Geology 106 CH 23
4.4(5)
Card Sorting
1/65
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Last updated 5:35 PM on 11/22/22
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
66 Terms
1
New cards
Paleogene (66-23 Ma)
Neogene (23-2.6 Ma)
Quaternary (2.6 Ma - present)
Epochs - recent/holocene, pleistocene, pliocene, miocene, oligocene, eocene, paleocene
Neogene (23-2.6 Ma)
Quaternary (2.6 Ma - present)
Epochs - recent/holocene, pleistocene, pliocene, miocene, oligocene, eocene, paleocene
What are the different periods of the Cenozoic? List their timeline. Also, name different epochs of those periods.
2
New cards
Alpine-Himalayan and circum-Pacific belts
Locate the region where Cenozoic tectonism was concentrated.
3
New cards
True
Statement: The old Tethys Sea closed during the Cenozoic when the African plate collided with the Eurasian plate to the north. (True/False)
4
New cards
Evaporite
What type of deposition occurred when the sea dried up?
5
New cards
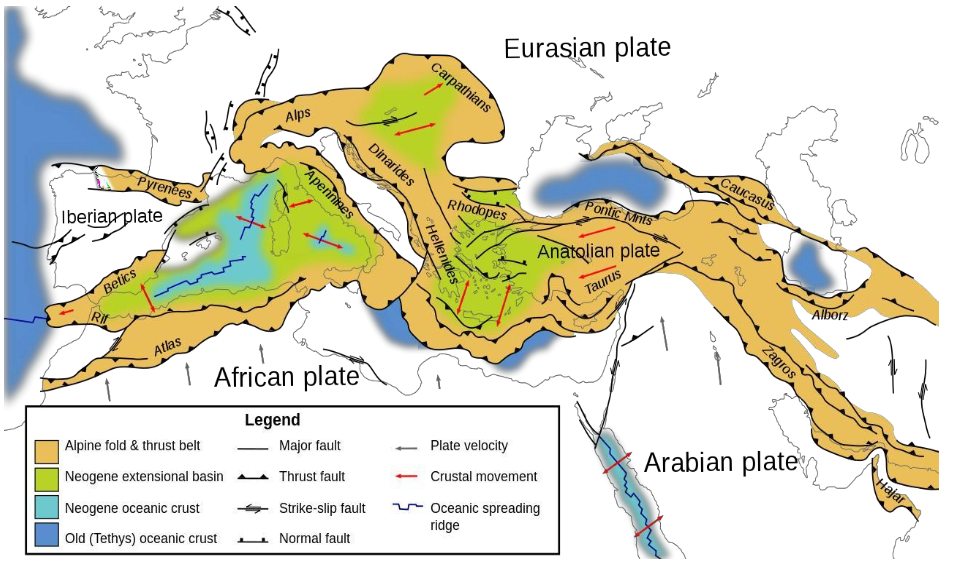
the Alps in Switzerland, the Apennines in Italy, the Pyrenees between Spain and France
Identify location of different mountain ranges that created in the Alpine-Himalayan belt
due to convergence?
due to convergence?
6
New cards
Early Cretaceous
When did the collision of Indian and Asian plate happen?
7
New cards
- Andes Aleutians Cascades
- Islands of Japan
- Island of the Philippines
- Islands of Japan
- Island of the Philippines
Which areas are included in Circum-Pacific orogenic belt?
8
New cards
Alaska to central Mexico
North American Cordillera extends from ____ to _______.
9
New cards
Widespread mountain building, volcanism, uplift, and deep erosion
What types of geologic events experienced by the Cordillera during Cenozoic?
10
New cards
Near horizontal subduction of the Farallon plate beneath North America
How did the uplifts form in the Laramide orogeny?
11
New cards
Eruptive volcanism
How did Caldera form?
12
New cards
Northern California to British Columbia
The Cascade Range consists of some of the most majestic and highest mountains in the Cordillera. Identify the extension of the Cascade Range.
13
New cards
False (Juan de Fuca plate)
Statement: Cascade range mountains are the result of volcanism activity related to the
subduction of the remnant of Farallon plate under North American plate. (True/False)
subduction of the remnant of Farallon plate under North American plate. (True/False)
14
New cards
Composed of crust that has been stretched and thinned
Basin and Range province, centered on Nevada, has many North-South trending small mountain ranges. What are they composed of?
15
New cards
Changed from tropical to arid as the mountains blocked the moist Pacific air
What type of climate exists in the interior of the continent bounded by the mountains of Basin-Range province? What is the reason for that?
16
New cards
2 mm/year
Rio Grande rift extends north to south about 1000 km from Central Colorado through New Mexico. The rift is active still today. What’s the rate of this rifting now?
