Chemistry Final
Unit 3-1: Structure of Atoms
Atoms are the fundamental building blocks of matter and are made up of three key components: protons, neutrons, and electrons. Protons, which are positively charged particles, and neutrons, which are neutral particles, are found in the nucleus at the center of the atom. Electrons, on the other hand, are negatively charged particles that orbit around the nucleus.
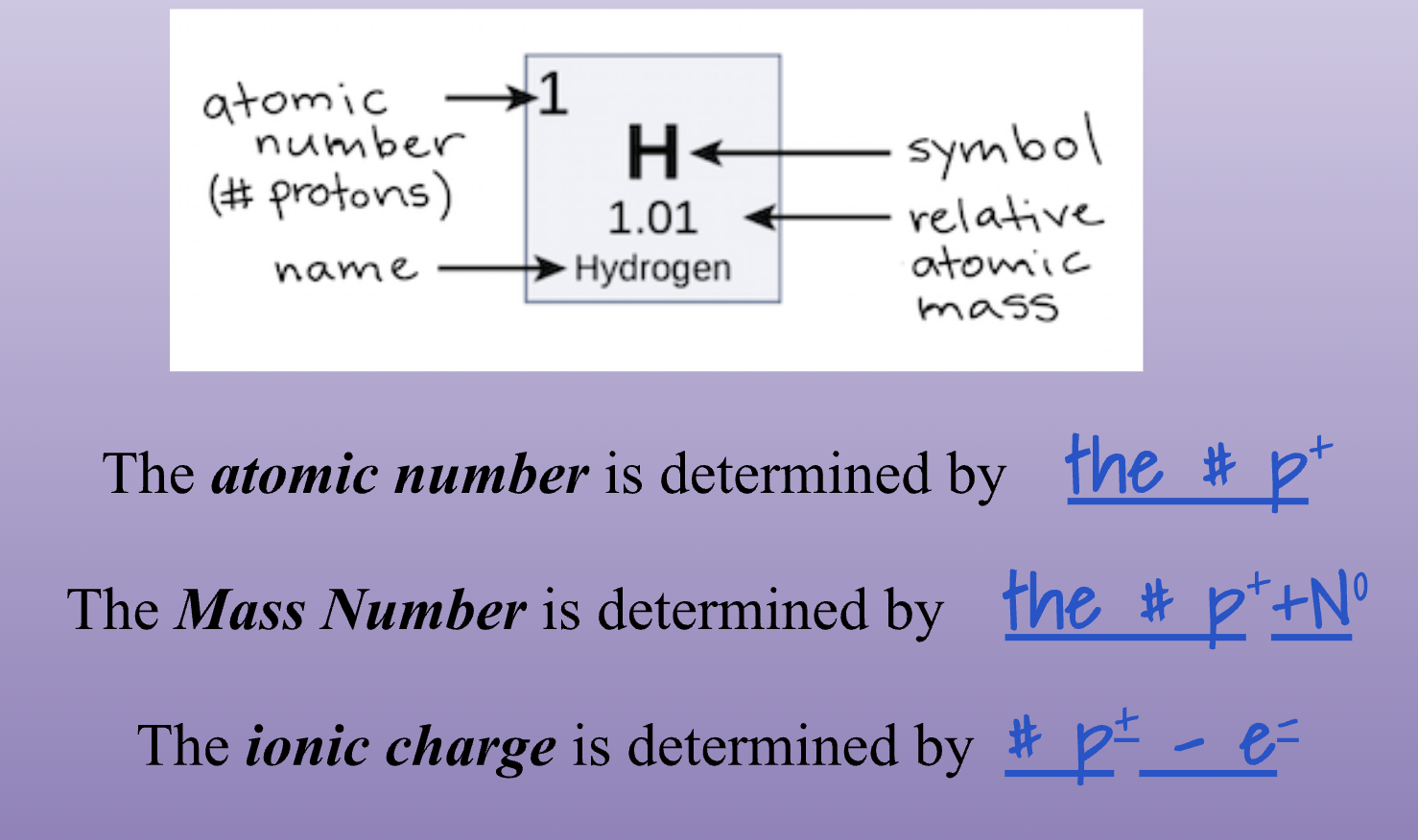
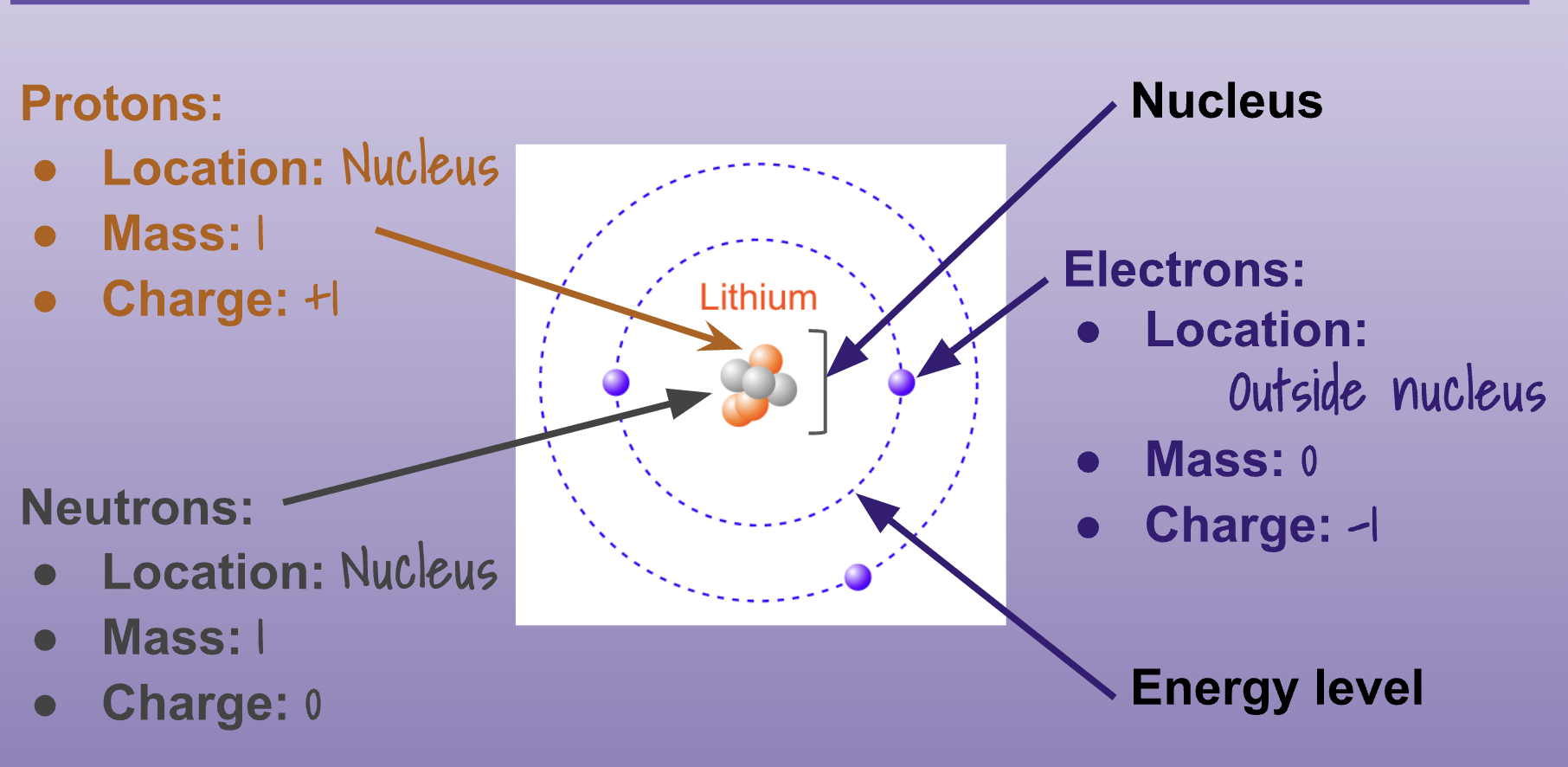
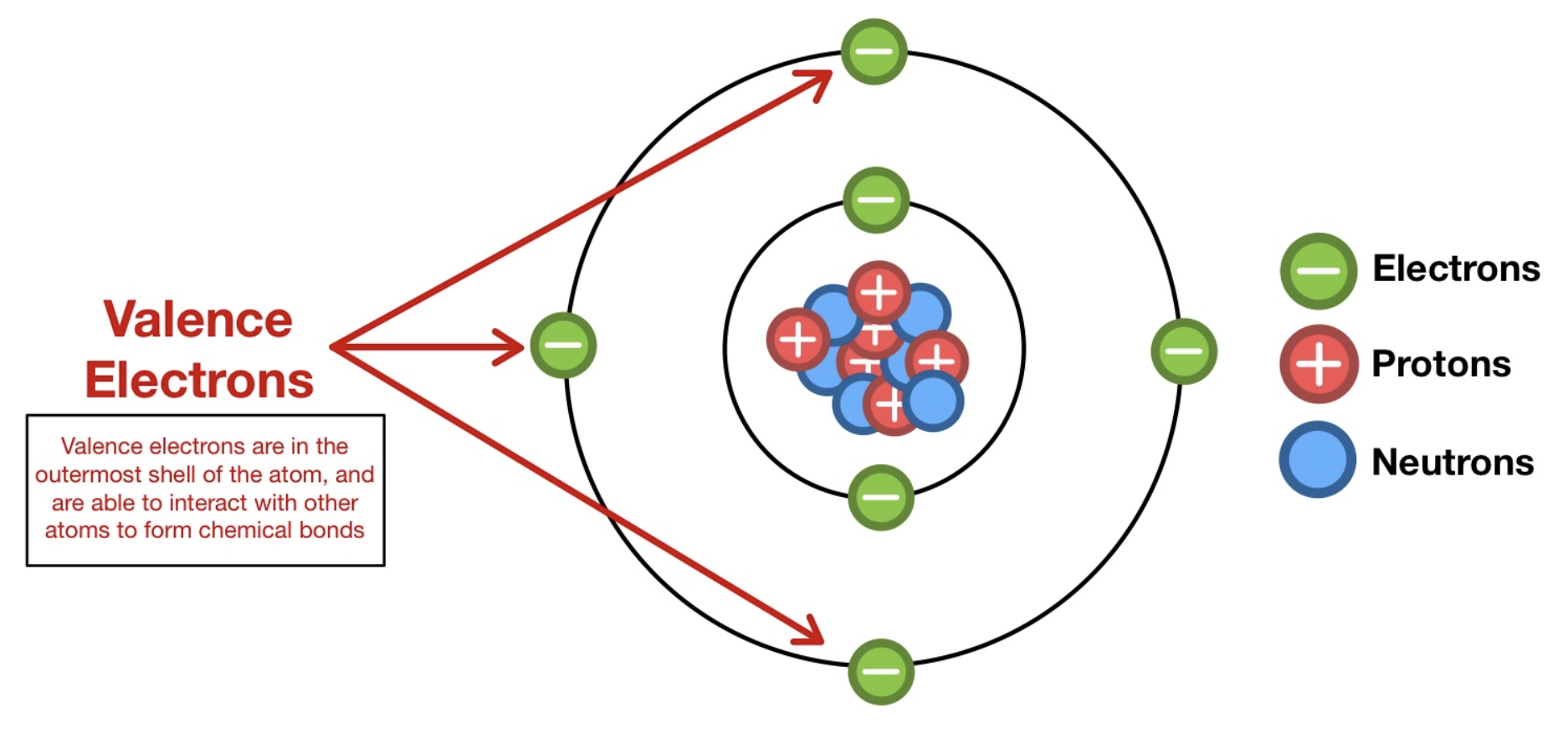
Unit 3-1 Continued -
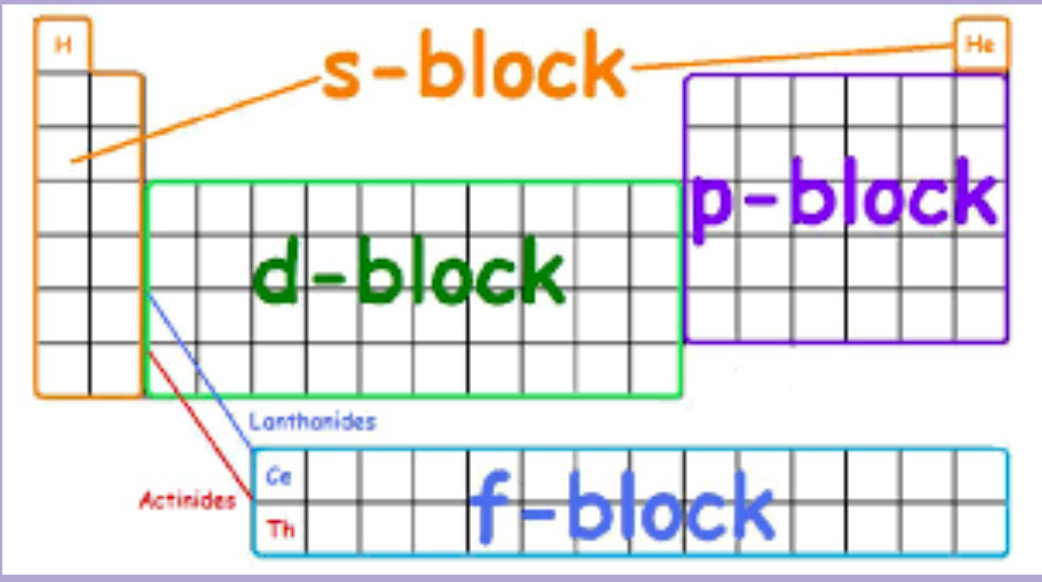
