Grade 7 Science: Unit D Structures and Forces
1/43
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
44 Terms
Frame structure
A frame structure is a structure that has a skeleton

Shell structure
A shell structure is a structure that doesn't have a frame, and is hollow from the inside.

examples of mass structures
mountains, cookies, Great Pyramids of Egypt
examples of frame structures
houses, humans, chair
examples of shell structures
ice cream cone, milk carton, egg shell
interior forces
forces that act from the inside of an object.
4 types of internal forces
tension, torsion, compression, and shear.
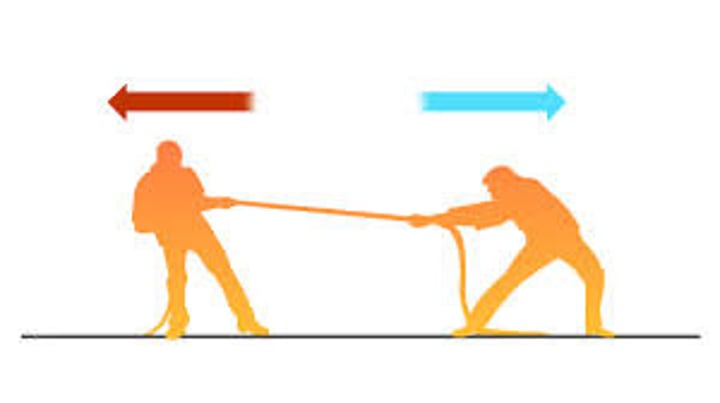
tension (internal)
pulling an object in opposite directions (tug of war)
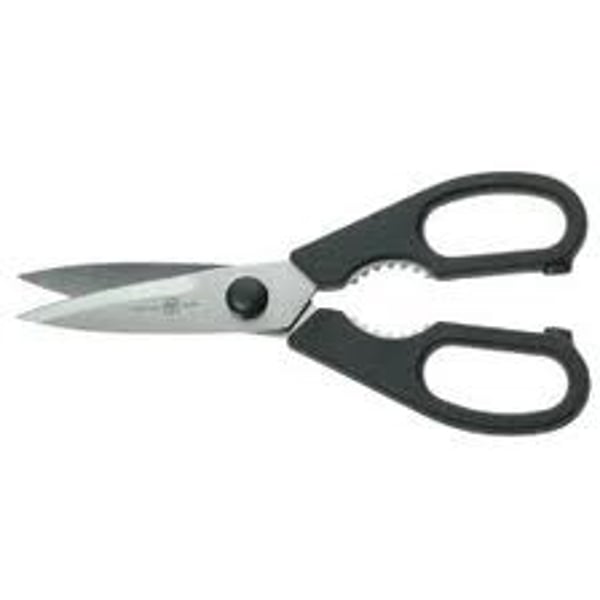
shear (internal)
ripping or pulling an object in two opposite directions (scissors)

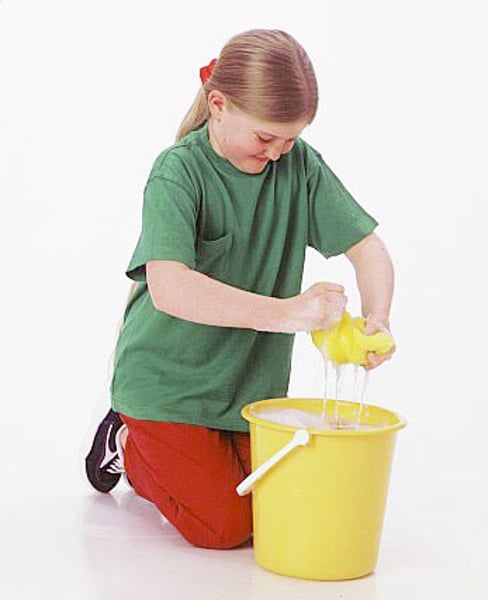
torsion (internal)
twisting an object in two opposite directions (wringing out a sponge)

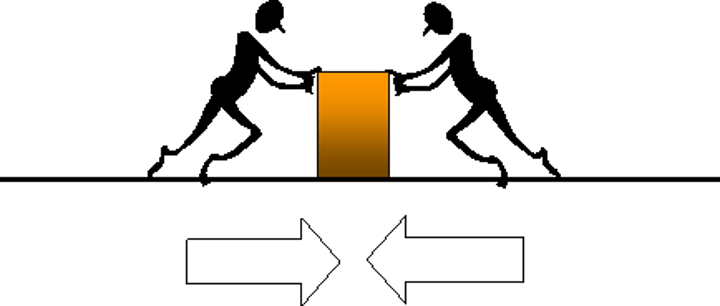
compression (internal)
(squishing) - the force which is transferred through an object when it's pushed on by a load

