Chemistry revision 2 separation methods
1/15
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
16 Terms
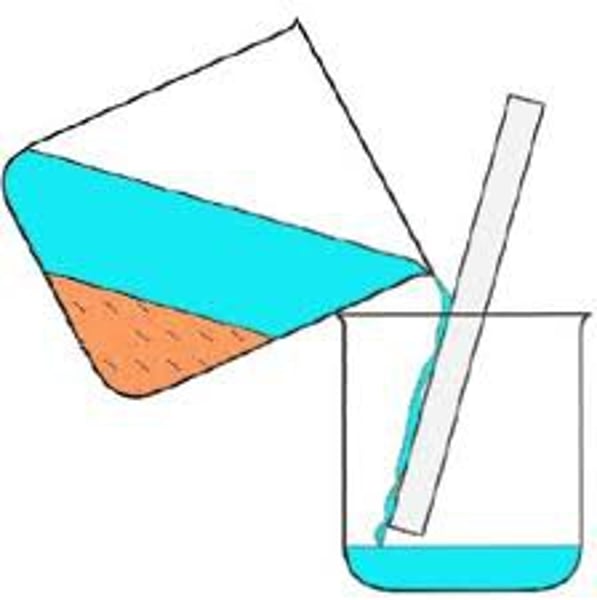
Decanting
The pouring of a liquid from a settled solid
Used to separate liquid from undissolved solids quickly
E.g. sand from water
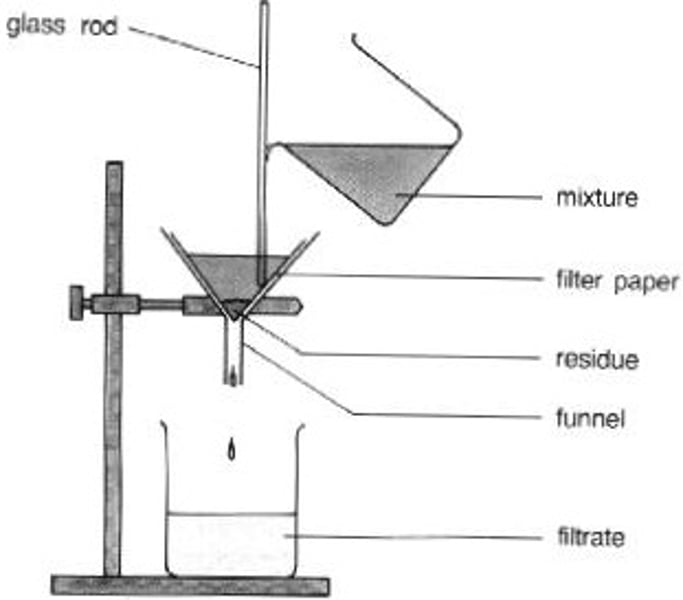
Filtration
Decanting can be used to separate components of a mixture prior to or with filtration
Often used to separate liquid or solution from insoluble solid
E.g. salt soluble in water but sand is insoluble, sand taken out with filter paper
Evaporation
recovery of a dissolved solid from a solution
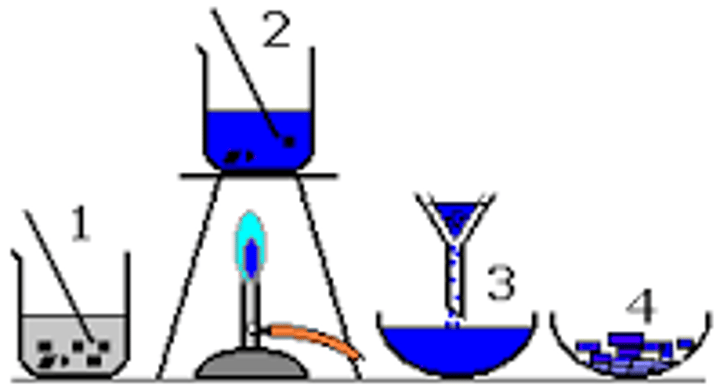
crystallisation
depends on the components of a mixture having different solubilities in a selected solution
E.g. a mixture of salt and baking soda can be separated by dissolving in hot water and then cooling the resultant solution
Recrystallisation
often used to purify impure substances
E.g. sugar refining
1. impure substance dissolved in a minimum amount of solvent at high temp
2. hot mixture is filtered to remove insoluble impurities
3. filtrate is cooled, causing crystals of the pure substance to form
4. crystals can be filtered, leaving any impurities in the filtrate
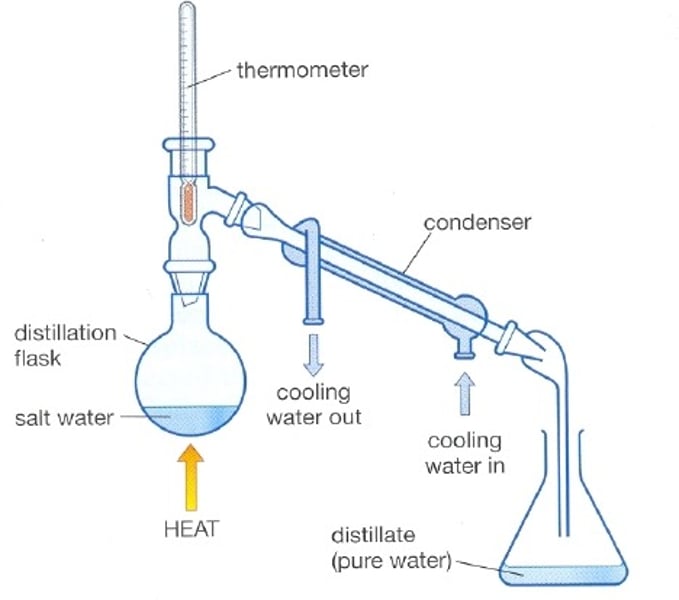
Distillation
Used to purify liquids
Effective when mixtures have different boiling points
1 liquid evaporates
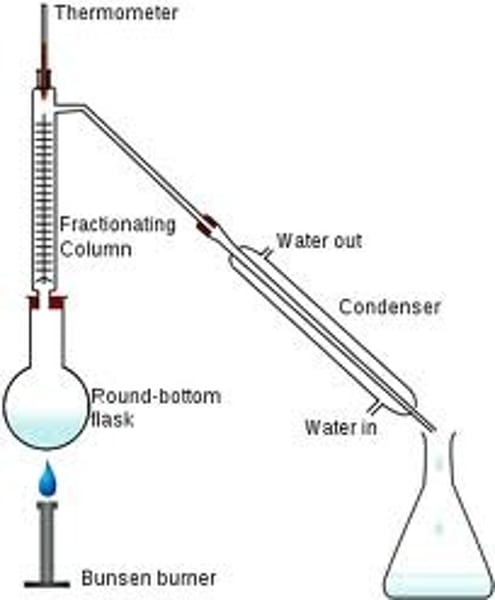
Fractional Distillation
separation of 2 or more liquids from a mixture
E.g. alcohol form wine
petrol, kerosene + oil from crude oil
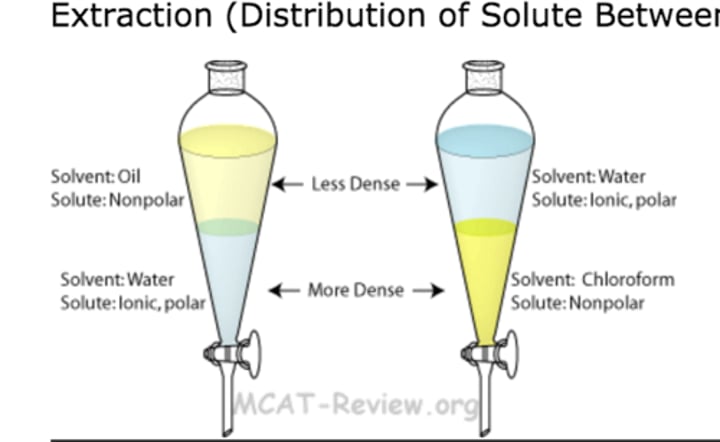
Solvent extraction
Separate substances because of their different solubilities in 2 immiscible liquids
E.g. salt and iodine
1. dissolve mixture in water and add separating funnel
2. solvent is added and mixture is shaken
3. mixture settles salt will dissolve
4. 2 liquids separated by running lower layer through tap
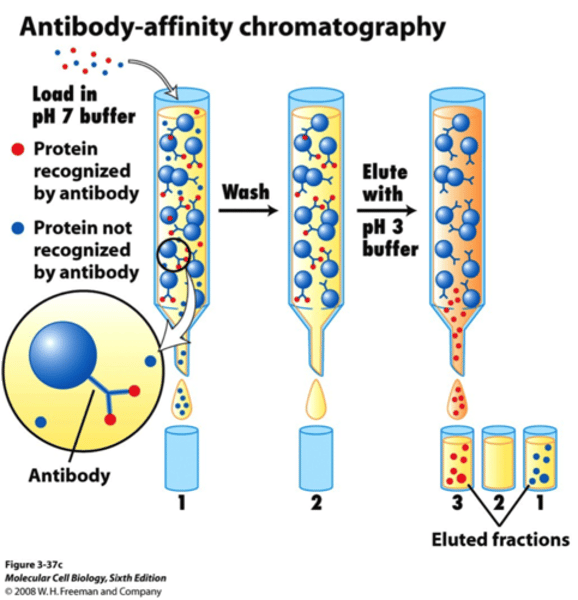
Chromatography
Used to separate components in small quantities of mixtures
