Biology chapter 3 review pt 1
5.0(1)
5.0(1)
Card Sorting
1/35
Study Analytics
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
36 Terms
1
New cards
what is the order of human structures?
1. cell
2. tissues
3. organs
4. organ systems
5. organism
2
New cards
what are the four types of tissue/cells in humans?
* connective tissue
* epithelial tissue
* muscle tissue
* nervous tissue
* epithelial tissue
* muscle tissue
* nervous tissue
3
New cards
epithelial tissue (epithelium)
**Structure:** Sheets of tightly packed cells
**Examples:** Skin, lining of digestive system
**Function:** protection and lining
**Examples:** Skin, lining of digestive system
**Function:** protection and lining
4
New cards
what does the Epithelial Tissue look like?
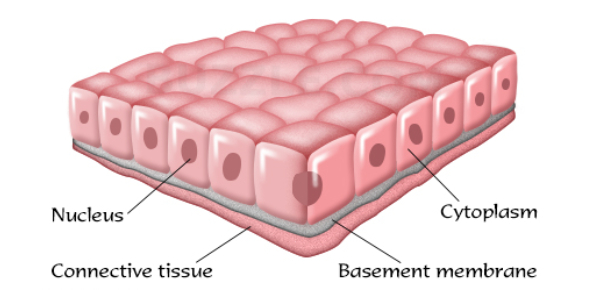
5
New cards
nerve tissue
**Structure:** Long, thin cells that transmit electrical impulses
**Examples:** brain, nerves
**Function:** sensing environment, communication, coordination
\n
**Examples:** brain, nerves
**Function:** sensing environment, communication, coordination
\n
6
New cards
what does the nervous tissue look like
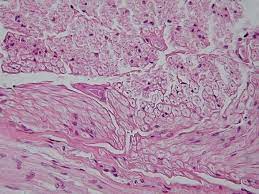
7
New cards
3 types of nerve cells
* **Sensory Neurons**
* **Motor Neurons**
* **Interneurons**
* **Motor Neurons**
* **Interneurons**
8
New cards
sensory neurons
carries information from body to brain or spinal cord
9
New cards
motor neurons
carries information from brain or spinal cord to another body part
10
New cards
interneurons
connects sensory and motor neurons
11
New cards
connective tissue
**Structure:** Composed of different types of cells that support and protect and connect the body’s organs
**Examples:** bone, blood
**Function:** support, insulation
**Examples:** bone, blood
**Function:** support, insulation
12
New cards
what does the connective tissue look like
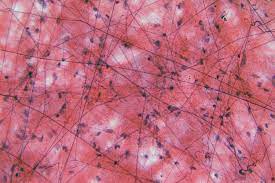
13
New cards
muscle tissue
**Structure:** Bundles of long cells that can shorten or contract
**Examples:** Heart, hamstrings, biceps, digestive system
**Function:** movement
**Examples:** Heart, hamstrings, biceps, digestive system
**Function:** movement
14
New cards
what does the muscle tissue look like?
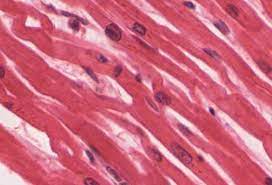
15
New cards
skeletal muscle
* Striated (striped)
* Used for voluntary movement
* Used for voluntary movement
16
New cards
cardiac muscle
* Striated (striped)
* Used for involuntary movement
* Causes heart to pump
* Used for involuntary movement
* Causes heart to pump
17
New cards
smooth muscle
* Not striped
* Used for involuntary movement
* Lines circulatory and digestive system
* Used for involuntary movement
* Lines circulatory and digestive system
18
New cards
stem cell
an undifferentiated cell that can divide to form specialized cells
19
New cards
cellular differentiation
cells that develop in different ways to perform particular functions in a process
20
New cards
what does every cell in your body originally come from?
a small group of stem cell
21
New cards
what does scientists believe studying stem cells will do?
they believe the stem cells may be used to treat injuries and diseases by regenerating organs
22
New cards
what are stem cells capable of doing in the human body?
they capable of becoming any cell in the human body
23
New cards
Stem cell 🡪 unspecialized cell
can form specialized cells when exposed to proper environmental conditions, or they can remain unspecialized and actively divide for long periods of time
24
New cards
what are the two types of stem cells?
embryonic and tissue
25
New cards
embryonic stem cells
are found in the embryo and are able to differentiate into other cell types
26
New cards
tissue stem cells
are involved in the replacement of damaged tissue
Example location of tissue stem cells: skin, blood, neural tissue
Example location of tissue stem cells: skin, blood, neural tissue
27
New cards
cord blood cell banking
It is possible to harvest a few stem cells from the blood in the umbilical cord
These cells are similar to tissue stem cells and the blood containing them can be “banked” for future use.
These cells are similar to tissue stem cells and the blood containing them can be “banked” for future use.
28
New cards
what are the four stages of processing food?
1. ingestion
2. digestion
3. absorption
4. elimination
29
New cards
mechanical/chemical break down of food into smaller units is what?
digestion
30
New cards
absorption
taking in nutrients into the blood stream
31
New cards
removal of waste is?
elimination
32
New cards
what is considered eating?
ingestion, the taking in of nutrients
33
New cards
digestive tract
a long tube in the body with two ends
in humans: mouth, esophagus, stomach, small and large intestine and anus
in humans: mouth, esophagus, stomach, small and large intestine and anus
34
New cards
what does the mucus do?
allows material to pass smoothly and protects the tube from digestive enzymes
35
New cards
what is the length of the digestive tract lined with?
the epithelial tissue which secrete mucus via goblet cells
36
New cards
layers of muscle tissue and nerve cells are also included in?
the digestive tube