17
New cards
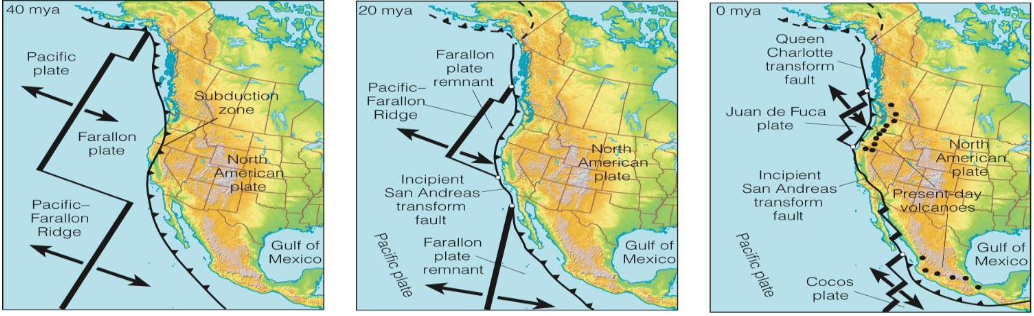
Juan de Fuca plate and Explorer and Gorda Plates
What are the two remnants of Farallon plate?
18
New cards
Continuing movements of the Pacific and North American plates
What is the cause of seismic activity in the San Andreas?
19
New cards
In transitional and marine environments
Where did the eroded sediments from the Laramide highlands deposit?
20
New cards
The area experienced deformation during the Proterozoic and Paleozoic. Extensive erosion and block-faulting with the break up of Pangaea occurred in the Mesozoic.
What happened in the Appalachian mountain regions during the Cenozoic era? Where did the eroded sediments from the Appalachian mountains deposit?
21
New cards
Salt domes
What type of sediments are deposited in the different Gulf coast regions?
22
New cards
Yes
Is near-shore sands and off-shore clays deposition favorable for trapping oil and gas?
23
New cards
almost 25% of state revenue, 6% of state's workforce employed in petroleum, 12% of total wages in LA
Describe the importance of petroleum extraction and mining activity in Louisiana.
24
New cards
Himalayans, the Andes, the Aleutians, Japan and the Philippines
Which locations have relatively more active tectonism and orogenic activity in Pleistocene and Holocene epochs?
25
New cards
Major glaciation events: Nebraskan, Kansan, Illinoian, and Wisconsinan
Evidences: terminal moraines, erratics and drumlin fields
Evidences: terminal moraines, erratics and drumlin fields
What were the major glaciation events in North America during the Pleistocene? And, what
are the evidences of Pleistocene glaciation events?
are the evidences of Pleistocene glaciation events?
26
New cards
True
Statement: Most natural lakes are the result of glacial activity. (True/False)
27
New cards
Proglacial: formed by meltwater that accumulates along the margin of the glaciers
Pluvial: formed by precipitation and runoff
Pluvial: formed by precipitation and runoff
What are the differences between proglacial and pluvial lakes?
28
New cards
- Oil in thick sedimentary rocks, trapped by Cenozoic folding and faulting.
- Placer deposits of gold, as well as sand and gravel.
- Evaporite minerals such as borax and halite.
- Abundant lignite coals occur in North Dakota and
along the Gulf Coast.
- Diatomite, composed of the siliceous shells of microscopic diatoms, is used to filter contaminants out of water, fruit juices, and other products.
- Placer deposits of gold, as well as sand and gravel.
- Evaporite minerals such as borax and halite.
- Abundant lignite coals occur in North Dakota and
along the Gulf Coast.
- Diatomite, composed of the siliceous shells of microscopic diatoms, is used to filter contaminants out of water, fruit juices, and other products.
Make a list of Cenozoic mineral resources.
29
New cards
Angiosperms, seedless vascular plants, gymnosperms
Which types of plant were common in Cenozoic? List all of the types.
30
New cards
They have jagged edges; Paleocene and Eocene
How can plant leaves indicate about the climate? Which type of leaves can adapt to a warm climate?
31
New cards
Paleocene-Eocene Thermal Maximum
Which was the warmest epoch of Cenozoic?
32
New cards
A decrease in precipitation reduced the vast forests to dry savannahs and finally to grasslands that cover the plains today.
Describe the climate changes that happened at the end of Eocene.
33
New cards
Owls, hawks, ducks, penguins and vultures
Which birds were the first member in different bird orders that evolved in Paleogene?
34
New cards
Neogene
When did the number of songbirds increase?
35
New cards
Walk, run, heavy body, climb, eat insects, burrow, swim, glide and fly
List the adaptations made by Mammals.
36
New cards
Cynodonts
Which reptile is believed to be the ancestor of Mammals?
