physics criterion A 18.04 electricity
1/28
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
29 Terms
What do amperes(A) measure?
Electric current
What is electric current?
The flow of electricity in a circuit, or the amount of electricity flowing through a circuit.
What do coulombs(C) measure?
Electrical Charge
What is Electrical Charge?
A measure of how strongly something will interact with electromagnetic fields.
What causes an electrical charge?
As electrons have a negative charge, when they are added to an object, it becomes negatively charged. When electrons are removed from an object, it becomes positively charged.
What do joules(J) measure?
energy: the total amount of work we can do with a given amount of electricity.
What do ohms(Ω) measure?
Resistance
What is resistance?
A measure of the opposition to current flow in an electrical circuit.
What do volts(V) measure?
Voltage
What is voltage?
Electric potential difference, or the size/pressure of the force that pushes charged electrons through a circuit.
What do watts(W) measure?
Power
What is power?
the rate of transfer of electrical energy within a circuit.
What are some common electrical conductors?
Aluminium, Brass, Copper, Gold, Bronze,
What are some common electrical insulators?
Glass, Plastic, Rubber, Air, Wood
What is Static Electricity?
It’s caused by an imbalance between negative and positive charges in an object. These charges can build up on the surface of an object until they find a way to be released or discharged.
How is static electricity produced?
Friction, Induction, Conduction.
What is Coulomb’s Law?
There are forces of attraction between unlike charges and forces of repulsion between like charges
What is electrostatic phenomena?
When materials come into contact or are rubbed together and electrons are transferred from one material to another, creating an electrostatic charge buildup.
What is the formula for electrostatic force?

What are electrical field lines?
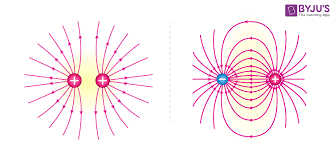
What happens when the distance between charges changes?
As the distance increases, the electrical force between them decreases, and vice versa.
What is the sign of the force for opposite charges and identical charges?
The force between opposite charges is attractive and often positive.
The force between identical charges is repulsiveand often negative.
What is electric current in solid metallic condutors?
A flow of negatively charged electrons.
What is the formula for electrical current?
Current = Charge*Time
What can be used to indicate the presence of a current in a circuit?
Lamps and LEDs.
How to measure current and voltage in a circuit?
Ampmeter and Voltmeter.
What is the Effect of chnaging resisatcne on the current in a circuit?
If resistance increases, current decreases, and vice versa, provided the voltage remains constant.
What is the Ohm’s Law Equation?
Voltage = Current x Resistance
What is the major characteristic of voltage across two compoenents in parallel?
It is the same.