MCAT Chemistry
1/47
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
48 Terms
Keq
Ratio representing the concentrations of products over reactants in a reversible reaction
ΔG=ΔH-TΔS
Gibbs free energy in a system
ΔG
Gibbs free energy. If negative reaction is spontaneous. if positive reaction is nonspontaneous.
ΔH
Enthalpy. Shows a change in heat
ΔS
Entropy. Shows a change in chaos
Lewis acid
takes electrons
Arrhenius base
gives OH-
Bronsted Lowry Acid
gives hydrogen
Bronsted Lowry Base
takes hydrogen
Why is ammonia a gas but ammonium is not
Ammonium’s positive charge allows it to interact with water which prevents it from being gaseous
In a spontaneous reaction, do reactants or products have larger ΔG?
Reactants
Are spontaneous reactions exergonic or endergonic
exergonic
In a spontaneous reaction, do reactants or products have lower activation energy?
reactants
ΔG=-RT ln(Keq)
Free energy in standard conditions
ΔG=-RT ln(Q/Keq)
Free energy in non standard conditions
Coordinate covalent
bond where 2 electrons in the bond come from the same atom
Polar covalent bond
bond where the two bonding atoms have very different electronegativities
What is the electron configuration of silver
1s22s22p63s23p64s23d104p65s14d10
What does the principle quantum number, n, show
The highest energy level of a atom
Arrhenius acid
gives H+
pKw=pH + pOH
pk of water equation
What are the pH and pOH values in water
They are equal
pH=-log[H+]/pOH= -long[OH-]
pH and pOH equations
As Ka increases, what happens to acid strength
It increases
When in salt forms, how is Ka determined
Stronger conjugate bases have weaker acids and smaller Ka’s
Ka= [X-][H+]/[XH]
Disassociation constant equation
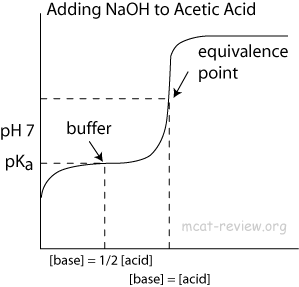
What does a buffering zone look like in a titration
Each Ka in a compound will create a buffering zone which has a flat area followed by a sharp drop or rise
Ideal gas equation
PV=nRT
What does a catalyst do?
Affects the activation energy of a reaction by lowering it
First order kinetics
Depends on one reactant
Second order kinetics
depends on two reactants
Third order kinetics
depends on 3 reactants
Is the slow or fast step rate determining
Slow step
Gibbs free energy with R
ΔG=-RTlnKeq
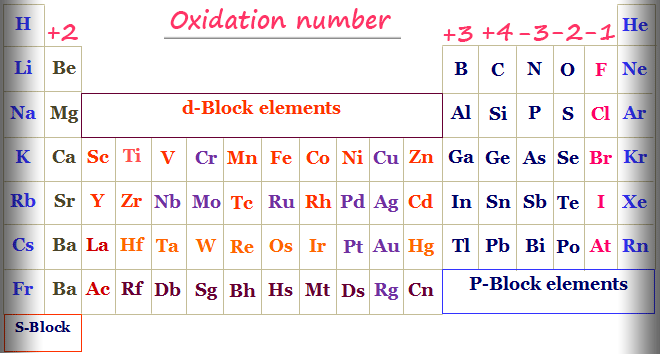
How to calculate oxidation numbers
Based on electronegativity of bonded atoms, electrons will move away or toward the atom of interest. Losing electrons increases oxidation and vice versa
What is a colloid
A heterogenous mixture
What is a electrolytic solution
A solution where a compound dissociates
How must H and OH relate for neutralization to occur
moles of H a nd moles of OH must be equal
What is fractional distillation
A method to separate liquids where a mixture is heated up till the liquids evaporate at their different boiling points
Titration equation
VaNa=VbNb. Where V is volume of acid/base and N is number of protons donated/accepted
What is a reducing agent
Molecule that is oxidized
What is a oxidizing agent
Molecule that is reduced
How does acid acidity relate to conjugate base stability
A very acidic acid will produce a stable conjugate base