external forces
forces that act from the outside of an object.
2 types of load
live load (moving) and dead load (can not move).
live load
non permanent forces that act on an object like cars, or wind.
dead load
permanent load that acts on an object like the objects own weight.
mobile joints
joints that allow movement.
rigid joints
attach parts together
rigid joints come in five different categories:fasteners, ties, interlocking shapes, adhesives, and melted joints.
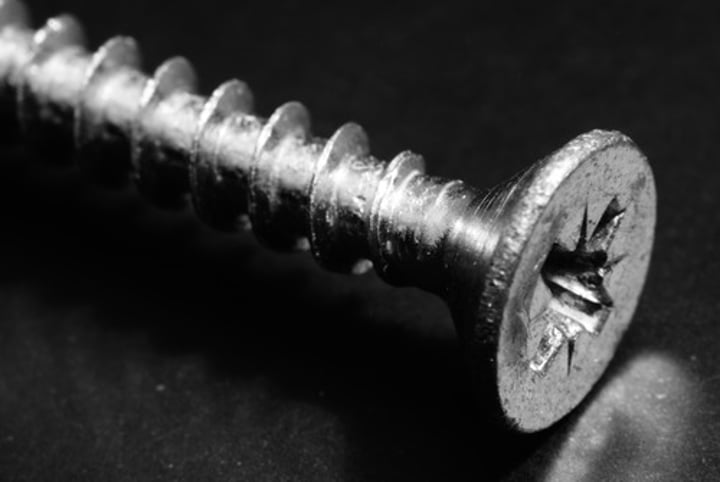
fasteners
nails, bolts, screws, rivets, and dowels.

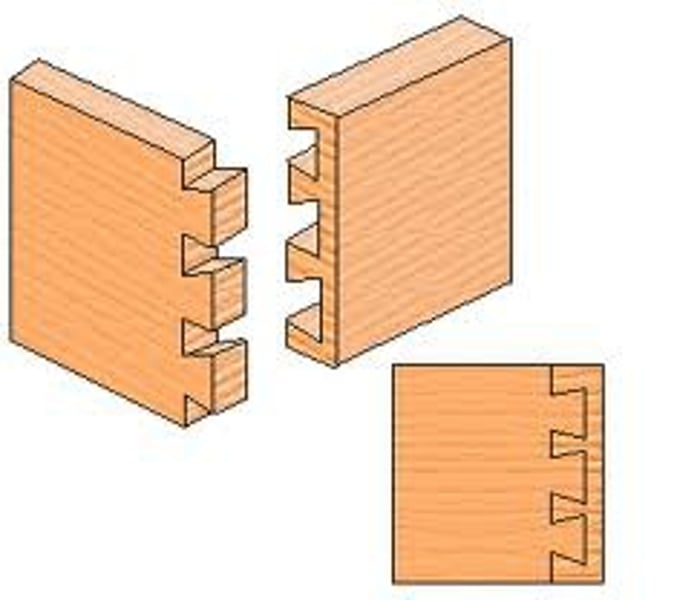
interlocking shapes
carefully shaped parts that hold them self together like Lego.
ties
thread, string, and rope can also fasten things together.

adhesives
sticky substances called adhesives or glues can hold things together.

meting
pieces of metal or plastic can be melted together.
common functions of structures
support (chair) and protection (shoe; car seat)
aesthetics
the quality vof beauty; making a structure beautiful
3 types of functions in natural structures
1) support (skeletons); 2) materials and structures to gain food (leaves to collect sunlight); 3)materials and structures to gain motion (feathers and wings; fins and flippers)
3 categories of natural structures
1) structures in plants (leaves, trees); 2) structure of animals (an insect's eye, a bird's wing); 3) structures that animals build (a beaver dam; a spider web)

3 types of external forces
1) gravity (weight); 2) friction; 3) wind
structural fatigue
repeated, excess stress on a structure (e.g. chair)

structural failure
a structure can't rebound from the load (force). It falls apart.

3 types of structural failure
1) bending (a shelf); 2) buckling (crushing a can); 3) fracturing (driveway, roads)
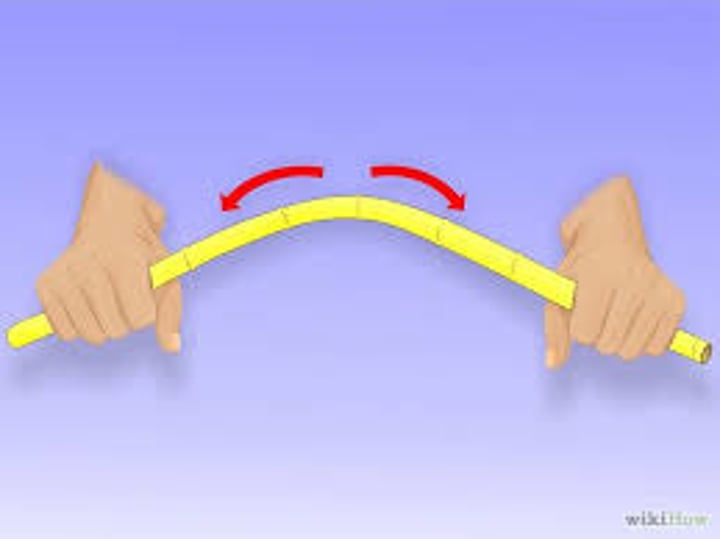
deformation
When stress causes a material to change shape
direction
the force being applied upward, downward, or at an angle
location
where is the force being applied. Example wind blowing on a flag pole.