The Table of Elements can be separated into 4 different blocks, These blocks will be used to write Electron Configurations.
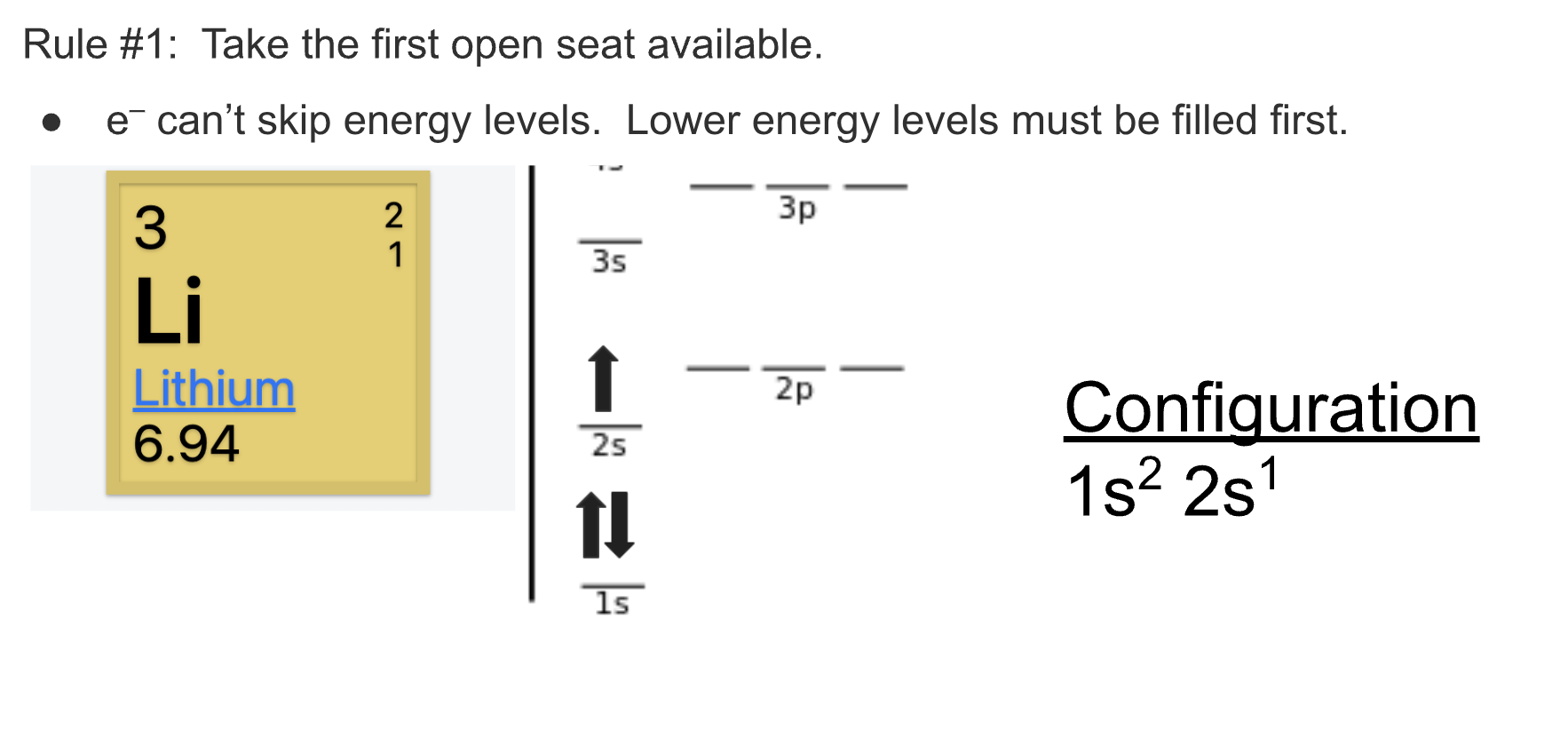
When writing out electron configuration you must fill out all lower levels before moving on to the next one. Like electrons, they want to stay as far away as