37
New cards
Artiodactyls - even-toed (antelope, camel, giraffe, goat, pig)
Perissodactyls - odd-toed (horses, rhinos, tapirs)
Perissodactyls - odd-toed (horses, rhinos, tapirs)
What are Artiodactyls and Perissodactyls? Give some examples.
38
New cards
herbivores
All ungulates were _______ (herbivores/carnivores)
39
New cards
Grazers eat grass and browsers eat woody vegetation.
High-crowned molars are better adapted for a diet of chewing grass and resisting wear from the grit.
High-crowned molars are better adapted for a diet of chewing grass and resisting wear from the grit.
What the difference of grazers and browsers? What was the role of high-crowned chewing teeth?
40
New cards
Grazers
Before Miocene, all horses were ______ (grazers/browsers)
41
New cards
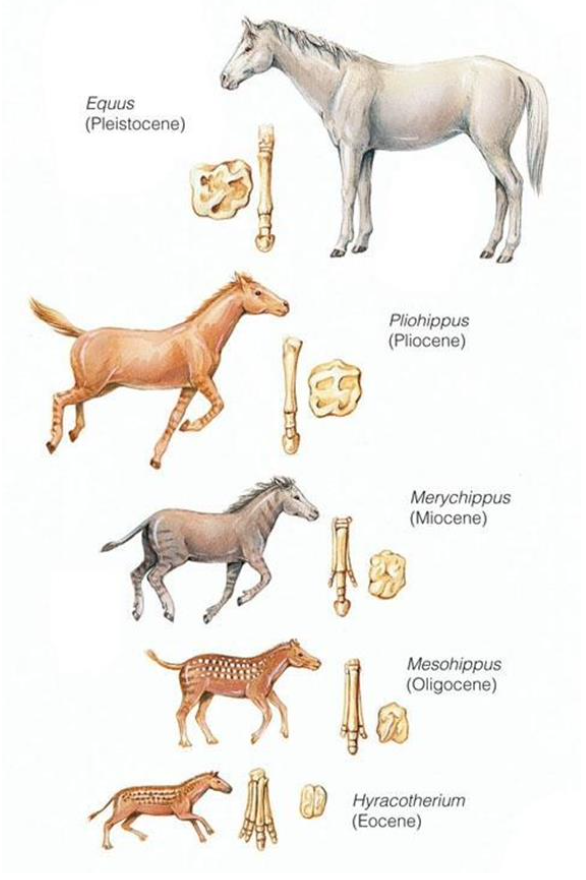
Eocene (Hyracotherium) --> Oligocene (Mesohippus)--> Miocene (Merychippus) --> Pliocene (Pliohippus) --> Pleistocene (Equus)
Today’s horse (Equus) evolved from a tiny Eocene horse (Hyracotherium). Identify the
evolutionary changes of Equus.
evolutionary changes of Equus.
42
New cards
Camels evolved in North America in the Pleistocene.
Cattle and goats evolved in the Neogene in Europe and Asia
Cattle and goats evolved in the Neogene in Europe and Asia
Identify time and location of Camel, Cattle and Goat evolution.
43
New cards
Well-developed canine teeth for slashing and tearing, most with an extra pair of shearing teeth (carnassials) as in the saber-toothed tiger.
What were the evolutionary changes in carnivorous mammals?
44
New cards
Vestigial rear limbs and teeth more similar to their land dwelling ancestors
Which body parts of the Whales were retained from its land dwelling ancestors?
45
New cards
- Increased brain size
- Opposable thumbs
- Freely rotating shoulder joint
- Nails and free fingertips instead of claws
- Stereoscopic vision
- Color vision
- Longer infancy, increased care of young
- Upright posture (various degrees of this)
- Opposable thumbs
- Freely rotating shoulder joint
- Nails and free fingertips instead of claws
- Stereoscopic vision
- Color vision
- Longer infancy, increased care of young
- Upright posture (various degrees of this)
What are the evolutionary changes in Primates?
46
New cards
Lemur: Prosimii, Lemuroidea
Monkey: Anthropoidea, Ceboidea and Cercopithecoidea
Apes and Humans: Anthropoidea, Hominoidea
Monkey: Anthropoidea, Ceboidea and Cercopithecoidea
Apes and Humans: Anthropoidea, Hominoidea
What are the Superfamily and Suborder of Lemur, Monkeys, Apes and Humans.
47
New cards
Oldest primate lineage
Include lemurs, lorises, tarsiers, and tree shrews (long snouts, lateral ears, large eyes, forward to provide stereo vision)
Include lemurs, lorises, tarsiers, and tree shrews (long snouts, lateral ears, large eyes, forward to provide stereo vision)
Identify characteristics of Prosimians. Give some examples.
