Chapter 1
1/49
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
50 Terms
Three Themes:
Continuity of Development
Nature & Nurture
The “Active” Child
Continuity of Development
“Are we consistently and gradually changing across development or do we make big shifts to qualitatively new behaviors?”
Nature & Nuture
Nature: our biological endowment
Nuture: environment, physical and social
How do they work together?
The “Active” Child
The Active/Passive Child Debate: to what degree do children influence their own development?
Passive Child
children are at the mercy of their environment- they can’t change how they develop
John Locke’s “Blank Slate”
Active Child
children are participating in their own development
elicit different responses from adults, other kids
different interests lead to different expertise
Five Foundational Perspectives of Child Development
The Biological Perspective
The Learning Perspective
The Psychodynamic Perspective
The Cognitive/Development Perspective
The Contextual Perspective
The Biological Perspective
Key Assumption: Development is rooted in biology
Maturational Theory
Dr. Arnold Gesell
Ethological Theory
Konrad Lorene & “Imprinting”
Maturational Theory
The idea that reflects a specific and prearranged scheme or plan within the body
Major limitation: fails to consider any major environmental factors
Dr. Arnold Gesell: based on 50 years of observational research. There’s a strong focus on growth of the nervous system - as the nervous system grows the min develops and behavior changes accordingly
Ethological Theory
views development from an evolutionary perspective
behaviors are adaptive: we develop in a certain way because it aids in our survival
Critical/Sensitive Period: the time in development when a specific type of learning can take place; before or after the critical period, the same learning is difficult or even impossible
Konrad Lorene & “Imprinting”
Eg. learning languages
The Learning Perspective
Key Assumption: Development is determined largely by a child’s environment (nature)
Operant Conditioning
B.F. Skinner
Social Cognitive Theory
Albert Bandura
Operant Conditioning
consequence of behavior
Skinner’s Rats
Social Cognitive Theory
behaviors develop as children observe a combination of reward, punishment, and others’ behaviors
children will mimic those they see rewarded and avoid behavior when someone is punished
Albert Bandura - The Bobo Doll Study
The Psychodynamic Perspective
Key Assumption: Development unfolds according to resolution/lack of resolution of “conflicts” at different stages