possible. Based on the letter blocks in the photo above, you can find out what letter and number to use for electron configuration.
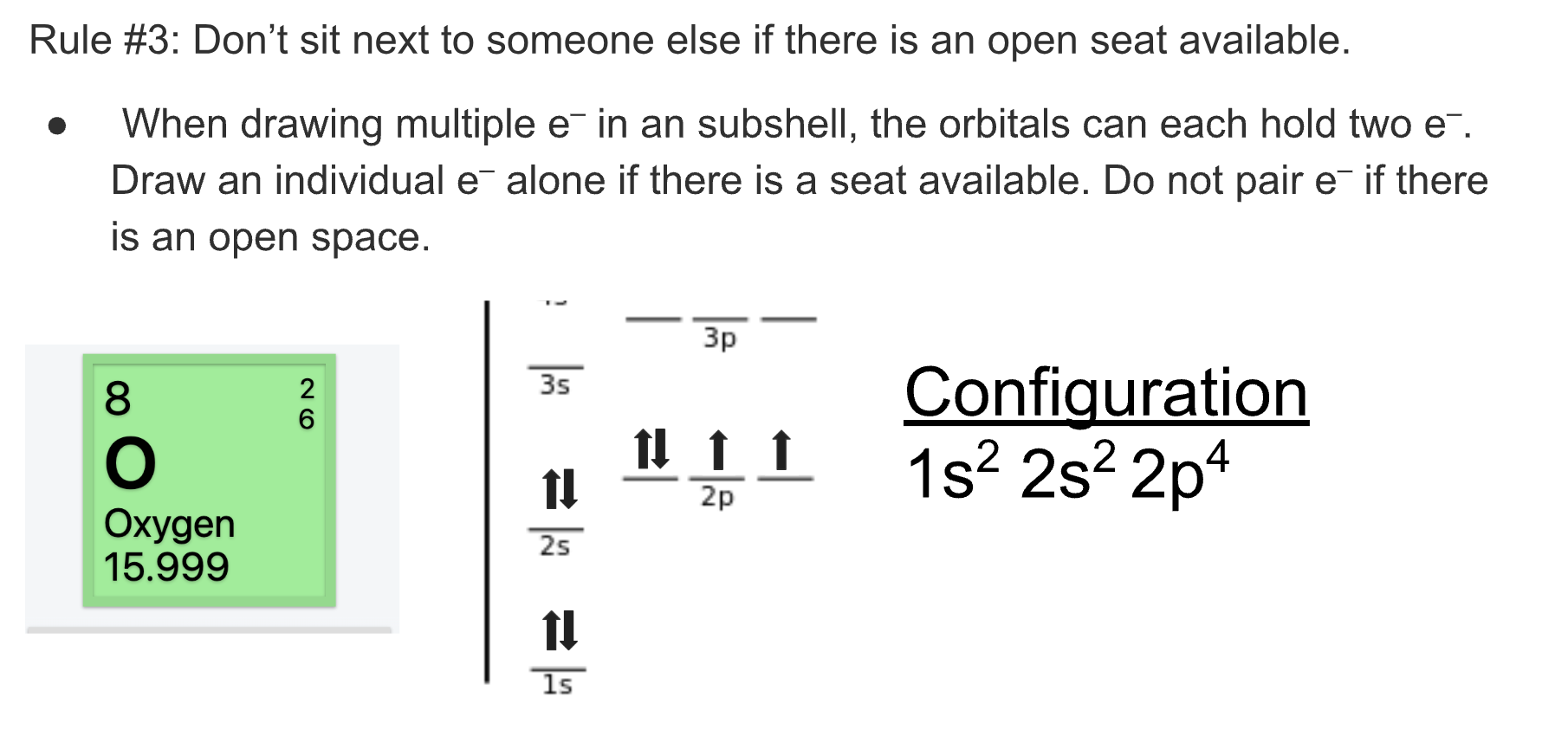
Another rule you have to include is that if there is an open seat the electron must take it. Electrons don’t like being by each other.
