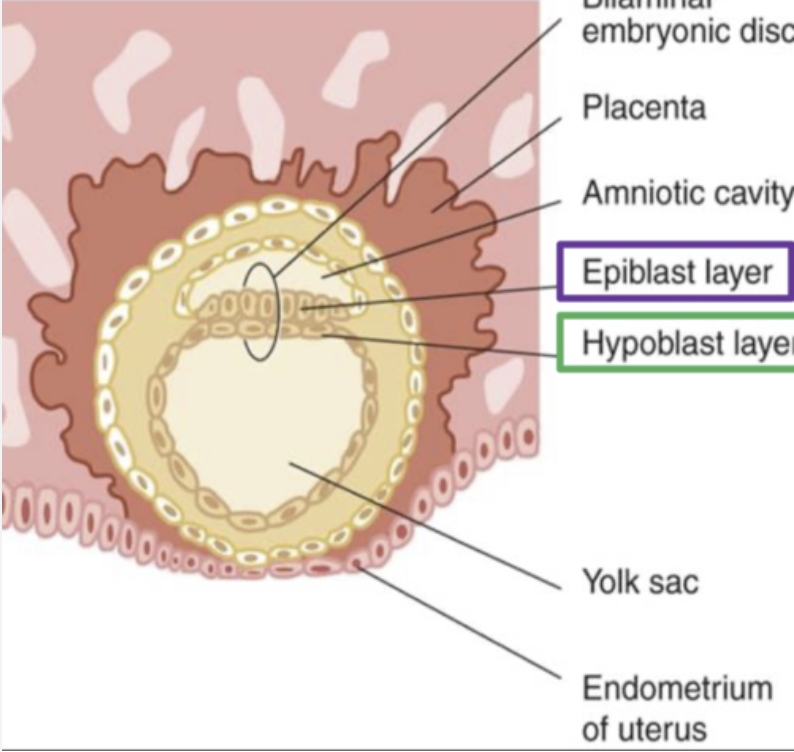
Bilaminar embryonic disc (and when is it formed?)
Two-layered structure (epiblast + hypoblast) formed during week 2.
Heuser’s (Exocoelomic) membrane
Thin hypoblast-derived lining of the primitive yolk sac.
Primitive (primary) yolk sac
First yolk sac lined by Heuser’s membrane below the hypoblast.
Extraembryonic mesoderm
Loosely arranged cells between trophoblast and yolk/amnion; splits to form extraembryonic coelom.
Extraembryonic coelom
Fluid cavity surrounding amnion and yolk sac except at connecting stalk; becomes chorionic cavity.
Extraembryonic somatic mesoderm
Layer lining trophoblast and covering amnion; part of chorion.
Extraembryonic visceral (splanchnic) mesoderm
Layer covering yolk sac.
Connecting stalk
Band of extraembryonic mesoderm attaching embryo to trophoblast; becomes umbilical cord.
Chorion
Combination of cytotrophoblast + extraembryonic somatic mesoderm; forms chorionic sac.
Chorionic villi
Projections of trophoblast into maternal tissue; primary (cytotrophoblast), secondary (with mesoderm), tertiary (with blood vessels).
Lacunae
Maternal blood-filled spaces within syncytiotrophoblast establishing uteroplacental circulation.
Decidua
Endometrial stromal tissue transformed by implantation (glycogen/lipid rich).
Secondary yolk sac
Smaller yolk sac formed after extraembryonic coelom pinches off primary yolk sac.
Prochordal plate
Thickened endodermal area marking future mouth and cranial end of embryo.
Gastrulation
Formation of three germ layers via primitive streak (~day 15).
Primitive streak
Longitudinal midline thickening of epiblast (caudal); site of cell ingress during gastrulation.
Primitive node
Cranial swelling of primitive streak controlling notochord formation.
Primitive pit
Depression within primitive node leading to notochordal canal.
Intraembryonic mesoderm
New germ layer inserted between ectoderm and endoderm by epiblast cells during gastrulation.
Cloacal membrane
Caudal ectoderm-endoderm fusion site; future anus.
Oropharyngeal membrane
Cranial ectoderm-endoderm fusion at prochordal plate; future mouth.
Notochord
Midline mesodermal rod derived from primitive node cells; basis for axial skeleton and induces neural plate.
Sacrococcygeal teratoma
Tumor from persistent primitive streak cells; contains tissues from all germ layers.
Neurulation
Process by which neural plate folds to form neural tube (brain and spinal cord).
Neural plate
Thickened ectoderm induced by notochord; precursor to neural tube.
Neural folds
Elevated lateral margins of neural plate that fuse to close neural tube.
Anterior neuropore
Cranial opening of neural tube; failure to close causes anencephaly.
Posterior neuropore
Caudal opening of neural tube; failure to close causes spina bifida/meningomyelocele.
Paraxial mesoderm
Mesodermal columns beside notochord that segment into somites.
Somite
Paired mesodermal blocks forming sclerotome, myotome, dermatome; appear day 20 onward (≈35 pairs).
Sclerotome
Somite derivative forming vertebrae and ribs.