Psychodynamic Theory (Freudian Theory)
Psychosocial Theory
Erik Erikson
Psychodynamic Theory
early experiences establish patterns that endure throughout a person’s life
Conflict
Id, Ego, Superego
Sigmund Freud
Id
primitive instinct
Ego
rational/practical aspect, directly influenced by the real world
Superego
moral aspect
Psychosocial Theory
development consists of a sequence of stages, each defined by a key crisis/challenge, people grow due to their responses to crises in their lives
Erik Erikson
The Cognitive-Developmemtal Perspective
Key Assumption: Development reflects children trying to make sense of the world
Jean Piaget’s Theory
Jean Piaget’s Theory
different stages of thinking that develop through children’s shifting competencies and changing theories of the world
The Contextual Perspective
Key Assumption: Development is driven by the interaction of a child’s immediate and distant environments (“all nurture” - but includes direct and indirect influences)
Lev Vygotsky’s Sociocultural Theory
Lev Vygotsky’s Sociocultural Theory
emphasizes the role “experts” in converting cultural expectations and knowledge to the next generation
children’s development is enmeshed with the culture in which they grow up
The Scientific Method
Choose a question
Formulate a hypothesis
Develop a method to test the hypothesis
Draw a conclusion
Measurements
Systematic observation
Sampling behaviors with task
Self-reports
Physiological measures
Systematic Observation
Naturalistic (watched in re-life) and Structured (researchers create a setting)
Strengths
allows researchers to study “natural” behaviors
can allow access to behavior that is difficult to measure experimentally
Weaknesses
must be aware that observation alone could distort behavior
lack of control over potential confounding variables
Sampling Behaviors with Tasks
Create an activity that will elicit the behavior of interest
Strengths
convenience
a bit more “controlled” than simple observation
Weaknesses
have to be very careful that measure is valid
Self-reports
children’s answer to questions about the topic of interest (questionnaire/interview)
Strengths
convenience
are often a direct measurement of the topic
Weaknesses
answers may not be accurate
relying on memory
Response bias
Response Bias
participants are more likely to give “socially acceptable” answers rather than the truth
Physiological Measures
measuring children’s physiological response to stimuli
less common and usually used in conjunction with other behavioral measures
strengths