Electron Dot diagrams are a simple but crucial step to understand in chemistry. Electron dot diagrams are a way of showing and keeping track of Valence Electrons. To write one, Put the symbol of the element then, put the dot of each valence electron

Unit 3-1 Study Tools
https://phet.colorado.edu/sims/html/build-an-atom/latest/build-an-atom_en.html
Unit 1
Extensive and Intensive Properties
Intensive: Boiling Point, Temperature, Luster. Extensive: Weight, Length, Volume
Which word describes the process of a liquid becoming a gas?
A. condensation
B. deposition
C. vaporization
D. sublimation
A container of oxygen has a volume of 30.0 mL and a pressure of 4.00 atm. If the pressure of the oxygen gas is reduced to 2.00 atm, what is the new volume of the oxygen gas?
Unit 2-2: Heat Transfer
Terms to Know: Conduction is the transfer of thermal energy between two objects of two different temperatures that are touching. Convection The transfer of thermal energy between two objects that have different temperatures By circulating air particles and making them hotter which then they move faster. Radiation is the transfer of thermal energy in the form of electromagnetic waves, such as infrared light and visible light.
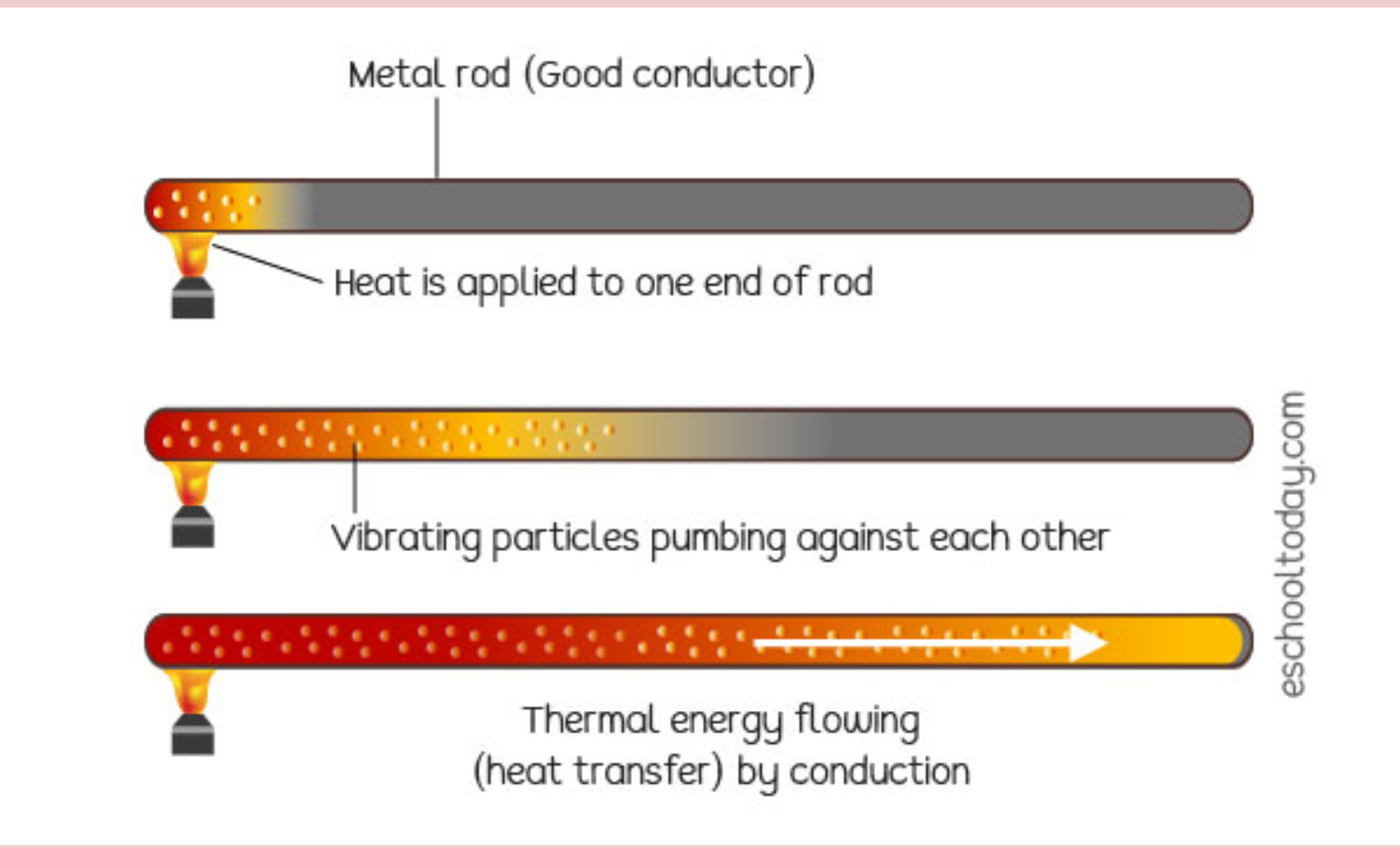
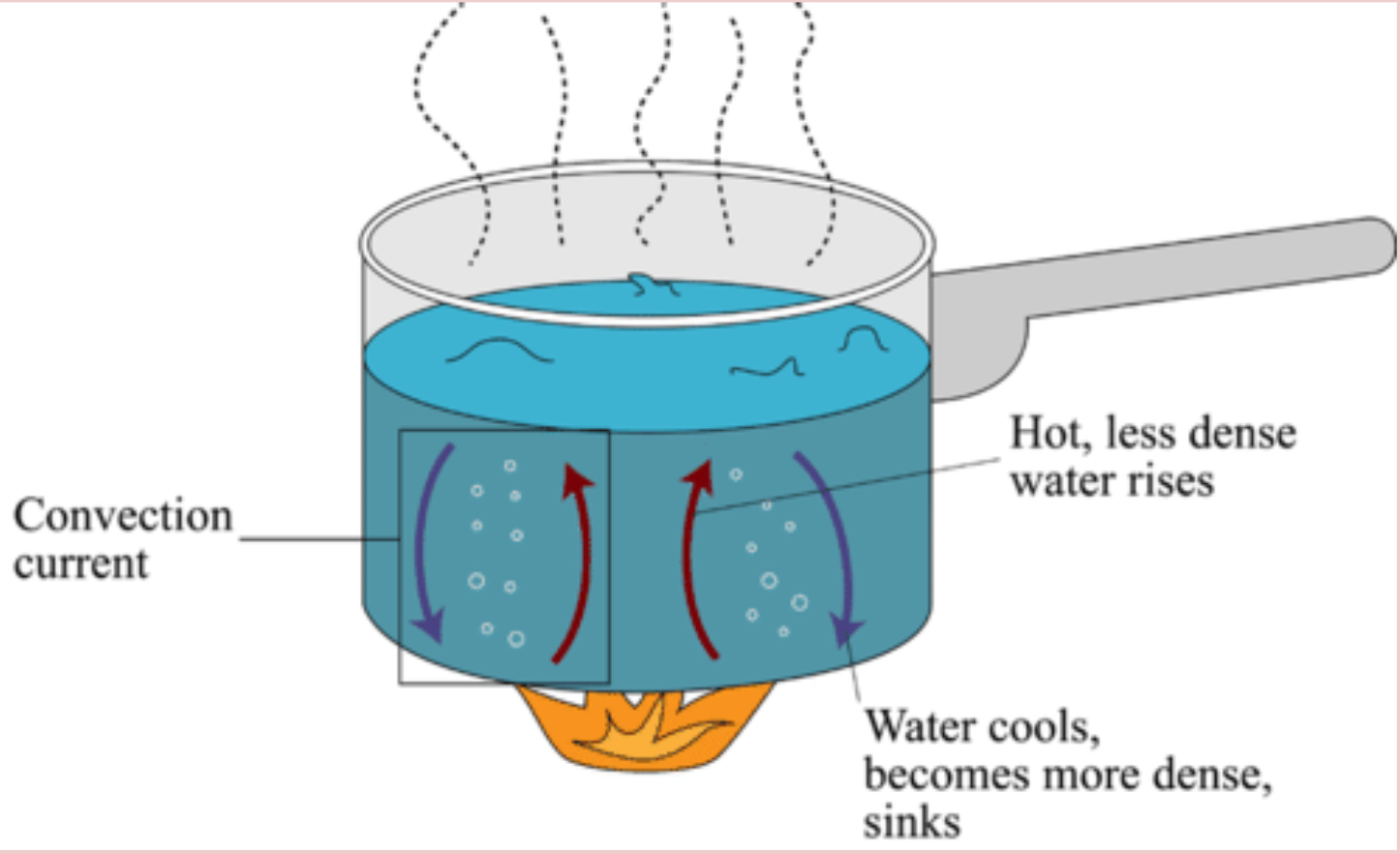
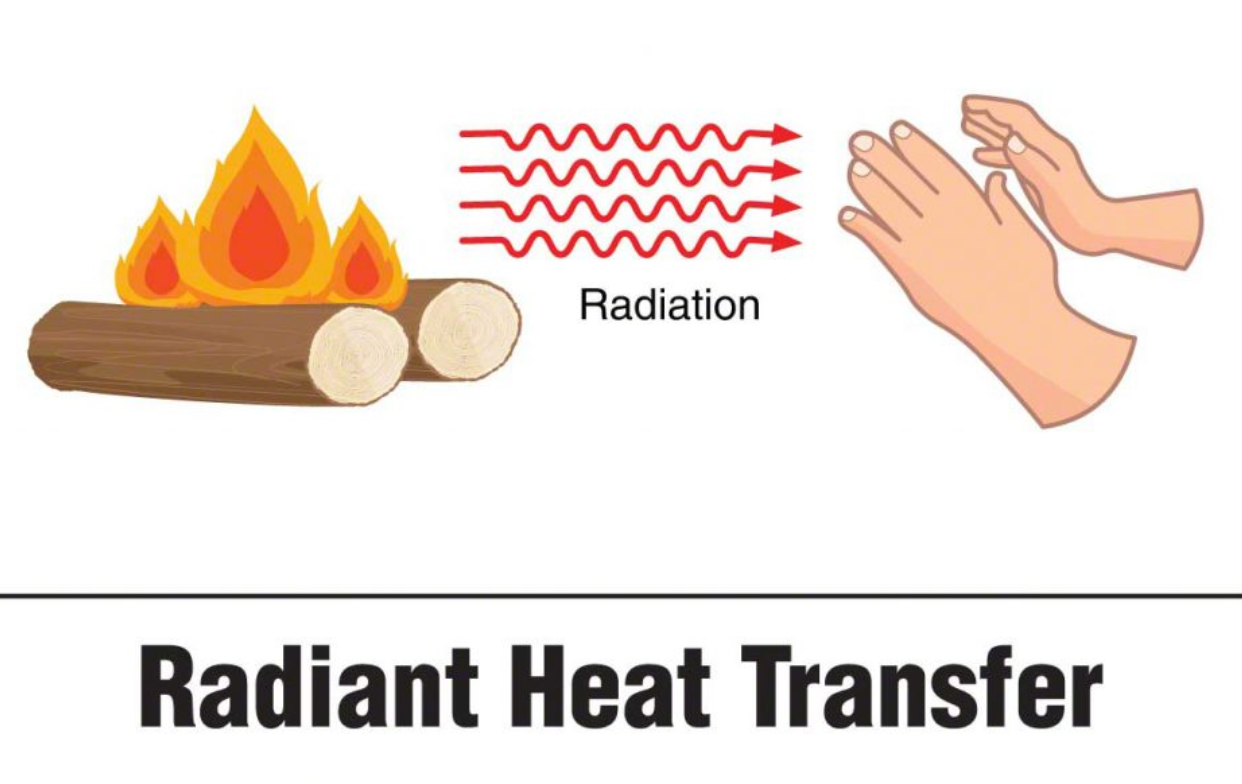
Unit 2-2 Continued - Heat Capacity