E.g. dyes or drugs
1. mixture is passed over inert substance
2. separation of components occurs because they cling to surface of inert substance
3. less absorbing components pass through
Ionic bond
Lattice structure
Form as a result of electrostatic attraction between anion and cation
ionic bond properties
Melting point
- high melting and boiling point due to high electrostatic force so lots of energy and thermal heat needed to break it
Brittleness
- brittle as it you move the lattice the positive will repel the positive and negative will repel the negative
Electrical conductivity
dont have mobile charge carriers in solid state but do in molten (liquid) state
Metallic bonds
Bond between 2 metals
formed by electrostatic attraction between delocalised electrons and the lattice of positively charged ions
Metallic bonding Properties
Melting point
- high melting point as there is a high electrostatic attraction between delocalised electrons and the +ve ions
Electrical Conductivity
- free mobile charge carriers - delocalised electrons that can carry charge
Thermal Conductivity
- good thermal conductors as electrons transfer Ek throughout the structure very quickly
Malleable + Ductile
- metallic bonds are non-directional so they can be bent and shaped easily
Covalent bonds
occurs between non metals - electrons shared
very strong bonds as they share electrons
Covalent molecular structures
small group of atoms bonded together
Properties
Melting point
- Low melting point as weak INTERmolecular forces between them (not INTRA)
Conductivity
- dont conduct electricity as they dont have mobile charge carriers
Malleable
- easy to form into shapes due to weak intermolecular force
Covalent network structures
continuing lattice structures bonded together
Properties
Melting point
- high melting point as large amount of energy required to break electrostatic attraction
Brittle
- strong bonds and wont change shapes
Conductivity
- only graphite conducts electricity as it is the only one with mobile charge carriers