48
New cards
Late Miocene
Characteristics: erect posture, large complex brain, tool-using capabilities, strong community organization
Oldest: Sahelanthropus tchadensis
Characteristics: erect posture, large complex brain, tool-using capabilities, strong community organization
Oldest: Sahelanthropus tchadensis
When did Hominids first evolve? What are their characteristics? What is the oldest known Hominids?
49
New cards
Longer
The Ischium bone is much _____ in human compared to gorilla. (smaller/longer)
50
New cards
Species:
A. anamensis (4.2-3.9 Ma),
A. afarensis (3.6-2.9 Ma),
A. africanus (3.2-2.3 Ma),
A. robustus (1.9-1.5 Ma),
A. boisei (2.3-1.4 Ma)
Characteristics:
- Skulls more ape-like than
human
- No chin
- Brain-size of chimpanzee
- Walked erect (pelvic and leg bones)
- ape-like brow ridges
- forward-jutting jaws
- teeth were intermediate between apes and humans
A. anamensis (4.2-3.9 Ma),
A. afarensis (3.6-2.9 Ma),
A. africanus (3.2-2.3 Ma),
A. robustus (1.9-1.5 Ma),
A. boisei (2.3-1.4 Ma)
Characteristics:
- Skulls more ape-like than
human
- No chin
- Brain-size of chimpanzee
- Walked erect (pelvic and leg bones)
- ape-like brow ridges
- forward-jutting jaws
- teeth were intermediate between apes and humans
List the species of Australopithecines. What were their individual timeline. What are the characteristics of Australopithecus afarensis?
51
New cards
larger brain size and use of stone tools
What are the characteristics of genus Homo?
52
New cards
Homo erectus
Which Homo species migrated out of Africa for the first time?
53
New cards
Multiregional: states that humans came from separate populations in Eurasia
Out of Africa: states that all humans descended from a single woman in Africa
Out of Africa: states that all humans descended from a single woman in Africa
What are “multiregional” and “out of Africa” hypothesis?
54
New cards
Neanderthals: inhabited Europe and the Near East between 200,000 and 30,000 years ago and were not much different from us, only more robust and with differently shaped skulls. They made specialized tools and weapons, took care of their injured, and buried their dead.
Cro-Magnons: succeeded the Neanderthals and lived from about 35,000 to 10,000 years ago. They were highly skilled nomadic hunters, formed living groups of various sizes, and were also skilled cave painters.
Cro-Magnons: succeeded the Neanderthals and lived from about 35,000 to 10,000 years ago. They were highly skilled nomadic hunters, formed living groups of various sizes, and were also skilled cave painters.
What were the characteristics of Neanderthals and Cro-Magnons?
55
New cards
Rapid climate change:
- Why didn't the big mammals simply migrate?
- Lack of correlation between extinctions and glacial advances and retreats.
Prehistoric overkill:
- Extinctions coincided with human arrival
- How could small human populations affect so many large mammals?
- Only a few human artifacts have been found among the remains of the large mammals.
- Why didn't the big mammals simply migrate?
- Lack of correlation between extinctions and glacial advances and retreats.
Prehistoric overkill:
- Extinctions coincided with human arrival
- How could small human populations affect so many large mammals?
- Only a few human artifacts have been found among the remains of the large mammals.
There are two explanations for Pleistocene extinction- 1) Rapid climate change, 2)
Prehistoric overkill. But none of them are undoubtful. What are the confusions about both explanations?
Prehistoric overkill. But none of them are undoubtful. What are the confusions about both explanations?
56
New cards
Indian/Asian
The Himalayas formed when the _____ plate collided with the ____ plate.
57
New cards
Laramide orogeny
Which orogeny took place much farther inland from a convergent plate boundary in North American plate?
58
New cards
True
The Cascade Range was formed due to volcanism initiated through a process of subduction when the Juan de Fuca Plate (oceanic crust) dove under the North American Plate (continental crust).
59
New cards
Pacific and North American plate slide past each other
What is the geological reason behind high probability of earthquake in California?
60
New cards
Carbonate shelf sediment
Which type of sediment dominates in the Florida section of the Gulf Coast region?
61
New cards
False
Proglacial lakes formed far from the glaciers because of the overall greater precipitation and cooler temperatures, which lowers the evaporation rate.
62
New cards
i and iii
What were the characteristics of plants that adapted to cool climates?
options:
i) small leaves
ii) incised-margin leaves
iii) smooth-margin leaves
options:
i) small leaves
ii) incised-margin leaves
iii) smooth-margin leaves
63
New cards
True
High-crowned chewing teeth is important for grazers as those teeth are resistant to abrasion (caused by the uptake of tiny pieces of sand with grasses).
64
New cards
carnassials teeth
One of the defining features of the carnivorous mammals is-
65
New cards
False
The Brain size was getting smaller with primate evolution.
66
New cards
Homo erectus
Which Homo genus was the first to migrate out of Africa?