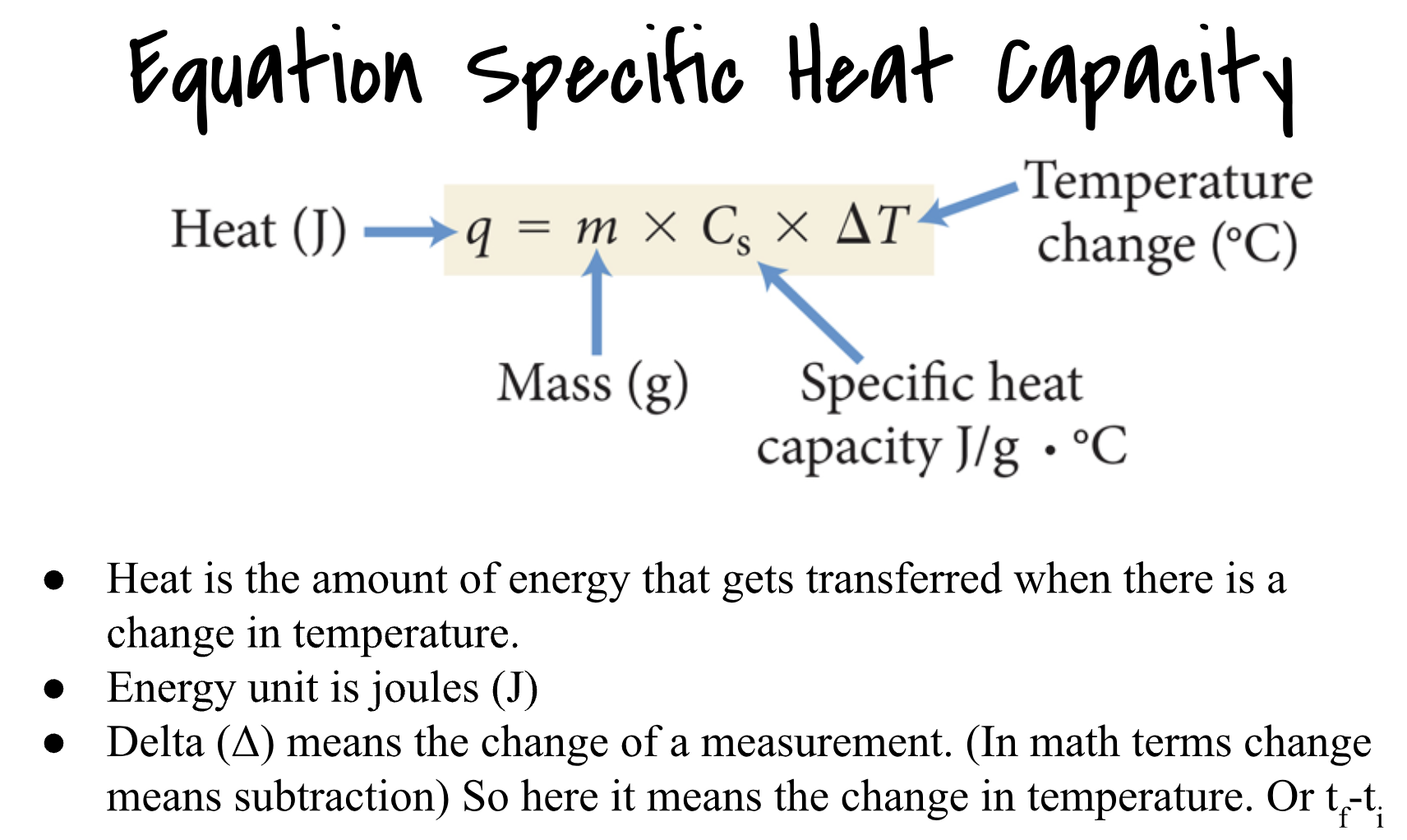
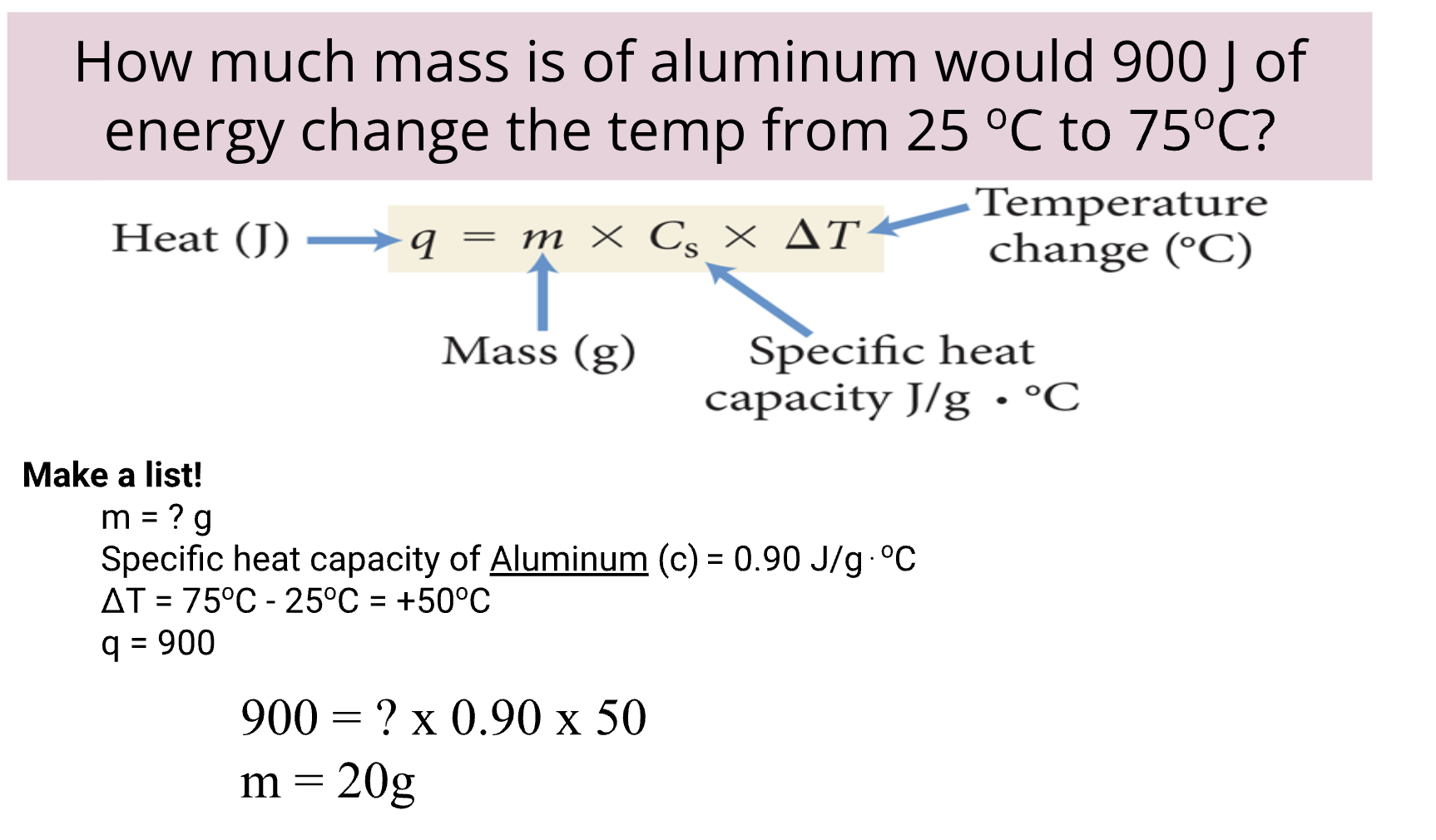
Heat Capacity: general measure of the amount of heat something can hold.
Specific Heat Capacity: Amount of energy to raise 1 C for material.
Entropy: Entropy is the measure of randomness or disorder in something. An example of entropy is a liquid and the opposite would be a solid.
Unit 2-3 and Unit 2-2
Atoms: Fundamental building blocks of matter made of protons (positively charged), neutrons (neutral), and electrons (negatively charged) in orbit around the nucleus.
Protons: Determine the atomic number and identity of an element.
Neutrons: Contribute to atomic mass and form isotopes of elements.
Electrons: Orbit the nucleus in various energy levels, determining the element's chemical properties.
Electron Configuration: Electrons fill lower energy levels first (Aufbau principle) and prefer to occupy empty orbitals (Hund's rule).
Electron Dot Diagrams: Represent valence electrons around the element's symbol to predict bonding behavior.
Heat Transfer: Involves conduction (contact), convection (fluid movement), and radiation (electromagnetic waves).
Heat Capacity: Amount of heat an object can hold, specific heat capacity is the energy needed to change temperature by 1 °C.
Entropy: Measure of disorder or randomness in a system, influencing the direction of chemical reactions.