provides converging evidence that confirms behavioral findings
Weaknesses
not practical/available for all areas of study
Reliability
will your result hold up over time
Validity
are your results genuine
Representative Sampling
use of participants that together accurately reflect the population of interest
Population
broad group of interest
Sample
a subset of the population (used for study)
Research Design
conceptual approach to your study (the outline)
correlational and experimental studies
Correlational Study
examine the relation between variables as they exist naturally in the world
will tell you if variables the data points organized in a discernable pattern (positive, negative, no correlation)
Correlational Study Strengths and Weaknesses
convenience
behavior is measured as it occurs naturally
correlation does NOT mean causation
Experimental Study
investigator systematically varies the independent variable to assess the impact on the dependent variable
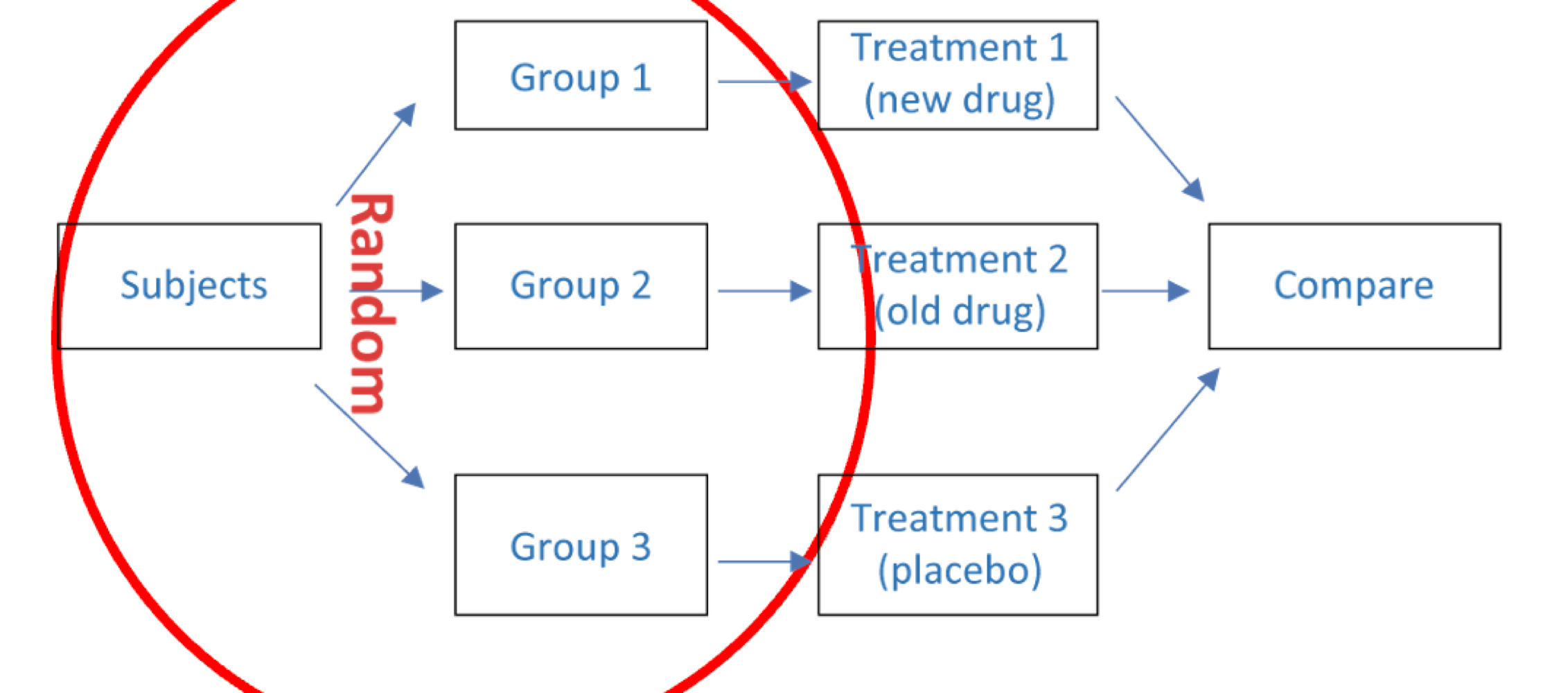
Experimental Study Strengths and Weaknesses
only way to assess causality
sometimes not possible given your research questions
Capturing change overtime - age-related methods
longitudinal design
cross-sectional design
longtidinal-sequential
Longitudinal Design
the same individuals are observed or tested repeatedly at different points in their lives
Longitudinal Design Strengths and Weaknesses
most direct way to watch growth occur
only way to answer the continuity of growth
takes A LOT of time and resources
cohort effects
selective attrition
practice effects
Cohort Effects
a group of people who share a common set of demographic characteristics or experiences
Practice Effects
improvements in cognitive test performance due to repeated evaluation with the same or similar test materials
Selective Attrition
certain participants drop out over time
Cross-Sectional Design
different groups of children are tested at developmental points of interest
Cross-Sectional Design Strengths and Weaknesses
convenient
solves many of the issues with longitudinal design (cohort and practice effects)
does not tell you about continuity of development
Longitudinal-Sequential Design
sequences of samples, each tests longitudinally (is both longitudinal and cross-sectional)
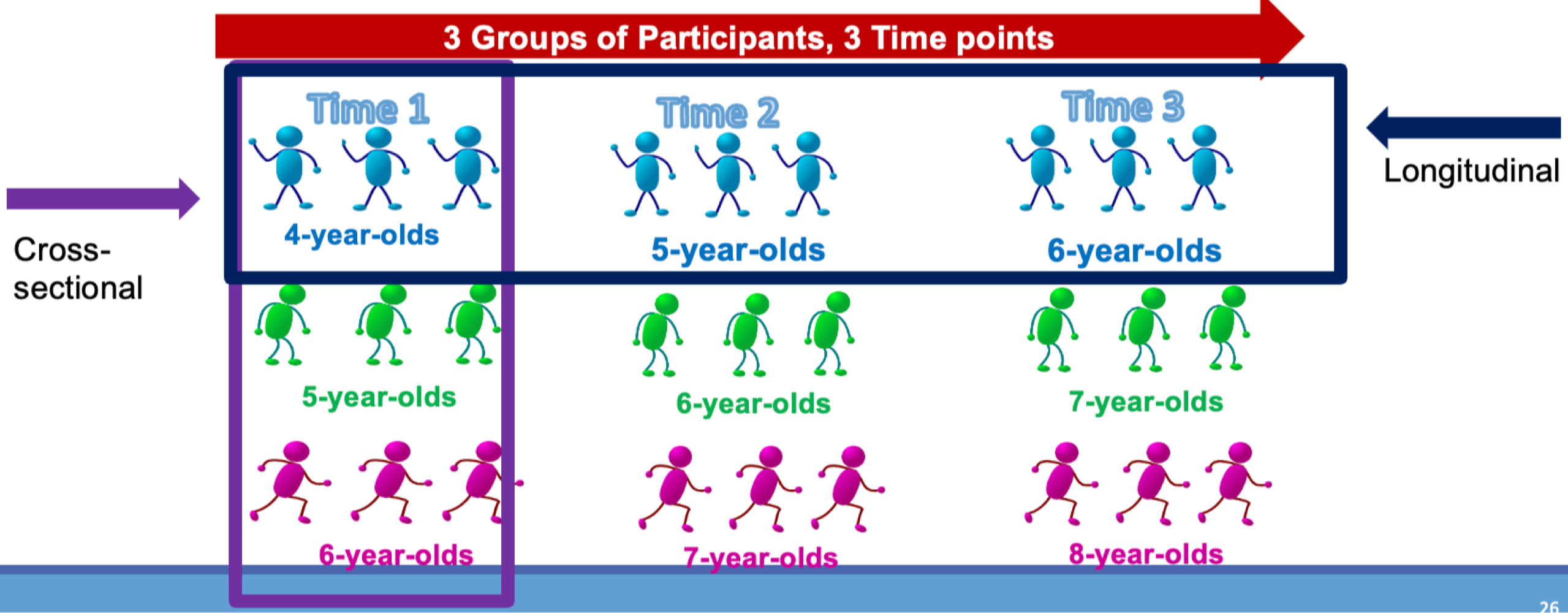
Longitudinal-Sequential Design Strengths and Weaknesses
provides information about continuity
attenuates risk of practice and potential cohort effects
not as much continuity as pure longitudinal
more time consuming than pure cross-sectional