L18a: Male Gonads: Testicles, Testosterone
1/57
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
58 Terms
Gametogenesis
development from primordial germ cells to mature gametes: oogenesis in females and spermatogenesis in males
Pampiniform plexus
arrangement of the testicular vein into an elaborate, convoluted network that creates many intimate finger-like "wrappings" surrounding the testicular artery
Acrosome reaction
exocytic secretory event within the sperm head that releases proteolytic enzymes for zona pellucida penetration
Capacitation
final functional maturation of the spermatozoa, it includes enhancement of flagellar activity (hyperactivation) & acrosome reaction
Differentiation
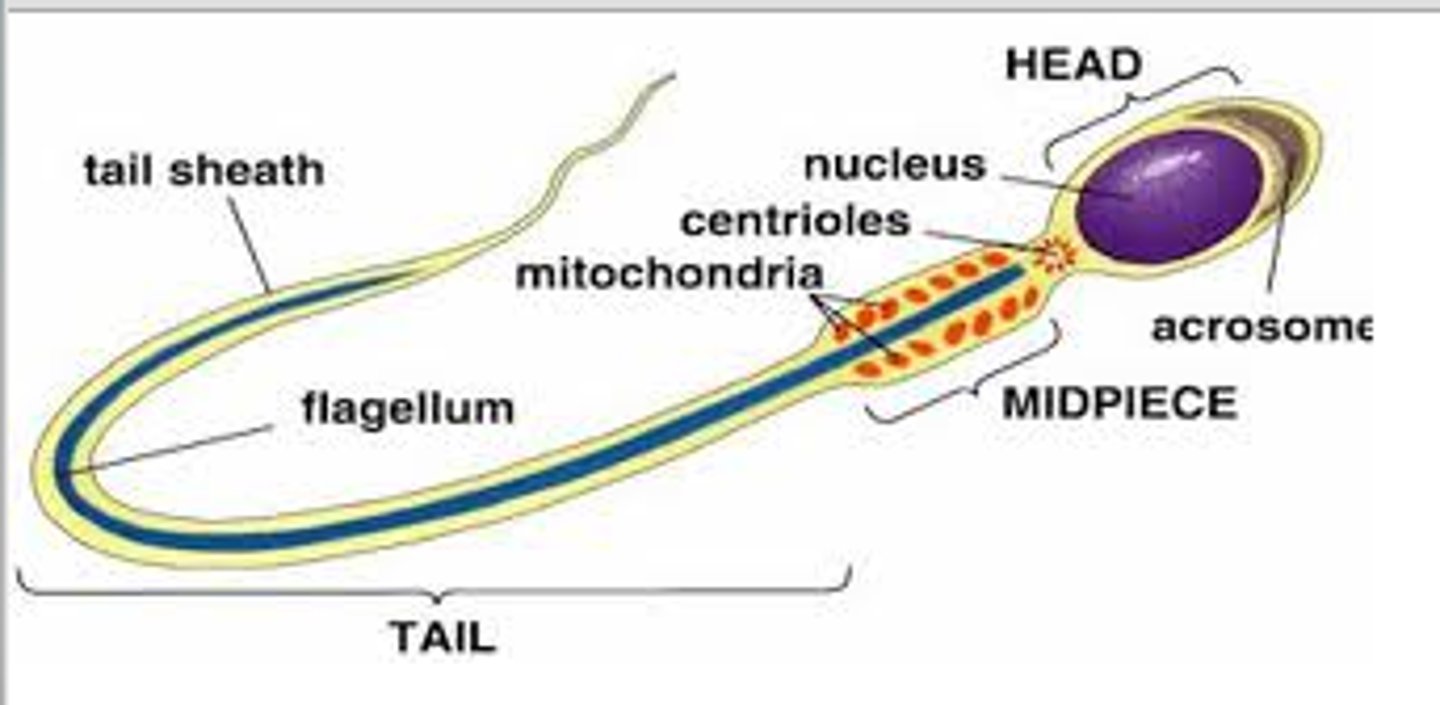
a spherical undifferentiated spermatid undergoes a remarkable transformation that results in the production of a highly specialized spermatozoon containing a head and a flagellum including a midpiece (with a mitochondrial helix) and a principal piece (tail)
Diploid
containing two complete sets of chromosomes, one from each parent
Haploid
containing a single set of chromosomes
Proliferation phase
stage that involves cells undergoing repeated mitotic divisions
Spermatogenesis
process that involves the division and transformation from diploid stem cell to haploid spermatozoon
Spermiogenesis
process by which haploid round spermatids complete an extraordinary series of events to become streamlined spermatozoa capable of motility
What is gametogenesis?