Myotome
Somite derivative forming skeletal muscle of trunk/limbs.
Dermatome
Somite derivative forming dermis of skin.
Prosencephalon
Forebrain; subdivides into telencephalon and diencephalon.
Telencephalon
Forms cerebral hemispheres and lateral ventricles.
Diencephalon
Forms thalamus, hypothalamus, optic structures, third ventricle.
Mesencephalon
Midbrain; forms tectum, cerebral peduncles, aqueduct of Sylvius.
Rhombencephalon
Hindbrain; divides into metencephalon and myelencephalon.
Metencephalon
Forms pons, cerebellum, upper 4th ventricle.
Myelencephalon
Forms medulla oblongata, lower 4th ventricle.
Pharyngeal (branchial) arches
Six paired mesodermal bars in head-neck (4th week) each with nerve, artery, cartilage, muscle derivatives.
Mandibular arch (First arch)
Forms maxilla, mandible, malleus, incus, muscles of mastication; contains Meckel’s cartilage.
Hyoid arch (Second arch)
Forms stapes, styloid process, lesser horn of hyoid, muscles of facial expression; has Reichert’s cartilage.
Third pharyngeal arch
Forms greater horn of hyoid and part of thymus.
Fourth pharyngeal arch
Forms thyroid & epiglottic cartilages, intrinsic palate muscles.
Sixth pharyngeal arch
Forms laryngeal cartilages (cricoid, arytenoid, corniculate) and intrinsic laryngeal muscles.
Meckel’s cartilage
Cartilage core of first arch giving rise to mandible template, malleus, incus.
Reichert’s cartilage
Second arch cartilage forming stapes, styloid process, hyoid lesser horn.
Pharyngeal pouches
Endodermal outpocketings between arches that form internal neck organs.
First pharyngeal pouch
Forms auditory (eustachian) tube, middle ear cavity, tympanic membrane.
Second pharyngeal pouch
Forms palatine tonsils and tonsillar fossa.
Third pharyngeal pouch
Gives rise to thymus and inferior parathyroid glands.
Fourth pharyngeal pouch
Forms superior parathyroid glands.
Ultimobranchial body
Derived from 4th/5th pouch; incorporated into thyroid as parafollicular (C) cells producing calcitonin.
Fontanelle
Fibrous membrane area between skull bones; allows molding and brain growth.
Anterior fontanelle
Largest fontanelle at junction of frontal and parietal bones; closes ~2 years.
Posterior fontanelle
Fontanelle at junction of parietal and occipital bones; closes ~6 months.
Skull sutures
Fibrous joints (metopic, sagittal, coronal, lambdoid, squamous) between flat bones of neonatal skull.
Ectoderm derivatives
CNS, PNS, sensory epithelium of eye/ear/nose, epidermis, hair, nails, glands, enamel.
Mesoderm derivatives
Muscle, bone, cartilage, dermis, cardiovascular system, blood cells, kidneys, gonads, spleen, adrenal cortex.
Endoderm derivatives
Epithelial lining of GI and respiratory tracts, bladder, thyroid, parathyroids, liver, pancreas, auditory tube.
Day 0: Fertilization & Zygote
Fusion of sperm and ovum in the ampulla of the fallopian tube, forming the diploid zygote, the first diploid cell of the embryo.
Days 1-2: Cleavage Begins
Rapid mitotic divisions of the zygote produce smaller cells called blastomeres within the zona pellucida.
Day 3: Morula Stage
The embryo develops into a 16-cell solid ball, known as a morula, consisting of inner and outer cell masses.
Days 4-5: Blastocyst Formation
Fluid enters the morula, creating the blastocele cavity and transforming the embryo into a blastocyst, composed of an embryoblast (inner cell mass) and trophoblast.
Day 6: Implantation Onset
The blastocyst adheres to and begins invading the endometrial lining of the uterus.
Day 8: Amniotic Cavity & Early Bilaminar Disc
A fluid-filled amniotic cavity forms between the embryoblast and trophoblast, marking the beginning of the bilaminar embryonic disc formation.
Week 2 (Days 8-14): Extraembryonic Structure Development
The bilaminar embryonic disc fully forms (epiblast + hypoblast). Heuser’s membrane lines the primitive yolk sac. The extraembryonic mesoderm develops and splits to form the extraembryonic coelom (chorionic cavity).
~Day 15 (Week 3): Gastrulation Commences
Gastrulation begins with the formation of the primitive streak, through which epiblast cells ingress to form the three germ layers (ectoderm, intraembryonic mesoderm, endoderm).
Late Week 3: Notochord Formation & Neurulation
Cells from the primitive node form the notochord, which induces the overlying ectoderm to thicken and form the neural plate, beginning the process of neurulation.
Day 20: Somite Appearance
Paired mesodermal blocks called somites begin to appear from the paraxial mesoderm, marking a significant milestone in body segmentation.
~Day 25: Anterior Neuropore Closure
The cranial opening of the neural tube, the anterior neuropore, fully closes.
~Day 28: Posterior Neuropore Closure
The caudal opening of the neural tube, the posterior neuropore, fully closes.