structural joint
space between to or more surfaces
fixed joint
a joint that does not move (skull, camping shelter)
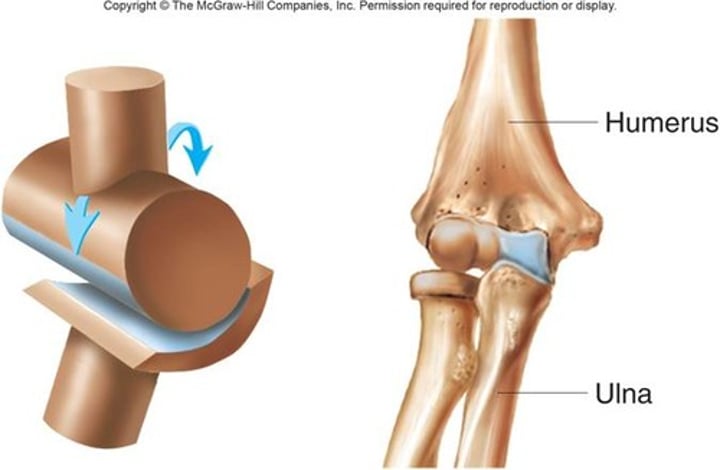
hinge joints
allow motion in one plane or direction (elbows)
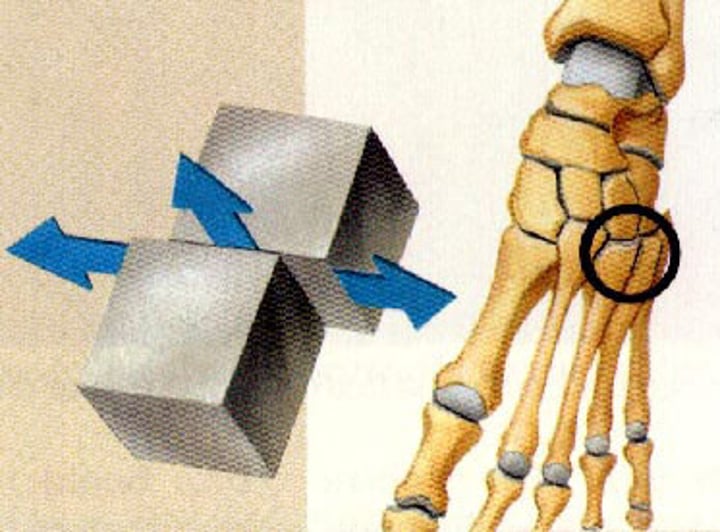
gliding joints
two flat surfaces that slide over one another (wrist and foot)
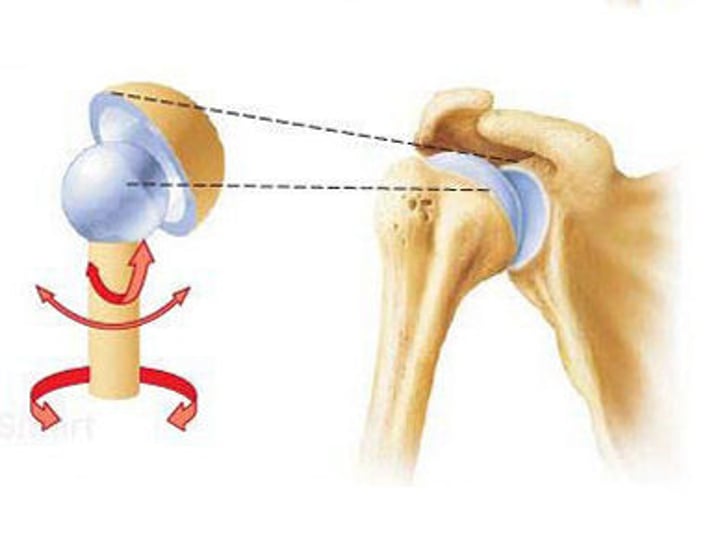
ball-and socket joints
allow a wide range of movement in many directions (shoulder; rear-view mirror)
Structure
is anything with a definite size, shape that is used for a specific purpose. The most important thing about structures is that they are made to be able to handle forces pushing and pulling.

Natural Structure
are not made by people. They are built by animals or created by nature. Natural structures can be living or non living.

Manufactured Structures
are made by people. Many structures are designed based on what people learned from natural structures.

solid (mass) structure
Are made by piling different substances on top of each other. Like a brick wall. They are solid and are held in place by their weight.

Frame Structure
have a skeleton (support system) of a very strong materials that are often covered with other materials. They are rigid and do not bend, They get strength by the way the pieces fit together

Shell Structure
have a thin, specifically-shaped outer layer of material that gives them their shape and strength. Shell structures are empty inside, so they are often used as containers.