process of development from primordial germ cells to mature gametes: oogenesis in females and spermatogenesis in males
When considering the flow of spermatozoa, what segment of the male reproductive tract continues the tail of the epididymis?
ductus deferens
Sperm cells partially mature in the
epididymus
The ductus deferens begins at the
tail of the epididymis
Main components of the male reproductive system
1. testis: high-speed production
2. epididymis: head & body: finishing shop
3. epididymis: tail: warehouse & shipping
4. accessory sex glands: final changes & packaging
5. ductus deferens, urethra, penis: delivery system
Blood supply to the testes
testicular artery
The testicular artery forms the
pampiniform plexus
The testicular vein "wrappings" around the testicular artery allows for
temperature regulation & counter-current exchange of testosterone
Spermatogenesis requires a temperature that is _____ cooler than body temp?
4-6 degrees
Testicular parenchyma is divided into
lobules by connective tissue septae
Site of spermatogenesis
seminiferous tubules
Internal organization of the testes
1. lobules
2. seminiferous tubules
3. straight tubules
4. rete testes
5. efferent ductules
6. head of epididymis
Site of fluid absorption & sperm maturation
epididymis
Ductus deferens
long, straight, tubular organ that originates at the scrotum & ends at the beginning of the urethra
The ductus deferens is responsible for
transporting the ejaculate out of the epididymis and into the pelvic urethra
4 accessory sex glands
1. ampulla of ductus deferens
2. vesicular gland
3. prostate
4. bulbourethral gland
What are the accessory sex glands responsible for?
providing an optimal environment and nourishment for the spermatozoa
The main function of the penis is to
serve as a organ of copulation & passage for semen and urine
What structure is responsible for sperm production?
seminiferous tubules
What is the function of the pampiniform plexus?
temperature regulation & testosterone exchange
Puberty
the process of acquiring reproductive competence
The male reproductive system is under control of the
Hypothalamic-Pituitary-Gonadal Axis
Tonic center of the hypothaamis
produces GnRH
What minimizes the function of the surge center in the male fetus?
testosterone freely enters the brain & transforms into estradiol
What happens to GnRH release after puberty in males?
the hypothalamus "wakes up" and GnRH is released in a pulsatile fashion along with LH & FSH from the anterior pituitary gland
Tubular component of the testis
site of spermatogenesis
Interstitial component of the testis
site of testosterone production
Leydig cells have
LH receptors & produce testosterone
Sertoli cells have
FSH receptors & produce inhibin
LH pulse
- LH binds to receptors on leydig cells which then release testosterone
- testosterone diffuses into sertoli cells
- testosterone converted into DHT & E2 and released into bloodstream
FSH pulse
FSH binds to receptors on sertoli cells, which then produce spermatogenic substances and INHIBIN
Spermatogenic substances
androgen binding protein (ABP) maintains a higher tubular testosterone concentration despite pulsatile release
What is the action of inhibin in the male reproductive system?
selectively inhibits FSH release
General effects of testosterone
- heat detection
- courtship
- sexual arousal/erection
- mounting/intromission/ejaculation
- memory
- increased metabolic rate
- muscle growth
- bone thickness
- skin thickness
- hair growth
- hair darkening
What is the purpose of the spines on the penis of a cat?
stimulate mechanoreceptors to induce ovulation in queens
What are the major reproductive hormones produced by the anterior pituitary gland?
FSH & LH
In the hypothalamus, males only have the tonic center/nuclei (true/false)
true
Spermatogenesis takes place entirely within the
seminiferous tubules
In most domestic species, spermatogenesis takes
40-60 days
Most immature sperm cells (spermatogonia) are located at
the periphery of a seminiferous tubule near the basement membrane
Three major phases of spermatogenesis
1. mitosis
2. meiosis
3. differentiation
Mitosis phase of spermatogenesis
proliferation phase, a primary spermatocyte is produced, stem cell renewal
What allows some spermatogonia to revert to stem cells?
loss of intercellular bridges
Meiosis I
DNA replication, primary spermatocytes become secondary spermatocyte
Meiosis II
produces haploid spermatids formed from secondary spermatocytes
Differentiation/Spermiogesis phase
results in the production of a fully differentiated, highly specialized spermatozoon containing a head & flagellum including a midpiece & tail (principal piece)
What are the three major phases of spermatogenesis?
mitosis, meiosis, differentiation
Where does sperm capacitation occur?
the female reproductive tract